Table 1
Study characteristics, overall and by sex.
| CHARACTERISTIC | FEMALE N = 1,531 | MALE N = 1,609 | TOTAL N = 3140 | P-VALUE‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 49·9 (7·4) | 52·3 (8·1) | 51·1 (7·8) | <0·001 |
| Age | <0·001 | |||
| 40–54 years | 1,137 (71·4%) | 996 (57·7%) | 2,133 (64·4%) | |
| 55–69 years | 394 (28·6%) | 613 (42·3%) | 1,007 (35·6%) | |
| Education | <0·001 | |||
| No schooling | 820 (62·4%) | 678 (48·4%) | 1,498 (55·3%) | |
| Primary | 542 (31·8%) | 560 (33·9%) | 1,102 (32·9%) | |
| Secondary | 109 (4·4%) | 249 (13·0%) | 358 (8·8%) | |
| College/Higher | 45 (1·4%) | 122 (4·7%) | 167 (3·1%) | |
| Residence | 0·3 | |||
| Rural | 830 (81·5%) | 857 (80·1%) | 1,687 (80·8%) | |
| Urban | 701 (18·5%) | 752 (19·9%) | 1,453 (19·2%) | |
| Division | 0·7 | |||
| Dhaka | 205 (6·6%) | 223 (6·6%) | 428 (6·6%) | |
| Barishal | 156 (19·4%) | 195 (18·8%) | 351 (19·1%) | |
| Chattogram | 150 (19·2%) | 167 (21·9%) | 317 (20·6%) | |
| Khulna | 211 (12·0%) | 216 (12·2%) | 427 (12·1%) | |
| Mymensingh | 226 (11·4%) | 220 (10·2%) | 446 (10·8%) | |
| Rajshahi | 218 (15·1%) | 212 (13·8%) | 430 (14·5%) | |
| Rangpur | 203 (10·7%) | 201 (11·1%) | 404 (10·9%) | |
| Sylhet | 162 (5·6%) | 175 (5·2%) | 337 (5·4%) | |
| Regular health visit | <0·001 | |||
| Yes | 945 (60·4%) | 652 (38·3%) | 1,597 (49·2%) | |
| No | 586 (39·6%) | 957 (61·7%) | 1,543 (50·8%) | |
| Ever measured cholesterol | 0·10 | |||
| Yes | 110 (5·2%) | 147 (7·0%) | 257 (6·1%) | |
| No | 1,421 (94·8%) | 1,462 (93·0%) | 2,883 (93·9%) | |
| Previous history of CVD | 0·2 | |||
| No | 1,305 (84·6%) | 1,392 (87·1%) | 2,697 (85·9%) | |
| Yes | 226 (15·4%) | 217 (12·9%) | 443 (14·1%) | |
| 10-year CVD risk (WHO-2019) | 3·8 (3·1) | 6·3 (4·4) | 5·1 (4·0) | <0·001 |
| 10-year CVD risk (ACC/AHA-2018) | 2·9 (3·6) | 9·4 (8·2) | 6·2 (7·1) | <0·001 |
| Eligible for statin use (WHO-2019) | 0·2 | |||
| No | 1,148 (74·7%) | 1,203 (77·7%) | 2,351 (76·2%) | |
| Yes | 383 (25·3%) | 406 (22·3%) | 789 (23·8%) | |
| Eligible for statin use (ACC/AHA-2018) | <0·001 | |||
| No | 1,077 (70·6%) | 734 (46·0%) | 1,811 (58·1%) | |
| Yes | 454 (29·4%) | 875 (54·0%) | 1,329 (41·9%) | |
[i] Notes: Data are presented as mean (SD) for continuous measures and n(unweighted) (%) for categorical measures. ‡Design-based t-test; Pearson’s X^2: Rao & Scott adjustment.
ACC, American College of Cardiology; AHA, American Heart Association; N, number of participants; SD, standard deviation; WHO, World Health Organization.
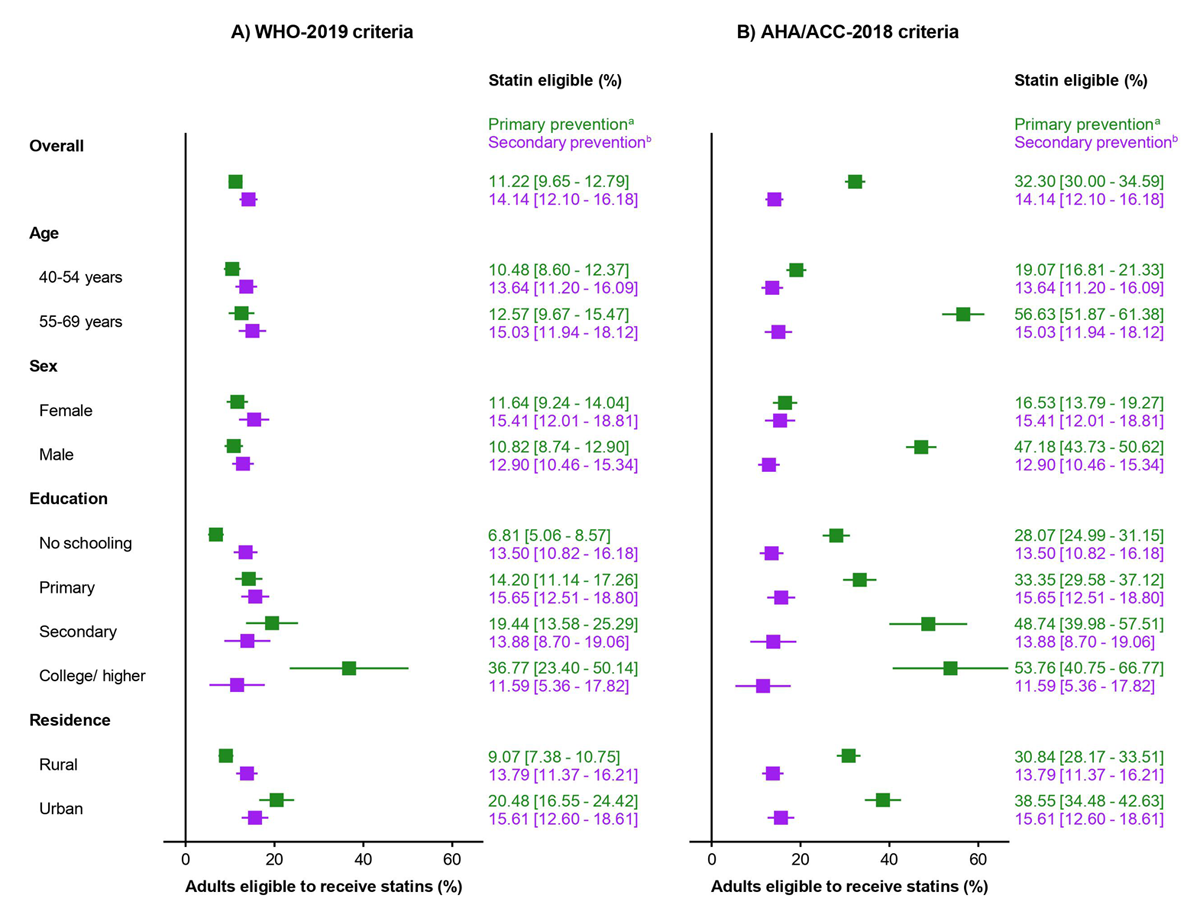
Figure 1
Proportion of Bangladeshi adults eligible for statin therapy according to the WHO-2019 and ACC/AHA-2018 guidelines, by primary and secondary prevention categories.
aAnalysis of the primary prevention category was performed among individuals without cardiovascular disease.
bOnly individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease were eligible for secondary prevention in both the guidelines.
Abbreviations: ACC, American College of Cardiology; AHA, American Heart Association; WHO, World Health Organization.
Table 2
Distribution and Kappa agreement of statin eligibility for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease according to the WHO-2019 and ACC/AHA-2018 guidelines.
| A. PRIMARY PREVENTION | STATIN USE ELIGIBILITY BASED ON ACC/AHA-2018 CRITERIA, N (%)A | KAPPA CO-EFFICIENT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YES | NO | |||
| Statin use eligibility based on WHO-2019 criteria, N (%)a | Yes | 346 (34·7%) | 0 | 0·46 |
| No | 540 (65·3%) | 1,811 (100%) | ||
| B. Secondary prevention | Statin use eligibility based on ACC/AHA-2018 criteria, N (%)a | Kappa co-efficient | ||
| Yes | No | |||
| Statin use eligibility based on WHO-2019 criteria, N (%)a | Yes | 443 (100%) | 0 | 1·00 |
| No | 0 | 0 | ||
[i] Notes: a: N = Number of participants; (%) = Column percentage (weighted). Kappa values were categorized as follows: <0·40 indicating poor to fair agreement, 0·41 to 0·60 as moderate agreement, 0·61 to 0·80 as substantial agreement, and 0·81 to 1·0 as almost perfect agreement.
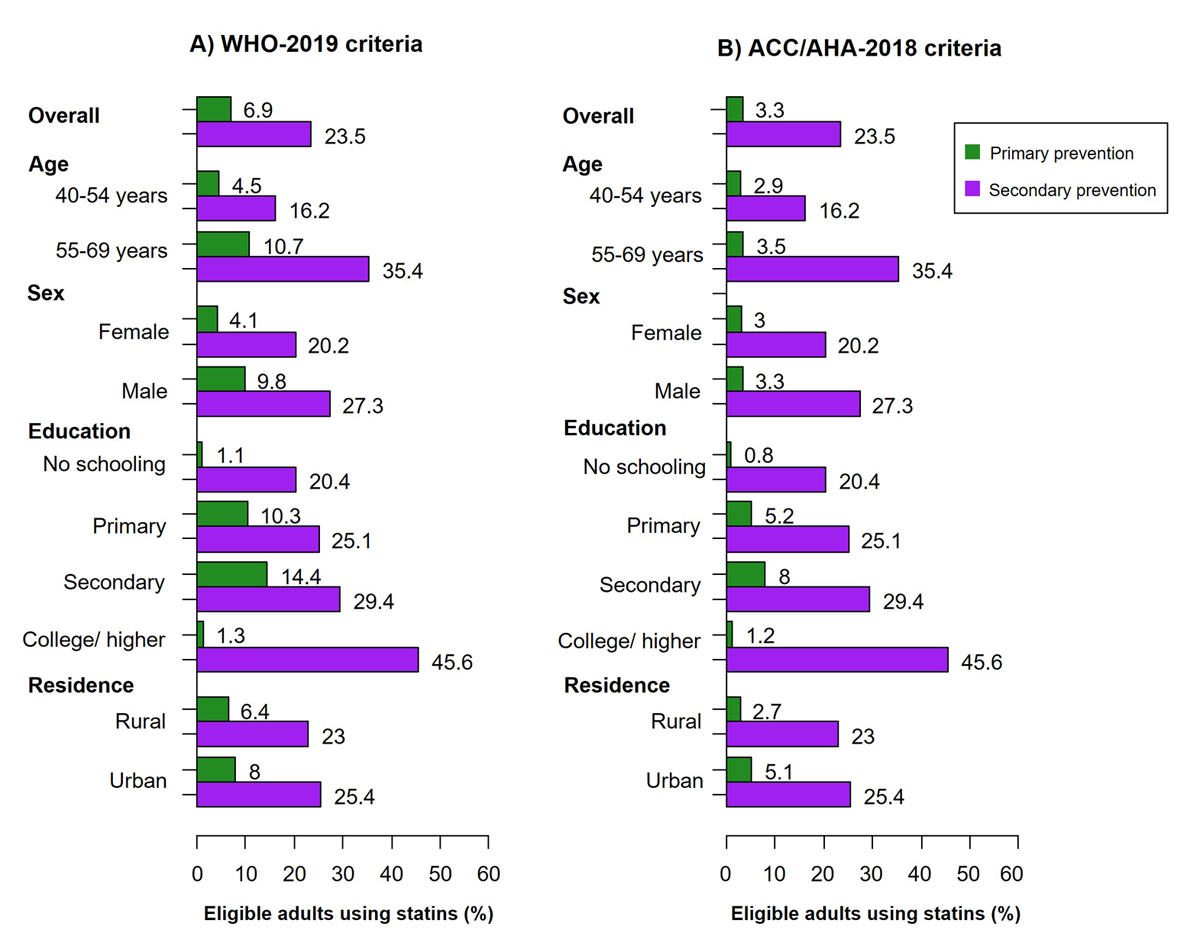
Figure 2
Proportion of individuals using statins among those eligible in each primary and secondary prevention group according to the WHO-2019 and ACC/AHA-2018 guidelines.
Abbreviations: ACC, American College of Cardiology; AHA, American Heart Association; WHO, World Health Organization.
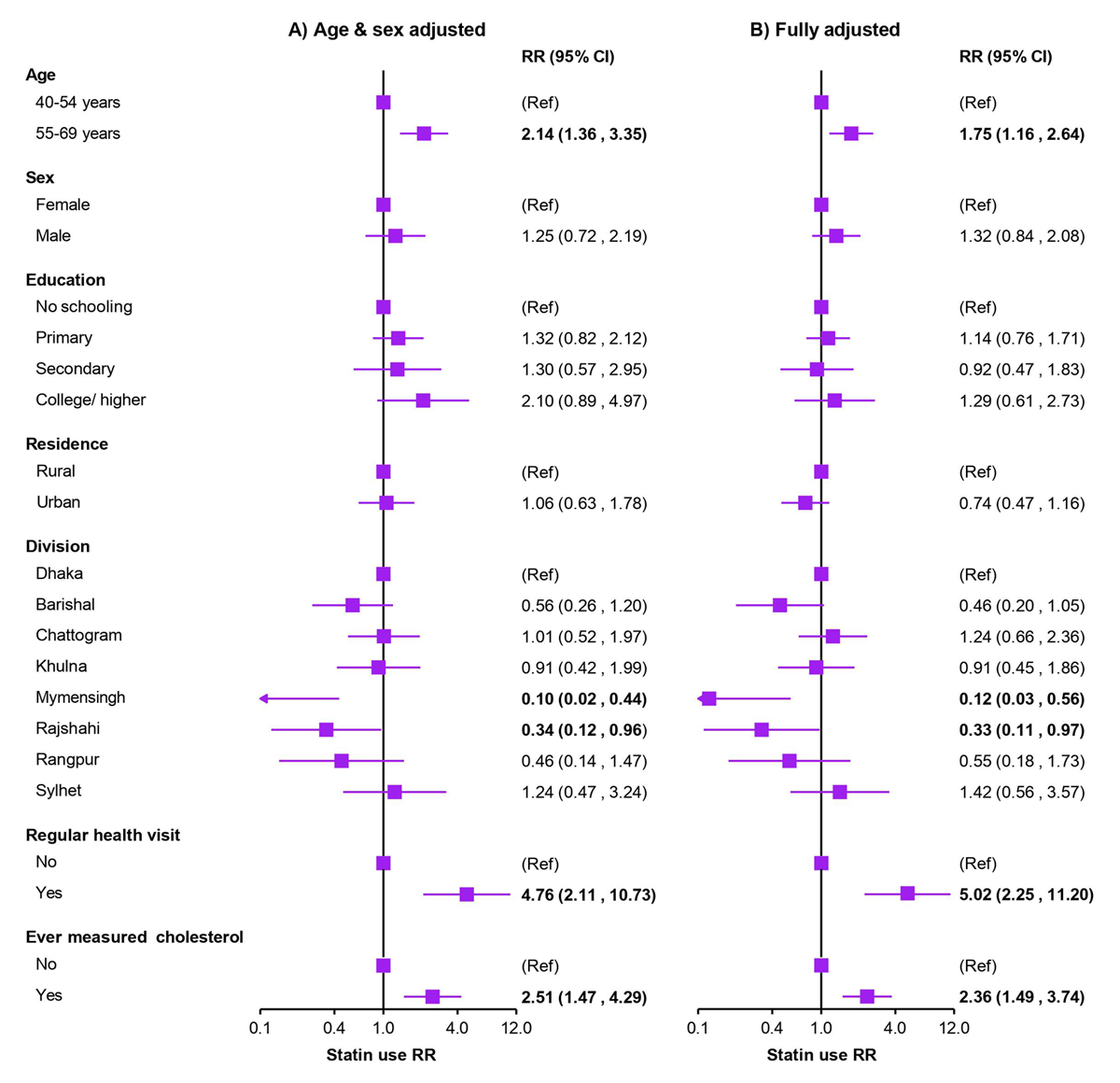
Figure 3
Modified Poisson regressions showing predictors of statin use among individuals eligible for statin therapy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease.
• Results are presented as RRs (95% CIs), obtained using modified Poisson regressions and applying appropriate survey weights during analysis. Analyses were restricted to the secondary prevention outcomes only due to a very lower number of individuals using statins for primary prevention. Estimates with a P-value <0.05 are marked in bold. RR = risk ratio.
| Abbreviation | Full Description |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| ACC | American College of Cardiology |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| LDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| LMIC | Low- and Middle-Income Countries |
| HIC | High-Income Countries |
