FIGURE 1.
FIGURE 2.
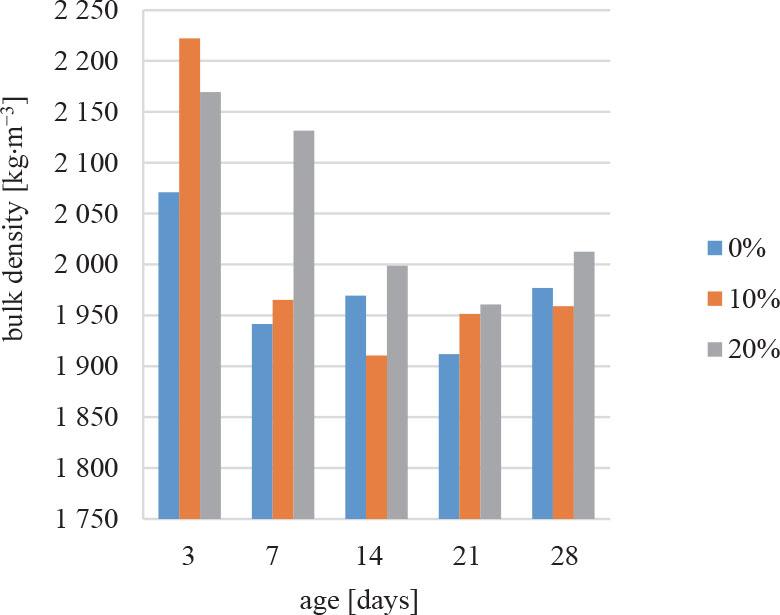
FIGURE 3.
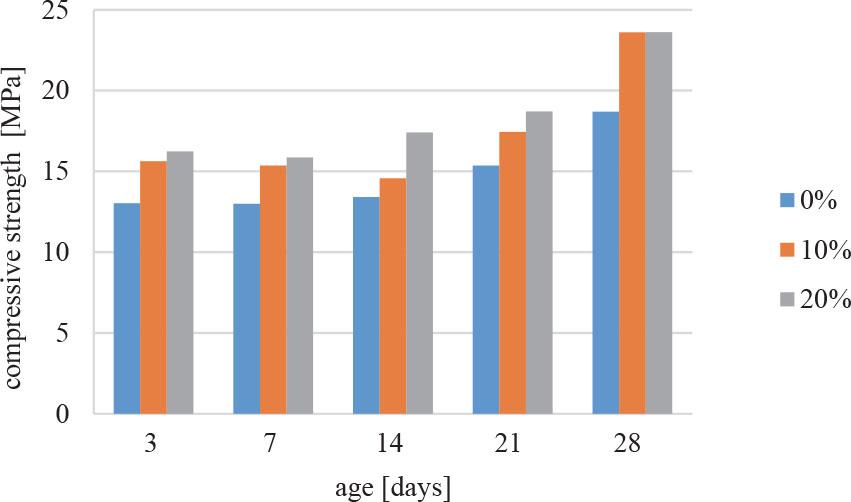
FIGURE 4.
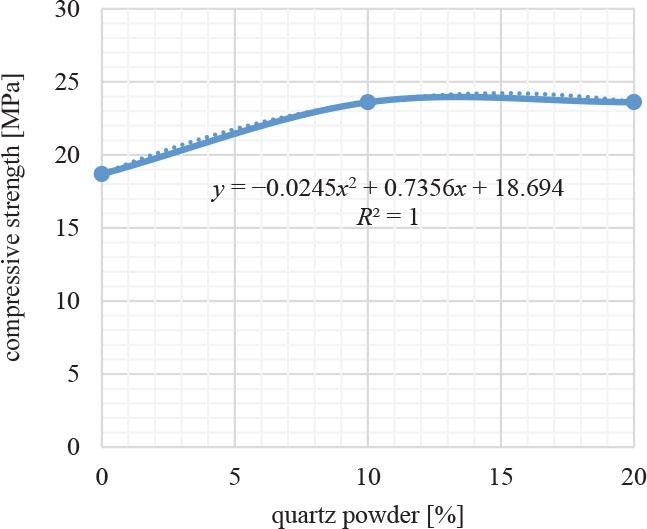
FIGURE 5.
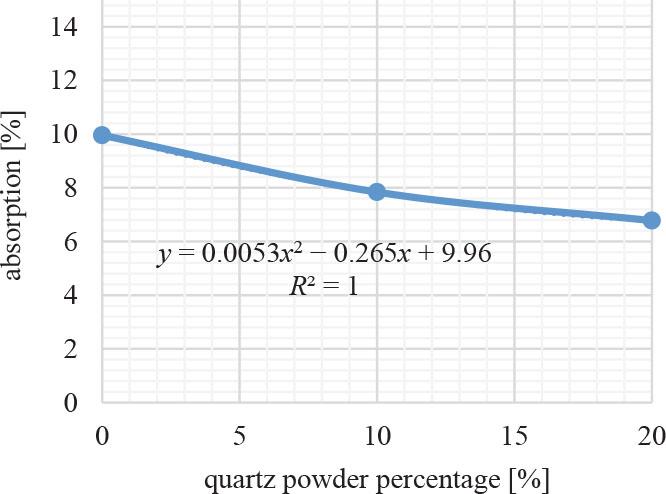
FIGURE 6.
Physical properties of quartz sand
| Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Bulk density [kg·m−3] | 1.760 |
| Organic content [%] | 3 |
| Water content [%] | 4.55 |
| Mud content [%] | 2.88 |
Size of paving blocks
| Variation | Thickness condition [mm] | Thickness [mm] | Tolerance | Length [mm] | Width [mm] | According to SNI 03-1691-1996 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 64.20 | 60 | ±8% | 210 | 105 | fulfilled |
| 10% | 59.50 | 60 | 210 | 105 | fulfilled | |
| 20% | 60.78 | 60 | 210 | 105 | fulfilled |
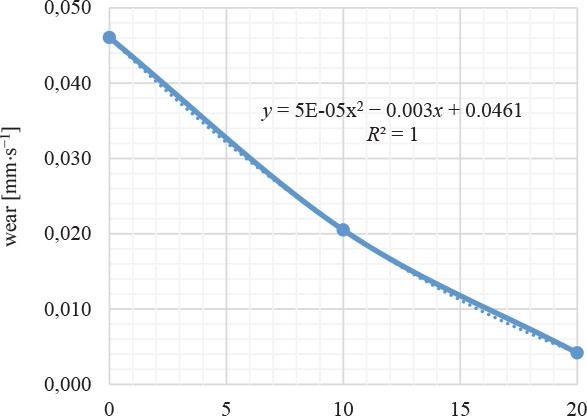
Wear of paving blocks
| Variation | Wear [mm·min−1] | SNI 03-0691 (classification) | Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | |||
| 0% | 0.046 | 0.103 | 0.149 | 0.184 | 0.251 | A |
| 10% | 0.021 | 0.103 | 0.149 | 0.184 | 0.251 | A |
| 20% | 0.004 | 0.103 | 0.149 | 0.184 | 0.251 | A |
Absorption of paving blocks
| Variation | Present absorption [%] | SNI 03-069 (paving block classification) | Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | |||
| 0% | 9.96 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 10 | D |
| 10% | 7.84 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 10 | C |
| 20% | 6.78 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 10 | C |
Characteristics of the fine aggregate
| Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Specific gravity [kg·m−3] | 2.646 |
| Fine modulus [-] | 3.030 |
| Bulk density [kg·m−3] | 1,523.65 |
| Fine particles less than 0.0075 mm [%] | 5.43 |
Constituents of cement composition
| Specification | Quantity [%] |
|---|---|
| Silicon dioxide (SiO2) | 23.04 |
| Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) | 7.40 |
| Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) | 3.36 |
| Calcium oxide (CaO) | 57.38 |
| Magnesium oxide (MgO) | 1.91 |
| Sulfur trioxide (SO3) | 2.0 |
| Loss on ignition (Lo1) | 3.94 |
| Free lime | 0.56 |
| Insoluble residue | 10.96 |
Mix design for paving blocks (volume of 1 m3)
| Variation | Cement | Fine aggregate | Coarse aggregate | Quartz powder | Water to cement ratio (w/c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 1 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 10% | 1 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| 20% | 1 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
Results of the chemical analysis of quartz powder
| Specification | Quartz powder content [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| samples from Mandor riverbank | samples from Mandor riverbank | |
| Silicon dioxide (SiO2) | 98.6 | 98.8 |
| Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) | 0.51 | 0.29 |
| Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Ilmenite dioxide (TiO2) | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| Calcium oxide (CaO) | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| Potassium dioxide (K2O) | 0.012 | 0.028 |
| Magnesium oxide (MgO) | – | – |
| Free calcium oxide | – | – |
| Water (H2O) | – | – |
Visual condition of paving blocks
| Variation | Description | Sample condition | According to SNI 03-1691-1996 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | STRUCTURE | ||
| flatness | flat | flat | |
| crack | no crack | no crack | |
| surface texture | rough | smooth | |
| FLANK | |||
| geometry | geometry | geometry | |
| sharpness | sharp | sharp | |
| strength | strong | strong | |
Characteristics of the coarse aggregate’s physical properties
| Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Absorption [%] | 0.188 |
| Bulk density [kg·m−3] | 1.668 |
| Water content [%] | 0.272 |
| Fine modulus | 4.9 |
| Aggregate abrasion [%] | 12.21 |
| Mud content [%] | 2.4 |
| Specific gravity [kg·m−3] | 2.455 |
Compressive strength of paving blocks
| Variation | Compressive strength at 28 days of age [MPa] | SNI 03-0691 (paving block classification) | Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | |||
| 0% | 18.69 | 35 | 17 | 12.5 | 8.5 | B |
| 10% | 23.60 | 35 | 17 | 12.5 | 8.5 | B |
| 20% | 23.61 | 35 | 17 | 12.5 | 8.5 | B |
