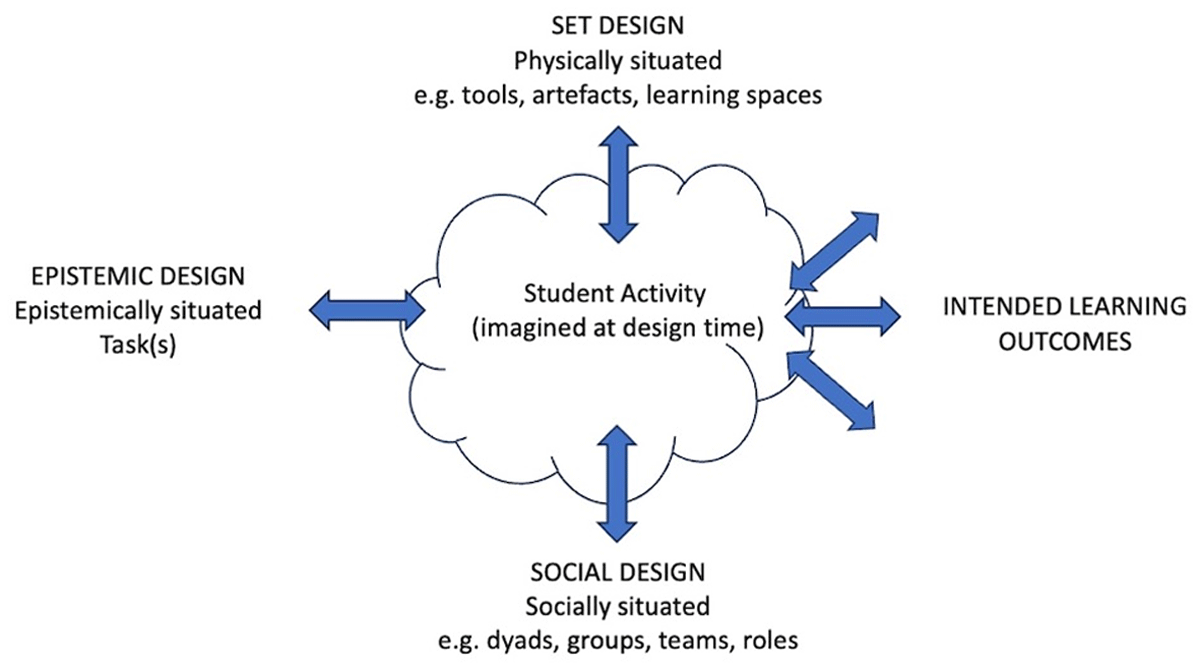
Figure 1
ACAD at design-time (Source: Goodyear, Carvalho & Yeoman 2021: 449).
Table 1
Elements described through the ACAD framework (adapted by Yeoman 2015).
| PHILOSOPHY | SET DESIGN LEARNING IS PHYSICALLY SITUATED | EPISTEMIC DESIGN LEARNING IS SUPPORTED THROUGH KNOWLEDGE-ORIENTED TASKS/ACTIVITY | SOCIAL DESIGN LEARNING IS SOCIALLY SITUATED |
|---|---|---|---|
| MACRO The global | Complex mix of digital and physical artefacts, texts, and tools (incl. global frameworks on AMR, digital systems) Diverse built/work sites across sectors and geographies Online learning platform. Internet infrastructure/networks in LMICs/remote locations | Scientific research and scientific methodologies (e.g. research on AMR, research on learning in professional settings, research on learning online) | Broader cultural context (e.g. rules, norms, division of labour re. organisation of work in health/vet settings in LMICs) |
| MESO The local | Site on the platform Modules’ site Physical space at work (e.g. facilities for teaching and meetings, computer lab) Physical space at home Local/Organisational digital and physical artefacts, texts and tools (incl. infrastructure for connectivity/broadband accessibility, and national and org policies, AMR Data (org/national level)) | Pathways designed per role Sequence of modules Module content Assessment framework | Distance learning modality Asynchronous learning Independent learning Individuals encouraged to connect with their professional communities Inter-dependency of roles and responsibilities |
| MICRO The detail | Access to work devices (e.g. PCs) Access to personal devices (e.g. laptops, mobile phones) Access to work equipment and spaces (e.g. disks, reagents, lab equipment, lab spaces Data – broadband accessibility Downloadable/printed materials in various formats (ePub, pdf etc) Multimedia resources/videos Time allocated for study | Selection of modules Tasks (incl. assessment) Pace of study | Social arrangements may be continually changing Connections include Tutor – students (indirect); Students – colleagues and wider AMR community |
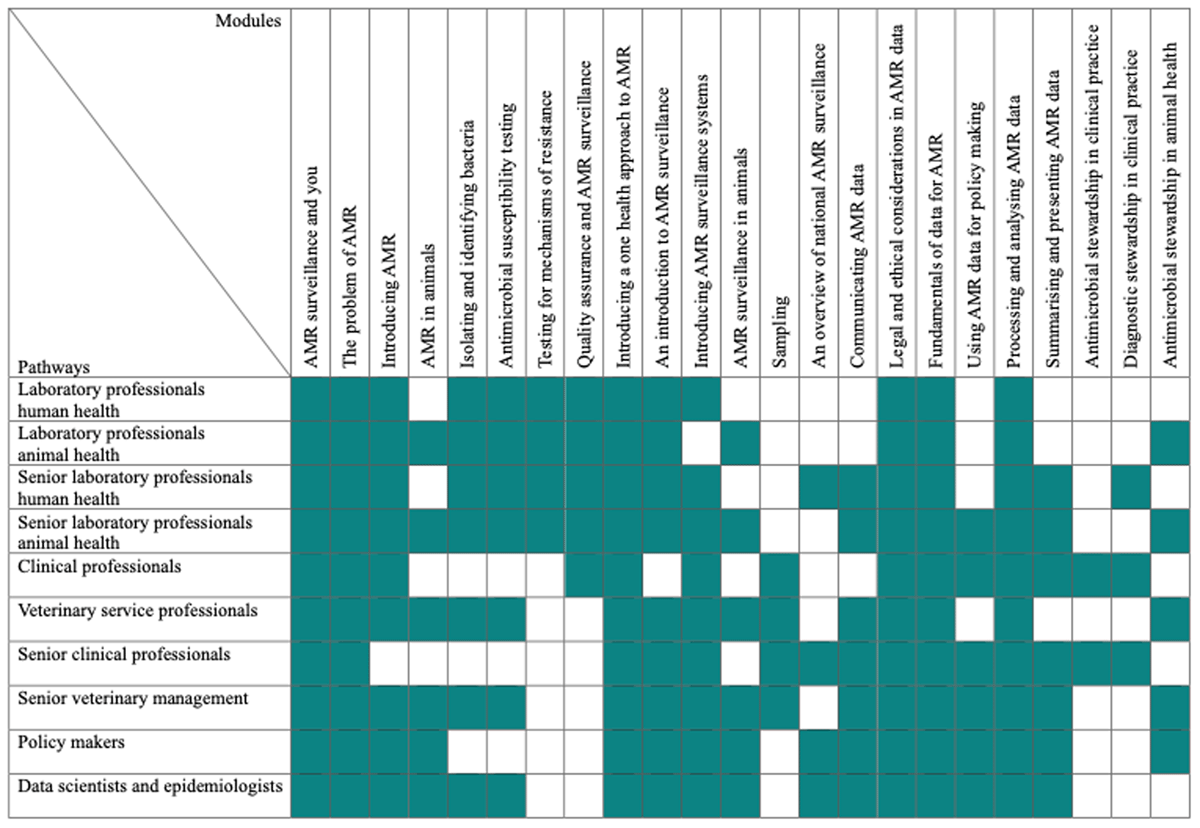
Figure 2
Modules and learner pathways in the global AMR curriculum.
