
Figure 1
Systematic Literature Research.
Table 1
Risk adjustment methods based on pharmaceutical information.
| Method | Cell Approach vs. Regression Model | Risk Factors used | Development Objective | Developing Institution | Developed by (primary author) | Calculation | All-encounter Model | No. of Groups | Comorbidities included | Grouping | Clinical meaningful/interpretable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDS | Aggregate model (Regression) | Age, Gender, Drug prescriptions | Measurement of chronic disease status | Center of Health Studies, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Seattle, WA, USA | Van Korff et al. [71] Clark et al. [70] | Prospective | No | 28 | Additive weights | Incomplete | Yes |
| Medicaid Rx | Aggregate model (Regression) | Age, Gender, Drug prescriptions for certain conditions | Development of risk-adjusted reimbursement/compensation systems for Medicaid | University of California, San Diego, CA, USA | Gilmer, Kronick, Dreifuß [22] | Prospective | No | 45/48 | Considered, cost weights are additive | Incomplete | Mostly yes |
| RxGroups | Aggregate model (Regression) | Age, Gender, Drug prescriptions | Risk-adjusted reimbursement/compensation systems for Medicare, Rrisk assessment, Efficiency audit of care providers, Calculation of premiums | Boston University, DxCG Inc., USA | Ash, Ellis, Pope et al.[65727374] | Prospective | No | 155 (aggregated to 17 ARCs) | Hierarchical, additive weights for drugs of different hierarchies | Complete | |
| RxRisk | Aggregate model (Regression) | Age, Gender, Drug prescriptions for certain conditions | Risk assessment, Evaluation of severity | Center of Health Studies, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Seattle, WA, USA | Fishman [7576]; von Korff [7071] | Prospective | No | 60 | Additive weights for drugs of different categories | Complete | |
| PCG | Full hierarchy as cell approach | Regularly outpatient prescriptions of common drugs for chronic conditions | Risk structure compensation system for statutory health insurance in the Netherlands | Erasmus University, Rotterdam, The Netherlands | Lamers & van Kliet [7778] | Prospective | No | 13/23 | Original: only the most cost-intense PCG considered; Since 2008: Individual weights are additive | Incomplete | Yes |
| PCG+DCG | Outpatient and inpatient prescriptions | Yes | 12 | ||||||||
| DxCG Rx Groups | Aggregate model (Regression) | Age, Gender, Drug prescriptions, Diagnoses | Prediction of future health costs, Development of a comprehensive Rx classification | DxCG, Inc., MedStat Market Scan | Zhao et al.[6679] | Prospective | Yes | 127(current expansion: 118) | Diagnoses of diverse categories are taken into account | Complete | Mostly yes |
Table 2
Risk adjustment methods based on diagnostic information.
| Method | Cell Approach vs. Regression Model | Risk Factors used | Development Objective | Developing Institution | Developed by (primary author) | Calculation | All-encounter Model | No. of Groups | Comorbidities included | Grouping | Clinical meaningful/interpretable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACG/ADG/ADG-PM | ACGs: cells approach, ADG-Hosdom: aggregate model (Regression) | Diagnoses, Age, Gender, Birthweight, Delivery | Evaluation of severity, Reimbursement/compensation of institutions | Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA | Starfield [83]; Weiner [4445]; Anderson | Concurrent | ACG: yes ADG: no | ACG: 93 ACG-PM: 236 | ACGs are based on combination of diseases | ACG/-PM: complete ADG: incomplete | ACG: no |
| HCC | Aggregate model (Regression) | Diagnoses, Age, Gender | Risk-adjusted reimbursement/compensation systems, Rrisk assessment | Boston University, USA | Ash, Ellis et al. | Prospective | Yes | 184 | Hierarchical, additive weights for non-related diseases | Complete | Yes |
| Rx HCC | Aggregate model (Regression) | Inpatient + outpatient diagnoses, Drug prescriptions | Calculation of individual risk scores | Medicare Part D, USA | Prospective | Yes | 197 | Hierarchical, additive weights | Complete | ||
| CMS-HCC | Aggregate model (Regression) | Inpatient + outpatient diagnoses | Calculation of individual risk scores | Medicare Part C, USA | Pope et al. [74] | Prospective | Yes | 70 | Hierarchical, additive weights | Incomplete | |
| DCG/DCG-HCC/PIP-DCG | DCG: complete hierarchy as cell approach, DCG-HCC: Aggregate model (Regression) | DCG/HCC: Inpatient or outpatient and inpatient diagnoses | Risk-adjusted reimbursement/compensation systems for Medicare, Risk assessment, Efficiency audit of care providers, Calculation of premiums | Boston University, DxCG Inc., USA | Ash, Ellis, Pope et al. [65727374] | Prospective | Original-DCG: no DCH-HCC: yes PIP-DCG: no | DCG: 13 DCG-HCC: 132 PIP-DCG: 10 | DCG: individual is assigned to most costly group HCC: hierarchical, additive cost weights | Complete | DCG: no |
| PCG+DCG | Full hierarchy as cell approach | Inpatient + outpatient diagnoses, Drug prescriptions, Age, Gender, Procedures, Region, Reason for insurance | Risk structure compensation system for statutory health insurance in the Netherlands | Erasmus University, Rotterdam, The Netherlands | Lamers & van Kliet [7778] | Prospective | Yes | 12 | Original: only the most cost-intense PCG considered; Since 2008: Individual weights of diseases are additive | Incomplete | Yes |
| CD-RISC | Aggregate model (Regression) | Inpatient + outpatient diagnoses, Age, Gender, Medicaid- eligibility, degree of disability | Reimbursement/compensation, Development of risk-adjusted equalization payments, | Rand Cooperation, Santa Monica, CA, USA | Carter; Bell; Dubois [8485]; Goldberg; Keeler; McAlearny; Post; Rumpel | Prospective | Yes | 215 | Hierarchical, Individual can be assigned to several hierarchies | Complete | |
| CDPS- Rx | Aggregate model (Regression) | Inpatient + outpatient diagnoses for chronic diseases and disabilities, Age, Gender, | Reimbursement/compensation | University of California, San Diego, CA, USA | Gilmer, Kronick, Dreifuß, Lee [8687] | Prospective | Yes | 19 | Considered, Individual can be assigned to more than one group | Complete | |
| CRG/CRxG | Aggregate model (Regression) | Inpatient + outpatient diagnoses, Age, Gender, Procedures, Drug prescriptions | Development of risk-adjusted equalization payments, Monitoring | 3M Health Information Systems, Wallingford, CT, USA; US Department of Commerce | Goldfield; Averill et al. | Prospective | Yes | 1081 | CRGs are based on combination of diseases, Individual is assigned to one of 9 health states | Complete | |
| AAPCC | Cell approach | Age, Gender, Medicaid status, Nursing home status, Employment status + coverage | Compensation of Medicare + choice organizations | HCFA | Prospective | No | 122 | Not taken into account | Incomplete | No | |
| ERG | Aggregate model (Regression) | Diagnoses, Age, Gender, Procedures, Drug prescriptions | Risk assessment, Efficiency audit of care providers, Calculation of premiums | Symmetry Health Data Systems, Inc., Phoenix, AZ, USA | Dunn et al. | Prospective | Yes | 120 | Individual can be assigned to more than one group | Complete | |
| HMG | Aggregate model (Regression) | Age, Gender, Disability pensioner, Inpatient and outpatient diagnoses (rarely prescription) | Risk structure compensation system for statutory health insurance in Germany | German healthcare act (GKV-WSG) | German healthcare act (GKV-WSG) | Prospective | Yes | 178 | Individual can be assigned to more than one HMG | Incomplete | |
| SQLape | Predominant diagnoses and procedures: Cell approach; Other diagnoses: Regression | Age, Gender, Inpatient Operations and diagnoses | Prognosis of hospital costs, Development of hospital quality indicators | University of Lausanne, CH | Yves Eggli [88] | Prospective | No | 360, Mapping into 17 groups available | Considered, except for predominant diagnoses and operations | Complete | Yes, rough classification |
| GRAM | Aggregate model (Regression) | Diagnoses, Age, Gender | Prognosis of costs for Managed-Care beneficiaries | Kaiser Permanente, USA | Hornbrook, Fishman [7589] | Prospective | Yes | 118/93 | Not considered, only highest-ranking diagnosis | Complete |
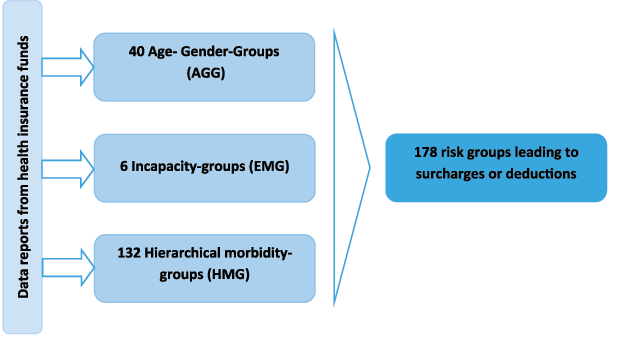
Figure 2
German morbidity-oriented risk structure compensation scheme [104].
