Figure 1:
Pearson correlation of LLS questionnaire_
| No. | Items | Pearson correlation | Sig. (2-tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Memory strategies | 1 | 0.939** | |
| 1 | I think of relationships between what I already know and new things I learn in English. | 0.879** | 0.772** |
| 2 | I use new English words in a sentence so I can remember them. | 0.727** | 0.641** |
| 3 | I connect the sound of a new word and an actual or mental picture of the word to help me remember the word. | 0.440* | 0.699** |
| 4 | I link the sound of new words to help me remember the word. | 0.834** | 0.782** |
| 5 | I use rhymes to remember new words with familiar words or sounds from either English or any language. | 0.834** | 0.811** |
| 6 | I use notes to remember new words. | 0.780** | 0.794** |
| 7 | I review speaking lessons often. | 0.706** | 0.866** |
| 8 | I remember new words or phrases by remembering their location on the page, on the board, or on a street sign. | 0.631** | 0.463* |
| Cognitive strategies | 1 | 0.960** | |
| 9 | I say or listen to new words several times. | 0.845** | 0.805** |
| 10 | I try to talk like native English speakers | 0.725** | 0.793** |
| 11 | I practice the sounds of new English words. | 0.838** | 0.794** |
| 12 | Use the words I know in different ways. | 0.780** | 0.794** |
| 13 | I start conversations in English. | 0.852** | 0.766** |
| 14 | I watch English episodes or videos. | 0.689** | 0.638** |
| 15 | I use available dictionaries, word lists, and grammar exercises to understand what I listen in the new language and then produce conversation. | 0.806** | 0.793** |
| 16 | I speak for pleasure in English. | 0.927** | 0.830** |
| 17 | I compare new words in English with words in my Arabic language | 0.897** | 0.832** |
| 18 | I make use of grammar and vocabulary formation rules to get the meaning of new words in a spoken text. | 0.856** | 0.585** |
| 19 | I find the meaning of a new word by dividing it into parts that I understand. | 0.897** | 0.832** |
| 20 | I try to translate spoken text into my own language in order to understand the meaning. | 0.845** | 0.805** |
| 21 | I try not to translate word-for-word. | 0.709** | 0.589** |
| Compensation strategies | 1 | 0.952** | |
| 22 | To understand unfamiliar English words, I make inferences. | 0.758** | 0.763** |
| 23 | I make up new words if I don’t know the right words in English. | 0.857** | 0.813** |
| 24 | I try to guess what the other person will say next in English | 0.838** | 0.794** |
| 25 | To try to understand a spoken text without looking up every new word. | 0.927** | 0.830** |
| 26 | If I can’t think of an English word, I use a word or phrase that means the same thing. | 0.830** | 0.761** |
| Metacognitive strategies | 1 | 0.950** | |
| 27 | Try to find as many ways as I can to speak. | 0.845** | 0.805** |
| 28 | I notice my mistakes and use that information to help me do better in speaking in future. | 0.766** | 0.712** |
| 29 | I pay attention when someone is speaking English. | 0.845** | 0.805** |
| 30 | Have clear objectives and goals for improving my speaking skills. | 0.806** | 0.793** |
| 31 | Decide the purpose of speaking. | 0.897** | 0.832** |
| 32 | I look for people I can talk to in English. | 0.709** | 0.589** |
| 33 | I look for opportunities to speak as much as possible in English. | 0.714** | 0.606** |
| 34 | Assess my progress in learning speaking skills. | 0.856** | 0.585** |
| Affective strategies | 1 | 0.948** | |
| 35 | Reduce anxiety about learning speaking using relaxation, deep breathing, laughter, games, mediation, and music. | 0.695** | 0.687** |
| 36 | Encourage myself to speak English even when I am afraid of making a mistake. | 0.922** | 0.845** |
| 37 | I give myself a reward when I speak well in English. | 0.852** | 0.766** |
| 38 | Notice if I am tense or nervous when I speak. | 0.901** | 0.810** |
| 39 | Write down my feelings about learning speaking in a diary. | 0.725** | 0.793** |
| 40 | Talk to someone else about how I feel toward learning speaking. | 0.856** | 0.585** |
| Social strategies | 1 | 0.856** | |
| 41 | Ask the other person to slow down or say it again if I do not understand something in speaking. | 0.612** | 0.856** |
| 42 | Ask people whose English is better than mine to correct me when 1 speak. | 0.692** | 0.495* |
| 43 | Practice speaking English with other students. | 0.856** | 0.585** |
| 44 | Ask for help from good speakers of English when doing a speaking task. | 0.689** | 0.638** |
| 45 | Ask questions about speaking tasks. | 0.866** | 0.614** |
Themataic breakdown of the semi-structured interview_
| Semi-structured interview questions | Themes | Codes | Interviewees’ responses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. How do you use Telegram to reduce your fear of negative evaluation? | Reducing fear of negative evaluation | Use of voice messages for authentic conversation | “Well, I used voice messages… because, um, I felt like real conversations.” (SSI = 1) |
| Active participation in group discussions without fear of judgment | “Uh …I do not feel shy speaking English in the group.” (SSI = 9) | ||
| 2. Have you participated in Telegram speaking discussion activities? If so, how did they affect your confidence? | Building confidence through interaction | Peer support and feedback in discussions | “Telegram gave me opportunities to participate actively, um, without worrying about mistakes.” (SSI = 8) |
| Encouragement from peers to participate | “Well, I was encouraged to answer the questions, like, voluntarily. I wasn’t worried about, you know, correcting my mistakes.” (SSI = 2) | ||
| 3. Which Telegram features help you feel more comfortable speaking English? | Tools and features for comfort | Voice messages | “I used voice messages to express myself more freely without the fear of judgment.” (SSI = 11) |
| Dictionaries and translation tools for vocabulary and pronunciation | “I used an online dictionary to learn the pronunciation of new words before speaking.” (SSI = 6) | ||
| 4. Do the constructive feedback in Telegram groups help reduce the fear of judgment or criticism? | Reducing judgment fear through feedback | Constructive peer feedback in group discussions | “Feedback in Telegram helped me improve by pointing out small mistakes. It felt less harsh than in class.” (SSI = 5) |
| Instant and supportive feedback | “I always listen to responses to understand areas that need improvement… um.” (SSI = 11) |
Internal consistency of the LLS questionnaire_
| No. | Strategies | No. of items | Reliability-Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Memory strategies | 8 | 0.83 |
| 2 | Cognitive strategies | 13 | 0.91 |
| 3 | Compensation strategies | 5 | 0.78 |
| 4 | Metacognitive strategies | 8 | 0.80 |
| 5 | Affective strategies | 6 | 0.79 |
| 6 | Social strategies | 5 | 0.76 |
| 7 | Overall | 45 | 0.93 |
Common features of the experimental group and control group_
| Qualities | Experimental group | Control group |
|---|---|---|
| Educational background | High school (science stream) | High school (science stream) |
| English language as a foreign language | 8 years at school | 8 years at school |
| Age | 18–20 | 18–20 |
| Gender | Male | Male |
| Nationality | Saudi Arabia | Saudi Arabia |
| Mother tongue | Arabic | Arabic |
| Use of smartphones | Yes | No |
| Level of study | First year: first semester | First year: first semester |
Analysis of FNE questionnaire_
| Application | Group | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Control | 35 | 3.95 | 0.695 | 0.78 | 68 | 0.437 | 0.19 (small) |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.83 | 0.580 | |||||
| Post | Control | 35 | 3.50 | 0.711 | 11.83 | 68 | 0.000 | 2.82 (very large) |
| Experimental | 35 | 1.92 | 0.348 |
Analysis of LLS questionnaire_
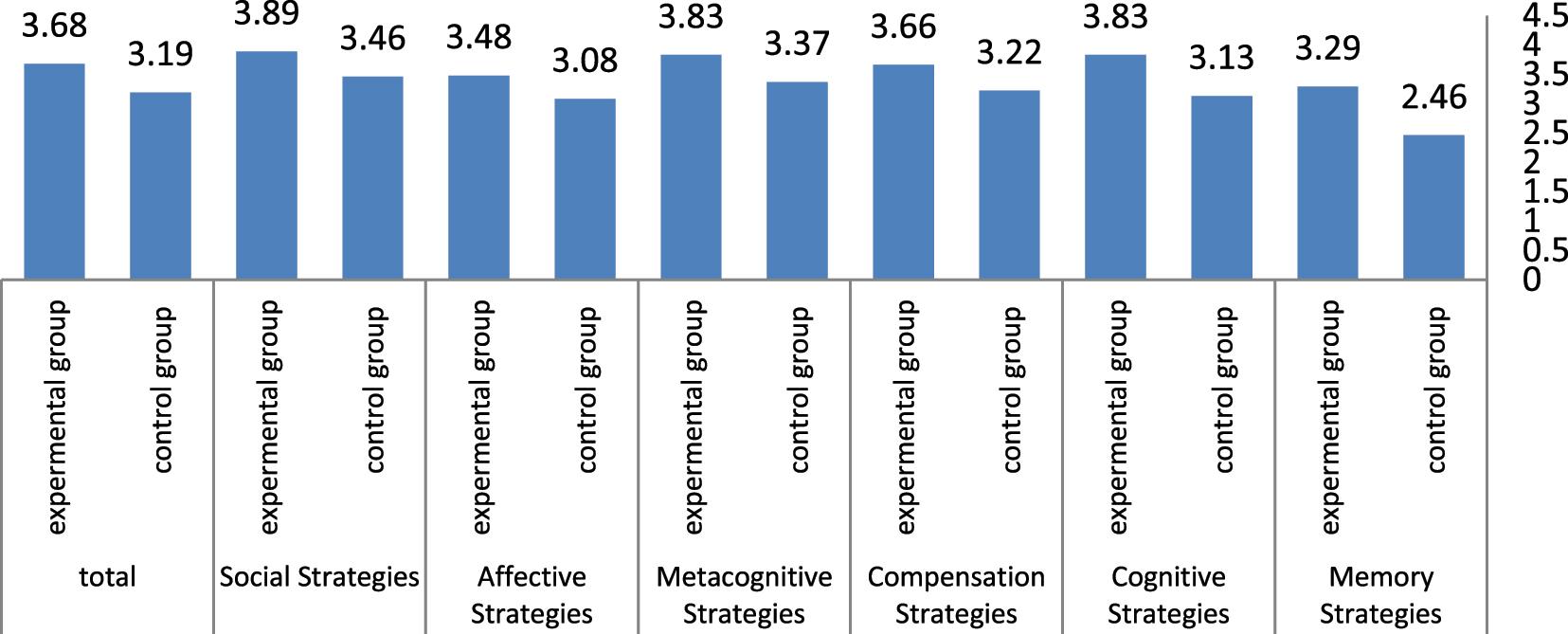
| Strategy | Group | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | |||||||
| Memory strategies | Control | 35 | 2.81 | 0.601 | −1.589 | 68 | 0.117 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.07 | 0.741 | ||||
| Cognitive strategies | Control | 35 | 2.93 | 0.518 | 0.624 | 68 | 0.534 |
| Experimental | 35 | 2.86 | 0.469 | ||||
| Compensation strategies | Control | 35 | 3.02 | 0.684 | 1.252 | 68 | 0.215 |
| Experimental | 35 | 2.83 | 0.571 | ||||
| Metacognitive strategies | Control | 35 | 3.42 | 0.722 | 1.290 | 68 | 0.202 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.21 | 0.623 | ||||
| Affective strategies | Control | 35 | 2.83 | 0.700 | 1.390 | 68 | 0.169 |
| Experimental | 35 | 2.61 | 0.613 | ||||
| Social strategies | Control | 35 | 3.22 | 0.709 | 1.664 | 68 | 0.101 |
| Experimental | 35 | 2.97 | 0.493 | ||||
| Total | Control | 35 | 3.00 | 0.465 | 1.065 | 68 | 0.291 |
| Experimental | 35 | 2.89 | 0.375 | ||||
| Post | |||||||
| Memory strategies | Control | 35 | 2.46 | 0.438 | −5.427 | 68 | 0.302 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.29 | 0.796 | ||||
| Cognitive strategies | Control | 35 | 3.13 | 0.492 | −5.657 | 68 | 0.000 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.83 | 0.546 | ||||
| Compensation strategies | Control | 35 | 3.22 | 0.580 | −2.847 | 68 | 0.005 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.66 | 0.695 | ||||
| Metacognitive strategies | Control | 35 | 3.37 | 0.592 | −3.29 | 68 | 0.000 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.83 | 0.573 | ||||
| Affective strategies | Control | 35 | 3.08 | 0.622 | −2.398 | 68 | 0.019 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.48 | 0.762 | ||||
| Social strategies | Control | 35 | 3.46 | 0.587 | −3.055 | 68 | 0.121 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.89 | 0.602 | ||||
| Total | Control | 35 | 3.68 | 0.570 | −3.677 | 68 | 0.166 |
| Experimental | 35 | 3.19 | 0.544 |
Pearson correlation of FNE questionnaire_
| No. | Item | Pearson correlation | Sig | No. | Item | Pearson correlation | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I tremble when I know that I’m going to be called on in English class. | 0.501* | 0.024 | 9 | I get nervous when the English teacher asks questions which I haven’t prepared in advance. | 0.951** | 0.000 |
| 2 | I keep thinking that the other students are better at English than I am. | 0.726** | 0.000 | 10 | I am afraid that my English teacher is ready to correct every mistake I make. | 0.854** | 0.000 |
| 3 | It embarrasses me to volunteer answers in my English class. | 0.709** | 0.000 | 11 | I feel very shy about speaking English about speaking English in front of the other students. | 0.870** | 0.000 |
| 4 | I get upset when I don’t understand what the teacher is correcting | 0.503* | 0.024 | 12 | I am frequently afraid of other students noticing my shortcomings when I speak in English. | 0.694** | 0.001 |
| 5 | I can feel my heart pounding when I’m going to be called on in English class. | 0.600** | 0.005 | 13 | I worry about what kind of impression that other students are making on me. | 0.768** | 0.000 |
| 6 | I always feel that the other students speak the English language better than I do. | 0.616** | 0.004 | 14 | I am afraid that the students and the teacher will track my mistakes when I speak in English. | 0.921** | 0.000 |
| 7 | I start to panic when I have to speak without preparation in English class. | 0.870** | 0.000 | 15 | The opinion of the teacher and the students about me bothers me. | 0.834** | 0.000 |
| 8 | I am afraid that the other students in the class will laugh at me when I speak in English. | 0.746** | 0.000 | 16 | If I know that the teacher and the students are judging me, it has big effect on me. | 0.951** | 0.000 |
Braun and Clarke’s (2006) thematic analysis (Adopted)_
| Phase | Description of the process |
|---|---|
| 1. Familiarising yourself with your data | Transcribing data (if necessary), reading and re-reading the data, noting down initial ideas. |
| 2. Generating initial codes | Coding interesting features of the data in a systematic fashion across the entire data set, collating data relevant to each code. |
| 3. Searching for themes | Collating codes into potential themes, gathering all data relevant to each potential theme. |
| 4. Reviewing themes | Checking in the themes work in relation to the coded extracts (Level 1) and the entire data set (Level 2), generating a thematic ‘map’ of the analysis. |
| 5. Defining and naming themes | Ongoing analysis to refine the specifics of each theme, and the overall story the analysis tells; generating clear definitions and names for each theme. |
| 6. Producing the report | The final opportunity for analysis. Selection of vivid, compelling extract examples, final analysis of selected extracts, relating back of the analysis to the research question and literature, producing a scholarly report of the analysis. |