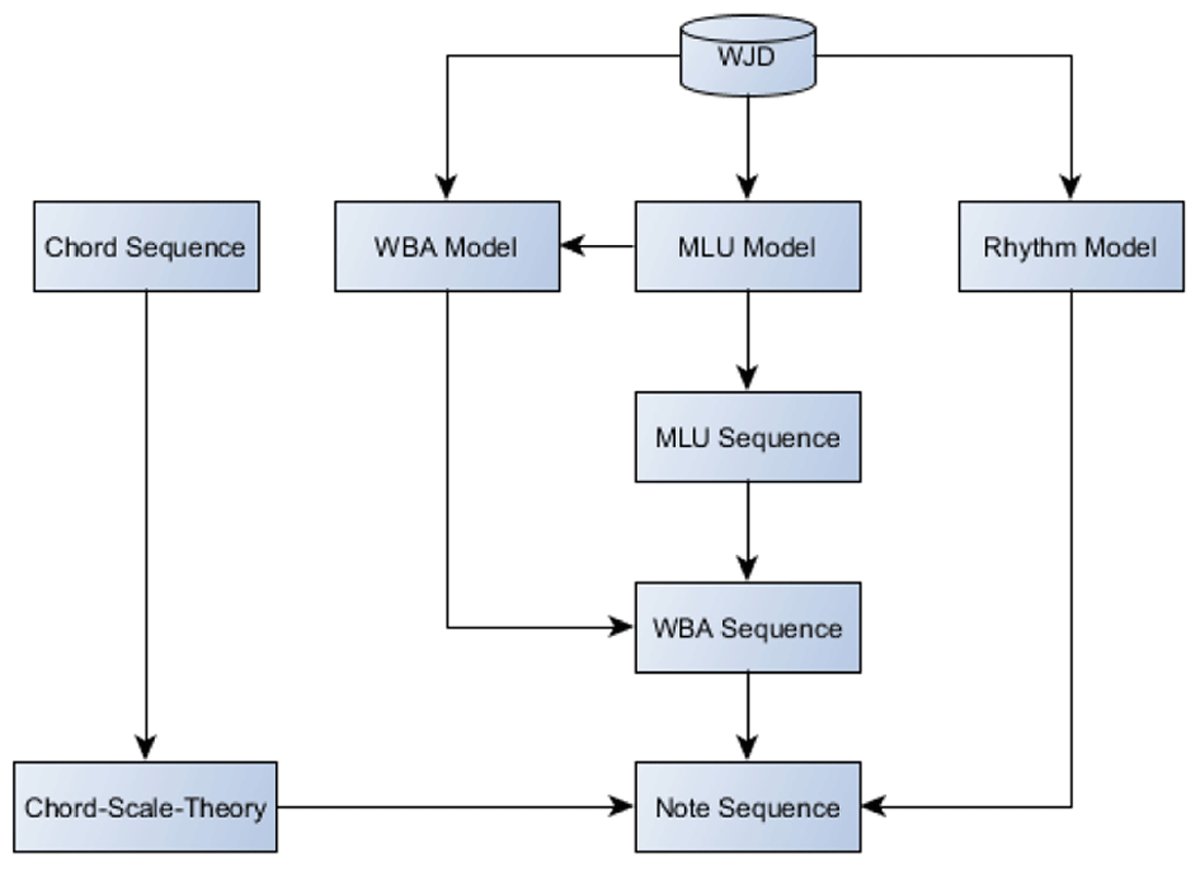
Figure 1
Overview of the generative model.
Table 1
Short overview of the Weimar Jazz Database.
| The Weimar Jazz Database | |
|---|---|
| Solos | 456 |
| Performers | 78 |
| Top Performers | Coltrane (20), Davis (19), Parker (17), Rollins (13), Liebman (11), Brecker (10), Shorter (10), S. Coleman (10) |
| Styles | Traditional (32), swing (66), bebop (56), cool (54), hardbop (76), postbop (147), free (5) |
| Instruments | ts (158), tp (101), as (80), tb (26), ss (23), other (68) |
| Time range | 1925–2009 |
| Tone events | 200,809 |
| Phrases | 11,802 |
| Mid-level units | 15,402 (containing 5.2 WBA atoms on average) |
| WBA atoms | 80,123 (average length: 2.3 intervals) |
Table 2
Overview of WBA atoms.
| Type | Subtype/Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scales | Diatonic (D) Chromatic (C) | Diatonic scale Chromatic scale |
| Approaches | F | Two intervals approaching a target pitch with a direction change (e. g., –2 +1) |
| Trills | T | Two alternating pitches |
| Arpeggios | Simple (A) Jump (J) | Sequence of thirds Sequence of intervals larger than a third |
| Repetitions | R | |
| X atoms | X Link (L) | Miscellaneous category X atoms of length 1 |
Table 3
Chord-scales used in the current model. Scale contents are given as pitch class vectors with 0 representing the root of the chord.
| Chord Type | Scales | Scale content |
|---|---|---|
| maj, maj7 | Ionian | [0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11] |
| min, min7 | Dorian | [0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10] |
| 7 | Mixolydian | [0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10] |
| Major Blues | [0, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9] | |
| Mixolydian ♯11 | [0, 2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10] | |
| Altered Scale | [0, 1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10] | |
| m7b5 | Locrian | [0, 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10] |
| Phrygian | [0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10] | |
| o, o7 | Octatonic Scale | [0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11] |
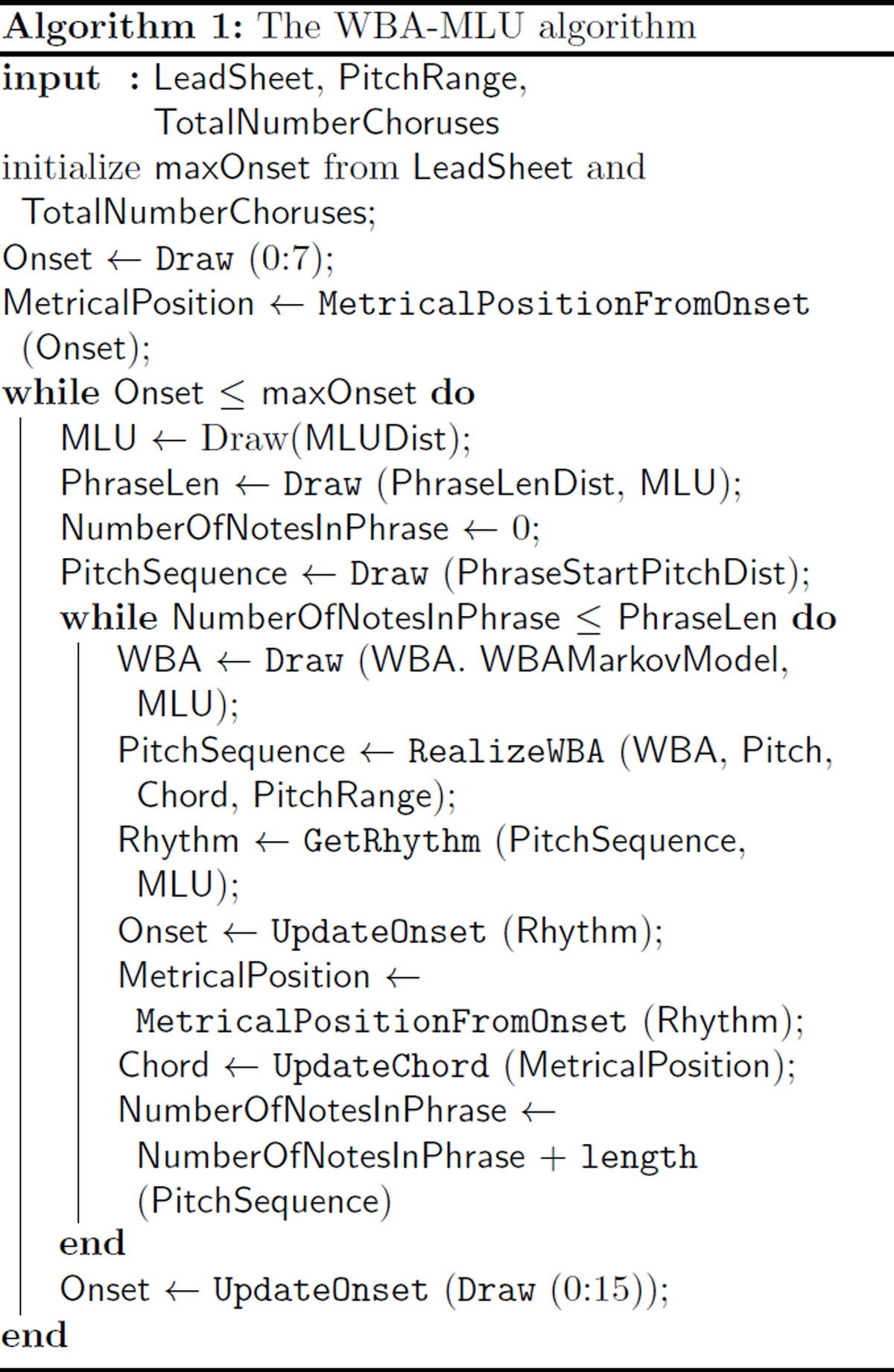
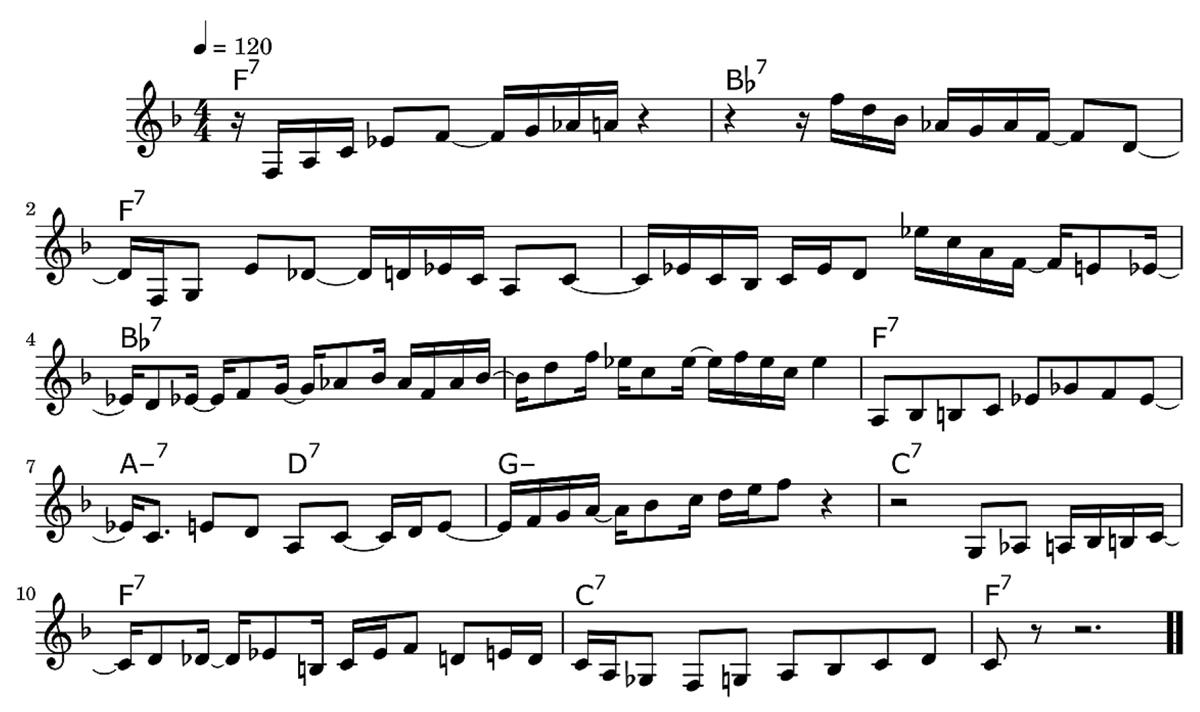
Figure 2
Example of a generated solo over an F-blues chord sequence, used in the evaluation (Algorithm-1-Original).
Table 4
Stimuli used for the evaluation. In column Performance Type specifics of the interpretation are given. Deadpan MIDI: Fully-quantized MIDI without dynamics; MIDI with microtiming: MIDI with semiautomatically added microtiming (swing); Audio: Recorded audio; Converted audio-to-MIDI: recorded audio converted to MIDI with Melodyne, keeping microtiming and dynamics; Recorded MIDI: human-played MIDI with microtiming and dynamics.
| Id | Solo ID | Generator | Performance Type | Solo Sound |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Algorithm-1-Original | WBA-MLU-Algorithm | Deadpan MIDI | tenor sax |
| 2 | Algorithm-1-Improved | WBA-MLU-Algorithm/AUT2 | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 3 | Algorithm-2-Original | WBA-MLU-Algorithm | Deadpan MIDI | tenor sax |
| 4 | WJD-Sonny Rollins | Sonny Rollins (“Vierd Blues”) | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 5 | WJD-Miles Davis | Miles Davis (“Vierd Blues”) | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 6 | WJD-Charlie Parker | Charlie Parker (“Billie’s Bounce”) | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 7 | Student-Beginner | Beginner | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 8 | Student-Intermediate | Intermediate | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 9 | Student-Advanced | Advanced | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 10 | Student-Graduated | Graduated | MIDI with microtiming | tenor sax |
| 11 | Author-Original | AUT2 | Audio | e-guitar |
| 12 | Author-MIDI | AUT2 | Converted audio-to-MIDI | tenor sax |
| 13 | Author-Original | AUT1 | Audio | piano |
| 14 | Author-MIDI | AUT1 | Recorded MIDI | tenor sax |
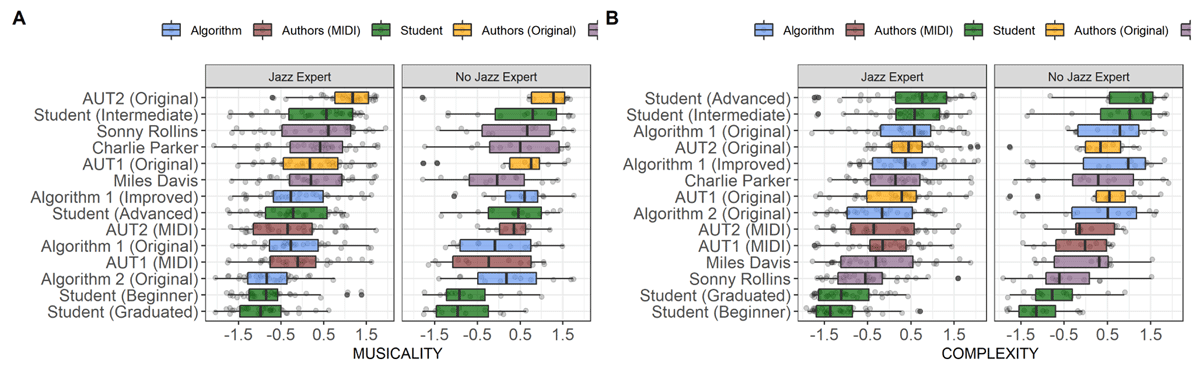
Figure 3
Boxplot of MUSICALITY (A) and COMPLEXITY (B) values for all solos, separately for rater expertise. Left panels: Jazz experts; right panels: non-experts; blue: algorithmic solos; brown: author (MIDI) solos; yellow: student solos; green: author (original) solos; violet: WJD solos.
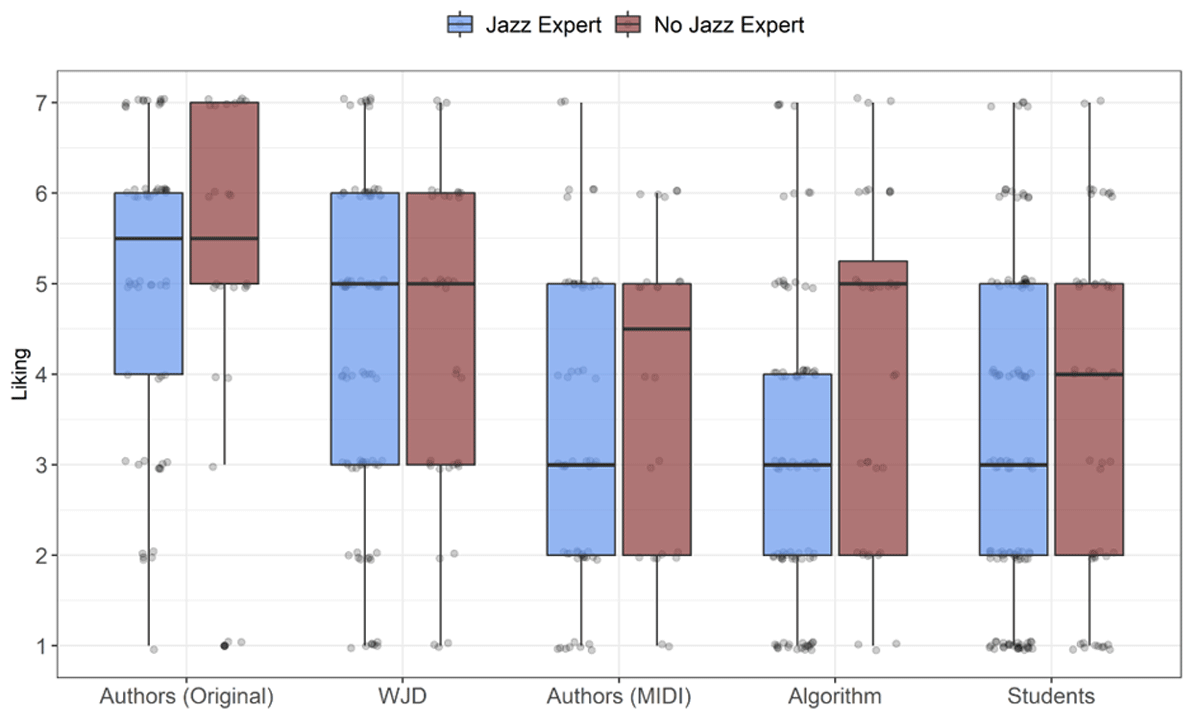
Figure 4
Boxplot of liking values for sources of solos, separately for rater expertise. Left boxes: jazz experts, right: non-experts.
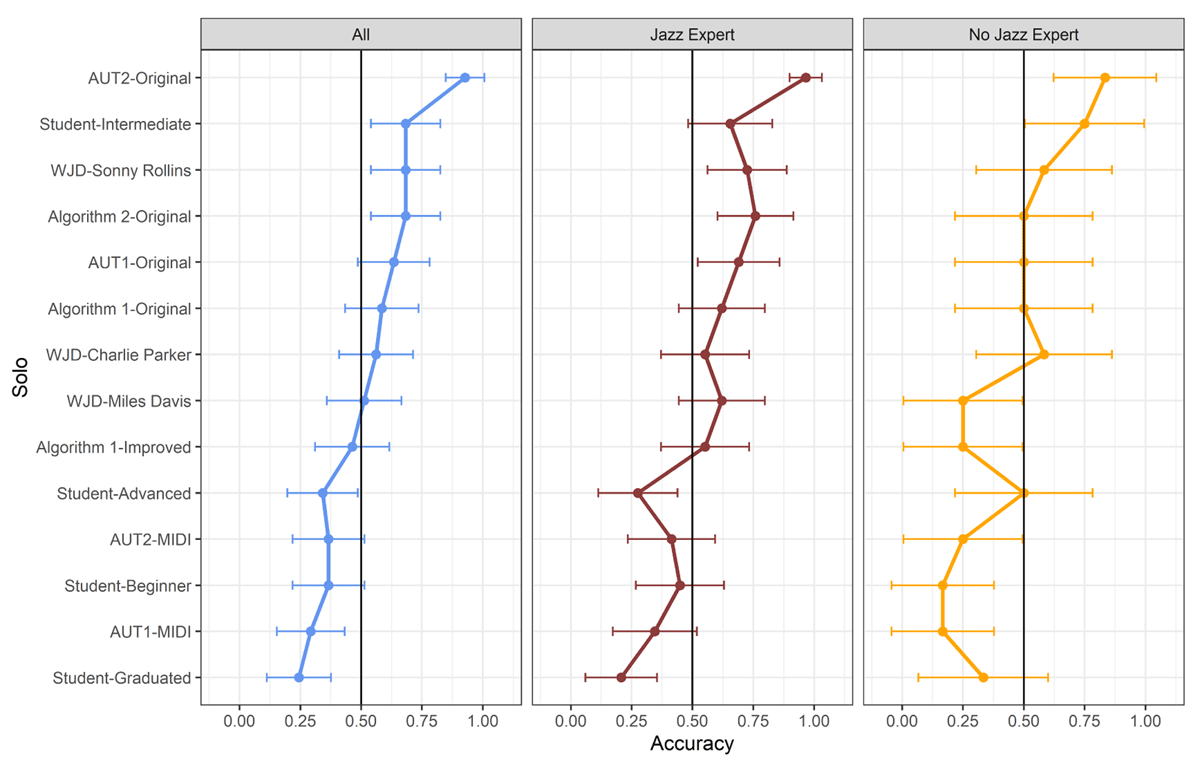
Figure 5
Recognition accuracy of all 14 stimuli by expertise level. Left: all, middle: jazz experts, right: no jazz experts. Error bars are 95% confidence interval of proportion.
