Figure 1

Figure 2

Figure 3

Figure 4

Figure 5
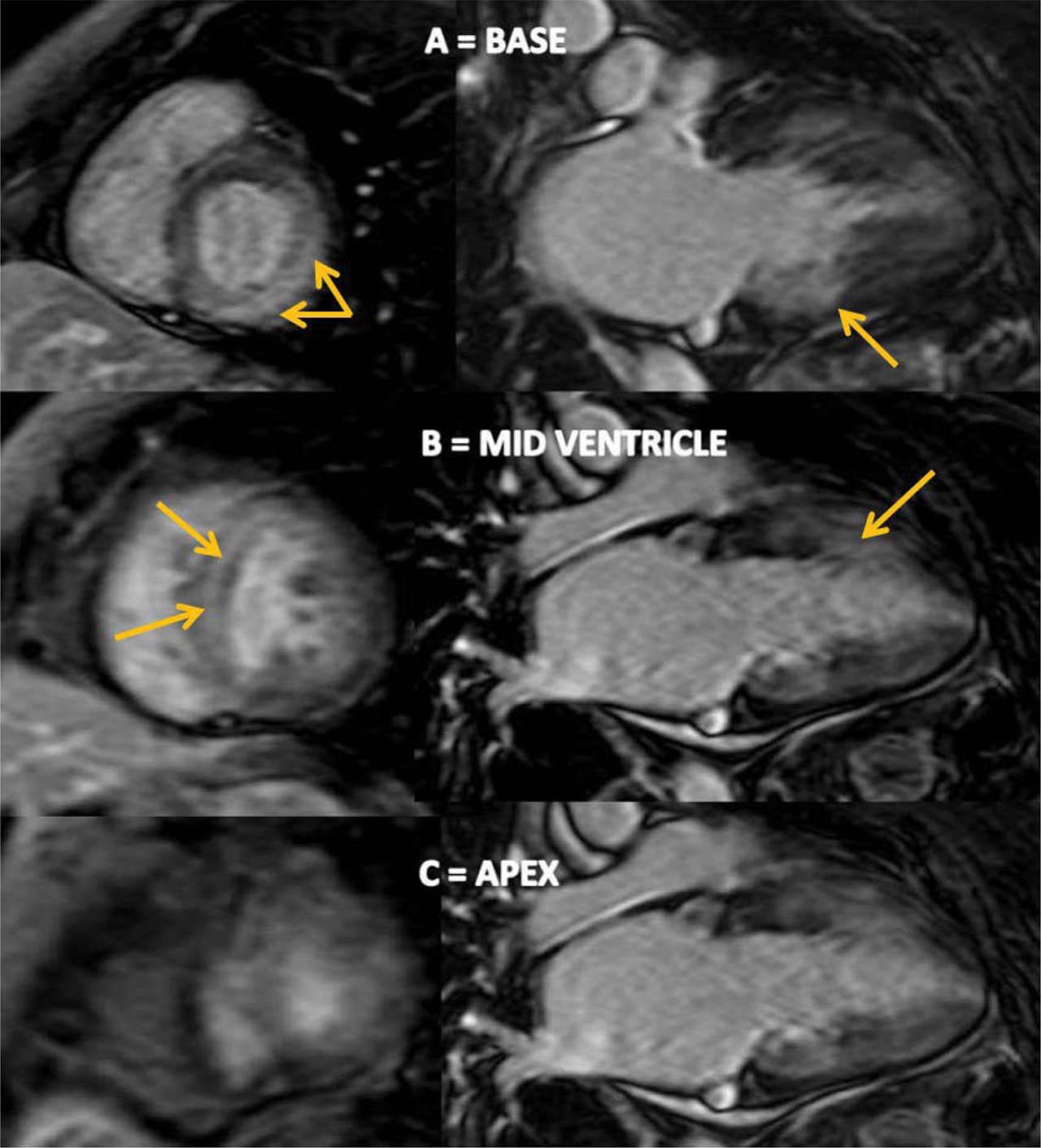
Figure 6

Figure 7








© 2022 Alexandra Maria Chitroceanu, Alina Ioana Nicula, Roxana Cristina Rimbas, Mihaela Andreescu, Cristina Popp, Claudiu Stoicescu, Dragos Vinereanu, published by Romanian Society of Cardiology
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.