Figure 1.
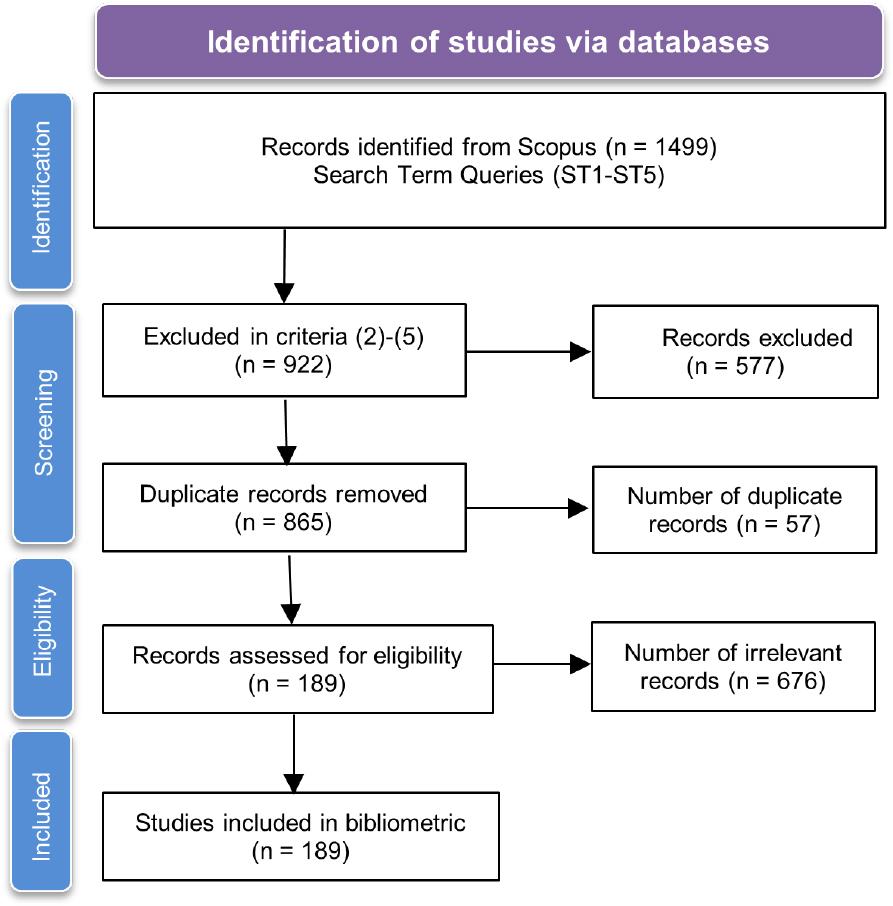
Figure 2.
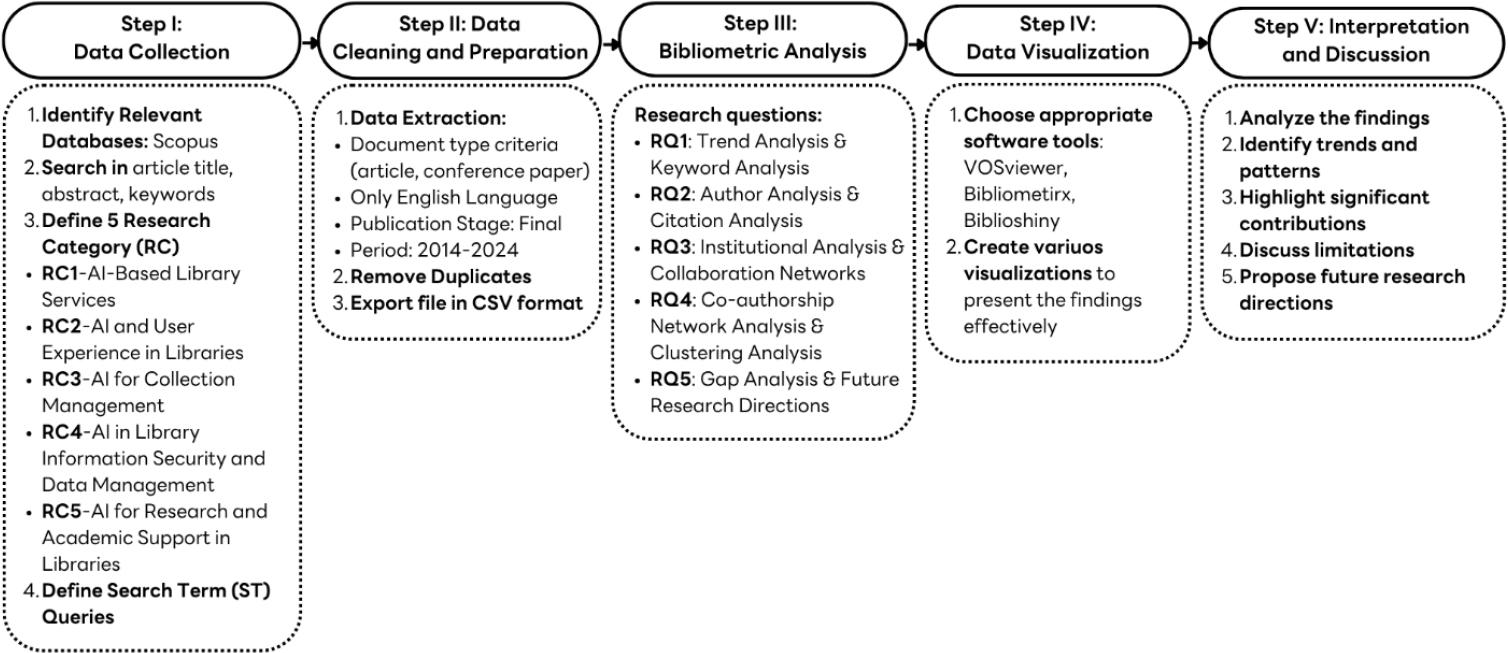
Figure 3.
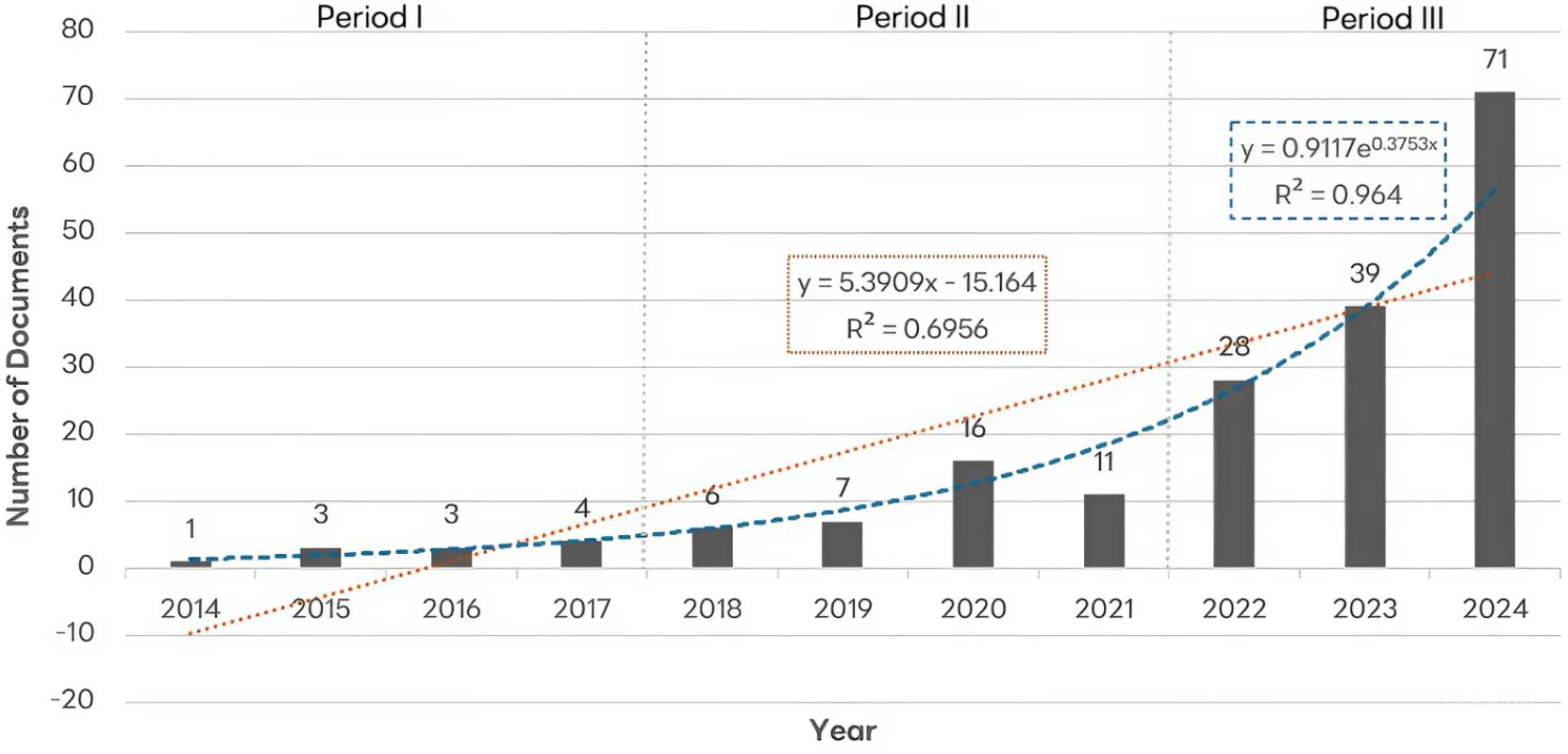
Figure 4.
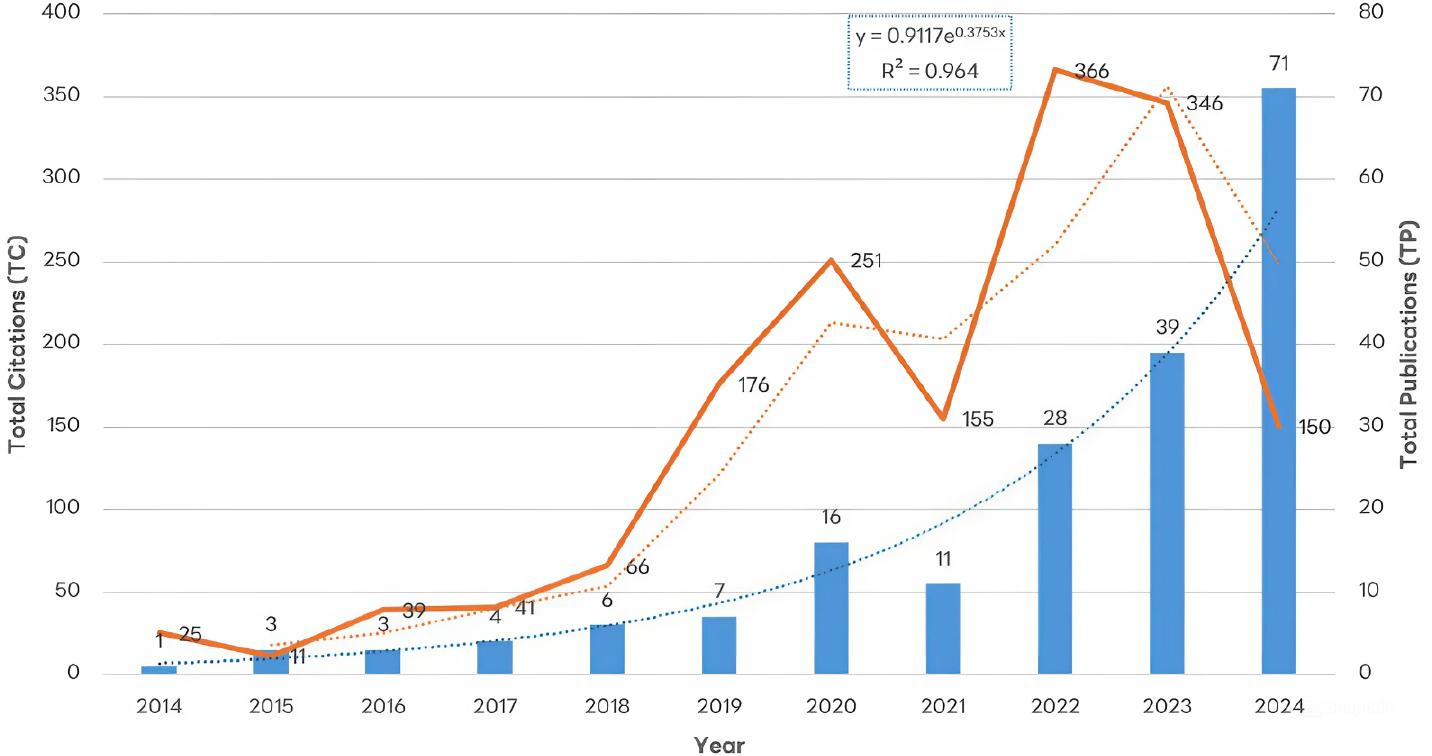
Figure 5.
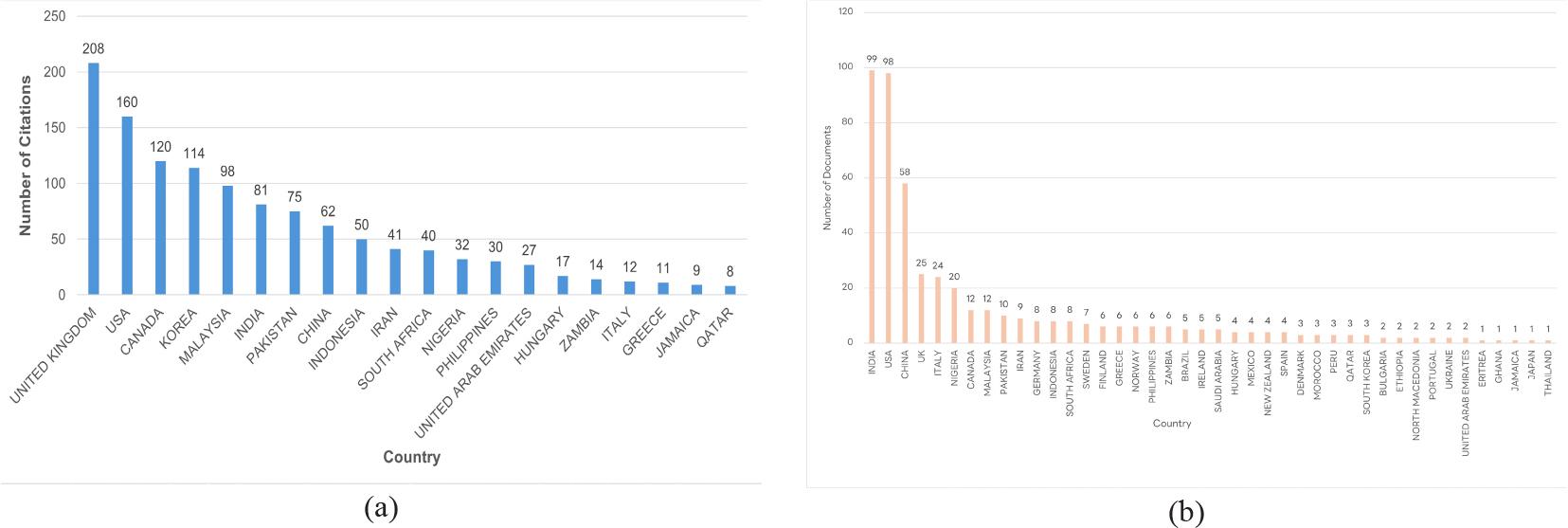
Figure 6.
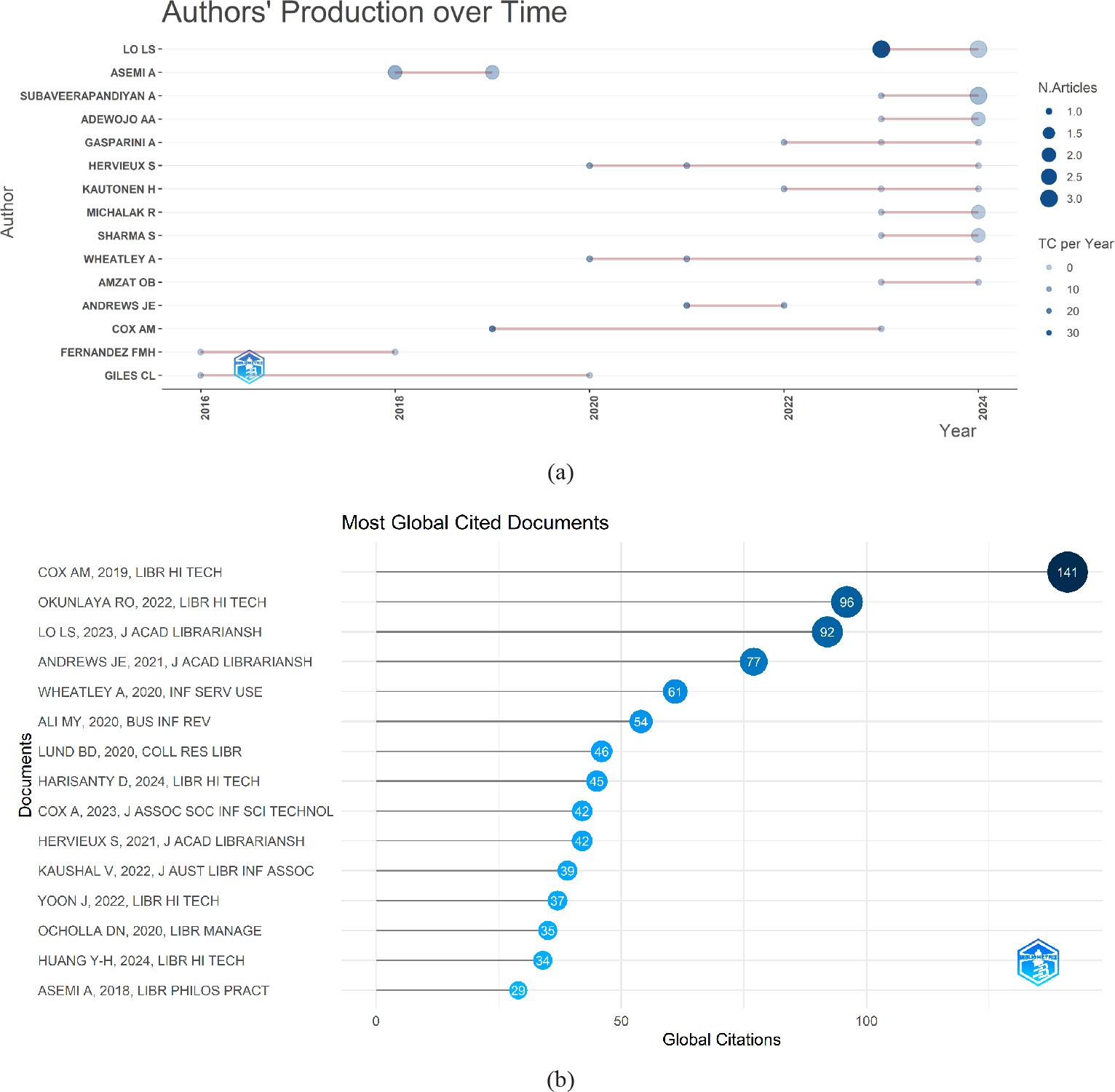
Figure 7.
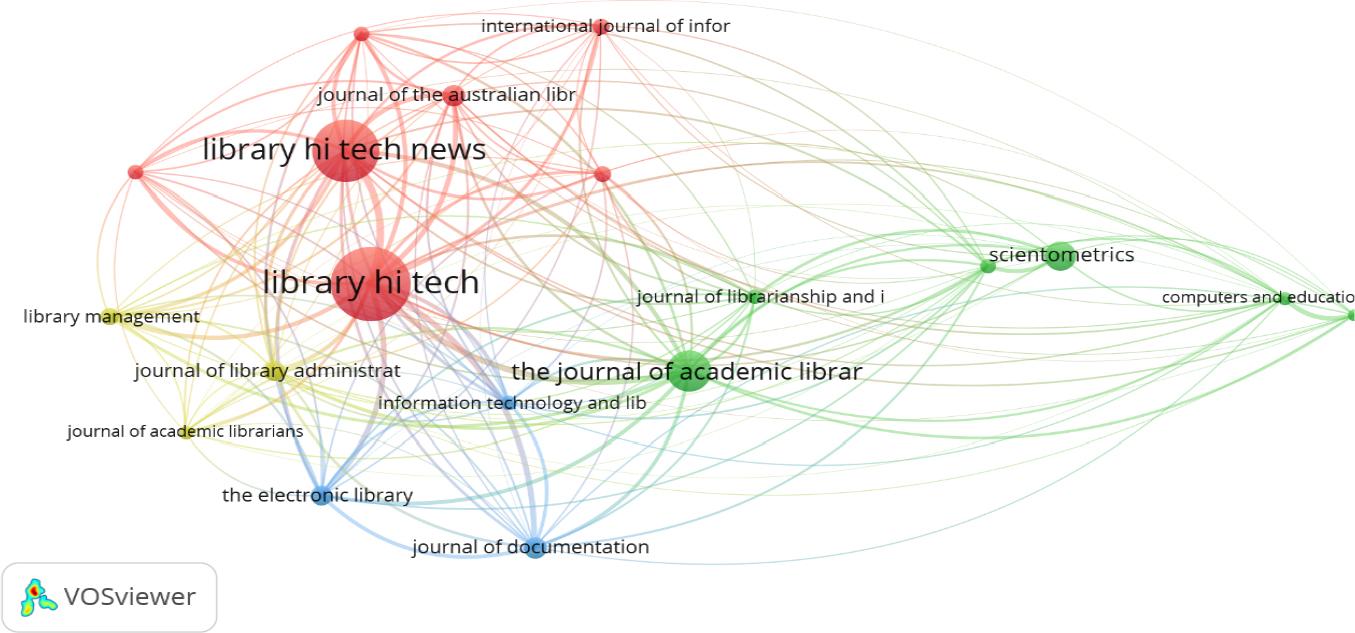
Figure 8.
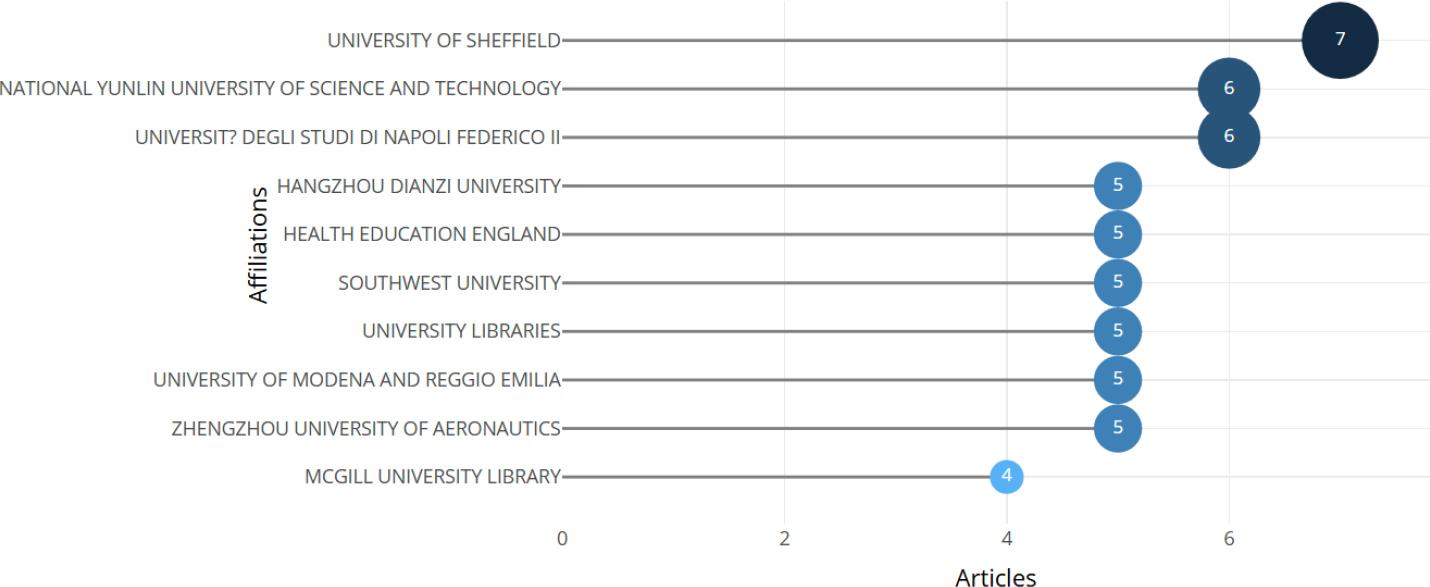
Figure 9.
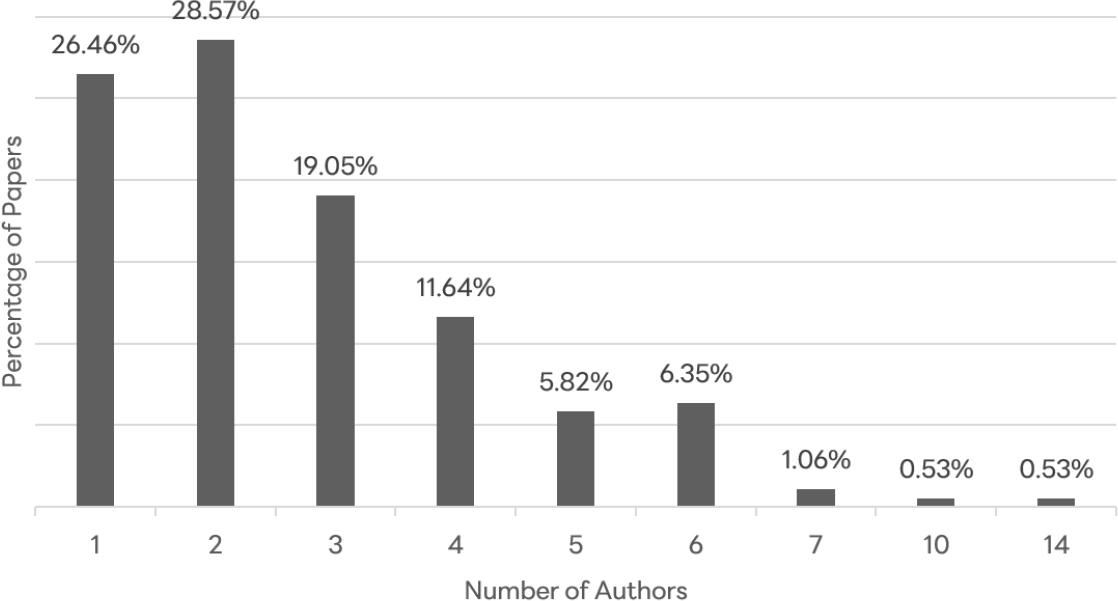
Figure 10.
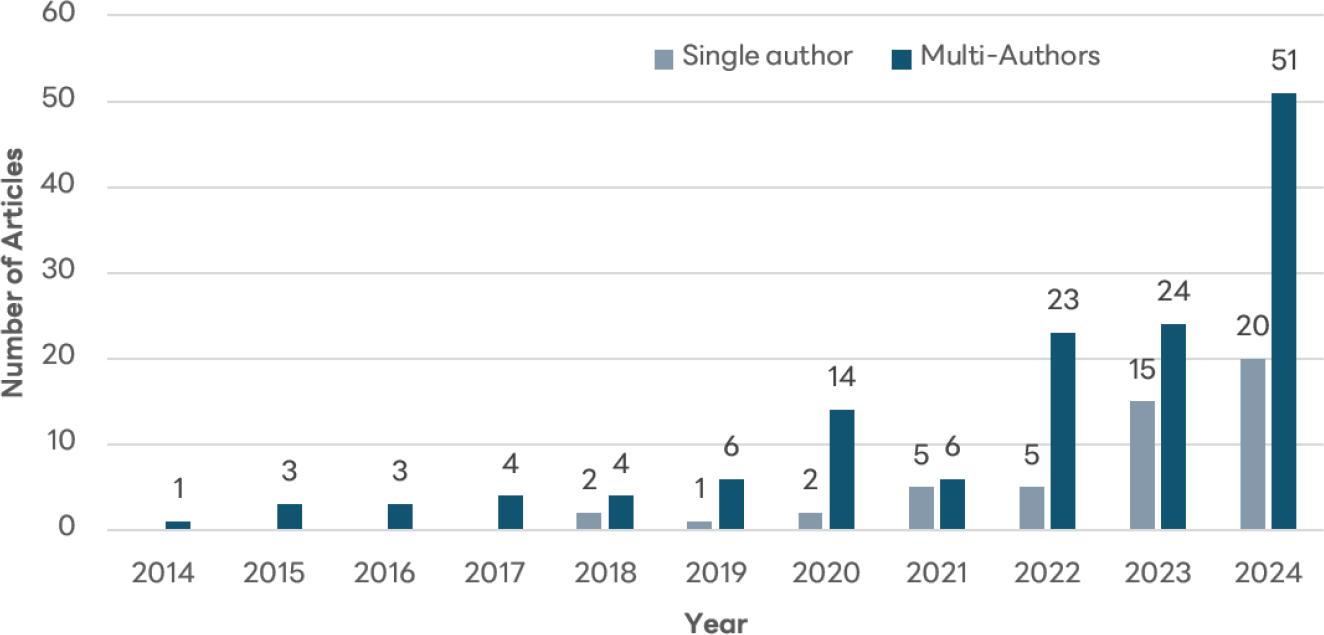
Figure 11.
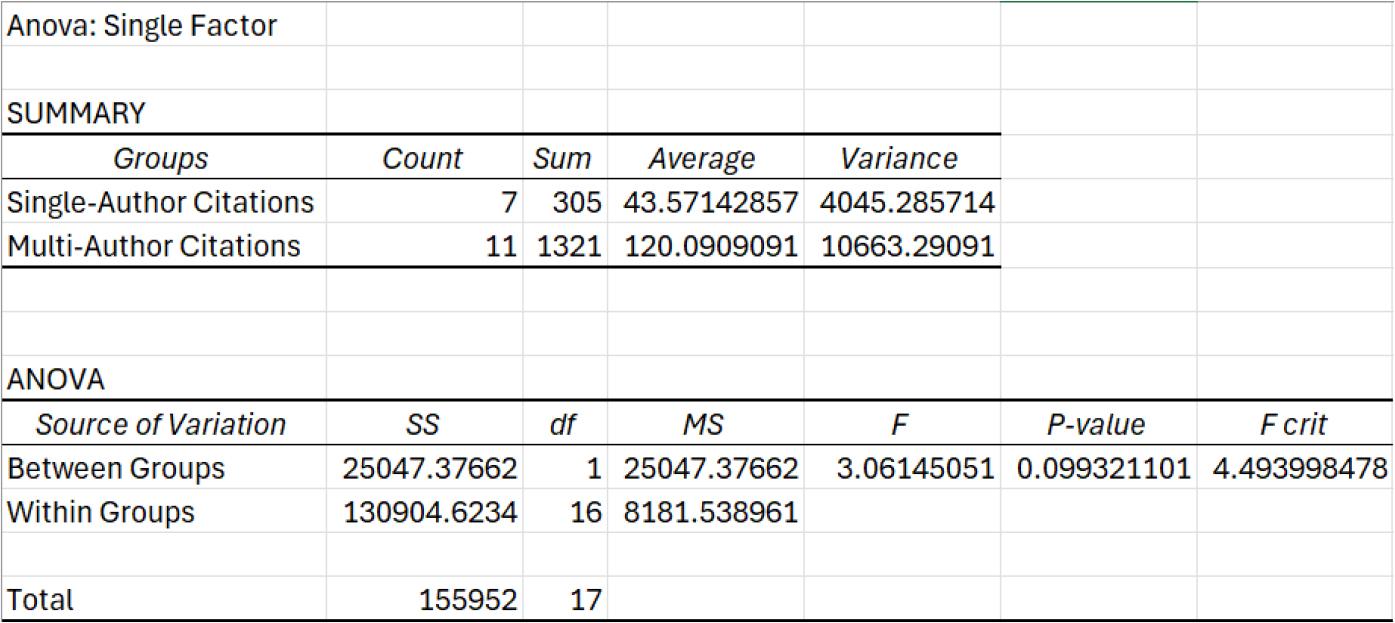
Figure 12.

Figure 13.
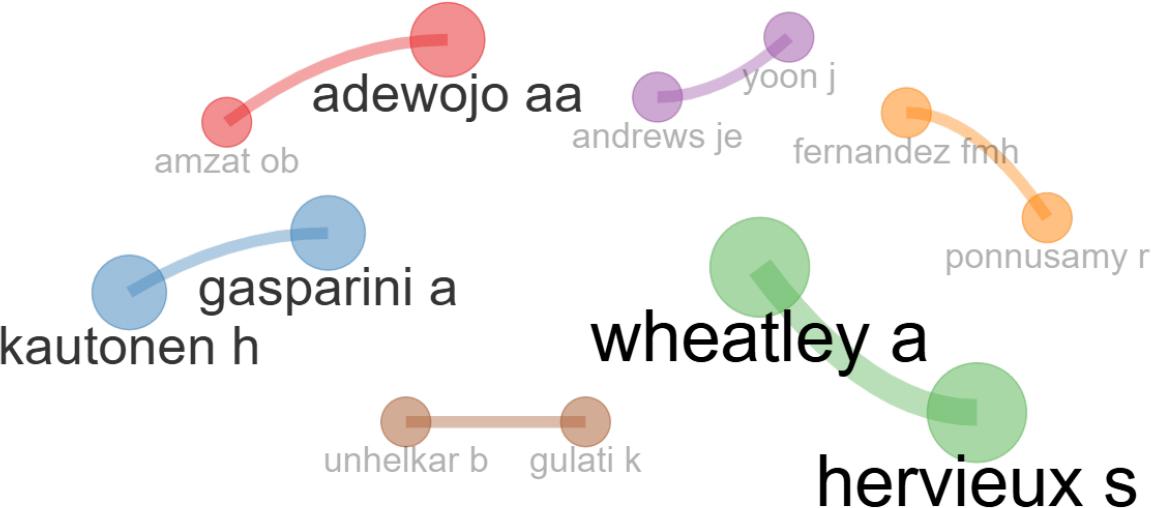
Figure 14.
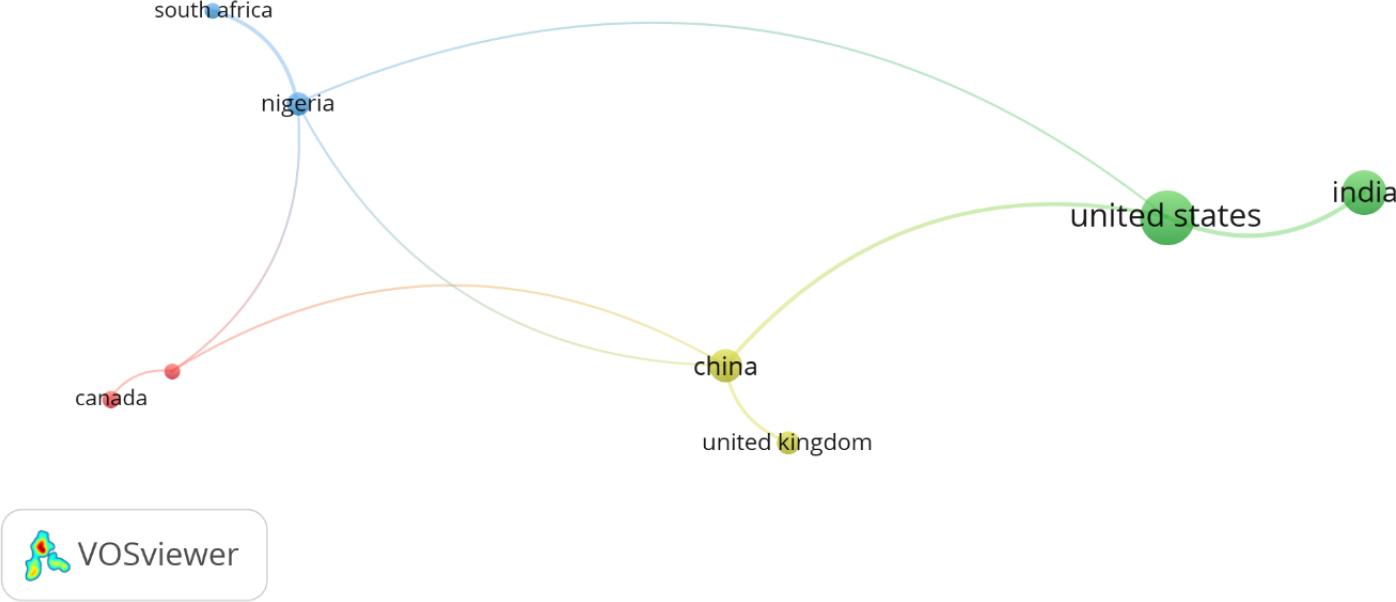
Figure 15.
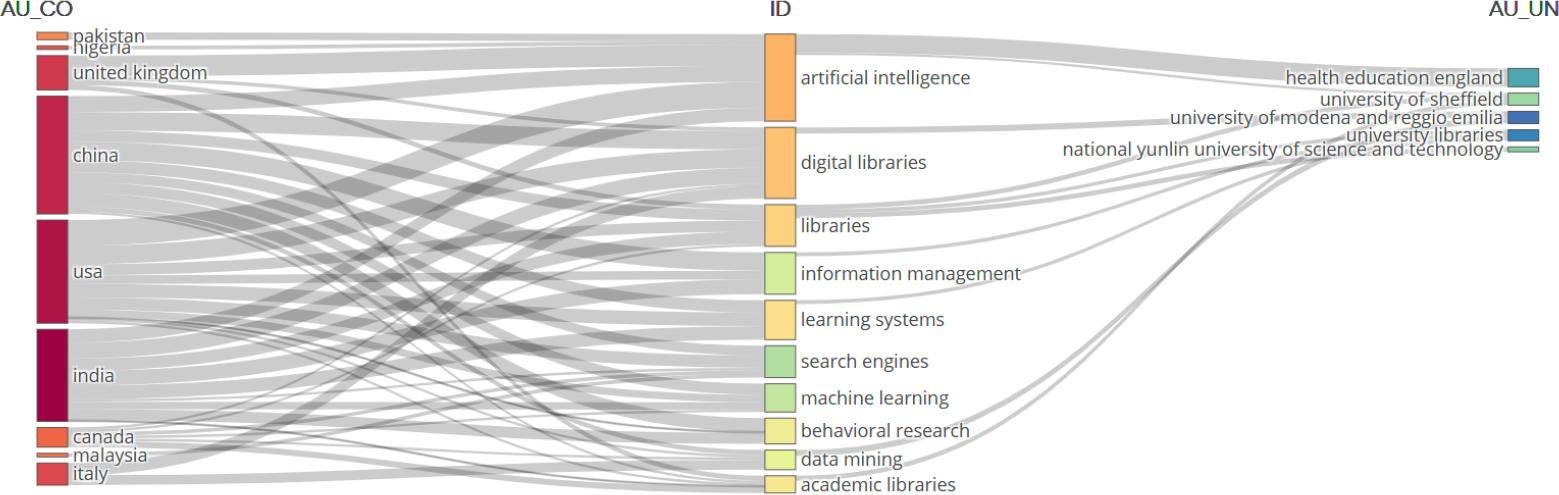
Figure 16.
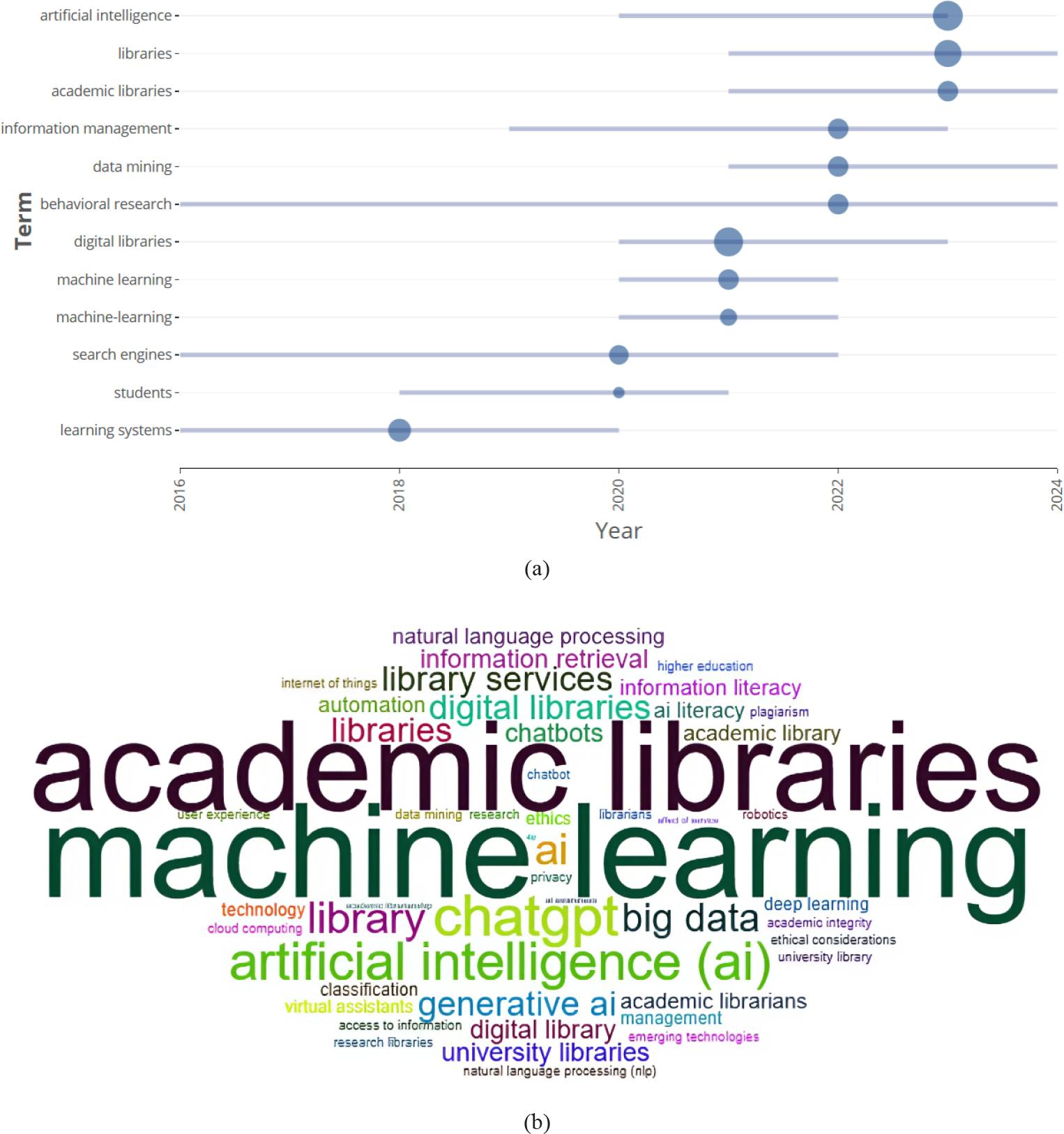
Figure 17.
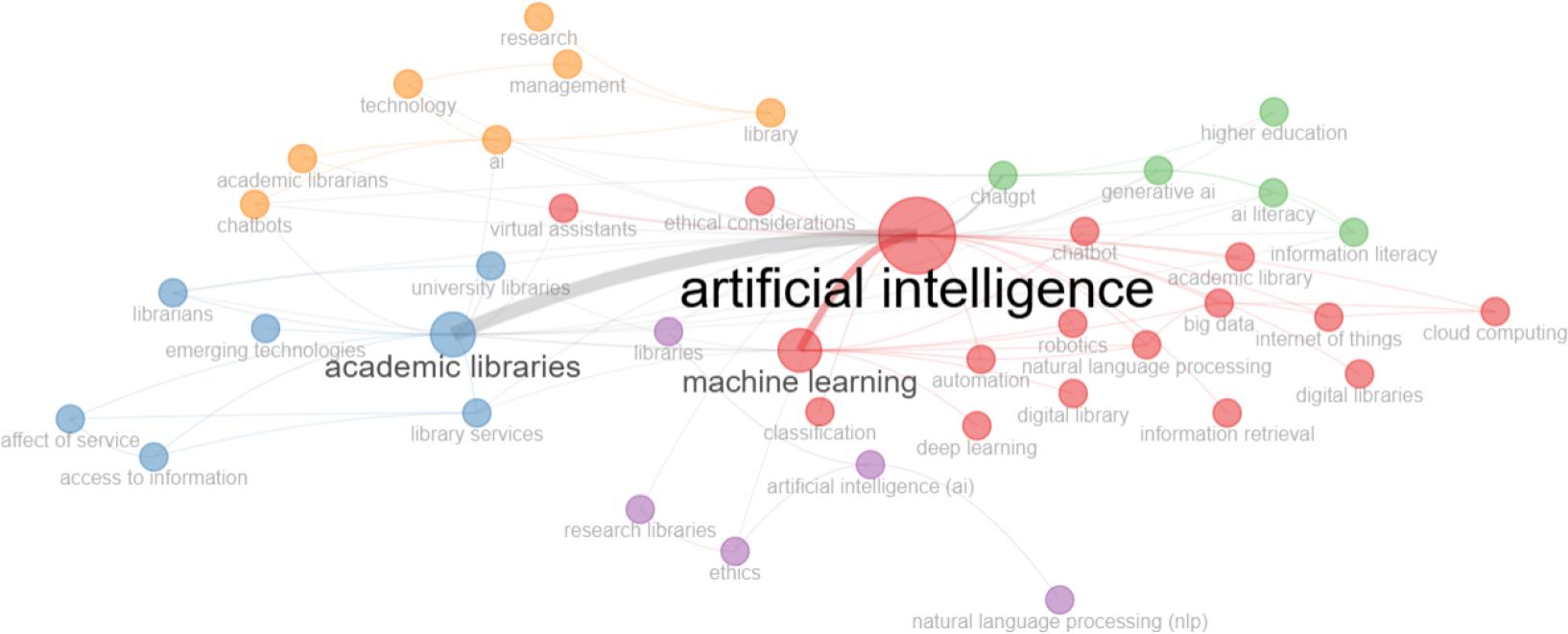
Figure 18.
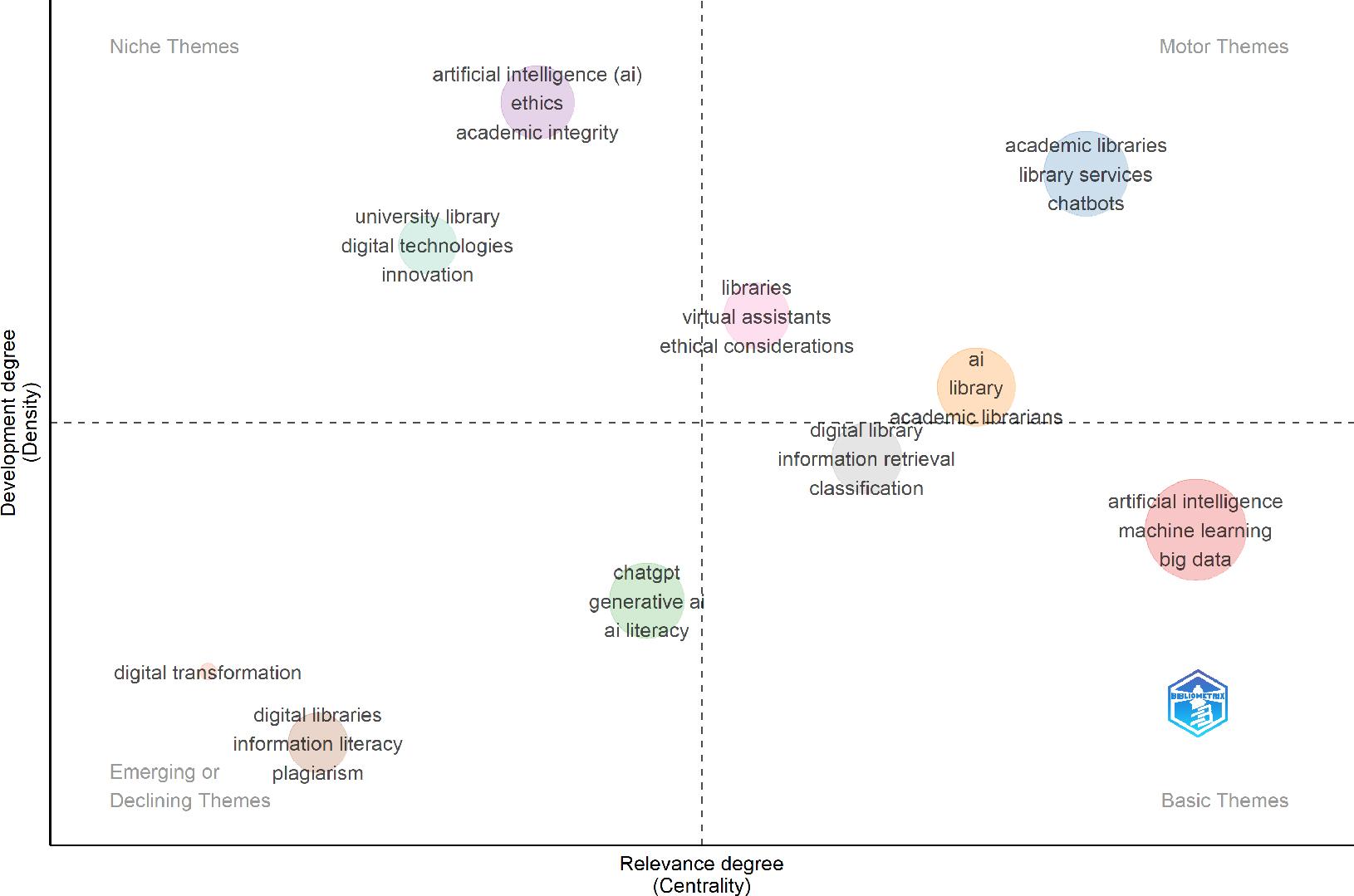
Figure 19.
Centrality metrics and cluster membership of authors in the co-authorship network on AI in academic libraries_
| Node | Cluster | Betweenness | Closeness | PageRank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adewojo aa (Adewojo et al., 2024) | 1 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Amzat ob | 1 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Gasparini a (Kautonen & Gasparini, 2024) | 2 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Kautonen h | 2 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Hervieux s (Hervieux & Wheatley, 2021; Wheatley & Hervieux, 2020) | 3 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Wheatley a | 3 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Andrews je (Andrews et al., 2021; Yoon et al., 2022) | 4 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Yoon j | 4 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Fernandez fmh (Fernandez & Ponnusamy, 2015; Provenzano et al., 2024) | 5 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Ponnusamy r | 5 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Gulati k (Kamal Gulati & Unhelkar, 2024) | 6 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
| Unhelkar b | 6 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.083 |
Author keyword co-occurrence network results_
| Cluster | Betweenness | Closeness | PageRank | Author-Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Red (17 items) | 610.241 | 0.02 | 0.216 | artificial intelligence |
| 122.336 | 0.014 | 0.08 | machine learning | |
| 1.556 | 0.012 | 0.025 | big data | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.007 | digital libraries | |
| 0 | 0.009 | 0.007 | digital library | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.007 | information retrieval | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.01 | academic library | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.019 | automation | |
| 0.167 | 0.012 | 0.019 | natural language processing | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.007 | classification | |
| 0 | 0.009 | 0.007 | deep learning | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.013 | virtual assistants | |
| 0 | 0.009 | 0.007 | chatbot | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.014 | cloud computing | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.007 | ethical considerations | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.016 | internet of things | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.012 | robotics | |
| 2 Blue (7 items) | 120.121 | 0.014 | 0.1 | academic libraries |
| 9.094 | 0.013 | 0.026 | library services | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.021 | university libraries | |
| 0 | 0.009 | 0.015 | access to information | |
| 0 | 0.009 | 0.007 | emerging technologies | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.018 | librarians | |
| 0 | 0.009 | 0.014 | affect of service | |
| 3 Green (5 items) | 3.095 | 0.012 | 0.041 | ChatGPT |
| 0.625 | 0.012 | 0.026 | generative AI | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.017 | AI literacy | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.017 | information literacy | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.011 | higher education | |
| 4 Purple (5 items) | 39.5 | 0.008 | 0.023 | artificial intelligence (AI) |
| 36 | 0.012 | 0.014 | libraries | |
| 38 | 0.012 | 0.019 | ethics | |
| 0 | 0.006 | 0.01 | natural language processing (NLP) | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.012 | research libraries | |
| 5 Yellow (7 items) | 9.766 | 0.013 | 0.038 | AI |
| 54.348 | 0.012 | 0.024 | library | |
| 0 | 0.012 | 0.024 | chatbots | |
| 0 | 0.011 | 0.012 | academic librarians | |
| 0.5 | 0.008 | 0.012 | management | |
| 21.652 | 0.011 | 0.017 | technology | |
| 0 | 0.008 | 0.008 | research |
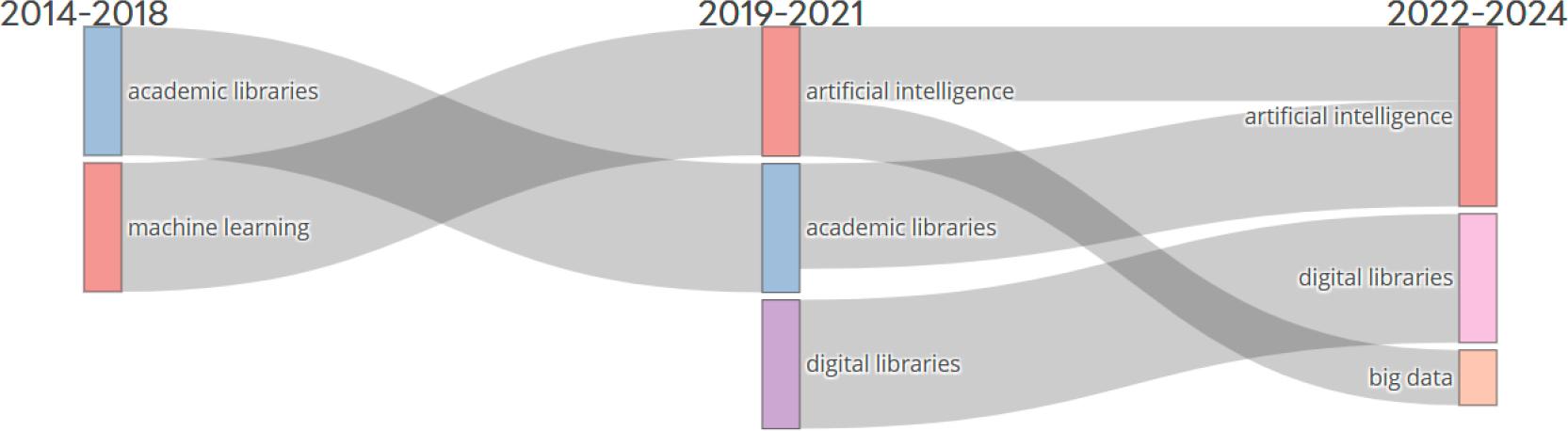
Annual publication and citation of AI in academic libraries (2014 to 2024)_
| Year | Total Publications | Total Citations | Total Citations per Year | Mean TP | Mean TC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 1 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 0 |
| 2015 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 3.67 | 0.33 |
| 2016 | 3 | 39 | 4 | 13 | 1.33 |
| 2017 | 4 | 41 | 15 | 10.25 | 3.75 |
| 2018 | 6 | 66 | 20 | 11 | 3.33 |
| 2019 | 7 | 176 | 26 | 25.14 | 3.71 |
| 2020 | 16 | 251 | 44 | 15.69 | 2.75 |
| 2021 | 11 | 155 | 63 | 14.09 | 5.73 |
| 2022 | 28 | 366 | 137 | 13.07 | 4.89 |
| 2023 | 39 | 346 | 335 | 8.87 | 8.59 |
| 2024 | 71 | 150 | 968 | 2.11 | 13.63 |
Papers found in Scopus until October 2024_
| Record Identified | Search Term | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST1 | ST2 | ST3 | ST4 | ST5 | |
| (1) Scopus searches within article title, abstract, keywords | 417 | 205 | 105 | 480 | 292 |
| (2) Document type criteria (article, conference paper) | 301 | 163 | 71 | 371 | 183 |
| (3) Only English Language | 400 | 203 | 100 | 465 | 282 |
| (4) Publication stage: Final | 384 | 204 | 102 | 473 | 286 |
| (5) Period: 2014-2024 | 386 | 174 | 103 | 449 | 262 |
| Number of articles that have been included in criteria (1)-(5) | 237 | 134 | 64 | 334 | 153 |
| Number of articles retrieved | 922 | ||||
| Duplicate articles removed | 57 | ||||
| Papers irrelevant to the research topic and research aim were removed | 676 | ||||
| Total number of articles in the bibliometric studies | 189 | ||||
The top 15 academic libraries’ co-cited scientific sources on AI applications and tools_
| Ranking | Scientific Source | Co-Citations | Links | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Library Hi Tech | 117 | 18 | 1247 |
| 2 | Library Hi Tech News | 100 | 17 | 836 |
| 3 | The Journal of Academic Librarianship | 66 | 17 | 712 |
| 4 | Scientometrics | 47 | 12 | 170 |
| 5 | Journal of Documentation | 34 | 17 | 485 |
| 6 | Journal of Australian Library and Information Association | 34 | 18 | 432 |
| 7 | The Electronic Library | 33 | 16 | 482 |
| 8 | Journal of Library Administration | 33 | 17 | 319 |
| 9 | Library Management | 28 | 17 | 327 |
| 10 | College & Research Libraries | 27 | 18 | 198 |
| 11 | International Journal of Information Management | 27 | 17 | 177 |
| 12 | Information Technology and Libraries | 24 | 17 | 332 |
| 13 | Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology | 24 | 18 | 258 |
| 14 | Journal of Librarianship and Information Science | 24 | 17 | 234 |
| 15 | Business Information Review | 23 | 17 | 340 |
Top 15 most cited documents on AI applications and tools in academic libraries_
| Title | Authors | Journal | Total Citations | TC per Year | Normalized TC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The intelligent library: Thought leaders’ views on the likely impact of artificial intelligence on academic libraries | Cox, Pinfield, et al. (2019) | Library Hi Tech | 141 | 20.14 | 5.61 |
| Artificial intelligence (AI) library services innovative conceptual framework for the digital transformation of university education | Okunlaya et al. (2022) | Library Hi Tech | 96 | 24.00 | 7.34 |
| The CLEAR path: A framework for enhancing information literacy through prompt engineering | Lo (2023b) | The Journal of Academic Librarianship | 92 | 30.67 | 19.37 |
| UTAUT as a Model for Understanding Intention to Adopt AI and Related Technologies among Librarians | Andrews et al. (2021) | The Journal of Academic Librarianship | 77 | 15.40 | 5.46 |
| Artificial intelligence in academic libraries: An environmental scan | Wheatley & Hervieux (2020) | Information Services & Use | 61 | 10.17 | 3.89 |
| Artificial intelligence tools and perspectives of university librarians: An overview | Ali et al. (2020) | Business Information View | 54 | 9.00 | 3.44 |
| Perceptions toward Artificial Intelligence among Academic Library Employees and Alignment with the Diffusion of Innovations’ Adopter Categories | Lund et al. (2020) | College & Research Libraries | 46 | 7.67 | 2.93 |
| Leaders, practitioners and scientists’ awareness of artificial intelligence in libraries: a pilot study | Harisanty et al. (2024) | Library Hi Tech | 45 | 22.50 | 21.30 |
| How artificial intelligence might change academic library work: Applying the competencies literature and the theory of the professions | Cox (2023) | Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology | 42 | 14.00 | 4.73 |
| Perceptions of artificial intelligence: A survey of academic librarians in Canada and the United States | Hervieux & Wheatley (2021) | The Journal of Academic Librarianship | 42 | 8.40 | 2.98 |
| The Role of Chatbots in Academic Libraries: An Experience-based Perspective | Kaushal & Yadav (2022) | Journal of the Australian Library and Information Association | 39 | 9.75 | 2.98 |
| Perceptions on adopting artificial intelligence and related technologies in libraries: public and academic librarians in North America | Yoon et al. (2022) | Library Hi Tech | 37 | 9.25 | 2.83 |
| Readiness of academic libraries in South Africa to research, teaching and learning support in the Fourth Industrial Revolution | Ocholla & Ocholla (2020) | Library Management | 35 | 5.83 | 2.23 |
| Exploring the implementation of artificial intelligence applications among academic libraries in Taiwan | Huang (2024) | Library Hi Tech | 34 | 17.00 | 16.09 |
| Artificial intelligence (AI) application in library systems in Iran: A taxonomy study | Asemi & Asemi (2018) | Library Philosophy and Practice | 29 | 3.63 | 2.64 |
Summary of research category with search term queries criterion_
| Research Category | Linked RQs | Justification of Search Term (ST) Queries | Search Term (ST) Queries |
|---|---|---|---|
| RC1: AI-Based Library Services | RQ1, RQ4, RQ5 | This category focused on AI tools used in front-facing library services such as cataloging, virtual assistants, book recommendations, and chatbots. The search string ST1 emphasizes keywords like library catalog, AI-powered services, virtual assistant, and chatbot, highlighting efforts to automate and enhance user service delivery within academic libraries. | ST1: (AI AND librar* catalog* OR academ* librar*) OR (AI AND librar* service* OR chatbot* OR virtual* assistant*) OR (AI-power* book recommen* OR person* service* AND librar*) |
| RC2: AI and User Experience in Libraries | RQ1, RQ4, RQ5 | ST2 captures research on how AI impacts user behavior, personalized content delivery, and digital user experience. Key phrases include user behavior, AI-enhanced user experience, and personal content. This aligns with studies analyzing how AI shapes patron engagement, interface design, and satisfaction within academic libraries. | ST2: (user* behav* AND AI OR mach* learn* AND librar*) OR (infoma* retriev* AND AI OR digital* librar*) OR (AI-enhanc* user* experie* OR personal* content* OR academ* resour*) |
| RC3: AI for Collection Management | RQ3, RQ4, RQ5 | This search string (ST3) explores the application of AI in managing and analyzing digital assets, predictive analytics, document digitization, and resource curation. Phrases like digital asset management, predictive analytics, and collection development focus on back-end library functions such as digital archiving, metadata classification, and trend-based resource planning. | ST3: (digital asset managem* AND AI OR mach* learn* AND lbirar*) OR (resource* curati* AND classificat* OR predictiv* analytic* AND academ* collect*) OR (predictv* analytic* AND collecti* develop* OR librar* managem*) OR (docum* digitiz* AND AI OR image* recognit* AND universit* archive*) OR (trend* analys* AND collect* enhance* OR librar* collecti* AND AI) |
| RC4: AI in Library Information Security and Data Management | RQ2, RQ4, RQ5 | In academic libraries, ST4 acknowledges the literature that discusses AI’s function in cybersecurity, data integrity, anomaly detection, and user authentication systems. The literature covers anomaly detection, AI-enabled security, and data privacy. Understanding how libraries safeguard their digital spaces and private data about AI technologies requires knowledge of this field. | ST4: (data privacy* OR securit* OR encrypt* AND AI OR mach* learn* AND librar* system*) OR (anomaly* detect* OR data securit* AND academ* librar*) OR (user authentica* OR AI-enhance* securit* AND academ* librar*) OR (anamaly* detect* AND user access OR data integrit* AND academ* librar*) |
| RC5: AI for Research and Academic Support in Libraries | RQ1, RQ3, RQ4, RQ5 | Studies on artificial intelligence tools support research activities, automated literature reviews, natural language processing, plagiarism detection, and research data management captured by ST5. This group captures the increasing integration of artificial intelligence into academic integrity tools, citation checking, resource discovery, and scholarly support services. | ST5: (literature* review* automat* AND AI OR natur* lang* process* AND resear* librar*) OR (resear* data manage* AND mach* learn* OR AI-drive* analy* AND librar*) OR (plagia* detect* AND citat* check* OR academ* integri* AND univers* librar*) OR (digit* content* analy* AND AI OR mach* learn* AND academ* resource*) OR (mach* learn* AND resource* discov* OR digit* librar* collect* AND AI) |
Summary of the criteria for irrelevant record exclusion_
| Exclusion Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Library Context Mismatch | Emphasized school and public libraries over academic ones |
| Superficial Keyword Use | Included keywords that were not thematically relevant (e.g., AI, library) |
| Domain Irrelevance | Applications of AI outside of libraries (e.g., health, robotics, engineering) |
| Non-AI Focus | Discussed digital tools or systems that do not involve machine learning or artificial intelligence |
| Non-Analytical Content | Theoretical works devoid of models or data |
| No Library Focus | Discussed educational technology that has nothing to do with the services or operations of libraries |