Table 1
Examples of conflict and no-conflict problems for the three reasoning tasks used in the battery: Base-rate neglect, Conjunction Fallacy, and Bat-and-ball. For convenience, the problem content is illustrated in English. The corresponding French material can be found in the Supplementary Material Section A.
| CONFLICT VERSION | NO-CONFLICT VERSION | |
|---|---|---|
| Base-rate neglect | This study contains writers and construction workers. Person ‘W’ is strong. There are 996 writers and 4 construction workers. Is Person ‘W’ more likely to be:
| This study contains writers and construction workers. Person ‘W’ is strong. There are 996 construction workers and 4 writers. Is Person ‘W’ more likely to be:
|
| Conjunction Fallacy | Kadin, 32, has previously studied astronomy and likes sci-fi. Is it most probable that the described person is:
| Kadin, 32, has previously studied astronomy and likes sci-fi. Is it most probable that the described person is:
|
| Bat-and-ball | In a park, there are 140 adults and children in total. There are 100 more adults than children. How many children are there?
| In a park, there are 140 adults and children in total. There are 100 adults. How many children are there in the park?
|
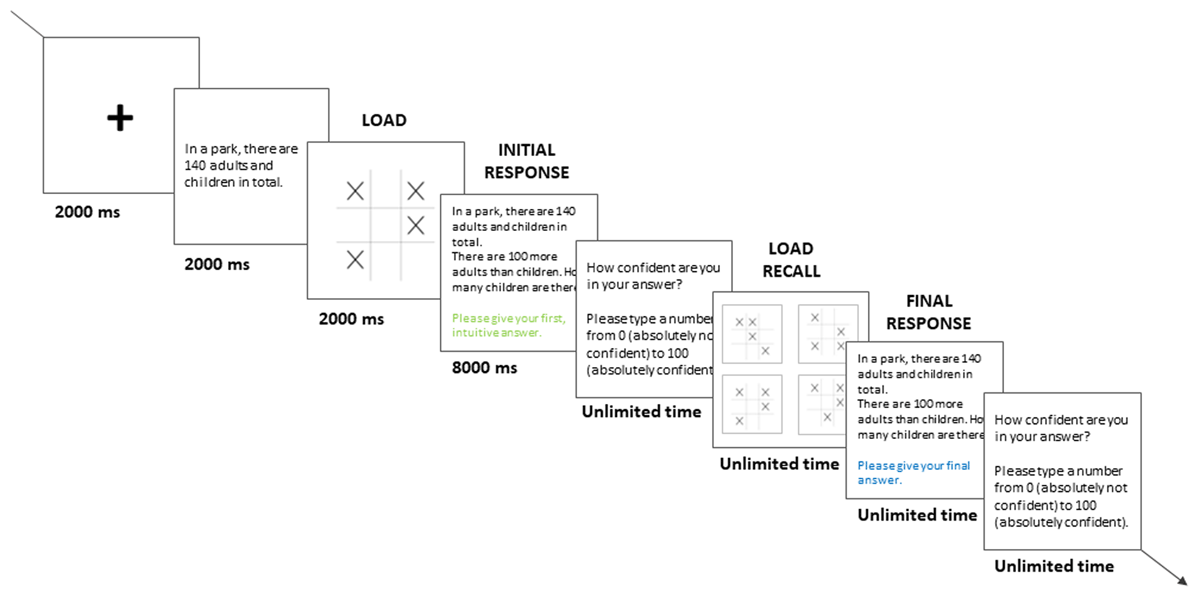
Figure 1
Time course of a typical two-response trial, with a bat-and-ball problem. For convenience, the problem content is illustrated in English.
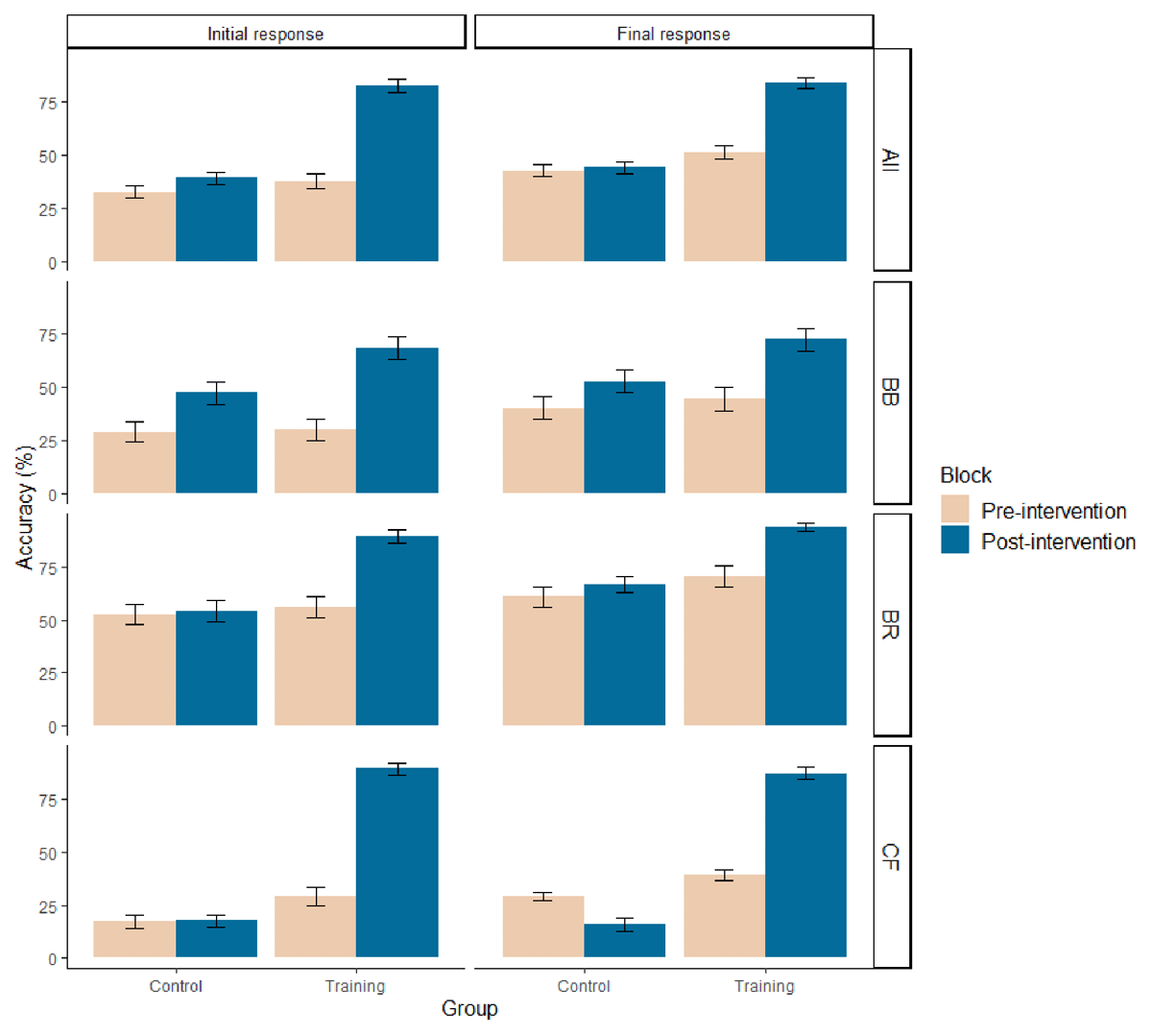
Figure 2
Mean accuracy (%) of correct initial and final responses on conflict problems for control and training groups, before and after the intervention, for each task (BB, BR, CF), and combined (All). Error bars are standard errors. BB = bat-and-ball, BR = base-rate neglect, CF = conjunction fallacy tasks, All = the composite mean across the three tasks.
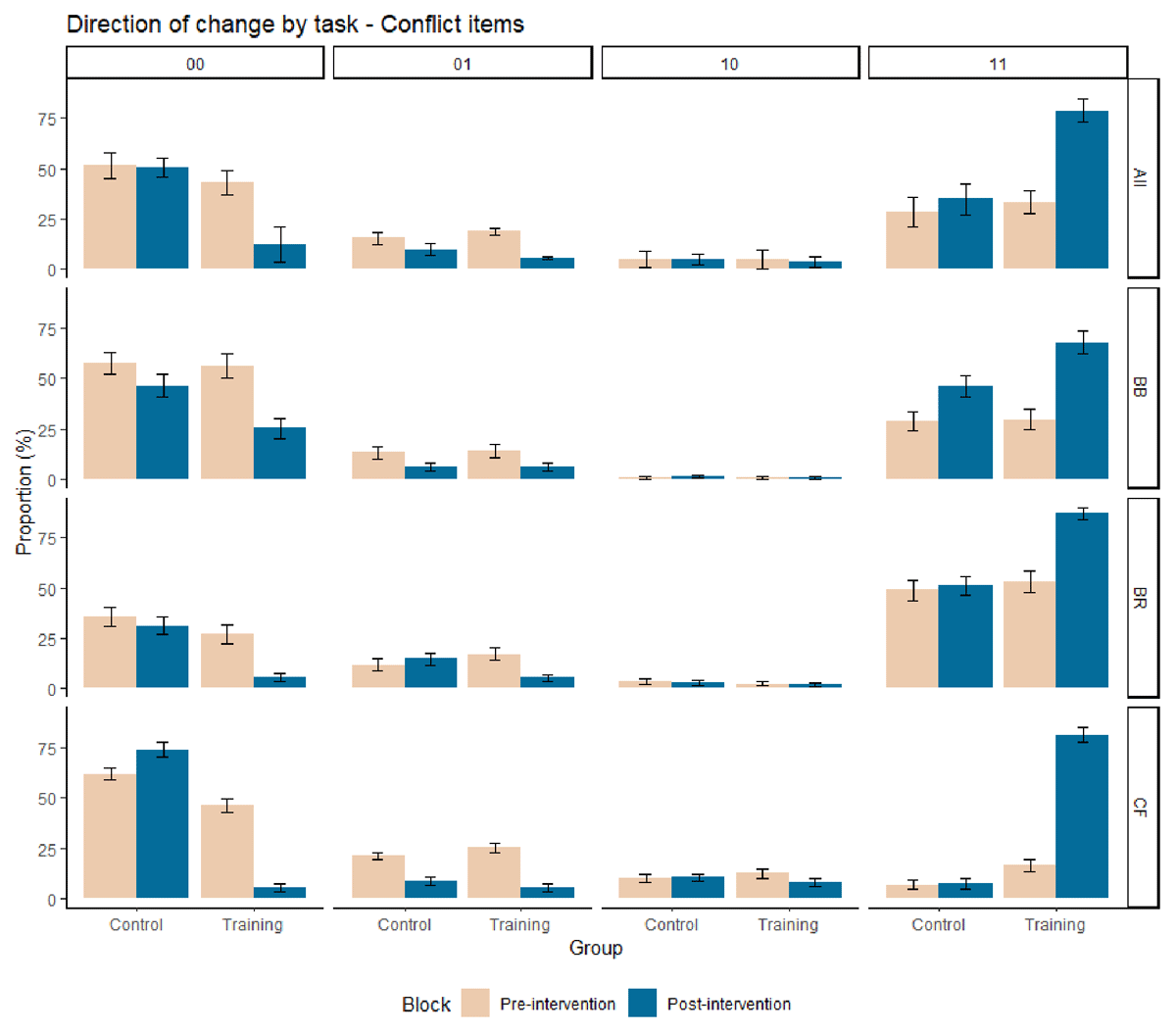
Figure 3
Proportion (%) of each direction of change (i.e., ‘00’ pattern, ‘01’ pattern, ‘10’ pattern, and ‘11’ pattern; 0 = incorrect response, 1 = correct response, first digit = initial response, second digit = final response) on conflict problems for control and training groups, before and after the intervention, for each task (BB, BR, CF), and combined (All). Error bars are standard errors. BB = bat-and-ball, BR = base-rate neglect, CF = conjunction fallacy tasks, All = the composite mean across the three tasks.
