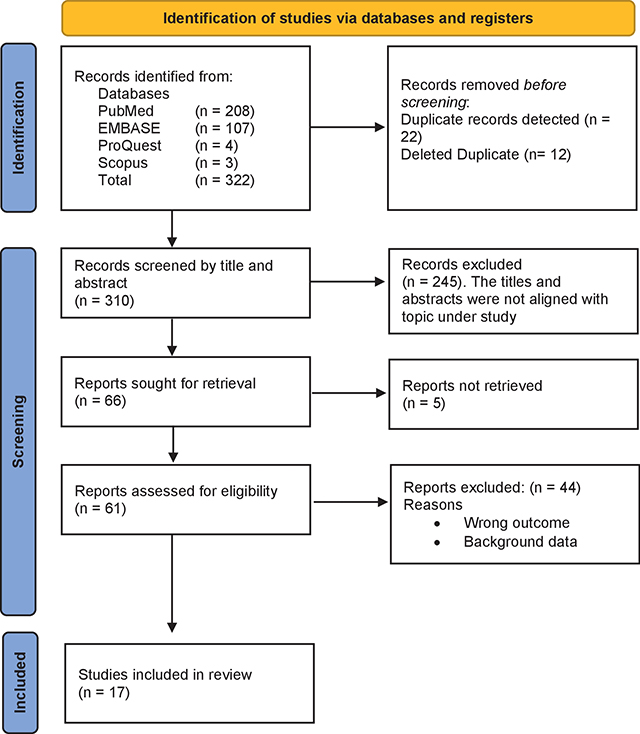
Figure 1
Study profile.
Table 1
General characteristics of the included articles.
| AUTHOR AND YEAR | JOURNAL | DATABASE | STUDY DESIGN | STUDY TIME FRAME | COUNTRY | POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu Y et al. 2023 [14] | BMC Medicine | PubMed | Epidem. and Economic Model | 2020–2021 | England | Age structure and non-pharma interventions | 27 countries |
| Bello-Chavolla et al. 2023 [15] | Intl J Infectious Diseases | PubMed | Retro. Cohort Design | 2020–2021 | Mexico | 18 years and older | 793,487 |
| McNamara LA et al. 2022 [16] | Lancet | PubMed | Ecological Analysis | 2020–2021 | USA | 18 years or older | 49 states |
| Pattni K et al. 2022 [17] | BMC Infectious Diseases | PubMed | SIR model | 2021 | England | Demographic data | 2,691,413 |
| Dunbar E et al. 2021 [18] | Infection Control and Hospital Epidem. | PubMed | Clinical trial | 2020 | United States | Health workers | Not provided |
| Steele MK et al. 2022 [19] | JAMA Network | PubMed | Modelling study | 2020–2021 | United States | Age groups of 18–49, 50–64 and older | 69 million infections |
| Shim E, 2021 [20] | Intl J Env Research and Pub Health | PubMed | Age-structured model | 2021 | South Korea | Age groups | 70% coverage |
| Homan T et al. 2022 [21] | Scientific Reports | PubMed | Retro Cohort study | 2021 | Italy | 16 years and older | 4.09 million |
| Kayano T et al. 2021 [22] | Scientific Reports | PubMed | Transition model | 2021 | Japan | All vaccinated individuals | Not specified |
| Tonnara G et al. 2022 [23] | Clinical Microbio and Infection | PubMed | Retro Observ study | 2021 | Republic of San Marino | 12 years and older | 32,126 |
| Chen X et al. 2022 [24] | Scientific Reports | PubMed | SIR model | 2020–2021 | United States | Not specified | Not specified |
| Childs L et al. 2022 [25] | Epidemics | PubMed | Model of COVID-19 Infection | 2020–2021 | Canada | Age groups | Not specified |
| Link-Gelles R et al. 2023 [26] | MMWR | PubMed | Model | 2022–2023 | United States | Age groups 18 years and older | 29,175 |
| Mancuso et al. 2021 [27] | Infectious Disease Modelling | Embase | Two strain-group Mechanistic model | 2020–2021 | United States | Groups of vaccinated and unvaccinated | Total pop in the community |
| Perez-Then et al. 2023 [28] | Open Forum Infectious Diseases | Embase | Case – Control study | 2021 | Dominican Republic | 18 years and older | 1,078 |
| Spreco et al. 2022 [29] | Vaccines | Embase | Case – Control study | 2021– 2022 | Sweden | 18 years and older | 1,760,000 |
| Wang et al. 2022 [30] | Vaccines | Embase | Structural Nested Mean Model | 2021 | United States | Vaccinated population | 4.55 million |
Table 2
Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in curbing the transmission and incidence of COVID-19 cases.
| AUTHOR | TYPE OF VACCINE | VARIANT | VACCINATION STATUS ASSESSMENT METHOD | VE OF FULL VACCINATION (95% CL) | OUTCOME |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu Y et al. 2023 [14] | mRNA vaccines Viral vector vaccines | Omicron | Not specified | mRNA vaccines – 0.85/0.7 Viral vector vaccines –0.75/0.65 | High disease burden minimized. Deaths reduced. |
| Bello-Chavolla et al. 2023 [15] | BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine | Delta B.1.1.519 | Self-reported by the evaluated person | 80.34 | Efficacy in combating SARS-CoV-2 infection. Preventing hospitalization. |
| McNamara LA et al. 2022 [16] | Not specified | Not specified | Data from the CDC | Not specified Oxford–AstraZeneca = 64% | Reduction in COVID-19 cases, reduced emergency department visits and hospital admissions. |
| Pattni K et al. 2021 [17] | Oxford–AstraZeneca Pfizer-BioNTech | Delta | Combined Intelligence for Population Health Action data | Pfizer-BioNTech = 84% | Reduces susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. |
| Dunbar E et al. 2021 [18] | Pfizer/BioNTech | Not specified | Not indicated | 95% | Decrease in COVID-19 infections. |
| Steele MK et al. 2022 [19] | mRNA-1273 BNT 162b2 | Delta | As reported to the CDC Sept 2021 | 95% | Averts hospital admissions, illnesses, and fatalities in the US. |
| Shim E, 2021 [20] | AstraZeneca-Oxford and Pfizer mRNA | Delta | Not specified | 55–56% | Re = 1.3, it would prevent 47% of symptomatic infections and lower the attack rate 9.2% to 4.9%. |
| Homan T et al. 2022 [21] | Ad26.CoV2.S or BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 or ChAdOx1-S | Alpha Delta | Surveillance data of Apulia Region | Overall effectiveness at 92.6% | Prevented illnesses. High efficiency against hospitalization for those who were fully vaccinated. |
| Kayano T et al. 2021 [22] | Gam-COVID-Vac(GAM) | Alpha | Data from RSM Health System | Gam-COVID-Vac(GAM) = 97.3% | Effective at preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
| Tonnara G et al. 2022 [23] | Gam-COVID-Vac or BNT162b2 | Alpha | RSM Health System | Gam-COVID-Vac = 84 % or BNT162b2 = 16% | Prevention against infection and protection against hospitalization. |
| Chen X et al. 2022 [24] | Sinovac Life Sciences Co, Vero cell, Pfizer or BioNTec, AstraZeneca | Not specified | Self-reported participant’s vaccination history | 31% | Reduction of symptomatic illness. Decreased the likelihood of COVID-19-related hospitalization. |
| Childs L et al. 2022 [25] | They were kept at constant during the study | Not specified | Vaccination coverage data | They were kept at constant during the study. | Reduction in infections. |
| Link-Gelles R et al. 2023 [26] | mRNA | Omicron BA.5–and XBB/XBB.1.5 | Self-reported | Provided per age group, no overall VE was provided | Provided additional protection against symptomatic XBB/XBB.1.5. |
| Mancuso et al. 2021 [27] | Pfizer or Mordena | Alpha (B.1.1.7) Wild type strain Delta | Bloomberg COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker Open Data | 67% against the Delta variant. Not specified for other variants | Reduction of COVID-19-related cases and deaths. |
| Perez-Then et al. 2023 [28] | Inactivated Vaccine (Corona Vac) | Ancestral Delta | Data collected through the questionnaire. | 31% | Provided a moderate level of protection against symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections, prevented COVID-19-related hospitalization. |
| Spreco et al. 2022 [29] | BNT162b2 mRNA | Alpha Delta | Data from the country wide health information systems | Odds ratio in the vaccinated group was 2.2 | Did not offer much protection against COVID-19 cases. |
| Wang et al. 2022 [30] | BNT162b2 or mRNA | Original strain | Data from JHU Resource Center and CDC | 90% | Notable decrease in disease prevalence within the US. |
