Table 1
Descriptive Statistics of Sub- and Total Samples, Differences among Means.
| Greek sample | Italian sample | Total sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | p | M | SD | |
| Political orientation | 4.45 | 2.22 | 4.92 | 2.56 | .005 | 4.63 | 2.37 |
| Economic vulnerability | 5.06 | 1.28 | 4.46 | 1.30 | <.001 | 4.83 | 1.32 |
| Cause1. Decadence of capitalism | 3.93 | 1.13 | 4.01 | 1.01 | .358 | 3.96 | 1.08 |
| Cause2. Finance system | 5.27 | 1.03 | 5.26 | .86 | .888 | 5.27 | .96 |
| Cause3. Conspiracy | 5.32 | 1.33 | 3.56 | 1.37 | <.001 | 4.65 | 1.59 |
| Cause4. System inequality | 5.18 | 1.38 | 5.14 | 1.12 | .618 | 5.17 | 1.29 |
| Cause5. Overconsumption | 4.93 | 1.41 | 3.99 | 1.22 | <.001 | 4.57 | 1.41 |
| Cause6. Political system | 6.28 | 1.03 | 6.03 | .98 | <.001 | 6.18 | 1.02 |
| Strategy1. Conforming EU requests | 2.44 | 1.10 | 3.44 | .98 | <.001 | 2.82 | 1.16 |
| Strategy2. Public sector rationalization | 5.65 | 1.23 | 5.21 | 1.04 | <.001 | 5.49 | 1.18 |
| Strategy3. EU Exit | 3.68 | 1.66 | 2.70 | 1.26 | <.001 | 3.30 | 1.59 |
| Activity1. Illegal activism | 2.28 | 1.25 | 1.46 | .86 | <.001 | 1.97 | 1.19 |
| Activity2. Legal activism | 4.07 | 1.42 | 3.16 | 1.51 | <.001 | 3.72 | 1.52 |
| Activity3. Economic resistance | 3.40 | 1.45 | 2.77 | 1.42 | <.001 | 3.16 | 1.47 |
| Activity4. Protectionism | 5.28 | 1.78 | 3.37 | 1.95 | <.001 | 4.55 | 2.07 |
[i] Note. Political orientation is on a 10-point scale, all the other variables on 7-point scales.
Table 2
Correlations among Key Variables.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Political ideology | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2. Economic vulnerability | –.08** | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 3. Cause1. Depletion of resources | .17*** | .03 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 4. Cause2. Finance system | –.09** | .05 | .45*** | 1 | |||||||||||
| 5. Cause3. Conspiracy Theories | –.07* | .19*** | .36*** | .30*** | 1 | ||||||||||
| 6. Cause4. Inequality system | –.27*** | .07* | .31*** | .40*** | .32*** | 1 | |||||||||
| 7. Cause5. Overconsumption | .06 | .07* | .38*** | .36*** | .33*** | .25*** | 1 | ||||||||
| 8. Cause6. Political system | .07* | .13*** | .30*** | .38*** | .31*** | .29*** | .29*** | 1 | |||||||
| 9. Strategy1. Conforming EU requests | .21*** | –.15*** | .10** | –.06 | –.34*** | –.19*** | –.02 | –.12*** | 1 | ||||||
| 10. Strategy2. Public sector rationalization | .10** | .03 | .10** | .26*** | .13*** | .01 | .24*** | .23*** | .03 | 1 | |||||
| 11. Strategy3. EU exit | –.14*** | .20*** | .07* | .01 | .36*** | .21*** | .08* | .07* | –.27*** | –.12*** | 1 | ||||
| 12. Activity1. Illegal activism | –.18*** | .26** | .01 | .01 | .33*** | .11** | .11** | .02 | –.21*** | –.13*** | .43*** | 1 | |||
| 13. Activity2. Legal activism | –.39*** | .19*** | –.01 | .13*** | .31*** | .24*** | .08* | .08* | –.26*** | .04 | .33*** | .42*** | 1 | ||
| 14. Activity3. Economic resistance | .09** | .25*** | .11** | .04 | .24*** | –.01 | .16*** | .09** | .01 | .04 | .29*** | .40*** | .22*** | 1 | |
| 15. Activity4. Protectionism | .07* | .20*** | .15*** | .06 | .36*** | .03 | .21*** | .23*** | –.20*** | .25*** | .27*** | .21*** | .31*** | .23*** | 1 |
[i] * p ≤ .05. ** p < .01. *** p ≤ .001.
Table 3
Predictors of the Causes of the Crisis: Regression Analyses.
| Causes of the crisis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Resources depletion | Finance system | Obscure power conspiracy | Inequality system | Over-consumption | Political system | |
| Β | Β | Β | Β | Β | Β | ||
| 1 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | –.03 | –.03 | .50*** | –.03 | .31*** | .12*** |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | –.16*** | –.08* | –.02 | –.05 | –.02 | –.08* | |
| Age | .11*** | .19*** | .13*** | .18*** | .07* | .07* | |
| R2 | .04*** | .04*** | .30*** | .03*** | .11*** | .02*** | |
| 2 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | –.051 | –.07 | .46*** | –.07* | .29*** | .08* |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | –.17*** | –.06 | –.01 | –.02 | –.02 | –.07* | |
| Age | .17*** | .21*** | .17*** | .18*** | .10** | .12** | |
| Political ideology (linear effect) | .22** | –.06 | –.01 | –.27*** | .14*** | .10 | |
| Political ideology (quadratic effect) | –.06 | .01 | .03 | .06° | –.11** | .02 | |
| Economic vulnerability | .08* | .10** | .13*** | .11** | .03 | .14*** | |
| R2 | .08*** | .05*** | .31*** | .11*** | .13*** | .05*** | |
| Δ R2 | .04*** | .01*** | .01*** | .08*** | .02*** | .03*** | |
[i] ° p < .07. * p ≤ .05. ** p < .01. *** p ≤ .001.
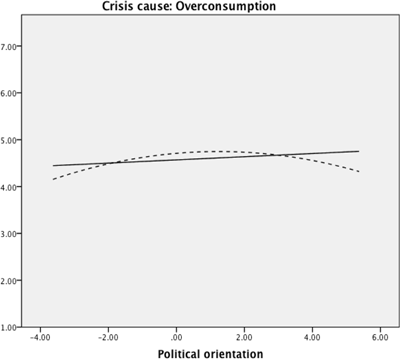
Figure 1
Graphic representation of the linear and quadratic (dashed lines) effects of political ideology on the crisis cause ‘Overconsumption’.
Note. Political ideology was measured on a 10-point scale, where 1 = extreme left and 10 = extreme right; the quadratic term was mean-centered. The cause was measured on 7-point scale.
Table 4
Predictors of the Strategies of the Crisis Management: Regression Analyses.
| Strategies of crisis management | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Conforming EU requests | Public sector rationalization | EU Exit | |
| Β | Β | Β | ||
| 1 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | –.40*** | .13*** | .30*** |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | –.04 | .01 | .05 | |
| Age | –.04 | .19*** | –.02 | |
| R2 | .18*** | .07*** | .09*** | |
| 2 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | –.39*** | .10** | .26*** |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | –.05 | .01 | .07* | |
| Age | –.02 | .24*** | –.01 | |
| Political ideology (linear effect) | .23*** | .18*** | –.17*** | |
| Political ideology (quadratic effect) | –.19*** | –.10** | .16*** | |
| Economic vulnerability | –.06* | .07* | .15*** | |
| R2 | .24*** | .10*** | .15*** | |
| Δ R2 | .06*** | .03*** | .06*** | |
[i] * p ≤ .05. ** p < .01. *** p < .001.
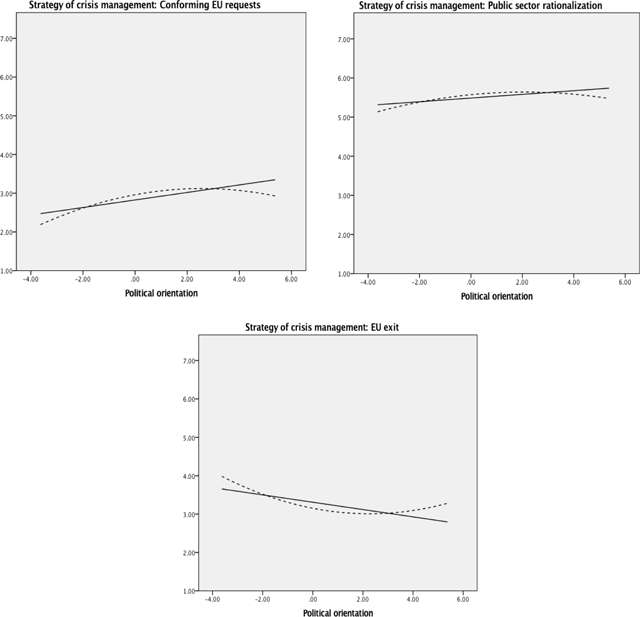
Figure 2
Graphic representations of the linear and quadratic (dashed lines) effects of political ideology on the strategies of crisis management ‘Conforming to EU requests’ (on top left), ‘Public sector rationalization’ (on top right), and ‘European Union Exit’ (at the bottom).
Note. Political ideology was measured on a 10-point scale, where 1 = extreme left and 10 = extreme right; the quadratic term was mean-centered. Causes were measured on 7-point scale.
Table 5
Predictors of the Political Participation Activities: Regression Analyses.
| Political participation activities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Illegal activism | Legal activism | Economic resistance | Protectionism | |
| Β | Β | Β | Β | ||
| 1 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | .35*** | .28*** | .24*** | .46*** |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | .14*** | –.07* | .07* | –.08* | |
| Age | –.15*** | .10** | –.17*** | .02 | |
| R2 | .15*** | .10*** | .07*** | .21*** | |
| 2 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | .30*** | .21*** | .19*** | .43*** |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | .17*** | –.03 | .08* | –.08* | |
| Age | –.14*** | .09** | –.10** | .08* | |
| Political ideology (linear effect) | –.24*** | –.37*** | –.09** | .14*** | |
| Political ideology (quadratic effect) | .19*** | .08* | .04 | .01 | |
| Economic vulnerability | .17*** | .14*** | .21*** | .13*** | |
| R2 | .24*** | .24*** | .12*** | .24*** | |
| Δ R2 | .09*** | .14*** | .05*** | .03* | |
| 3 | Country (0 = Italy; 1 = Greece) | .19*** | .11* | .09* | .32*** |
| Gender (0 = female; 1 = male) | .16*** | –.06° | .08* | –.07* | |
| Age | –.14*** | .06 | –.12*** | .02 | |
| Political ideology (linear effect) | –.20*** | –.30*** | –.06 | .09* | |
| Political ideology (quadratic effect) | .15*** | .04 | .04 | .01 | |
| Economic vulnerability | .13*** | .09** | .16*** | .07* | |
| Resources depletion | .01 | –.07° | .02 | .10* | |
| Finance system | .01 | .04 | .01 | –.07* | |
| Obscure power conspiracy | .16*** | .12** | .15*** | .06 | |
| Inequality system | –.02 | .08* | –.09* | –.05 | |
| Overconsumption | .04 | –.02 | .07 | –.02 | |
| Political system | –.04 | –.01 | .02 | .11** | |
| Conforming EU request | .05 | –.02 | .16*** | –.02 | |
| Public section rationalization | –.12*** | .05 | .01 | .18*** | |
| EU exit | .25*** | .19*** | .23*** | .17*** | |
| R2 | .34*** | .30*** | .21*** | .32*** | |
| ΔR2 | .10*** | .06*** | .09*** | .08*** | |
[i] ° p < .07. * p ≤ .05. ** p < .01. *** p < .001.
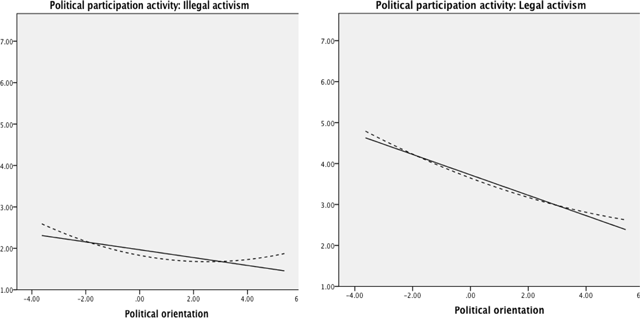
Figure 3
Graphic representations of the linear and quadratic effects (dashed lines) of political ideology on the political participation activity ‘Illegal activism’ (on the left side) and ‘Legal activism’ (on the right side).
Note. Political ideology was measured on a 10-point scale, where 1 = extreme left and 10 = extreme right; the quadratic term was mean-centered. Causes were measured on 7-point scale.
