Fig. 1
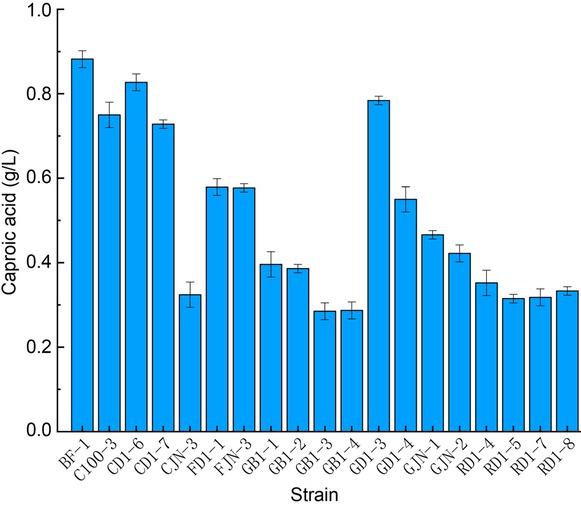
Fig. 2
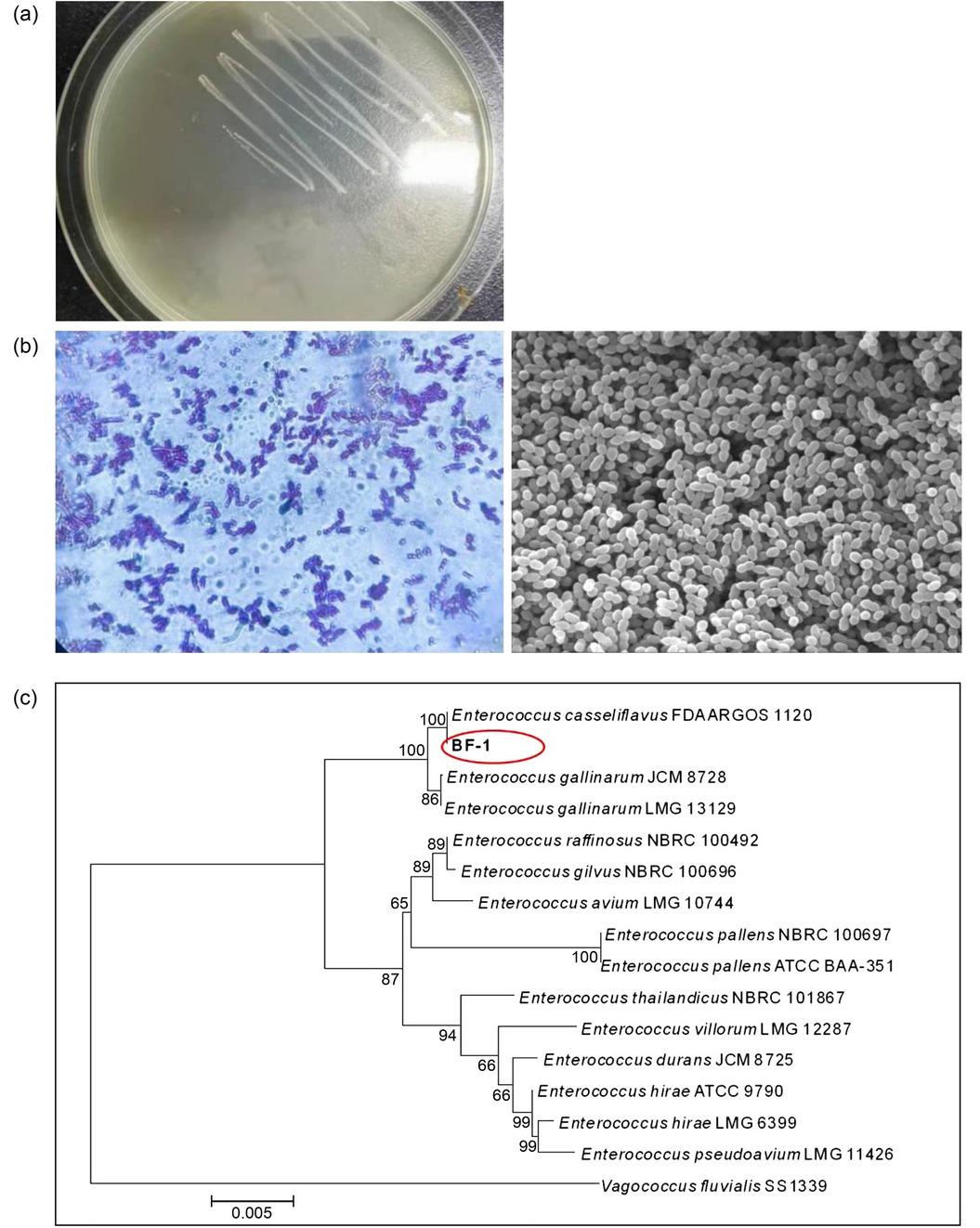
Fig. 3
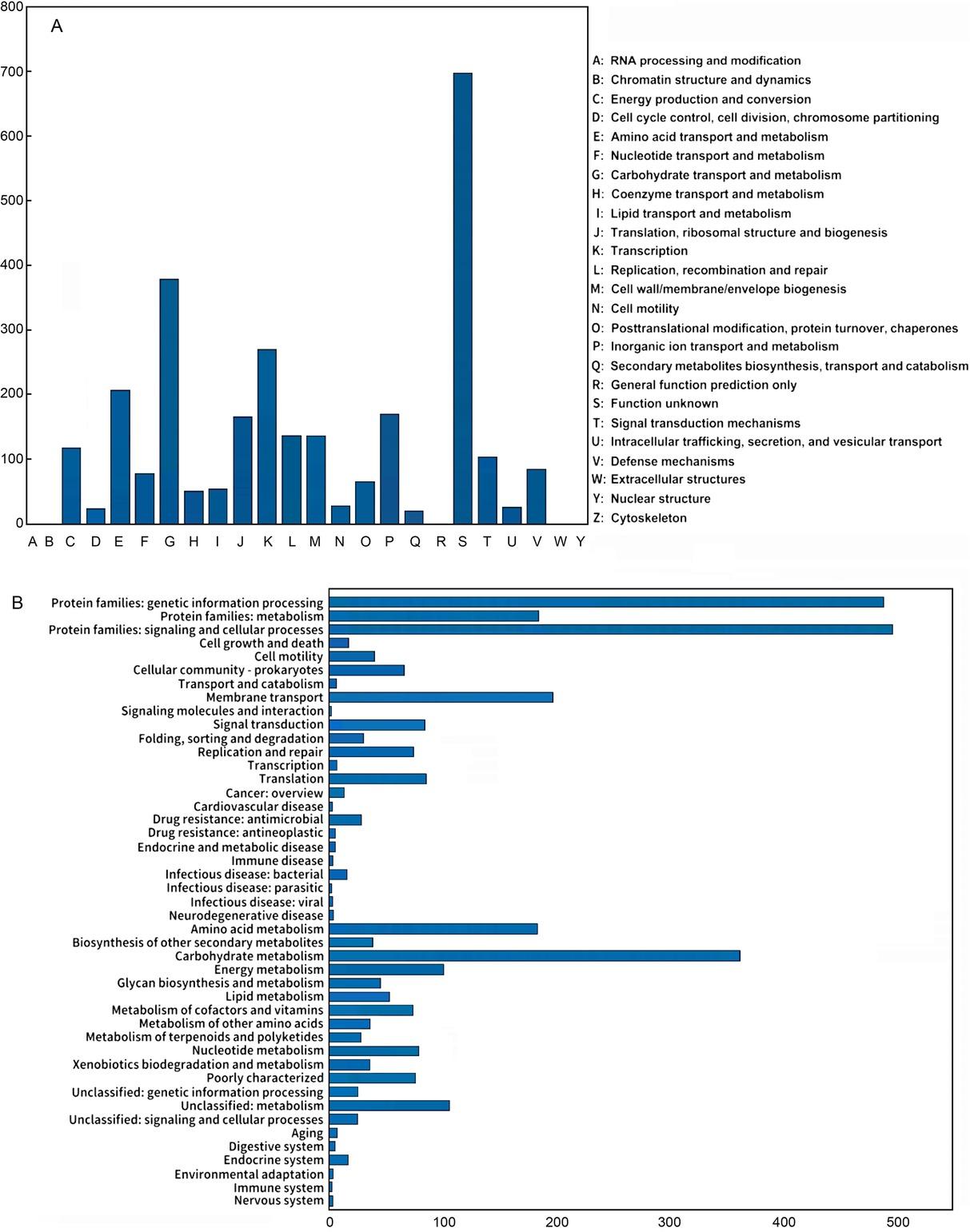
Fig. 4

Fig. 5
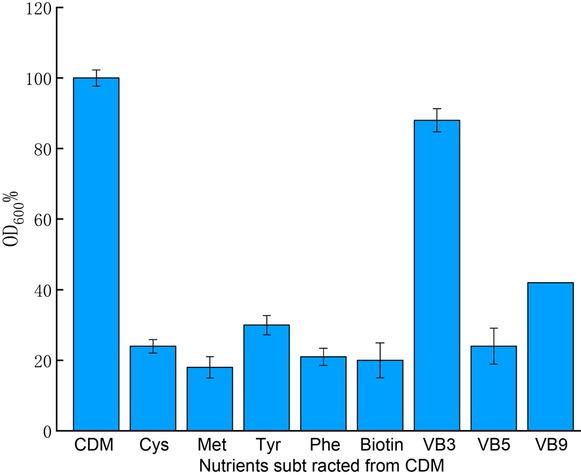
Fig. 6
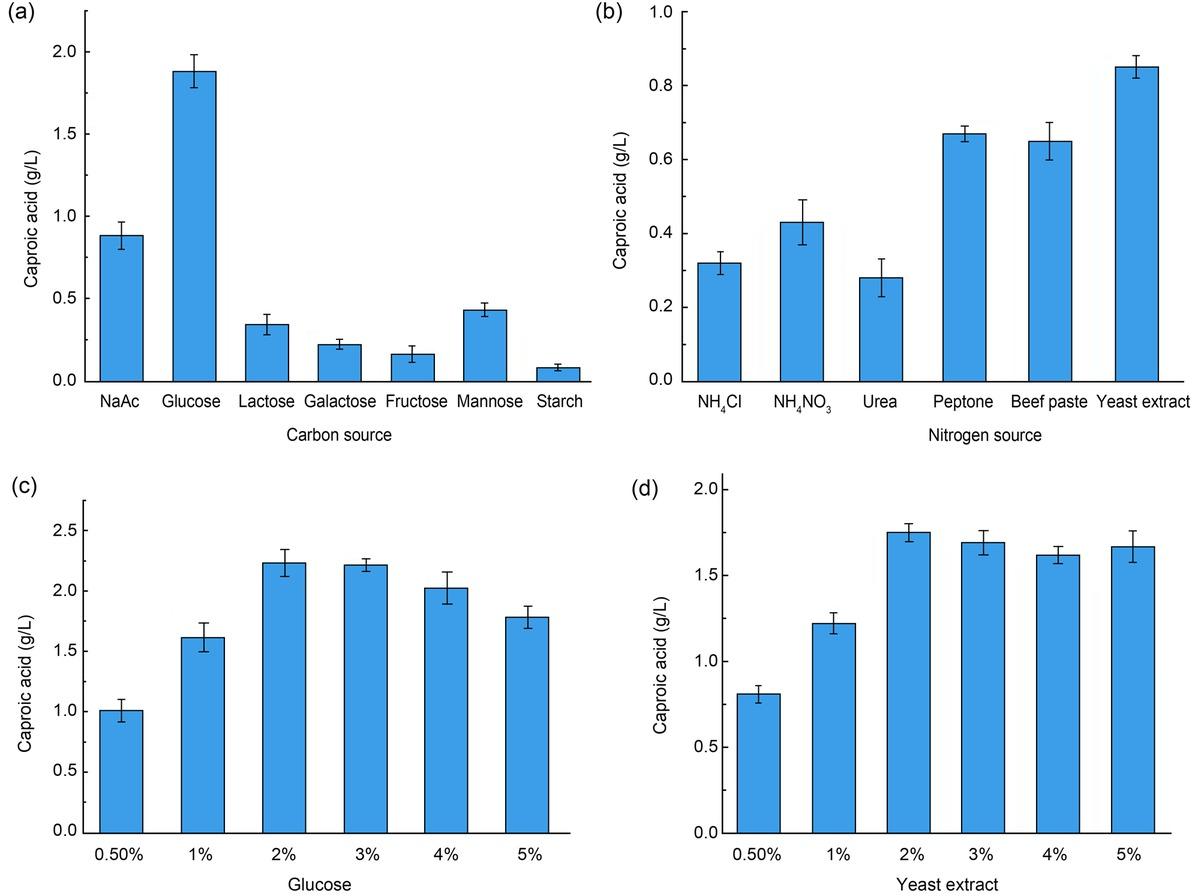
Fig. 7
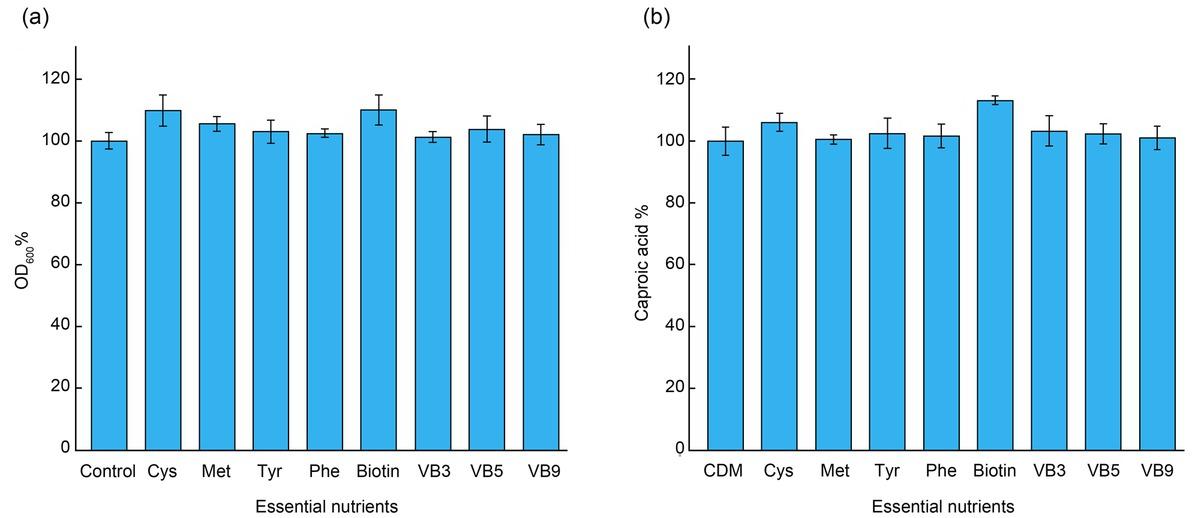
Fig. 8
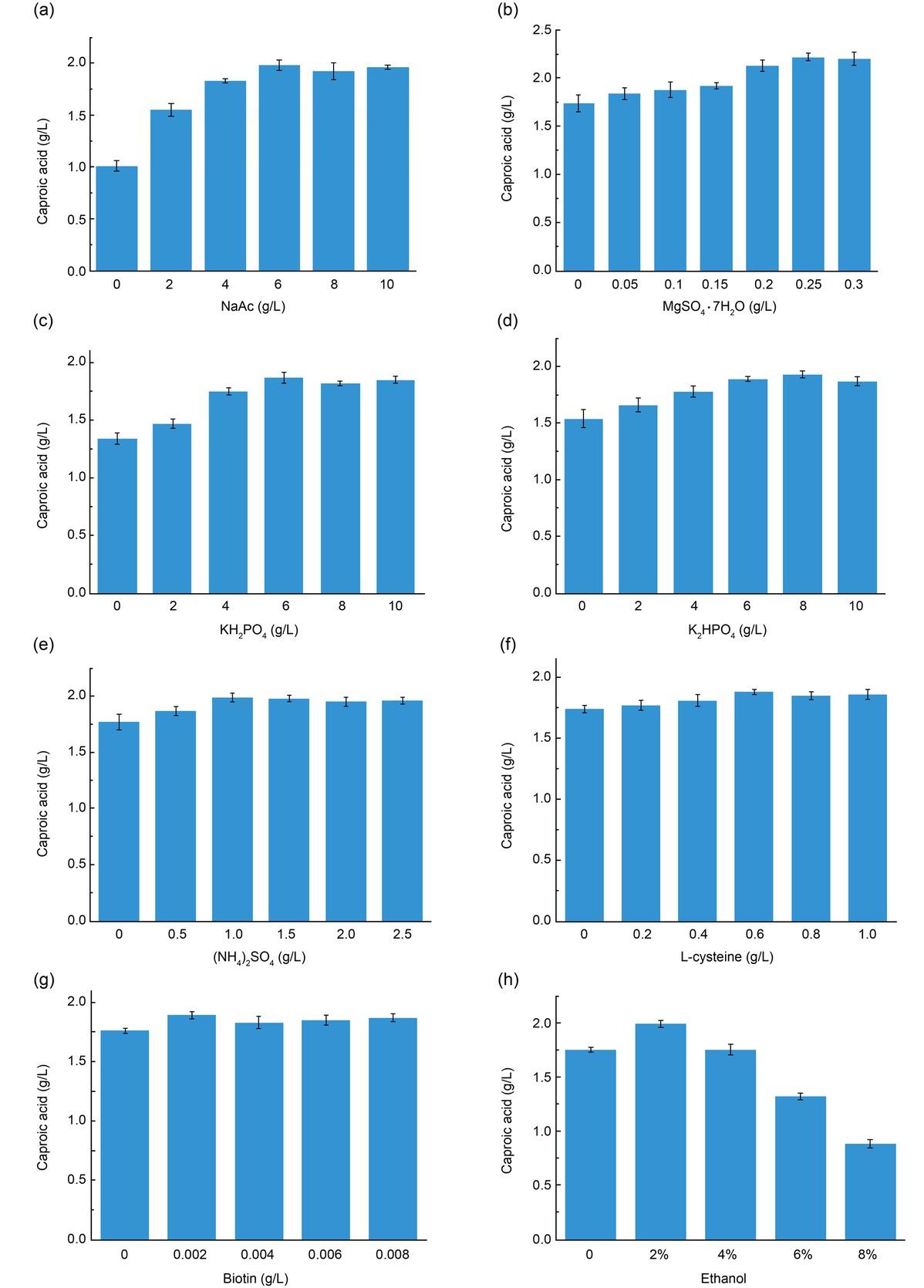
Results of L16 (44) orthogonal experiment_
| Glucose | Yeast extract | Sodium acetate | Ethanol | Caproic acid production (g/l) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.76 | |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.99 | |
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1.81 | |
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1.63 | |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2.33 | |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2.22 | |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2.79 | |
| 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1.96 | |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1.87 | |
| 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2.43 | |
| 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2.12 | |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1.96 | |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2.44 | |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2.56 | |
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2.08 | |
| 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1.56 | |
| K1 | 1.798 | 2.1 | 1.915 | 2.268 | |
| K2 | 2.325 | 2.3 | 2.09 | 2.127 | |
| K3 | 2.095 | 2.22 | 2.05 | 2.033 | |
| K4 | 2.16 | 1.777 | 2.322 | 1.95 | |
| R | 0.527 | 0.523 | 0.407 | 0.318 |
Basic characteristics of the genome of strain BF-1_
| Features | BF-1 |
|---|---|
| Read-Num | 8,697,842 bp |
| HQ reads | 8,663,546 bp |
| Genome size | 2,968,377 bp |
| G + C content | 43.52% |
| ORF number | 3270 |
| ORF density | 0.967 genes per kb |
| ORF average length | 907,76 bp |
| Intergenetic region length | 414,643 bp |
| Coding percentage | 87.74% |
| rRNA | 3 |
| tRNA | 53 |
| ncRNA | 113 |
| Q value | 40 |
| Q20-rate | 98.84 |
| Q30-rate | 95.83 |
| Contig N50 | 372,495 bp |
| Scaffold N50 | 570,209 bp |
| Contig total sequence length | 3,383,020 bp |
| Scaffold total sequence length | 3,383,020 bp |
Orthogonal experiment of four factors and four levels_
| Level | Factor A (glucose g/l) | Factor B (yeast extract g/l) | Factor C (sodium acetate g/l) | Factor D (ethanol %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 | 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 30 | 30 | 6 | 3 |
| 4 | 40 | 40 | 8 | 4 |
Variance analysis of the strain BF-1 orthogonal experiment_
| Variance source | Sum of squares | Freedom | Mean square | F-value | p-value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correction model | 1.766a | 12 | 0.147 | 14.537 | 0.025 | |
| Intercept | 70.183 | 1 | 70.183 | 6,933.032 | 0.000 | |
| Factor A | 0.583 | 3 | 0.194 | 19.182 | 0.018 | * |
| Factor B | 0.616 | 3 | 0.205 | 20.268 | 0.017 | * |
| Factor C | 0.345 | 3 | 0.115 | 11.354 | 0.038 | * |
| Factor D | 0.223 | 3 | 0.074 | 7.342 | 0.068 | – |
| Error | 0.030 | 3 | 0.010 | |||
| Total | 71.979 | 16 | ||||
| Corrected total | 1.796 | 15 |
The occurrence of virulence factor encoding genes in the strain BF-1 genome_
| Related genes | VFclass |
|---|---|
| ebpA, ebpC, srtC, efaA, slrA | Adherence |
| cpsA, cpsB, cpsJ | Antiphagocytosis |
| bopD | Biofilm formation |
| – | Toxin |
| – | Exoenzyme |
| ctpV | Copper up take |
| capD, cps4I, cpsY | Immune evasion |
| htrA/degP | Protease |
| cheY | Regulation |
Results of physiological and biochemical experiments_
| BF-1strain | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Voges-Proskauer test | – | Mannitol | + |
| MRtest | + | Fructose | + |
| Gelatin hydrolysis | – | Stachyose | + |
| Starch hydrolysis | + | Cellobiose | + |
| Nitrate reduction | – | Xylose | + |
| Lactose | + | Galactose | + |
| Sucrose | + | Glycerin | – |
| Raffinose | + | Mannose | + |