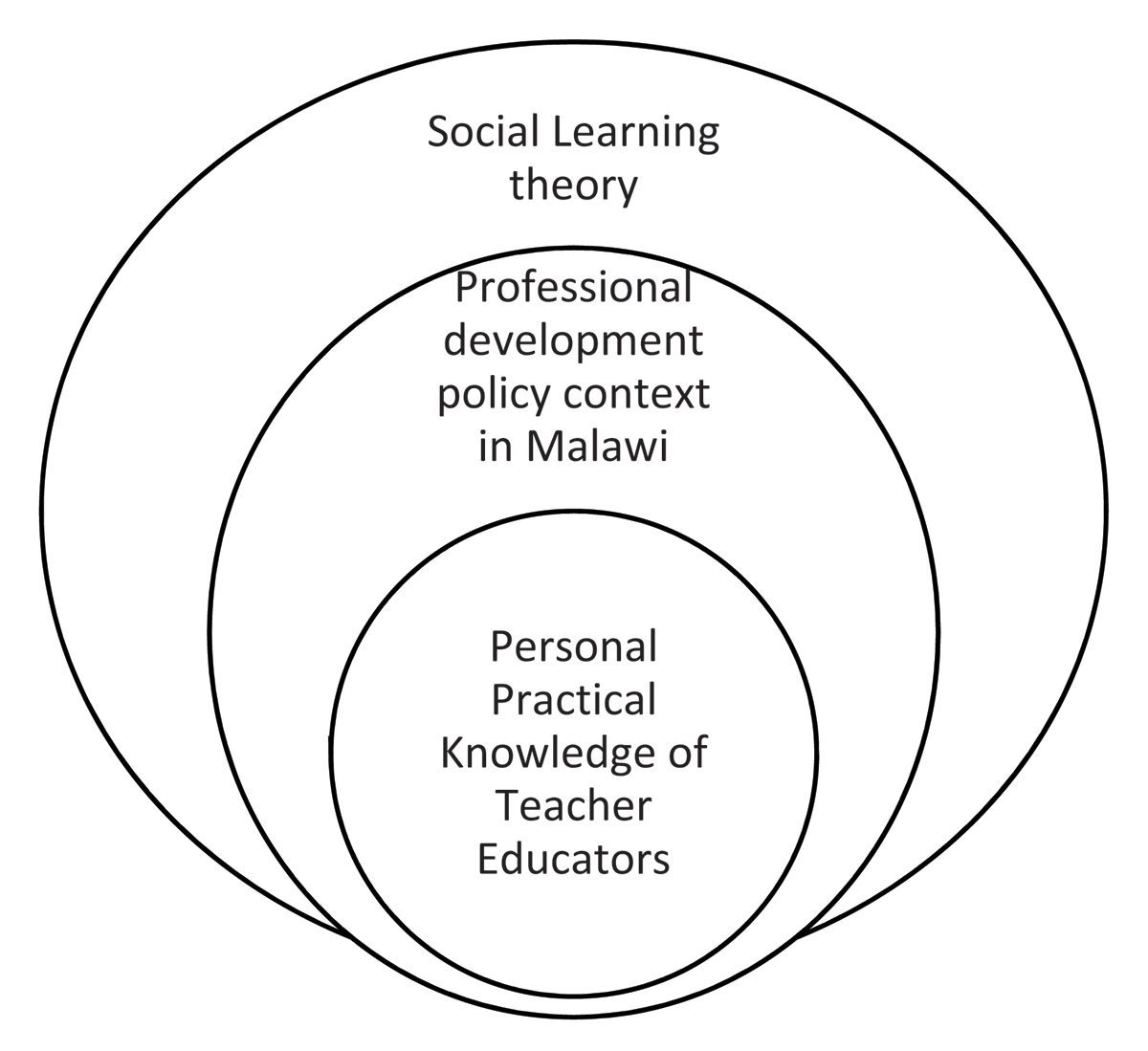
Figure 1
The combined theoretical framework of the study.
Table 1
Student teachers’ ways of learning about technology.
| ITEM | FREQ | % |
|---|---|---|
| I haven’t | 0 | 0 |
| By developing teaching and learning materials | 21 | 63.6 |
| By observing my lecturers | 14 | 42.4 |
| By discussing with fellow students | 15 | 45.5 |
| By working in primary/secondary school | 6 | 18.2 |
| By reading about it | 14 | 42.4 |
| By attending academic conferences, short courses, seminars | 2 | 6.1 |
| Other | 0 | 0 |
Table 2
Student teachers’ perspectives of coherence in teacher education programme.
| ITEM | STRONGLY AGREE | AGREE | DISAGREE | STRONGLY DISAGREE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FREQ | % | FREQ | % | FREQ | % | FREQ | % | |
| All my courses have been articulating a clear vision of instructional technology integration (N: 32) | 0 | 0 | 16 | 50 | 15 | 46.9 | 1 | 3.1 |
| All lecturers have been articulating a clear vision of instructional technology in education (N: 31) | 1 | 3.2 | 17 | 54.8 | 12 | 38.7 | 1 | .2 |
| I have been hearing similar views about instructional technology integration across all courses (N: 31) | 2 | 6.5 | 13 | 41.9 | 15 | 48.4 | 1 | 3.2 |
| I have had practical/hands-on experience and try out the theories, strategies, and techniques about technology (N: 32) | 10 | 31.3 | 16 | 50 | 4 | 12.5 | 2 | 6.3 |
| My lecturers are knowledgeable about instructional technology integration as a whole (N: 32) | 2 | 6.3 | 18 | 56.3 | 11 | 34.4 | 1 | 3.1 |
| I have been observing my lecturers using the same theories, strategies, and techniques they promote about instructional technology (N: 32) | 2 | 6.3 | 17 | 53.1 | 10 | 31.3 | 3 | 9.4 |
[i] Note: Items adapted from Canrinus, Klette, & Hammerness (2017).
Table 3
Teacher educators’ technology competencies based on students’ perspectives.
| ITEM | FREQ | % |
|---|---|---|
| They design instruction that utilizes content-specific technologies to enhance teaching and learning. | 19 | 57.6 |
| They align content with methods and appropriate technology. | 18 | 54.5 |
| They use online tools to enhance teaching and learning. | 18 | 54.5 |
| They use technology to differentiate instruction to meet diverse learning needs. | 11 | 33.3 |
| They use appropriate technology tools for assessment. | 15 | 45.5 |
| They use technology to connect globally with a variety of regions and cultures. | 3 | 9.1 |
| They address the legal, ethical, and socially responsible use of technology in education. | 3 | 9.1 |
| They engage in ongoing professional development and networking activities to improve the integration of technology in teaching. | 5 | 15.2 |
| Other: Lecturers’ level of competence is high… | 1 | NA |
[i] Note: Extracted from teacher educator technology competencies by Foulger et al. 2017.
Table 4
Student teachers’ most needed technology competencies.
| ITEM | FREQ | % |
|---|---|---|
| Designing instruction that utilizes content-specific technologies to enhance teaching and learning. | 22 | 66.7 |
| Aligning content with methods and appropriate technology. | 19 | 57.6 |
| Using online tools to enhance teaching and learning. | 17 | 51.5 |
| Using technology to differentiate instruction to meet diverse learning needs. | 18 | 54.5 |
| Using appropriate technology tools for assessment. | 15 | 45.5 |
| Using technology to connect globally with a variety of regions and cultures. | 5 | 15.2 |
| Addressing the legal, ethical, and socially responsible use of technology in education. | 11 | 33.3 |
| Engaging in ongoing professional development and networking activities to improve the integration of technology in teaching. | 11 | 33.3 |
| Other: coming up with models that involve learners in teaching. | 1 | NA |
[i] Note: Items extracted from Foulger et al. 2017.
