Figure 1:
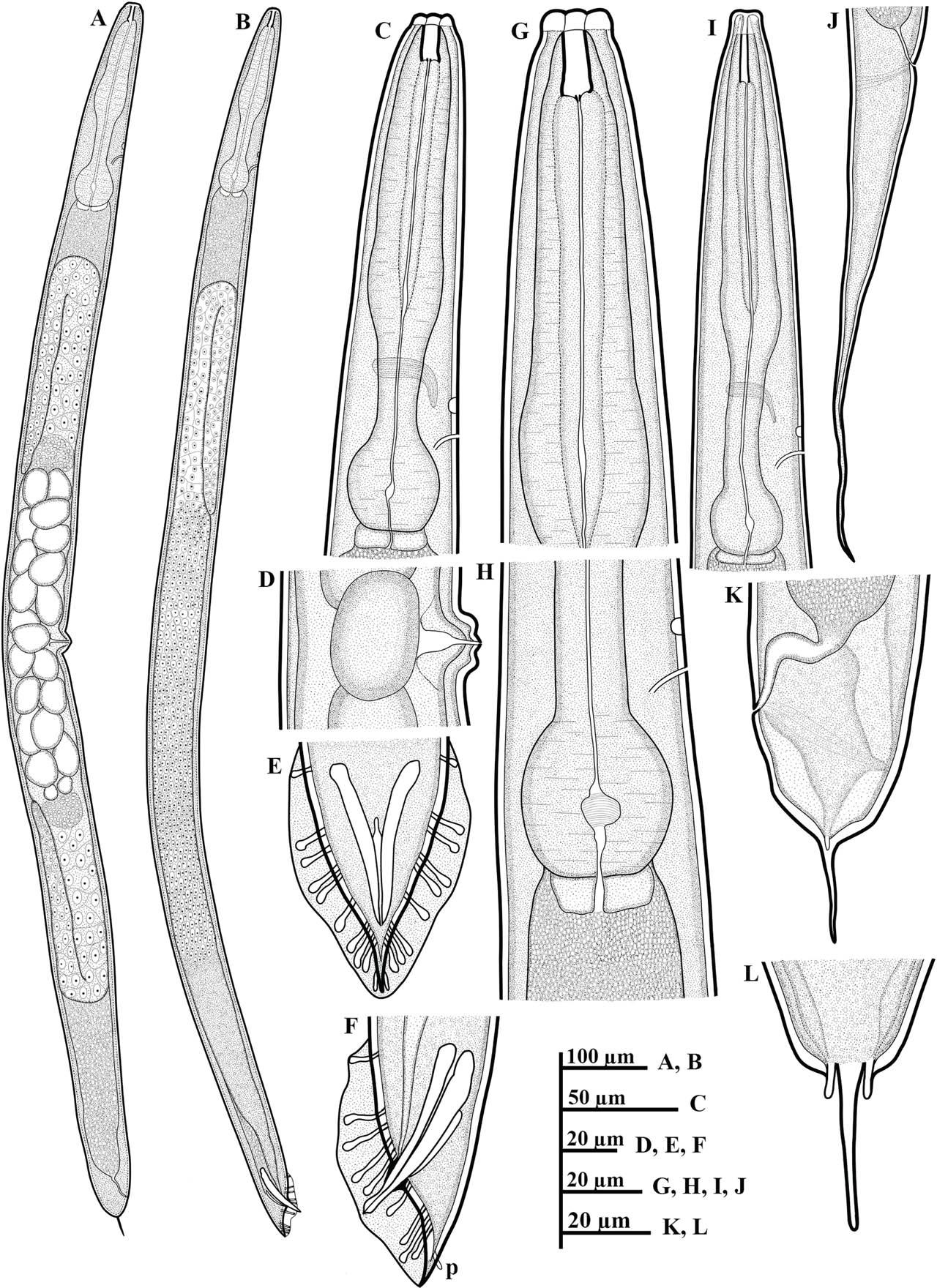
Figure 2:
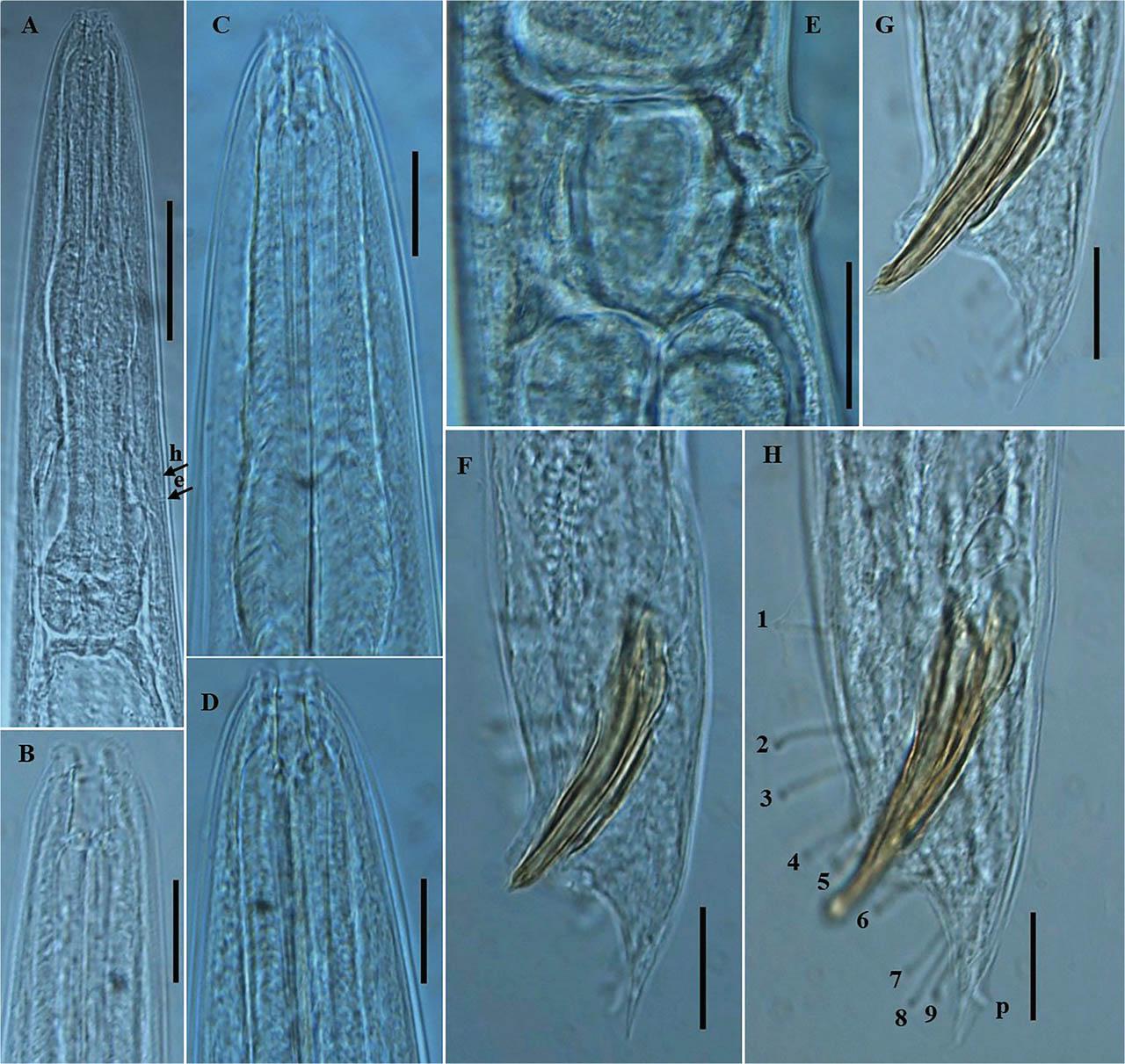
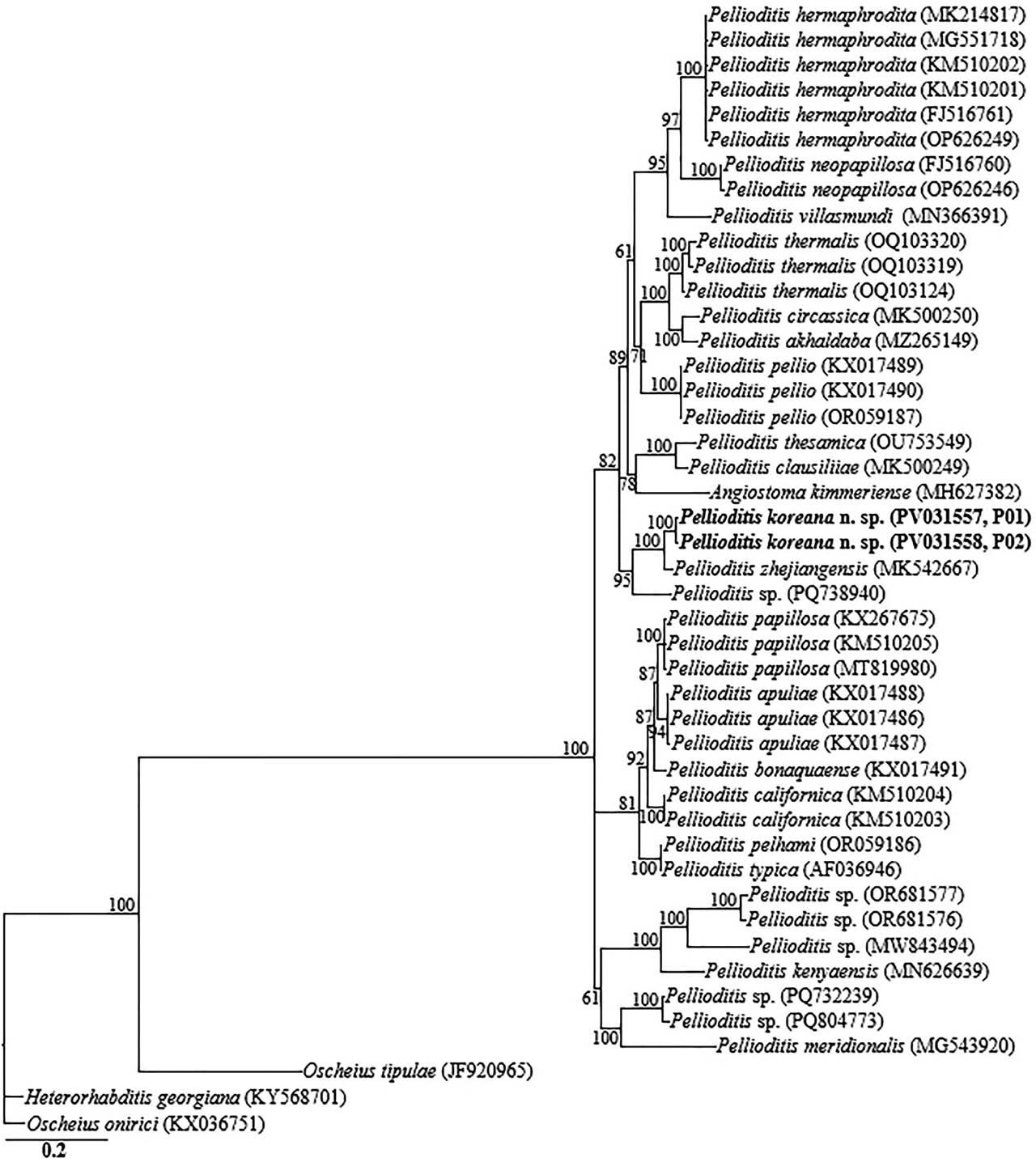
Figure 3:
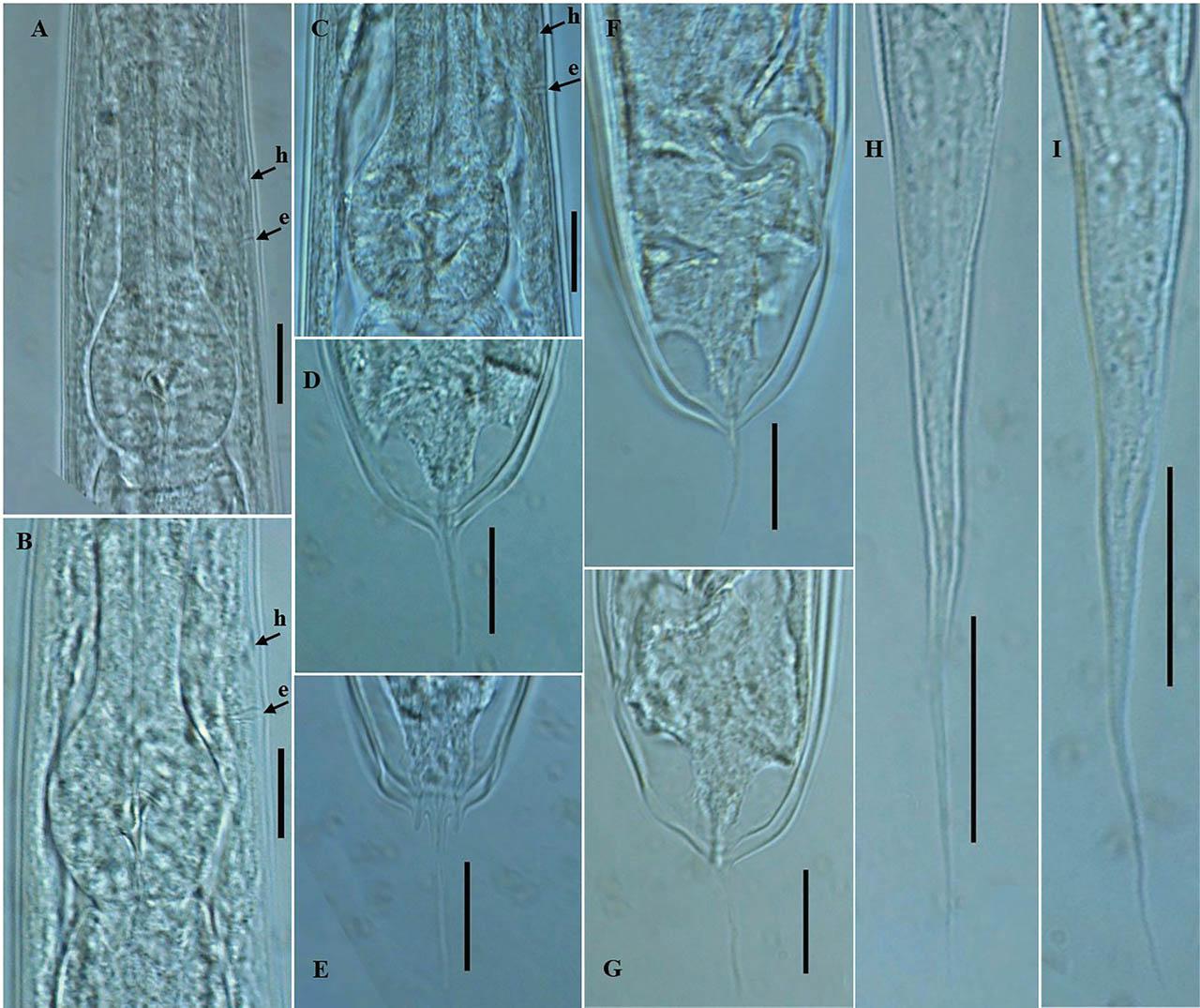
Figure 4:
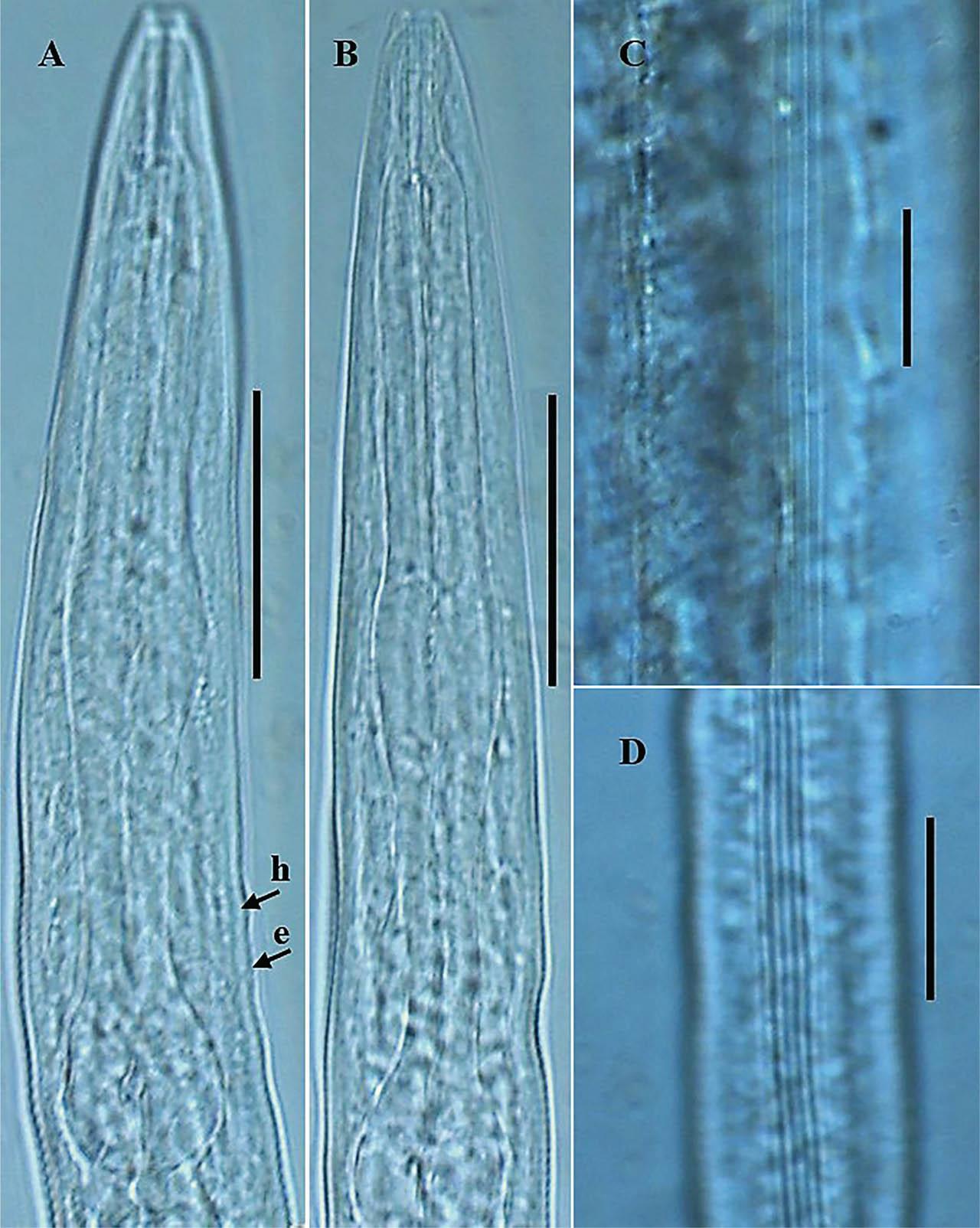
Figure 5:
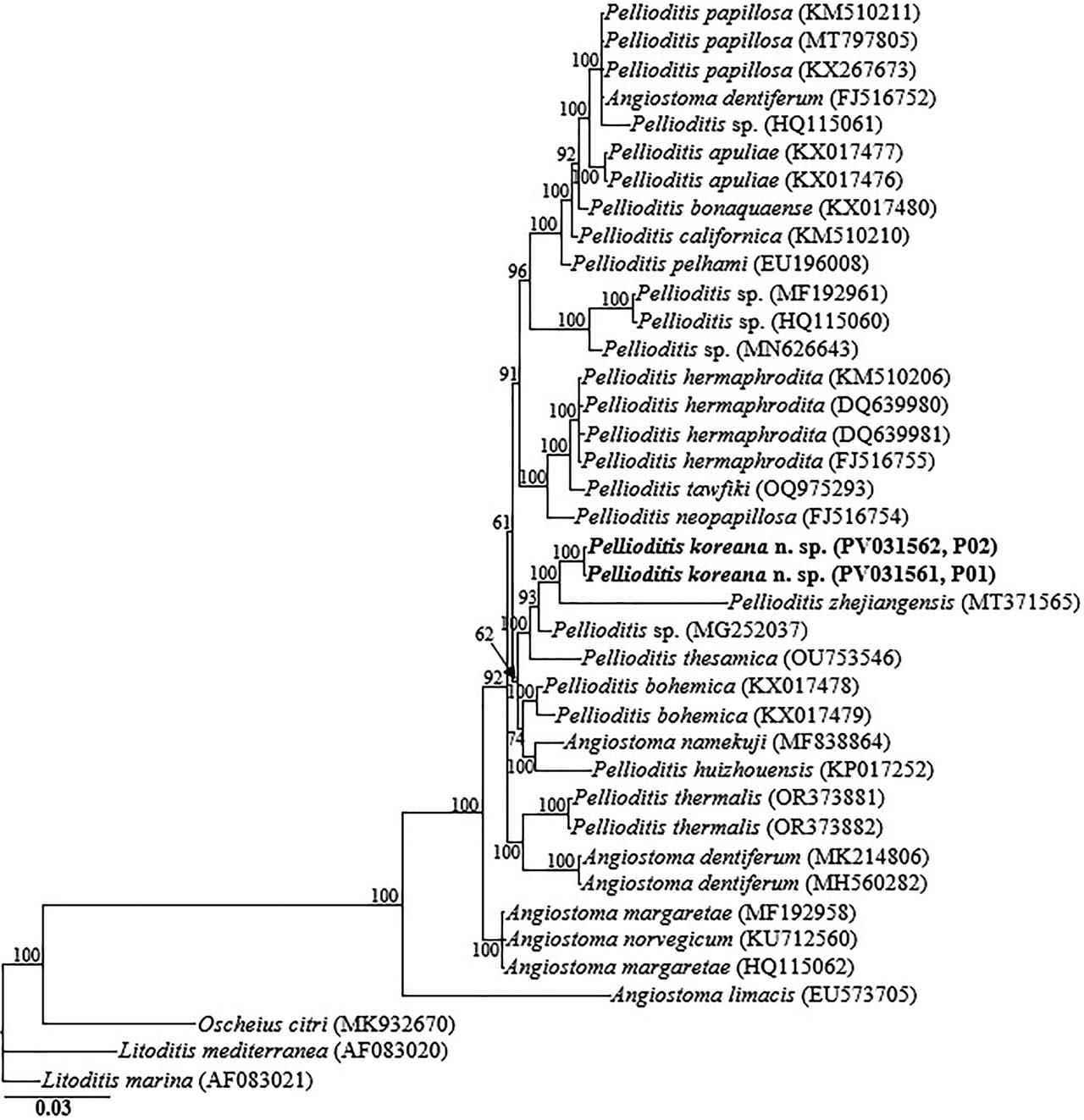
Figure 6:
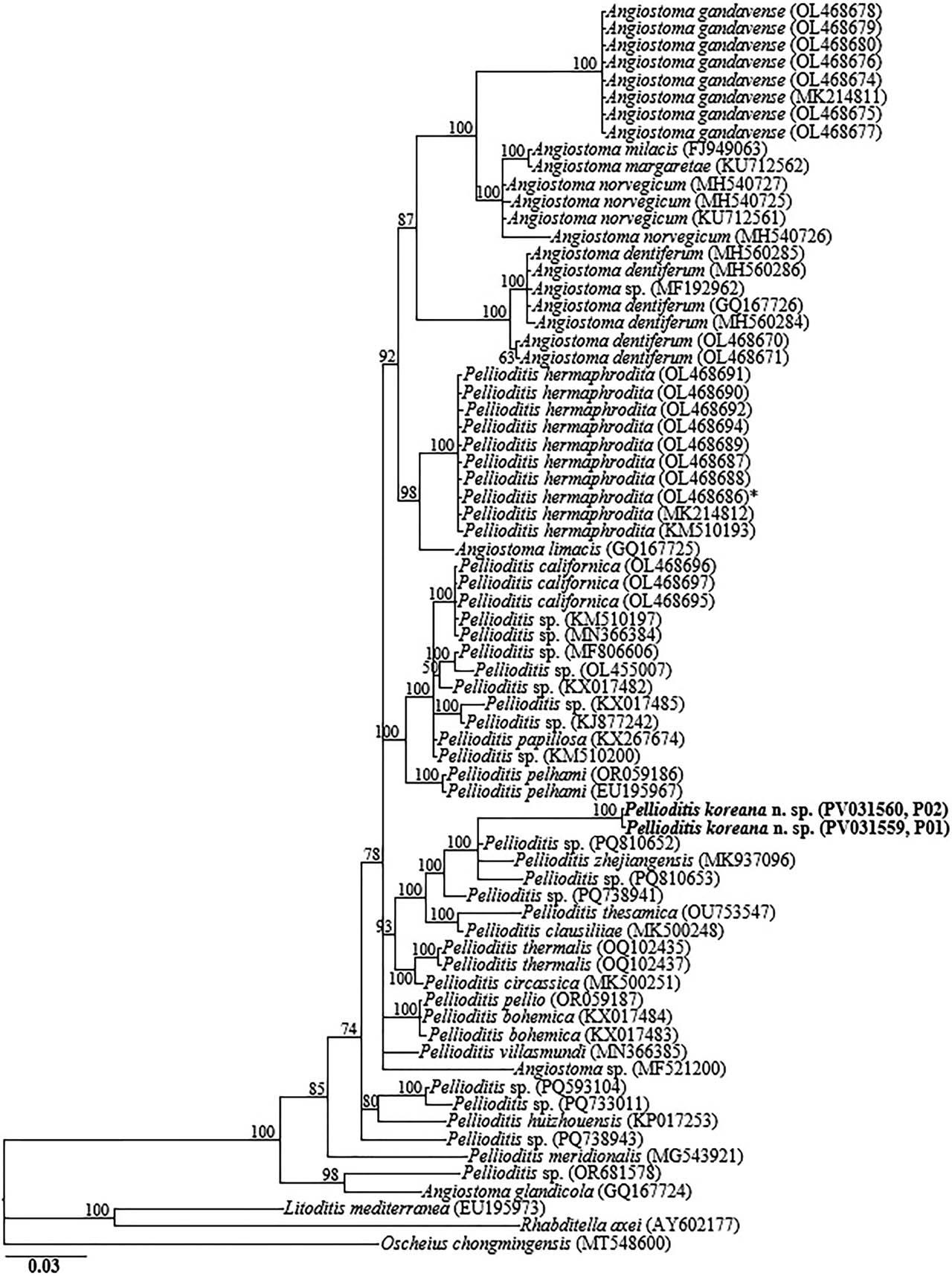
Figure 7:
Morphometrics of P_ koreana n_ sp_ from Korea_
| Character | Holotype ♀ | ♀♀ | ♂♂ | Dauer juveniles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| L | 1,530.0 | 1,520.0 ± 116.0 (1,265.0–1,734.0) | 1,181.4 ± 104.1 (998.0–1,374.0) | 585.9 ± 38.2 (517.0–643.0) |
| a | 18.1 | 19.7 ± 1.4 (17.2–23.7) | 22.0 ± 1.0 (20.4–23.6) | 22.9 ± 1.6 (20.7–26.8) |
| b | 6.6 | 6.8 ± 0.5 (5.7–7.4) | 6.1 ± 0.6 (4.3–6.7) | 4.5 ± 0.2 (4.1–4.7) |
| c | 29.1 | 27.4 ± 2.5 (23.3–31.0) | 34.8 ± 2.8 (30.0–39.3) | 4.9 ± 0.3 (4.4–5.4) |
| c' | 1.3 | 1.4 ± 0.1 (1.2–1.6) | 1.4 ± 0.1 (1.1–1.5) | 7.8 ± 0.7 (6.7–9.8) |
| V or T | 52.7 | 52.3 ± 1.0 (50.9–54.5) | 71.1 ± 2.9 (64.8–75.2) | – |
| G1% | 29.8 | 29.4 ± 2.8 (24.9–35.4) | – | – |
| G2% | 28.7 | 29.2 ± 3.0 (22.3–33.8) | – | – |
| Lip height | 6.5 | 5.1 ± 0.7 (4.0–6.5) | 5.1 ± 0.7 (3.0–6.5) | 2.0 ± 0.2 (1.5–2.5) |
| Lip diam. | 14.0 | 15.6 ± 0.9 (13.5–16.5) | 14.2 ± 1.0 (12.0–15.5) | 5.2 ± 0.5 (4.5–6.5) |
| Stoma length | 20.5 | 20.1 ± 0.5 (19.0–21.0) | 19.3 ± 1.3 (16.5–21.0) | 16.6 ± 0.9 (14.5–18.0) |
| Stoma diam. | 5.5 | 5.8 ± 0.5 (4.5–7.0) | 5.0 ± 0.7 (4.0–6.5) | – |
| Corpus length | 134.0 | 130.2 ± 4.8 (120.0–138.0) | 113.3 ± 5.1 (103.5–123.0) | 79.4 ± 5.1 (64.0–89.0) |
| Metacarpal diam | 29.0 | 30.2 ± 1.7 (26.0–34.0) | 26.7 ± 1.7 (23.0–29.5) | 13.7 ± 1.4 (10.5–16.0) |
| Isthmus length | 59.5 | 53.3 ± 5.1 (44.5–62.5) | 45.4 ± 3.6 (40.0–52.0) | 31.5 ± 2.6 (24.5–35.0) |
| Basal bulb length | 40.0 | 39.5 ± 1.6 (37.0–43.5) | 33.9 ± 2.9 (29.5–40.5) | 18.0 ± 1.3 (14.0–20.0) |
| Basal bulb diam. | 39.5 | 37.2 ± 2.5 (32.5–41.5) | 30.5 ± 1.9 (27.0–33.5) | 16.3 ± 1.0 (14.0–18.5) |
| Cardia length | 12.8 | 9.8 ± 2.9 (6.5–15.0) | 7.6 ± 1.8 (6.0–12.5) | 3.4 ± 0.4 (3.0–4.0) |
| Anterior end to nerve ring | 151.5 | 145.5 ± 6.2 (134.0–161.0) | 128.6 ± 8.0 (115.5–151.0) | 90.3 ± 6.8 (72.0–107.0) |
| Anterior end to hemizonid | 183.0 | 177.6 ± 9.2 (160–191.0) | 155.3 ± 8.9 (136.5–169.0) | 107.2 ± 8.1 (88.0–119.0) |
| Anterior end to Ex. pore | 198.0 | 191.8 ± 11.4 (171.0–206.0) | 170.6 ± 10.2 (148.5–185.5) | 115.3 ± 7.7 (99.0–129.0) |
| Pharynx length | 232.0 | 224.7 ± 7.3 (212.0–239.0) | 194.8 ± 12.7 (175.5–234.5) | 130.8 ± 6.2 (121.5–145.0) |
| Vulval body diam. | 84.5 | 76.9 ± 7.5 (63.0–88.0) | – | – |
| Maximum body diam. | 86.0 | 77.6 ± 7.8 (63.0–88.5) | 53.9 ± 4.9 (44.5–63.0) | 25.6 ± 2.1 (22.0–30.0) |
| Rectum | 39.5 | 40.6 ± 4.0 (34.0–49.0) | – | 20.8 ± 2.0 (17.0–24.0) |
| Anal/cloacal body diam. | 42.0 | 41.2 ± 4.3 (34.5–50.5) | 25.2 ± 3.0 (22.0–32.5) | 15.4 ± 1.4 (11.5–17.5) |
| Tail length | 52.5 | 55.7 ± 4.7 (46.0–62.5) | 34.0 ± 2.5 (30.0–39.0) | 118.9 ± 6.3 (112.0–132.0) |
| Tail spike length | 21.5 | 25.3 ± 4.3 (17.0–38.0) | – | |
| Spicules | – | – | 55.2 ± 5.6 (48.0–70.5) | – |
| Gubernaculum | 23.6 ± 1.8 (20.5–28.0) | |||