Fig.1
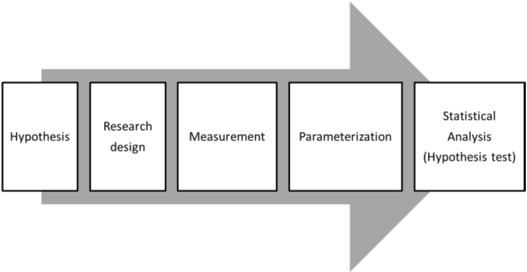
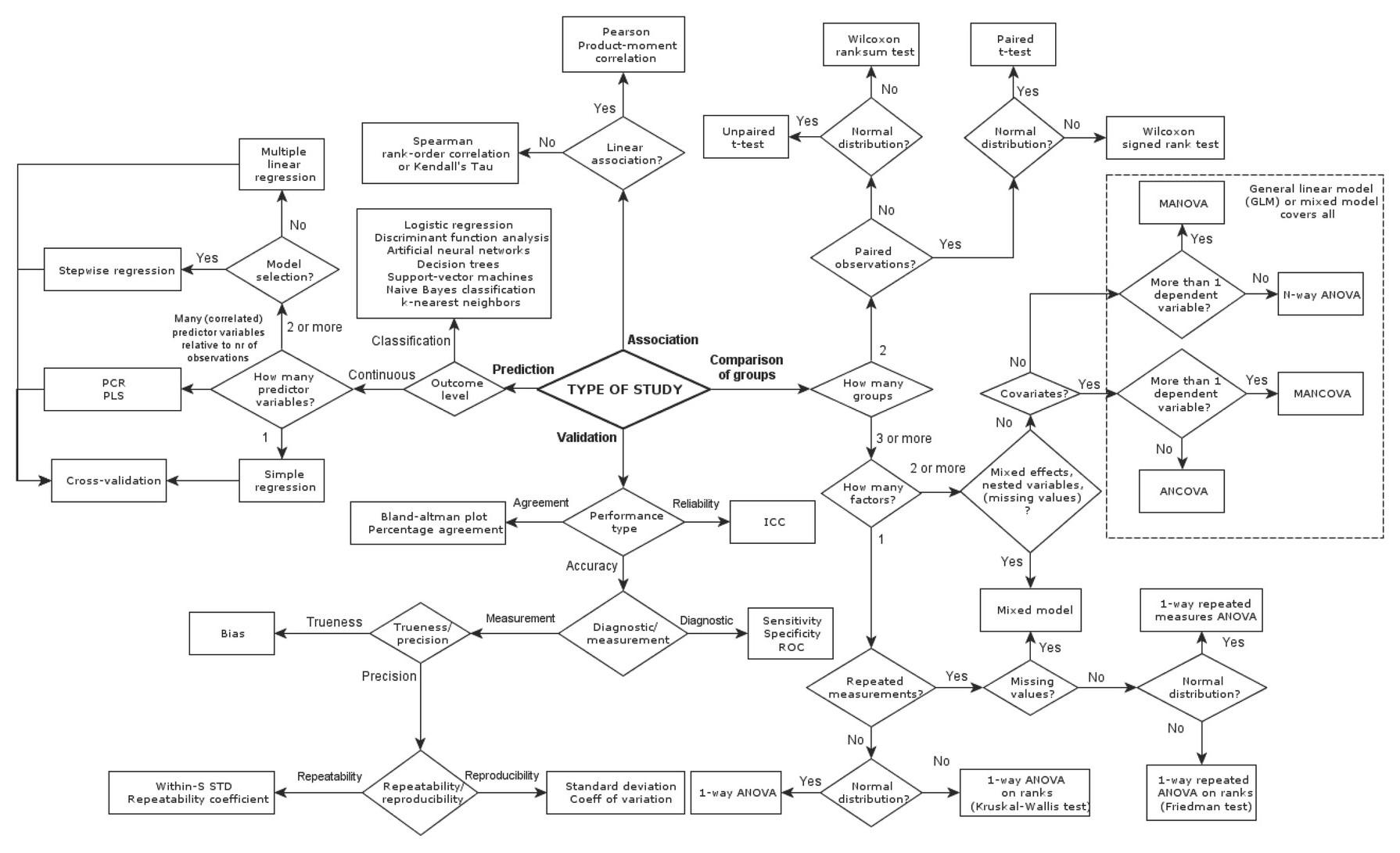
Fig.2
List of important terms in the validation of new measurement technology along with the most usual and recommended ways of reporting_ 1There are numerous different definitions in the literature, which can be inconsistent and confusing_ These definitions provide one version with the aim of reducing ambiguity_ 2Accuracy has previously been defined as the same as trueness only, but with ISO 5 725-1 [37], and reflected in the JCGM 200:2012 [19], the definition of accuracy has for the most changed to include both trueness and precision as given here_ The old definition is still in use in some areas_
| Term | Definition1 | Reported as |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement error | Measured quantity value minus a reference quantity value [19] | Quantity on the same scale as the measurement scale, relative error, percentwise error, mean square error, root mean square error. |
| Sensitivity | The sensitivity of a clinical test refers to the ability of the test to correctly identify those patients with the disease. [36]. | Eq. (1) |
| Specificity | The specificity of a clinical test refers to the ability of the test to correctly identify those patients without the disease. [36] | Eq. (2) |
| Agreement | The degree to which scores or ratings are identical [31] | Continuous: Bland-Altman plot |
| Trueness | Closeness of agreement between the average value obtained from a large series of results of measurement and a true value [37]. | Bias (i.e. the difference between the mean of the measurements and the true value) |
| Precision | Closeness of agreement between independent results of measurements obtained under stipulated conditions [37]. | Standard deviation, coefficient of variation |
| Repeatability | Precision determined under conditions where independent test results are obtained with the same method on identical test items in the same laboratory by the same operator using the same equipment within short intervals of time [37] | Within-subject standard deviation [38] |
| Reproducibility | Precision determined under conditions where test results are obtained with the same method on identical test items in different laboratories with different operators using different equipment [37] | Standard deviation, coefficient of variation |
| Accuracy2 | Closeness of agreement between the result of a measurement and a true value (both trueness and precision) [37] | Bias (trueness) and standard deviation/ coefficient of variation (precision) |
| Reliability | Ratio of variability between subjects or objects to the total variability of all measurements in the sample [31] | Intraclass correlation coefficient |