Table 1
Effects of interaction type, apology type, and measurement time on self-reported trust.
| F | df | p | f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within-participant effects | ||||
| Measurement time | 51.41 | 1.92, 507.87 | <0.001 | 0.44 |
| Measurement time × Education track | 2.30 | 1.92, 507.87 | 0.103 | 0.09 |
| Measurement time × Interaction type | 10.50 | 1.92, 507.87 | <0.001 | 0.20 |
| Measurement time × Apology type | 33.06 | 3.85, 507.87 | <0.001 | 0.50 |
| Measurement time × Interaction type × Apology type | 1.58 | 3.85, 507.87 | 0.181 | 0.11 |
| Between-participant effects | ||||
| Education track (covariate) | 8.42 | 1, 264 | 0.004 | 0.18 |
| Interaction type | 8.95 | 1, 264 | 0.003 | 0.18 |
| Apology type | 6.81 | 2, 264 | <0.001 | 0.23 |
| Interaction type × Apology type | 4.55 | 2, 264 | 0.011 | 0.18 |
Table 2
Apology contrast for overall trust and trust after manipulation of response time (third time point).
| Apology type | Univariate effects | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No apology | Apology | No apology vs. Apology | ||||
| M (SD) | M (SD) | F | df | p | f | |
| Overall trust | ||||||
| Interpersonal interaction | 1.96 (0.54) | 2.29 (0.59) | 11.85 | 1, 264 | 0.001 | 0.21 |
| Intergroup interaction | 1.91 (0.52) | 2.05 (0.55) | 1.78 | 1, 264 | 0.183 | 0.08 |
| Total | 1.94 (0.53) | 2.17 (0.57) | 10.94 | 1, 264 | 0.001 | 0.20 |
| Trust after manipulation (T3) | ||||||
| Interpersonal interaction | 1.49 (0.56) | 2.53 (0.84) | 62.15 | 1, 264 | <0.001 | 0.53 |
| Intergroup interaction | 1.41 (0.61) | 2.01 (0.76) | 17.88 | 1, 264 | <0.001 | 0.26 |
| Total | 1.45 (0.58) | 2.26 (0.84) | 71.63 | 1, 264 | <0.001 | 0.58 |
Table 3
Content contrasts for overall trust and trust after manipulation of response time (third time point).
| Apology type | Univariate effects | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No apology | Primary | Secondary | No apology vs. Primary | No apology vs. Secondary | Primary vs. Secondary | |||||||
| M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | F | p | f | F | p | f | F | p | f | |
| Overall trust | ||||||||||||
| Interpersonal interaction | 1.96 (0.54) | 2.25 (0.60) | 2.34 (0.57) | 6.64 | 0.011 | 0.16 | 11.23 | 0.001 | 0.21 | 0.52 | 0.473 | 0.04 |
| Intergroup interaction | 1.91 (0.52) | 2.23 (0.57) | 1.88 (0.46) | 6.96 | 0.009 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.770 | 0.02 | 9.45 | 0.002 | 0.19 |
| Total | 1.94 (0.53) | 2.24 (0.58) | 2.11 (0.56) | 13.59 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 3.83 | 0.037 | 0.13 | 2.71 | 0.101 | 0.10 |
| After manipulation (T3) | ||||||||||||
| Interpersonal interaction | 1.49 (0.56) | 2.39 (0.88) | 2.66 (0.80) | 34.56 | <0.001 | 0.37 | 59.20 | <0.001 | 0.51 | 2.85 | 0.092 | 0.10 |
| Intergroup interaction | 1.41 (0.62) | 2.13 (0.82) | 1.88 (0.70) | 19.70 | <0.001 | 0.27 | 8.98 | 0.003 | 0.18 | 2.29 | 0.131 | 0.09 |
| Total | 1.45 (0.58) | 2.25 (0.85) | 2.27 (0.84) | 52.96 | <0.001 | 0.48 | 55.91 | <0.001 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.888 | 0.01 |
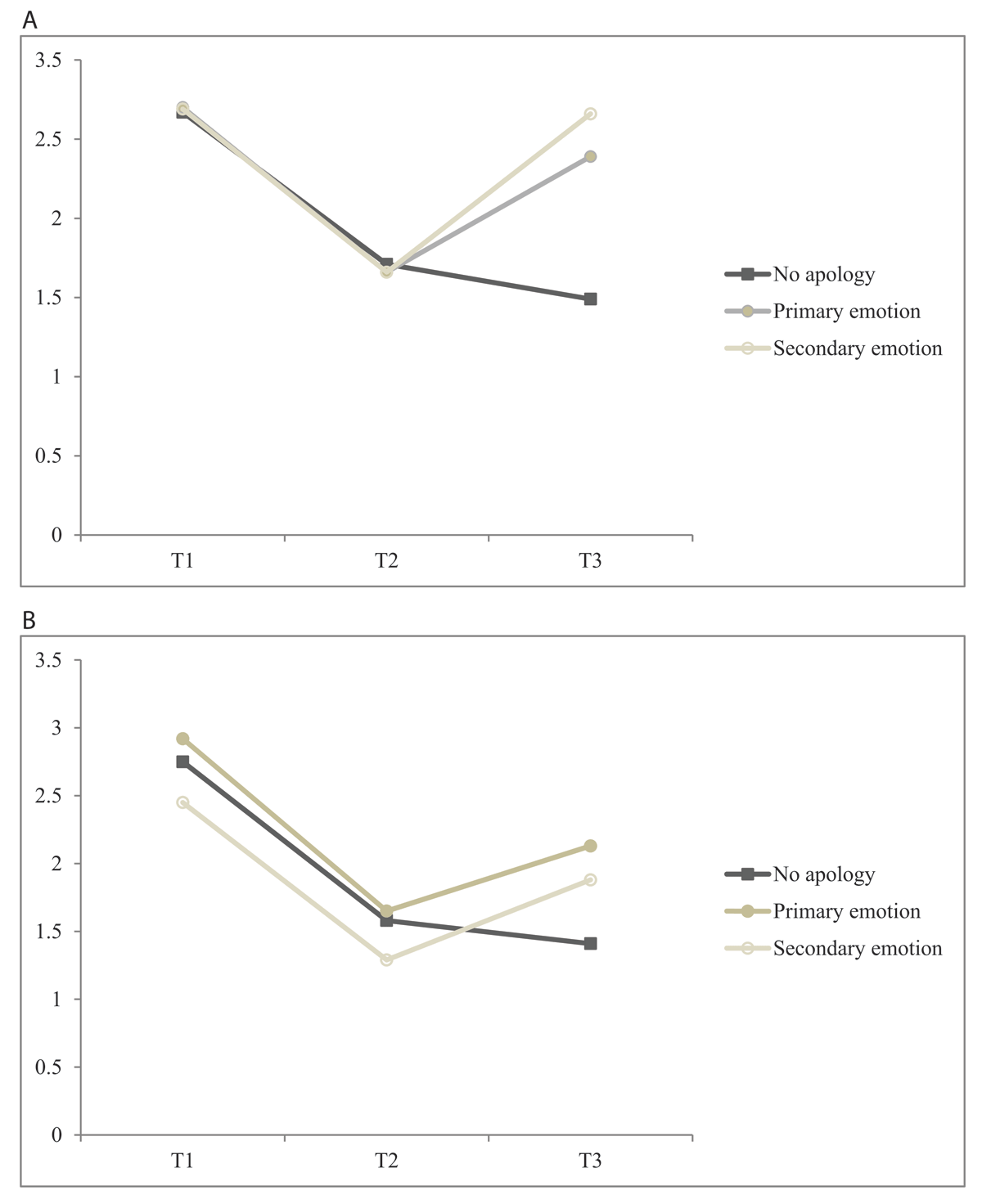
Figure 1
(a) Self-reported trust at T1, T2, and T3 by apology type in the interpersonal condition. (b) Self-reported trust at T1, T2, and T3 by apology type in the intergroup condition.
Table 4
Trusting behavior as a function of interaction type and apology type.
| Interaction type | Apology type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No apology | Primary emotions | Secondary emotions | Total | |
| M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | |
| Interpersonal | 1.87 (2.43) | 3.43 (2.54) | 3.55 (2.65) | 2.94 (2.63) |
| Intergroup | 1.18 (1.97) | 3.15 (1.49) | 2.21 (1.79) | 2.24 (1.91) |
| Total | 1.56 (2.25) | 3.29 (2.06) | 2.88 (2.34) | 2.60 (2.33) |
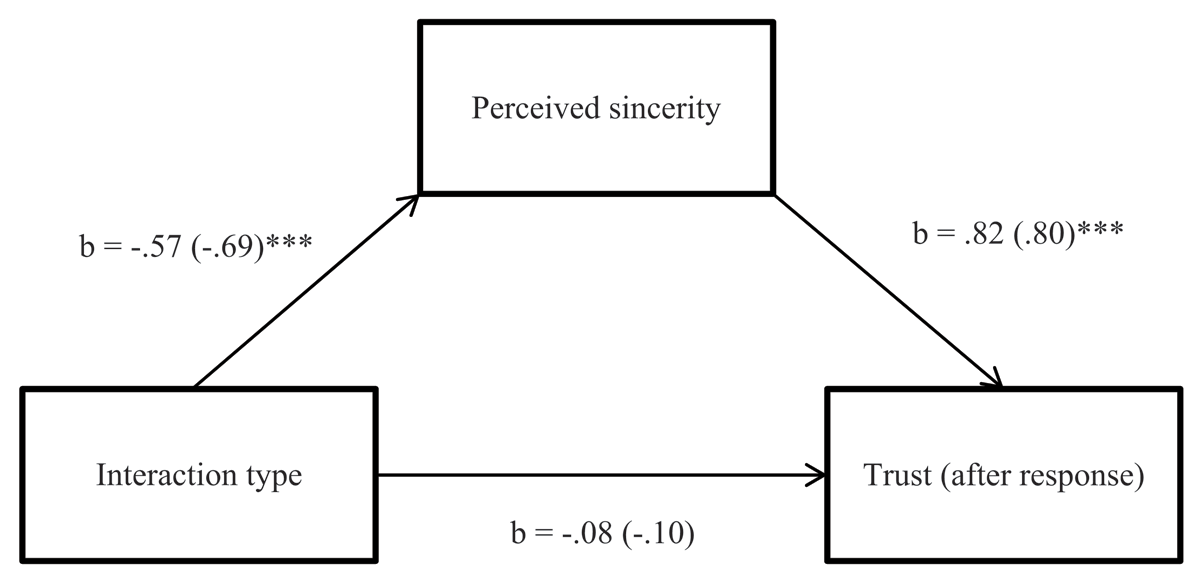
Figure 2
Indirect effect of interaction type on trust, mediated by perceived sincerity of apology. Note: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
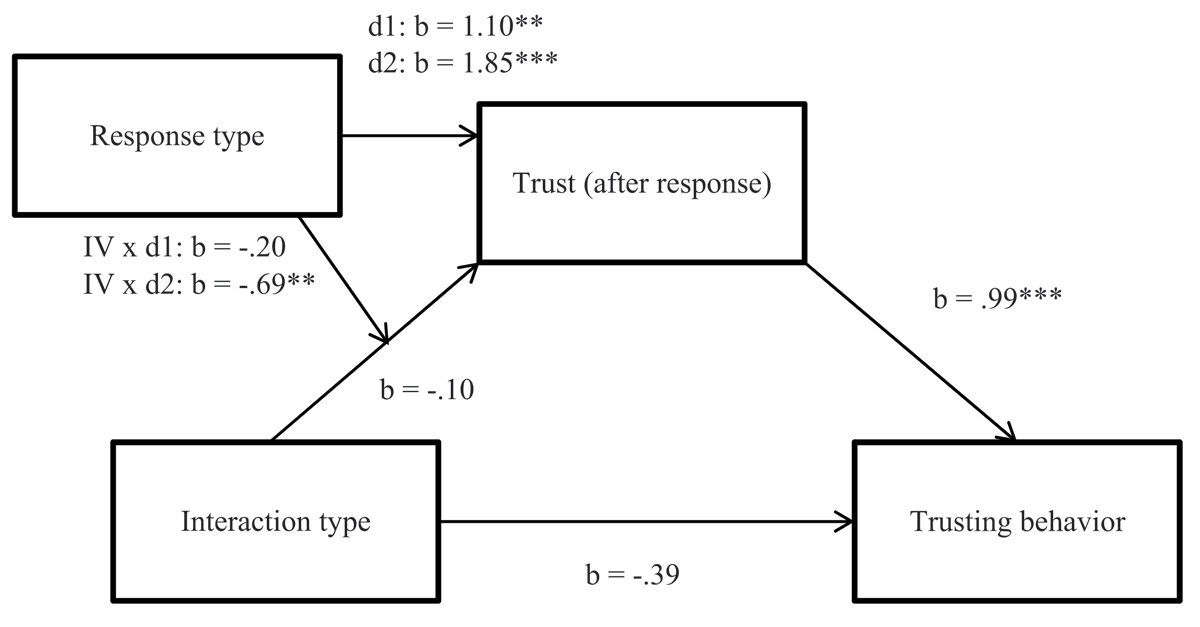
Figure 3
Indirect effect of interaction type on trusting behavior, mediated by trust and moderated by response type. Note: d1 = no response vs. apology with primary emotions; d2 = no response vs. apology with secondary emotions; * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001.
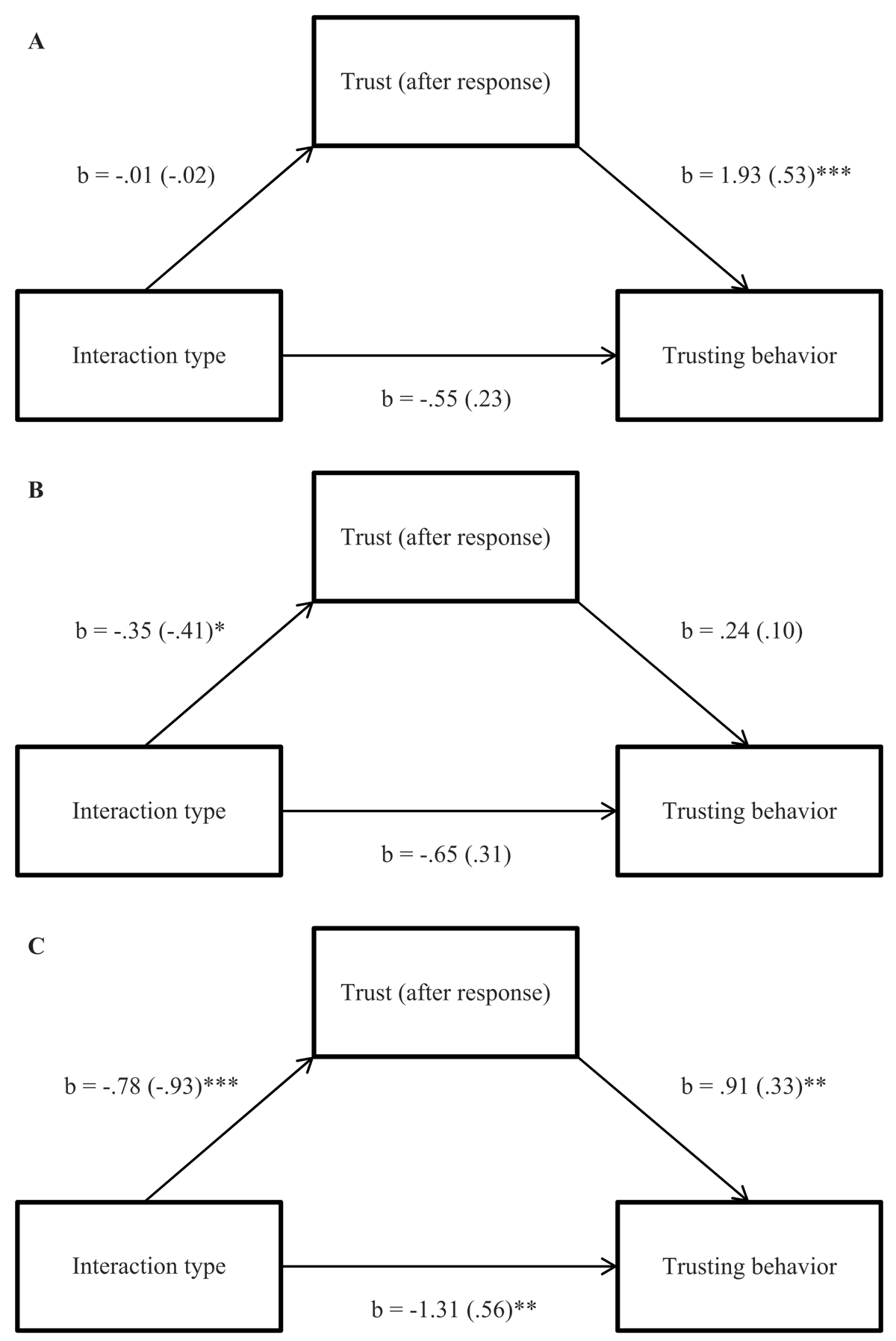
Figure 4
Indirect effect of interaction type on trusting behavior, mediated by trust; in the no apology condition (Panel A), apology-with-primary-emotions condition (Panel B), and apology-with-secondary-emotions condition (Panel C). Note: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
