Figure 1

Figure 2
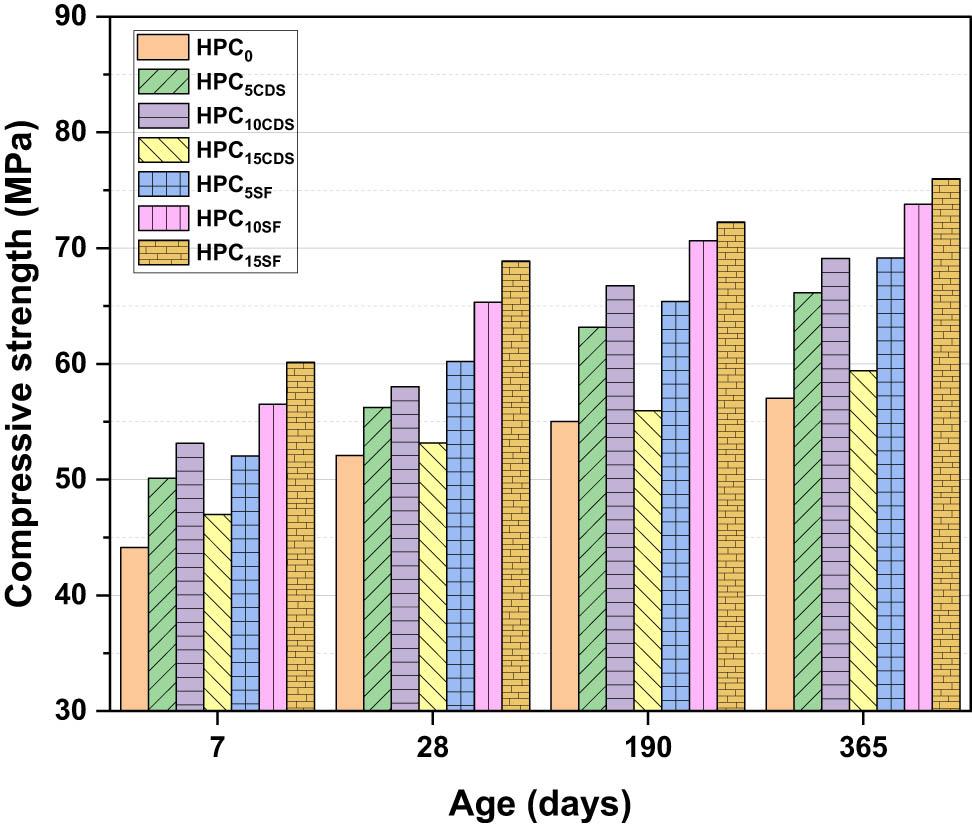
Figure 3
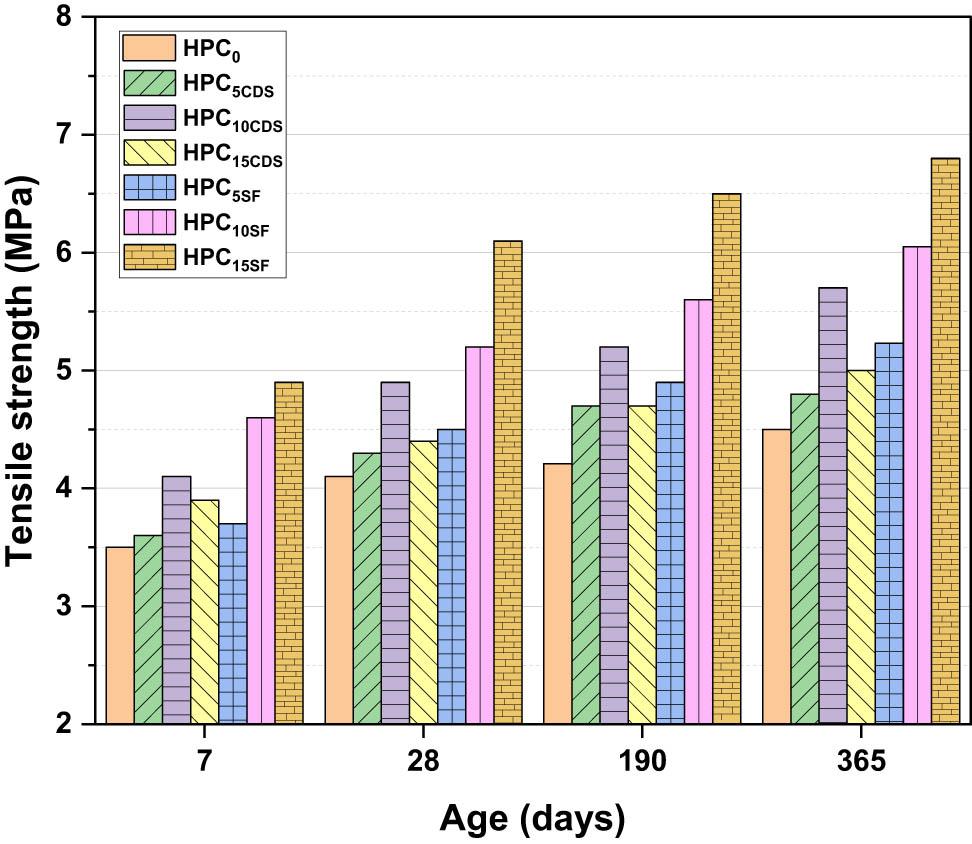
Figure 4
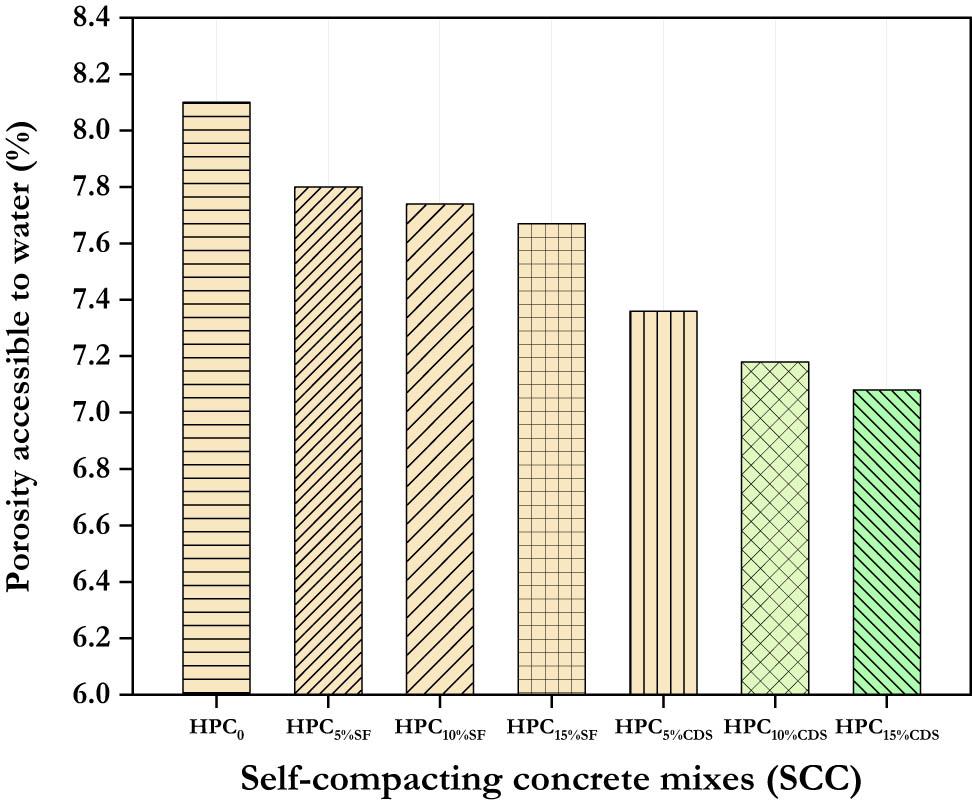
Figure 5
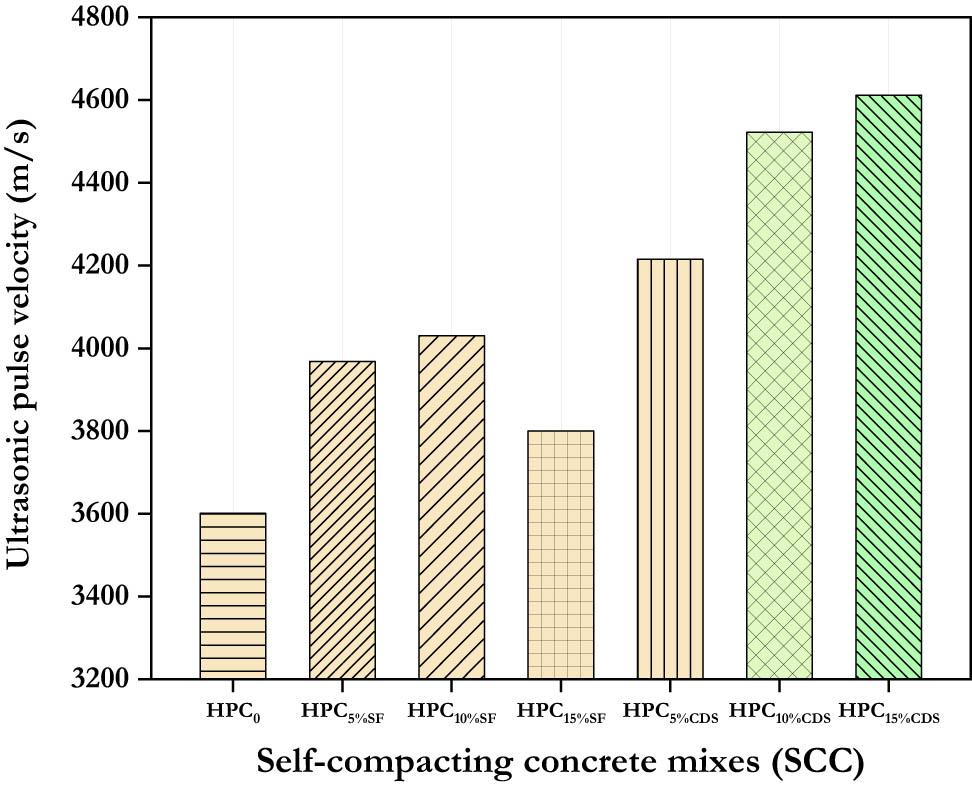
Figure 6
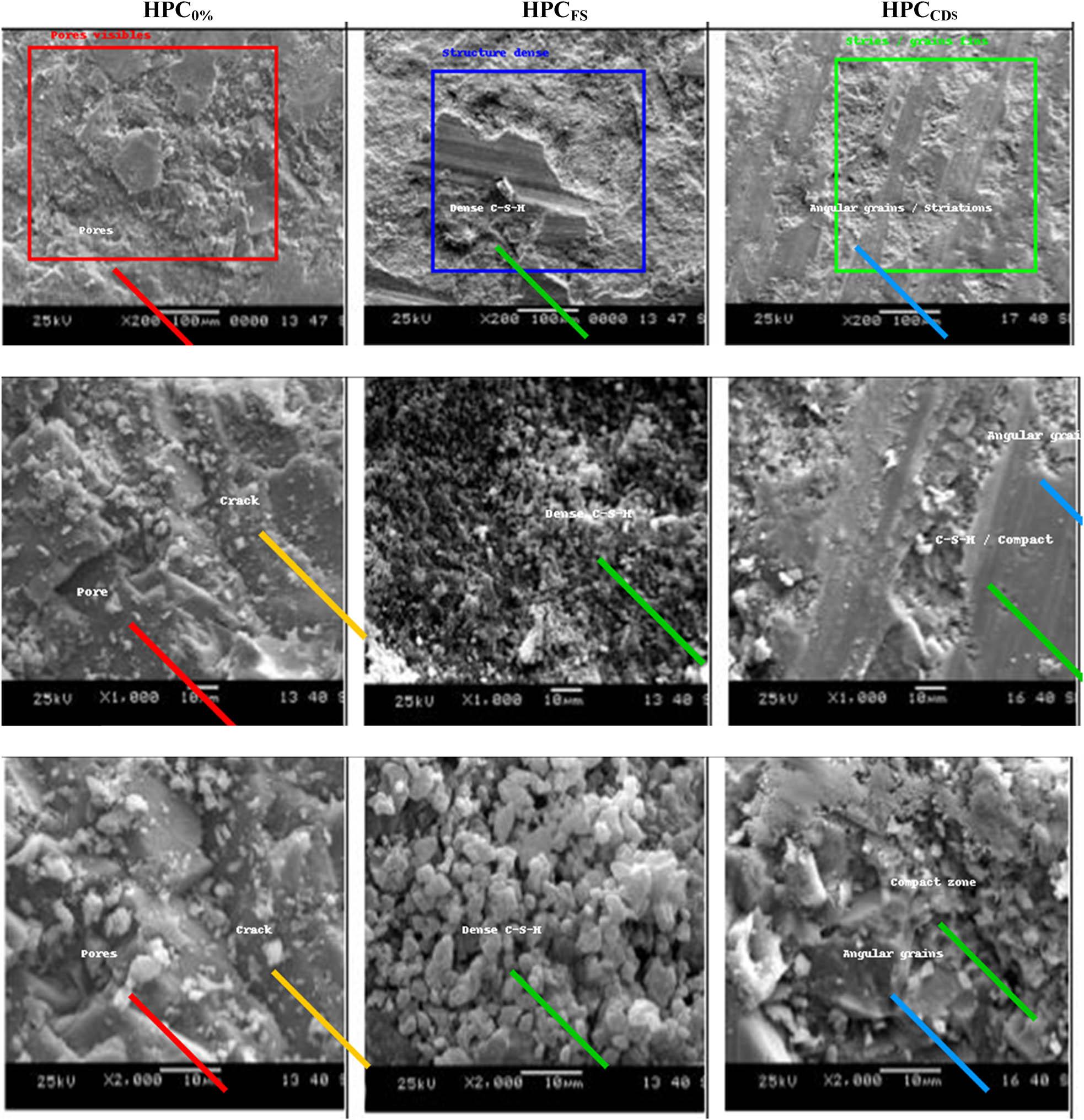
Figure 7
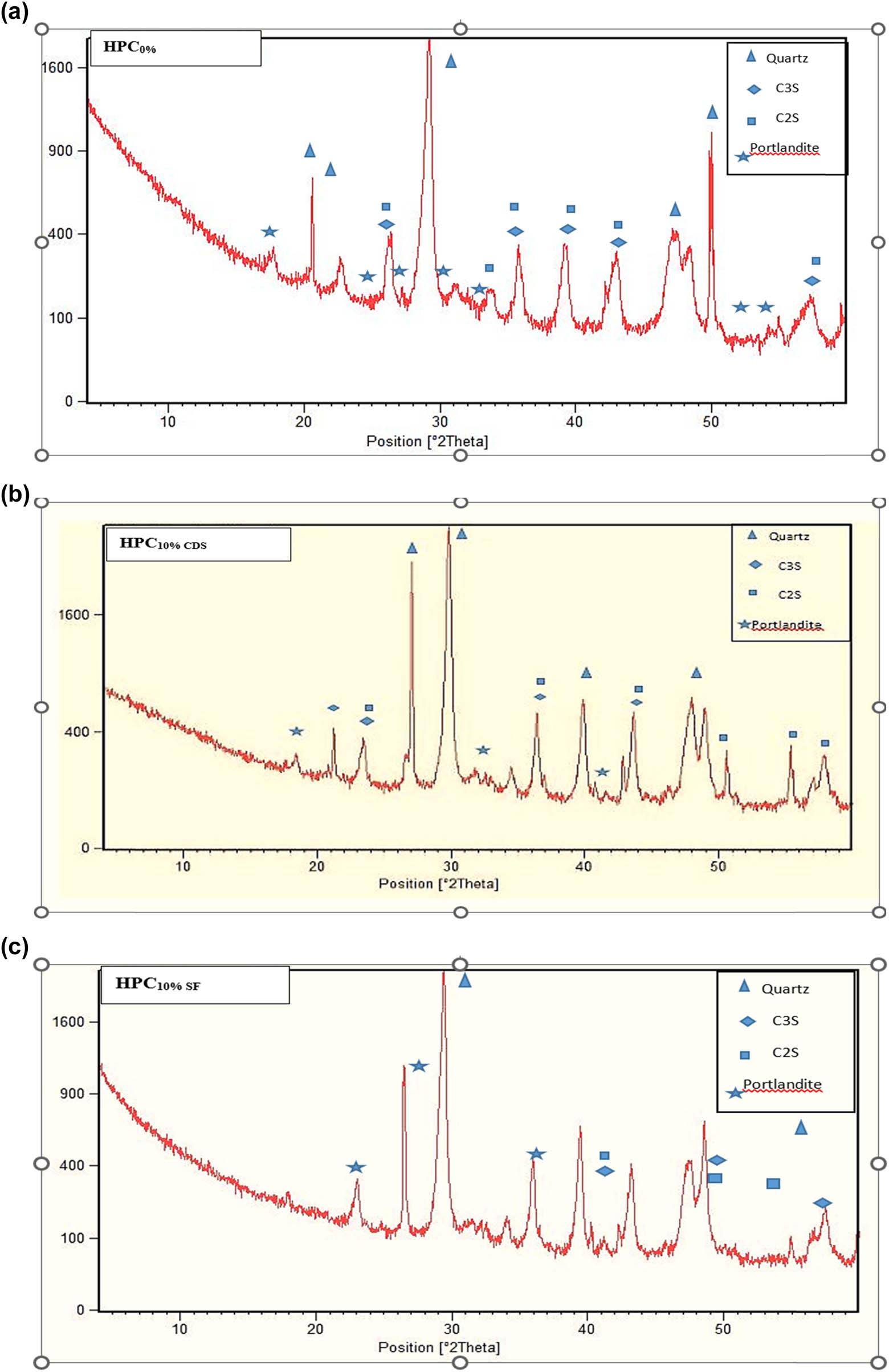
Sclerometric index of the concretes tested_
| Type of concrete | HPC0% | HPC5% CDS | HPC10% CDS | HPC15% CDS | HPC5% SF | HPC10% SF | HPC15% SF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rcavge | 49.9 | 54.23 | 55.75 | 50.78 | 59.45 | 63.15 | 66.01 |
| Rc28 (MPA) | 52.1 | 56.24 | 58.03 | 53.16 | 60.2 | 65.33 | 68.89 |
| Standard deviation | 2.2 | 2.01 | 2.28 | 2.38 | 0.75 | 2.18 | 2.88 |
Abbreviations for different concrete mixtures_
| Abbreviation | Concrete type |
|---|---|
| HPC0% | Reference concrete without mineral additions |
| HPC5% SF | Formulated with 5% of silica fume (SF) |
| HPC10% SF | Formulated with 10% of silica fume (SF) |
| HPC15% SF | Formulated with 15% of silica fume (SF) |
| HPC5% CDS | Formulated with 5% of crushed dune sand (CDS) |
| HPC10% CDS | Formulated with 10% of crushed dune sand (CDS) |
| HPC15% CDS | Formulated with 15% of crushed dune sand (CDS) |
Quality of concrete according to the speed of sound_
| Type of concrete | HPC0% | HPC5% CDS | HPC10% CDS | HPC15% CDS | HPC5% SF | HPC10% SF | HPC15% SF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc28 (MPA) | 52.1 | 56.24 | 58.03 | 53.16 | 60.2 | 65.33 | 68.89 |
| V (m/s) | 3,601 | 3,968 | 4,030 | 3,800 | 4,215 | 4,522 | 4,612 |
| Porosity accessible to water | 8.1 | 7.8 | 7.74 | 7.67 | 7.36 | 7.18 | 7.08 |
| Strength | Good | Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
Formulation of the different HPC (kg/m3)_
| Element (kg/m3) | HPC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPC0% | HPC5% SF | HPC5% CDS | HPC10% SF | HPC10% CDS | HPC15% SF | HPC15% CDS | |
| Cement | 500 | 475 | 475 | 450 | 450 | 425 | 425 |
| Crushed dune sand (CDS) | — | — | 25 | 00 | 50 | — | 75 |
| Silica fume (SF) | — | 25 | — | 50 | — | 75 | — |
| Sand (S) | 720.26 | 720.26 | 720.26 | 720.26 | 720.26 | 720.26 | 720.26 |
| Gravel (G) | 1050.22 | 1050.22 | 1050.22 | 1050.22 | 1050.22 | 1050.22 | 1050.22 |
| Superplasticizer | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Water (W) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| G/S | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.46 |
| W/C | 0.300 | 0.316 | 0.316 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.353 | 0.353 |
| Density | 2417.00 | 2409.29 | 2412.96 | 2402.63 | 2408.94 | 2395.51 | 2404.93 |