Figure 1
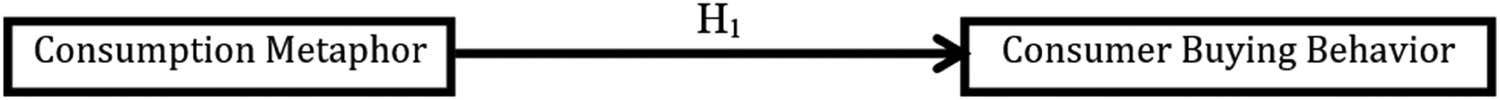
Figure 2
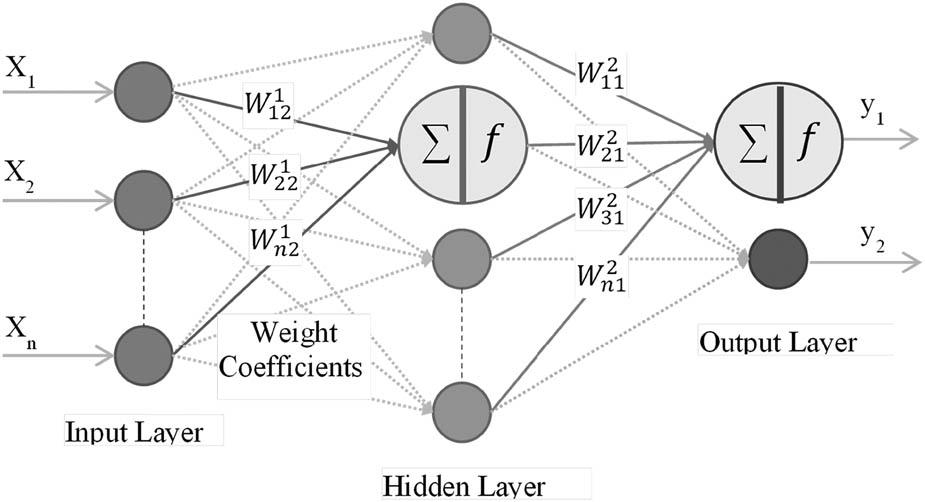
Figure 3
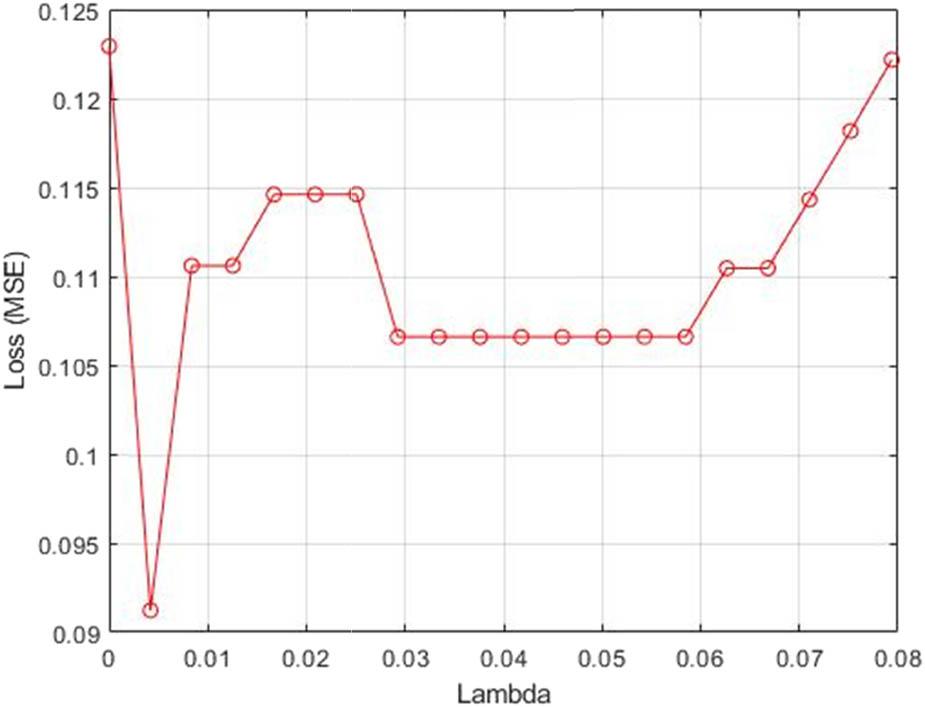
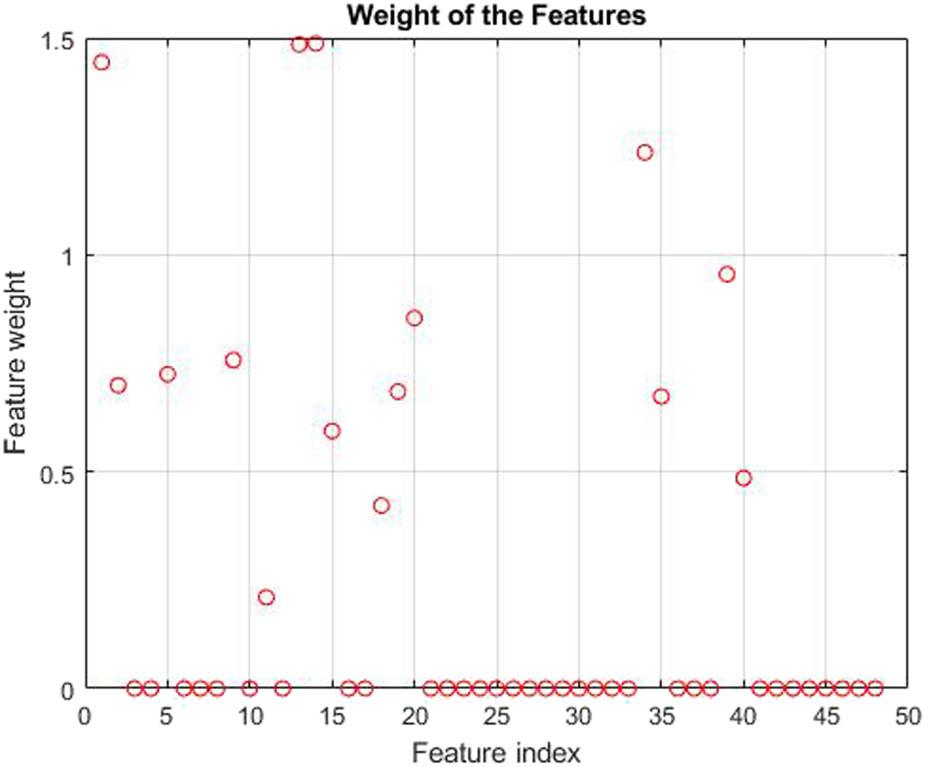
Figure 4
Cronbach’s alpha test_
| Scale | Number of expression | Cronbach alpha |
|---|---|---|
| CM | 4 | 0.823 |
| CBB | 11 | 0.792 |
Prediction with metaphor variables by using NCFS_
| Method | Accuracy | Specificity | Precision | Recall | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 72.86 | 83.56 | 79.78 | 62.88 | 69.25 |
| SVM | 70.06 | 69.75 | 70.00 | 70.92 | 69.60 |
| ELM | 78.33 | 79.51 | 79.34 | 77.55 | 78.12 |
The algorithm steps of kNN_
| 1 | Determine the value of |
| 2 | Calculate the distance between the new instance |
| 3 | Determine the |
| 4 | Determine the class of the new instance by majority voting. |
Prediction with selected features by using NCFS_
| Method* | Accuracy | Specificity | Precision | Recall | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 91.02 | 90.98 | 91.91 | 90.51 | 91.03 |
| SVM | 87.63 | 87.14 | 88.46 | 86.91 | 87.47 |
| ELM | 88.54 | 84.98 | 87.29 | 91.34 | 89.13 |
Distribution table of socio-demographic characteristics of the subjects participating in the study_
| Variables | Frequency (f) | Percent (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relationship (partner) | Yes | 132 | 34.9 |
| No | 246 | 65.1 | |
| Place of birth | Big city | 171 | 45.2 |
| Province | 99 | 26.2 | |
| County | 99 | 26.2 | |
| Village | 9 | 2.4 | |
| Living place | Big city | 243 | 64.3 |
| Province | 79 | 20.9 | |
| County | 46 | 12.2 | |
| Village | 10 | 2.6 | |
| Mother’s education level | Illiterate | 23 | 6.1 |
| Primary school | 156 | 41.3 | |
| Secondary education | 156 | 41.3 | |
| University | 43 | 11.4 | |
| Father’s education level | Illiterate | 8 | 2.1 |
| Primary school | 137 | 36.2 | |
| Secondary education | 162 | 42.9 | |
| University | 71 | 18.8 | |
| State of illness | Yes | 48 | 12.7 |
| No | 330 | 87.3 | |
| Total | 378 | 100 | |
Sample distribution table of the subjects participating in the study_
| Variables | Frequency (f) | Percent (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 180 | 47.6 |
| Male | 198 | 52.4 | |
| Age | 17–18 | 16 | 4.2 |
| 19–20 | 177 | 46.8 | |
| 21–22 | 137 | 36.2 | |
| 23–24 | 33 | 8.7 | |
| 25 and more | 15 | 4.0 | |
| Body type | Slim | 92 | 24.3 |
| Normal | 237 | 62.7 | |
| Large | 49 | 13.0 | |
| Educational level | Associate degree | 299 | 79.1 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 79 | 20.9 | |
| Science field | Social sciences | 324 | 85.7 |
| Science | 36 | 9.5 | |
| Health Sciences | 18 | 4.8 | |
| Level of income | 1,000 TL and less | 224 | 59.3 |
| 2,000 TL | 85 | 22.5 | |
| 3,000 TL | 24 | 6.3 | |
| 4,000 TL | 11 | 2.9 | |
| 5,000 TL and more | 34 | 9.0 | |
| Total | 378 | 100 | |
Chi-Square analysis results among CBB categories_
| Would you like to get a tattoo? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Total | |||
| Did you get a tattoo? | Yes, I did | Frequency | 213 | 8 | 221 |
| Did you get a tattoo? | 96.4% | 3.6% | 100.0% | ||
| Would you like to get a tattoo? | 29.3% | 1.3% | 16.5% | ||
| No, I did not | Frequency | 514 | 604 | 1,118 | |
| Did you get a tattoo? | 46.0% | 54.0% | 100.0% | ||
| Would you like to get a tattoo? | 70.7% | 98.7% | 83.5% | ||
| Total | Frequency | 727 | 612 | 1,339 | |
| Did you get a tattoo? | 54.3% | 45.7% | 100.0% | ||
| Would you like to get a tattoo? | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | ||
Kmo–Bartlett’s test_
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin measure of sampling adequacy | 0.835 | |
| Bartlett’s test of sphericity | Approx. chi-square | 5174.812 |
| df | 435 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
Goodness of fit indexes of scales_
| Scale model | ΔX 2 | sd | p | ΔX 2/sd | GFI | CFI | RMSEA | RMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 7.274 | 6 | 0.06 | 1.21 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| CBB | 5.489 | 3 | .23 | 1.83 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
Model fit criteria goodness of fit index reference ranges_
| Model fit criteria | Good fit | Acceptable fit |
|---|---|---|
| X 2 Uyum Testi | 0.05 < p ≤ 1 | 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05 |
| CMIN/SD | X 2/sd ≤ 3 | X 2/sd ≤ 5 |
| Comparative fit indexes | ||
| CFI | 0.97 ≤ CFI | 0.95 ≤ CFI |
| RMSEA | RMSEA ≤ 0.05 | RMSEA ≤ 0.08 |
| Absolute fit indexes | ||
| GFI | 0.90 ≤ GFI | 0.85 ≤ GFI |
| Residual compliance indexes | ||
| RMR | 0 < RMR ≤ 0.05 | 0 < RMR ≤ 0.08 |
Correlation analysis results_
| Measurement data | 1 | 2 |
| 1. CM | 1 | |
| 2. CBB | 0.315** | 1 |
The algorithm steps of ELMs_
| 1 | Assign weights |
| 2 | Calculate hidden layer output, H |
| 3 | Calculate output weight matrix , |
| 4 | Use |
NCA feature selection_
| 1 | Procedure |
| 2 | Initialization: |
| 3 | repeat |
| 4 | for I = 1, …, N do |
| 5 | Compute |
| 6 | for l = 1, …, d do |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 | if |
| 12 |
|
| 13 | else |
| 14 |
|
| 15 | until |
| 16 |
|
| 17 | return |
Prediction with all features_
| Method* | Accuracy | Specificity | Precision | Recall | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 89.77 | 87.33 | 89.26 | 91.64 | 90.27 |
| SVM | 87.54 | 85.46 | 87.49 | 88.72 | 87.84 |
| ELM | 87.32 | 81.48 | 85.49 | 91.60 | 88.23 |
Exploratory factor analysis_
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CM Cr. Alpha = 0.823 | Get experience with tattooing | 0.618 | |
| Desire to join a community | 0.847 | ||
| Socialization or group interaction | 0.902 | ||
| Social differentiation | 0.846 | ||
| CBB Cr. alpha = 0.792 | Do you have a tattoo? | 0.441 | |
| Would you like to get a tattoo? | 0.701 | ||
| What are the reasons why you don’t want to get a tattoo? | 0.650 | ||
| Do you want to get a permanent tattoo or a temporary tattoo? | 0.897 | ||
| On which part(s) of your body did you have your tattoo done or would you like to have it done? | 0.599 | ||
| Does anyone in your family have a tattoo? | 0.850 | ||
| Do any of your friends have tattoos? | 0.875 |