Figure 1.
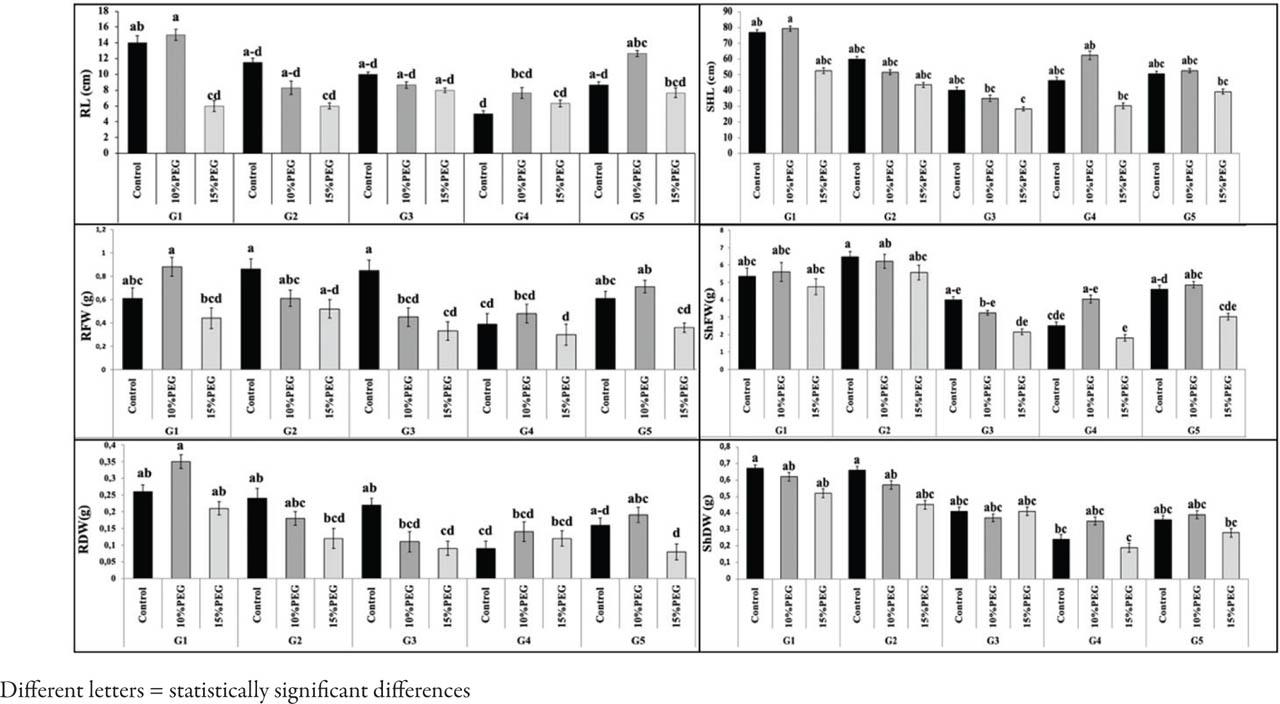
Figure 2.
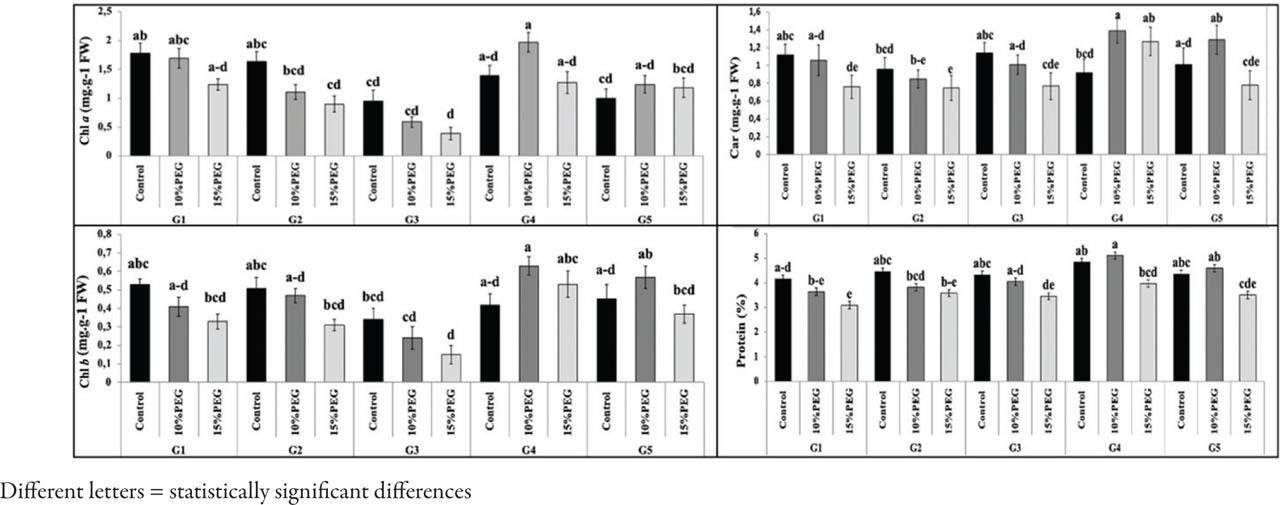
Figure 3.
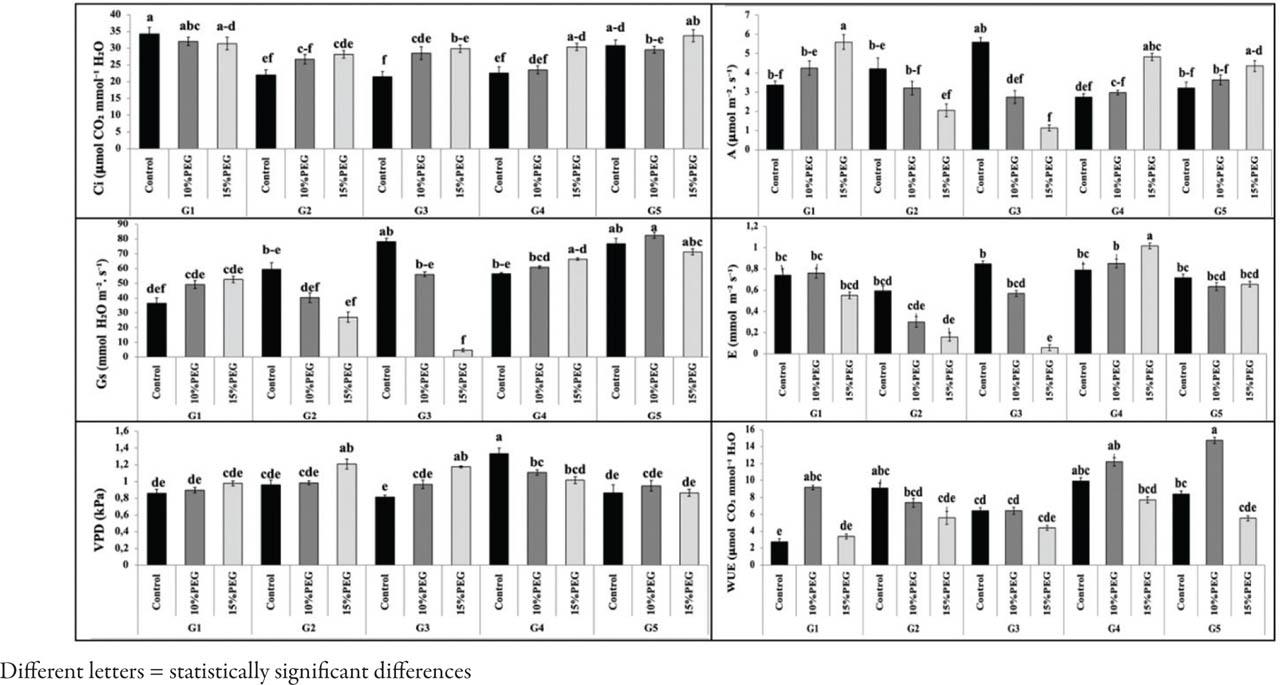
Figure 4.
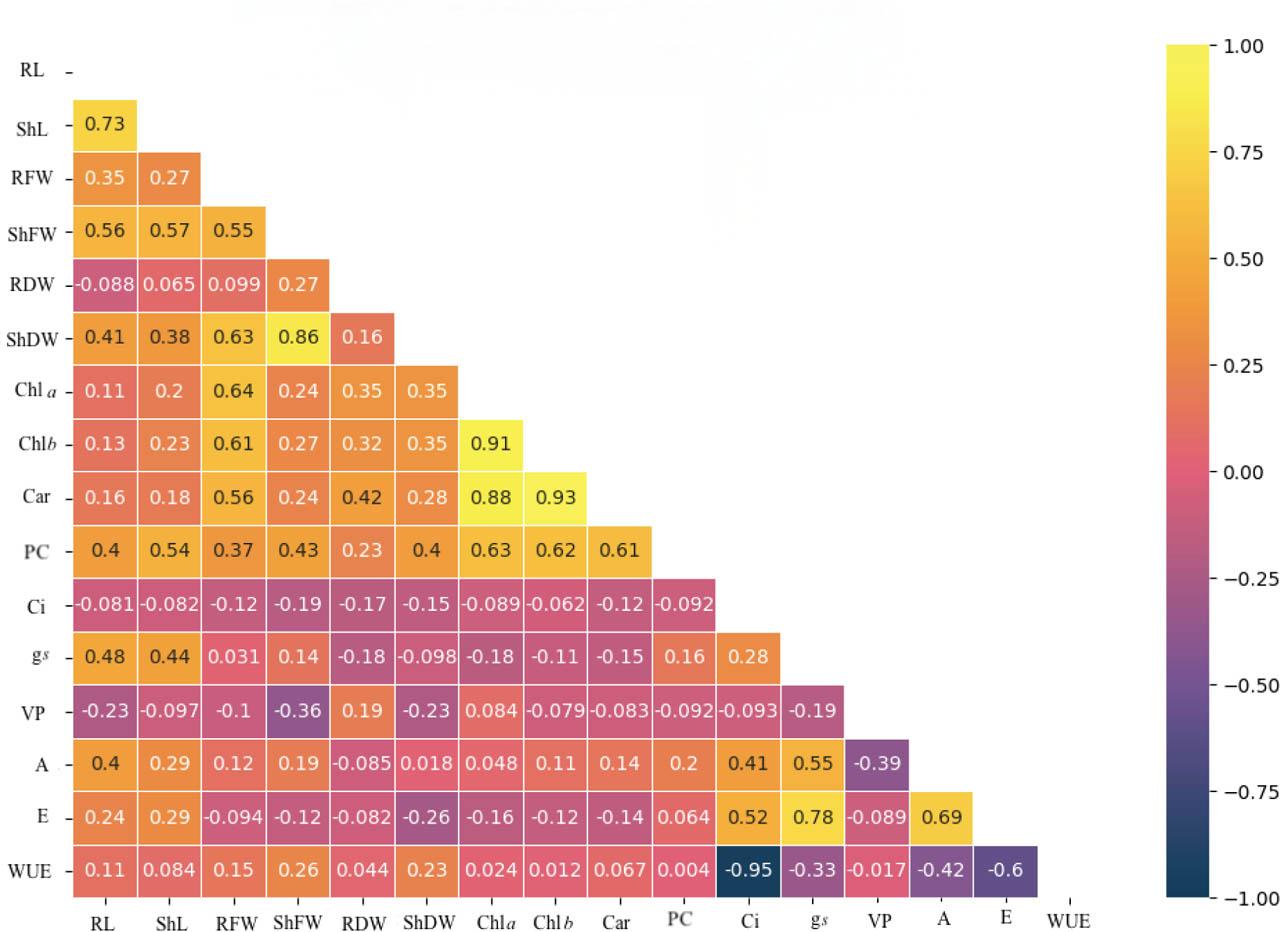
Figure 5.
Common bean genotypes used in this studyTabelle 1_ In dieser Studie verwendete Genotypen der Gartenbohne
| Common Bean | Location | Region | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | Likovc | Skenderaj | 42.6639°N 20.7535°E |
| G2 | Arllat | Drenas | 42.5475°N 20.7980°E |
| G3 | Dobroshec | Drenas | 42.5463°N 20.7882°E |
| G4 | Tupec | Prizren | 42.2031°N 20.6850°E |
| G5 | Landovica | Prizren | 42.2593°N 20.6811°E |
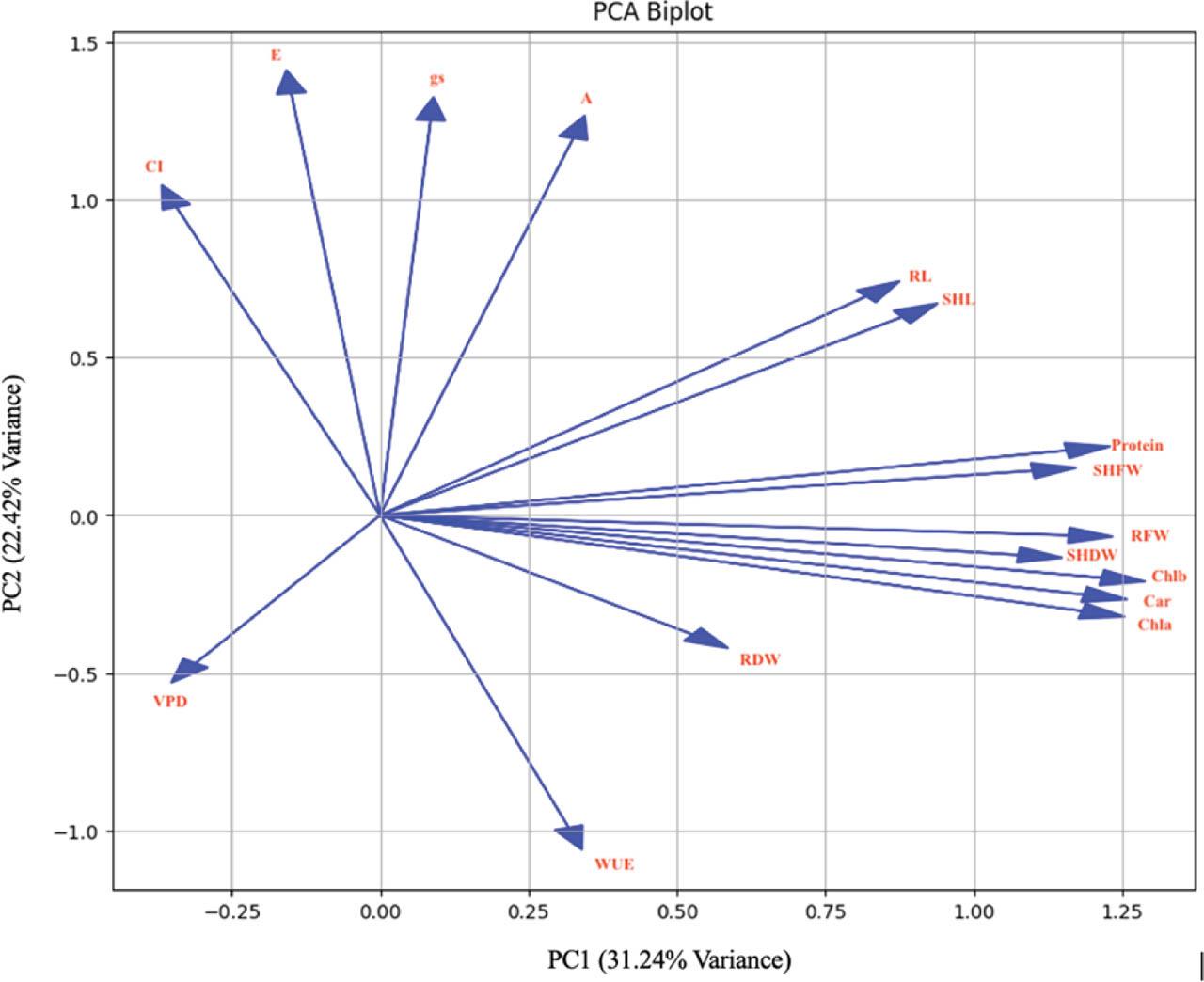
Overall means for morpho-physiologic traits of common bean affected by PEG treatmentsTabelle 3_ Gesamtmittelwerte für morphophysiologische Merkmale der Gartenbohne, beeinflusst durch PEG-Behandlungen
| Traits | Abbreviation | Unit | Control | 10% PEG | 15% PEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root length | RL | cm | 9.36b | 10.46a | 7.20c |
| Shoot length | ShL | cm | 54.87b | 57.6a | 44.87c |
| Root fresh weight | RFW | g | 0.61a | 0.58b | 0.38c |
| Shoot fresh weight | ShFW | g | 3.69b | 4.24a | 3.26c |
| Root dry weight | RDW | g | 0.11b | 0.14a | 0.07c |
| Shoot dry weight | ShDW | g | 0.53b | 0.58a | 0.37c |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration | Ci | μmol mol−1 H2O | 282.50a | 262.26b | 256.90c |
| Stomatal conductance | gs | mol m−2 s−1 | 122.70a | 49.79c | 54.40b |
| Vapor pressure deficit | VPD | kPa | 0.96c | 0.95b | 0.98a |
| Photosynthetic CO2 assimilation | A | μmol m−2 s−1 | 5.02a | 3.57b | 2.79c |
| Transpiration rate | E | mmol H2O m−2 s−1 | 1.18a | 0.48c | 0.54b |
| Water use efficiency | WUE | μmol CO2/mmol H2O | 6.11c | 7.76a | 7.71b |
| Chlorophyll a | Chl a | mg g−1 FW | 1.42a | 1.30b | 0.90c |
| Chlorophyll b | Chl b | mg g−1 FW | 0.66a | 0.57b | 0.41c |
| Carotenoids | Carot | mg g−1 FW | 1.46a | 1.35b | 0.94c |
| Protein concentration | PC | % | 4.44a | 4.24b | 3.52c |
Description of the measured morphological parametersTabelle 2_ Beschreibung der gemessenen morphologischen Parameter
| Traits | Description/Method |
|---|---|
| ShL | Maximum fresh shoot length (cm), measured from the base of the stem to the top of the plant |
| ShFW | Shoot fresh weight (g) |
| ShDW | Shoot dry weight (g) aher drying for 48 h at 70 ± 5 °C |
| RL | Maximum fresh root length (cm), measured from the node where it divides from the stem to the top of the main root |
| RFW | Root fresh weight (g) |
| RDW | Root dry weight (g) aher drying for 48 h at 70 ± 5 °C |
| PC | Protein concentration in %, determined by the Kjeldahl method (digestion of organic matter with sulfuric acid in the presence of a catalyst, rendering the reaction product alkaline, then distillation and titration of the liberated ammonia, calculation of the nitrogen content, and multiplication of the result by the conventional factor 6.25 to obtain the crude PC) |