
Figure 1
Bridging the gender digital divide through Education 4.0 pedagogical framework.
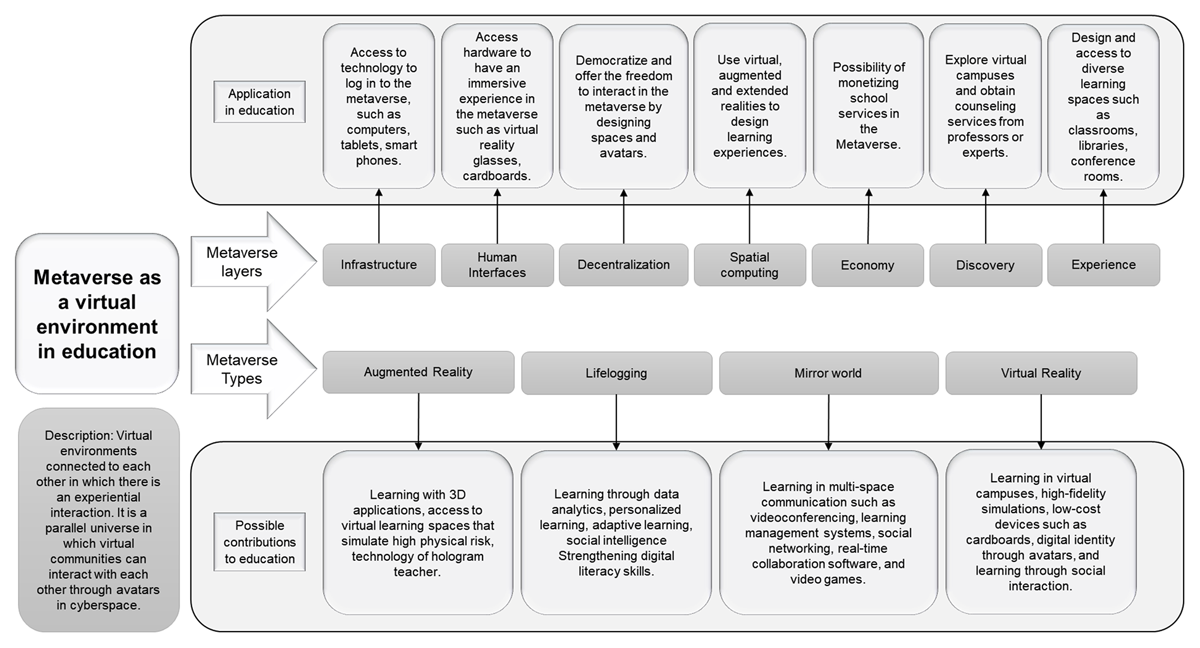
Figure 2
Metaverse composition.
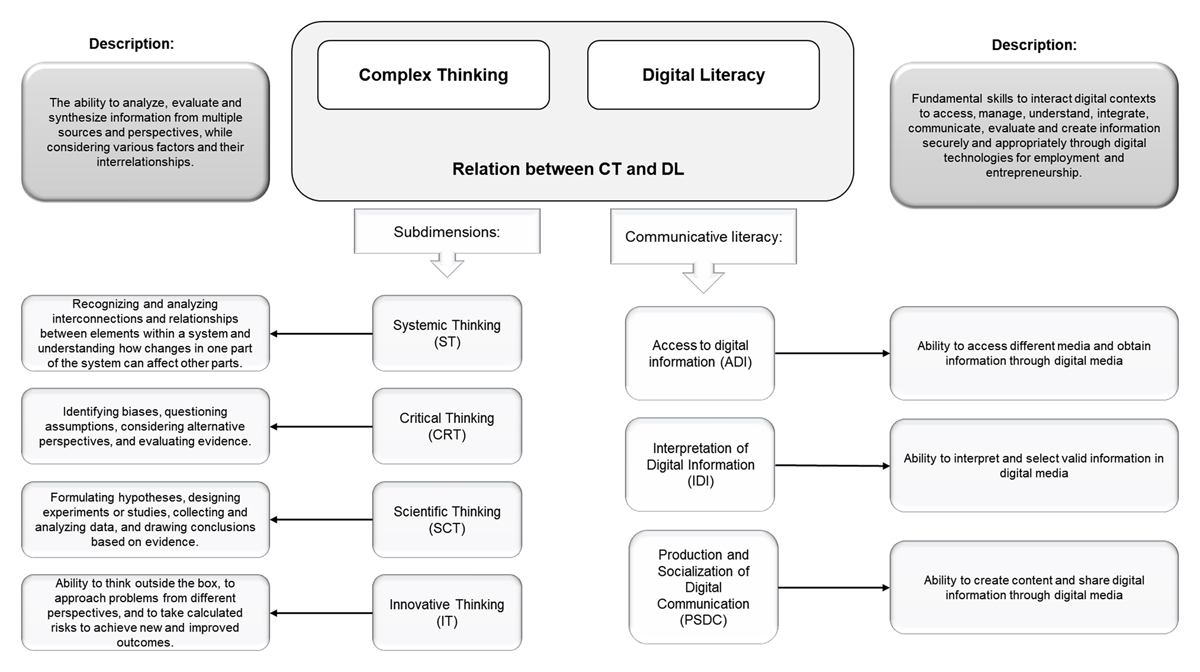
Figure 3
Components of complex thinking and communicative literacy.

Figure 4
Design and phases of the study.
Table 1
Items of the adaptation of the e-complexity scale to measure communicative literacy.
| DIMENSIONS OF COMMUNICATIVE LITERACY | SYSTEMIC THINKING (ST) | CRITICAL THINKING (CT) | SCIENTIFIC THINKING (SCT) | INNOVATIVE THINKING (IT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access to digital information (ADI) | I access different digital media to learn about the same information. | I know how to identify digital media that only covers some information. | I use information search strategies based on logical operators. | I recover and store information in digital media like Google Drive, Dropbox, Box, etc. |
| I know how to use search strategies to find updated information (last week/month/year). | I protect the information stored in my digital devices with biometric passwords. | I filter the information using web tools. | I protect my personal digital information using secure passwords. | |
| Interpretation of digital information (IDI) | To judge a piece of information, I contrast it with different sources. | I know how to estimate the credibility of information by differentiating between that which comes from reliable media and that which comes from unverified media. | I know how to use checking tools to validate the information from web pages and social networks. | I organize the information I recover using strategies such as shared folders, web bookmarks, local folders, social networks, etc. |
| I create categories of digital information for later use in a task or project. | Before using the information, I evaluate whether it is fake news. | I reference an official page or a recognized author to interpret the information. | Based on trending information, I can generate an objective debate in my social networks. | |
| Production and socialization of digital communication (PSDC) | I have shared information using various media such as web pages, social networks, videos, podcasts, etc. | I cite the sources from which I obtain information when producing and socializing digital content. | I use design strategies and techniques to elaborate digital information. | I have created content combining different media such as videos, audio, and images. |
| The information I share respects the rules of digital citizenship, such as equity, ethics, objectivity, non-discrimination, etc. | Before sharing digital information, I identify the recipients. | I can identify licenses and copyrights before using the information to produce my content. | I have built a digital identity to socialize the digital information I share. |
Table 2
Reliability coefficients of the dimensions.
| DIMENSIONS OF THE INSTRUMENT | CRONBACH’S ALPHA | MCDONALD’S OMEGA |
|---|---|---|
| Systemic Thinking | .825 | .887 |
| Critical Thinking | .757 | .764 |
| Scientific Thinking | .808 | .812 |
| Innovative Thinking | .749 | .760 |
Table 3
Content of the modules developed based on the pedagogical framework of Education 4.0 and to bridge the gender digital divide.
| MODULES | OBJECTIVE | PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK OF EDUCATION 4.0 | PEDAGOGICAL PRINCIPLES | BRIDGING THE GENDER DIGITAL DIVIDE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Module 1. Introduction to the workshop | To familiarize participants with the use and management of their avatar in the Mozilla Hubs platform and resolve doubts in the first interaction in this virtual world. | Peeragogy (peer-to-peer pedagogy) | Motivation | Support the use of technology by identifying the motivations and interests of the GDD, which lacks technological inclination (Rodríguez, 2018). |
| Confidence and inclusion | Support strengthens technological confidence in the GDD (Martínez-Cantos & Castaño 2017). | |||
| Cyber pedagogy | Interactive learning in a virtual world | Encourage interaction in the digital world to foster equal participation among learners, as required in the GDD (Kuroda et al. 2019; de Andrés delCampo et al. 2020). | ||
| Self-focused learning | Support interest and interaction in the digital world of young women to increase their technological self-efficacy (Gebhardt et al. 2019). | |||
| Module 2. Digital communication | To identify communication skills needed for life and their educational background. | Heutagogy | Learner autonomy | Fostering decision-making and leadership of female learners which are in short supply in GDD (Alozie & Akpan-Obong 2017). |
| Cyber pedagogy | Collaborative learning | Encourage female learners’ participation and collaboration in the digital world and social networks (Masanet, Pires & Gómez-Puertas 2021; Rai 2019). | ||
| Module 3. Social networks | To identify trending social networks and their uses as digital media for communication. | Heutagogy | Reflection and metacognition | Promote the elimination of self-exclusion of female students because of gender roles and stereotypes that occur in GDD (Alozie & Akpan-Obong 2017). |
| Non-linear learning | Supporting the different levels of digital skills of learners recognized in the GDD (Krchová & Höesová 2021). | |||
| Cyber pedagogy | Collaborative learning | Promote learners’ participation and collaboration in social networks and the digital world (Masanet, Pires & Gómez-Puertas2021; Rai 2019). | ||
| Module 4. My communicative skills developed in the workshop. | To create a video to describe the communicative skills that can be developed in a virtual room. | Heutagogy | Capability and self-efficiency | Develop digital skills necessary to effectively use digital technologies (Kuroda et al. 2019). |
| Cyber pedagogy | Collaborative learning | Stimulate the collaboration of female students in the digital world and social networks (Masanet, Pires & Gómez-Puertas 2021; Rai2019). |
Table 4
Linking workshop modules to communicative literacy from the complex thinking approach.
| MODULE | COMMUNICATIVE LITERACY | COMPLEX THINKING | ENVIRONMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Module 1. Introduction to the workshop | Access to digital information (ADI) | Critical thinking (CT) & systemic thinking (ST) | Computer laboratory (face-to-face environment) |
| Module 2. Digital communication | Interpretation of digital information (IDI) | Critical thinking (CT) & systemic thinking (ST) | 3D environments (Virtual Reality) Computer laboratory (face-to-face environment) |
| Module 3. Social networks | Interpretation of digital information (IDI) | Critical thinking (CT) & systemic thinking (ST) | 3D environments (Virtual Reality) Computer laboratory (face-to-face environment) |
| Module 4. My communicative skills developed in the workshop | Production and socialization of digital communication (PSDC) | Systemic thinking (ST), scientific thinking (SCT) & innovative thinking (IT) | 3D environments (Virtual Reality) Computer laboratory (face-to-face environment) |
[i] Source: Own elaboration.
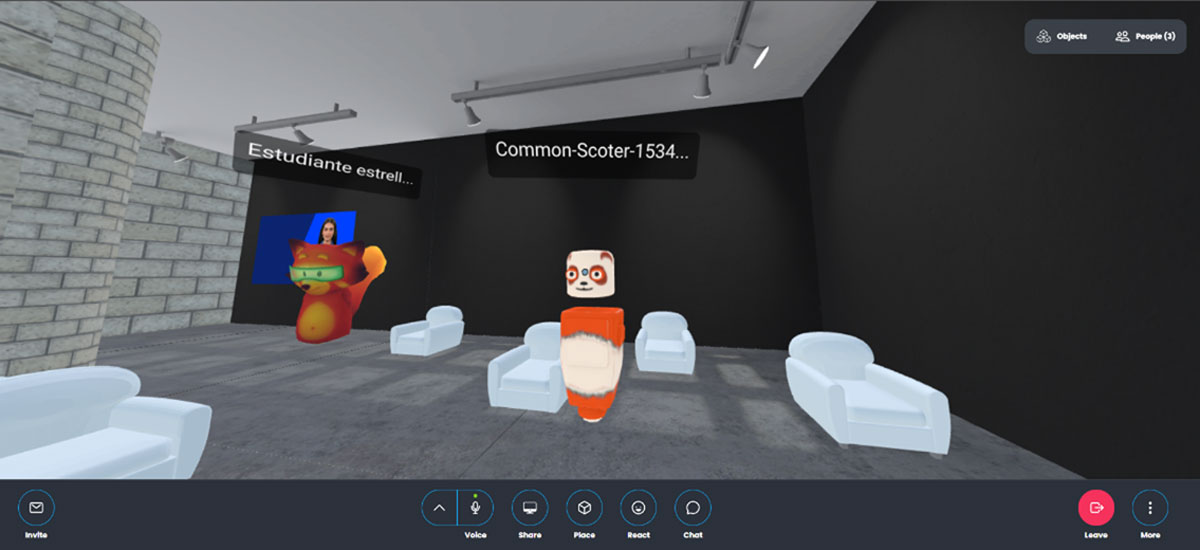
Figure 5
3D immersive environment developed through Mozilla Hubs for #unespaciovirtualentuescuela workshop.
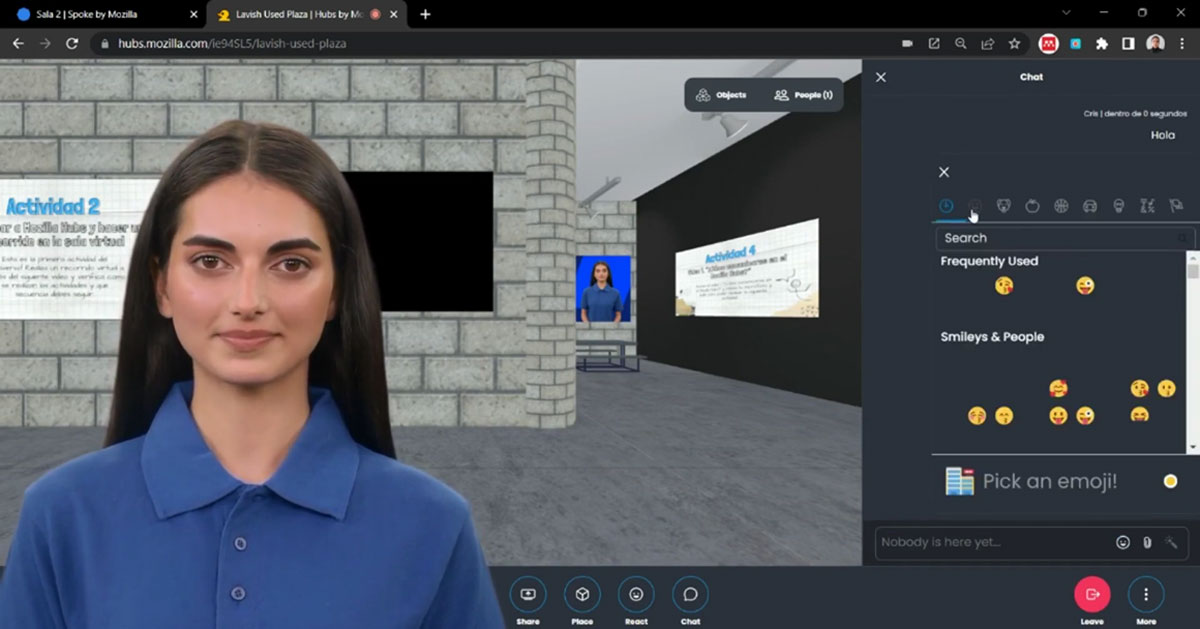
Figure 6
Video developed by Synthesia for #unespaciovirtualentuescuela workshop.
Table 5
Study population by gender and age.
| GENDER | AGE | TOTAL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 21 | ||
| Male | 11 | 30 | 29 | 2 | 1 | 73 |
| 15.1% | 41.1% | 39.7% | 2.7% | 1.4% | 100.0% | |
| Female | 8 | 15 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 44 |
| 18.2% | 34.1% | 36.4% | 9.1% | 2.3% | 100.0% | |
| Non-binary | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 42.9% | 42.9% | 14.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | |
| Total | 22 | 48 | 46 | 6 | 2 | 124 |
| 17.7% | 38.7% | 37.1% | 4.8% | 1.6% | 100.0% | |
Table 6
Descriptive statistics of communicative literacy and complex thinking.
| DIMENSIONS OF COMMUNICATIVE LITERACY AND COMPLEX THINKING | MALE | FEMALE | NON-BINARY | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | |
| Access to digital information (ADI) | 25.11 | 4.608 | 25.36 | 4.227 | 24.00 | 3.109 |
| Interpretation of digital information (IDI) | 24.01 | 4.898 | 24.64 | 4.989 | 24.43 | 3.259 |
| Production and socialization of digital communication (PSDC) | 23.89 | 4.659 | 25.32 | 4.376 | 24.43 | 2.149 |
| Systemic thinking (ST) | 18.22 | 3.568 | 19.45 | 3.454 | 17.71 | 2.563 |
| Critical thinking (CT) | 17.78 | 3.852 | 17.50 | 3.788 | 18.57 | 2.440 |
| Scientific thinking (SCT) | 18.59 | 3.378 | 19.00 | 3.355 | 18.43 | 1.988 |
| Innovative thinking (IT) | 18.42 | 3.480 | 19.36 | 3.349 | 18.14 | 3.024 |
| N | 73 | 44 | 7 | |||
Table 7
Mann-Whitney U test.
| TEST STATISTICS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMMUNICATIVE LITERACY | COMPLEX THINKING | |||||||
| ADI | IDI | PSDC | ST | CT | SCT | IT | ||
| Mann-Whitney U | 1521.500 | 1503.000 | 1331.000 | 1233.500 | 1459.500 | 1459.000 | 1416.500 | |
| Z | –0.478 | –0.582 | –1.557 | –2.113 | –0.830 | –0.833 | –1.073 | |
| Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.633 | 0.560 | 0.120 | 0.035 | 0.407 | 0.405 | 0.283 | |
| Hedges’ 𝑔 | 0.056 | 0.127 | 0.316 | 0.350 | 0.073 | 0.121 | 0.275 | |
[i] a. Grouping Variable: Gender.
Table 8
Level of correlation between the dimensions of communicative literacy and complex thinking.
| DIMENSIONS | ST | SCT | CT | IT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADI | Correlation Coefficient | .808 | .763 | .746 | .783 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | .000 | .000 | .000 | |
| IDI | Correlation Coefficient | .730 | .819 | .765 | .792 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | .000 | .000 | .000 | |
| PSDC | Correlation Coefficient | .776 | .746 | .775 | .777 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | .000 | .000 | .000 | |
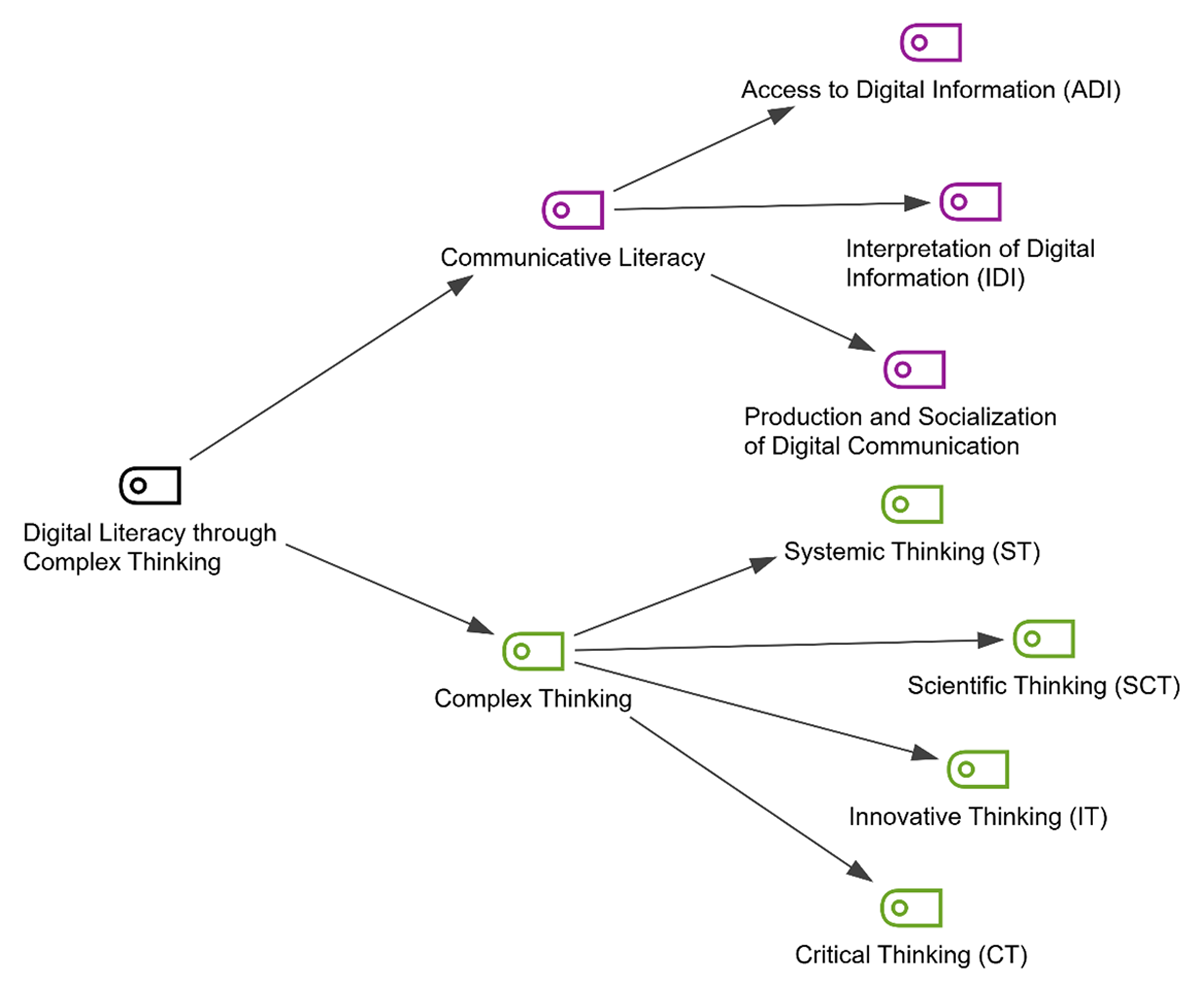
Figure 7
Coding analysis of communicative literacy and complex thinking approach.
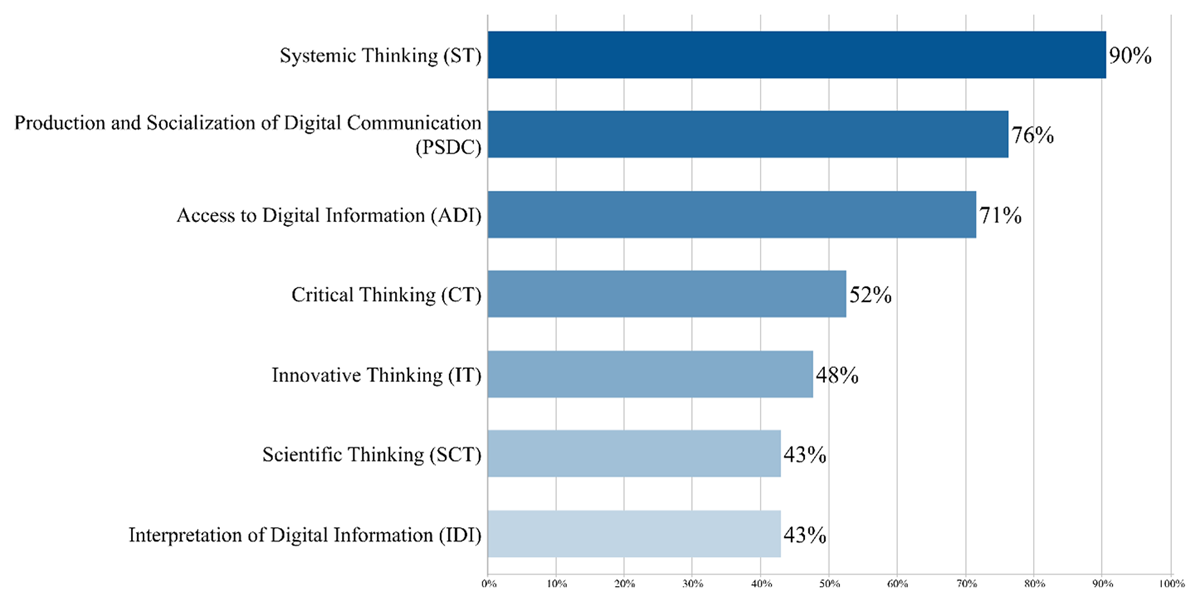
Figure 8
Frequency of communicative literacy and the complex thinking codes.
