Figure 1

Figure 2
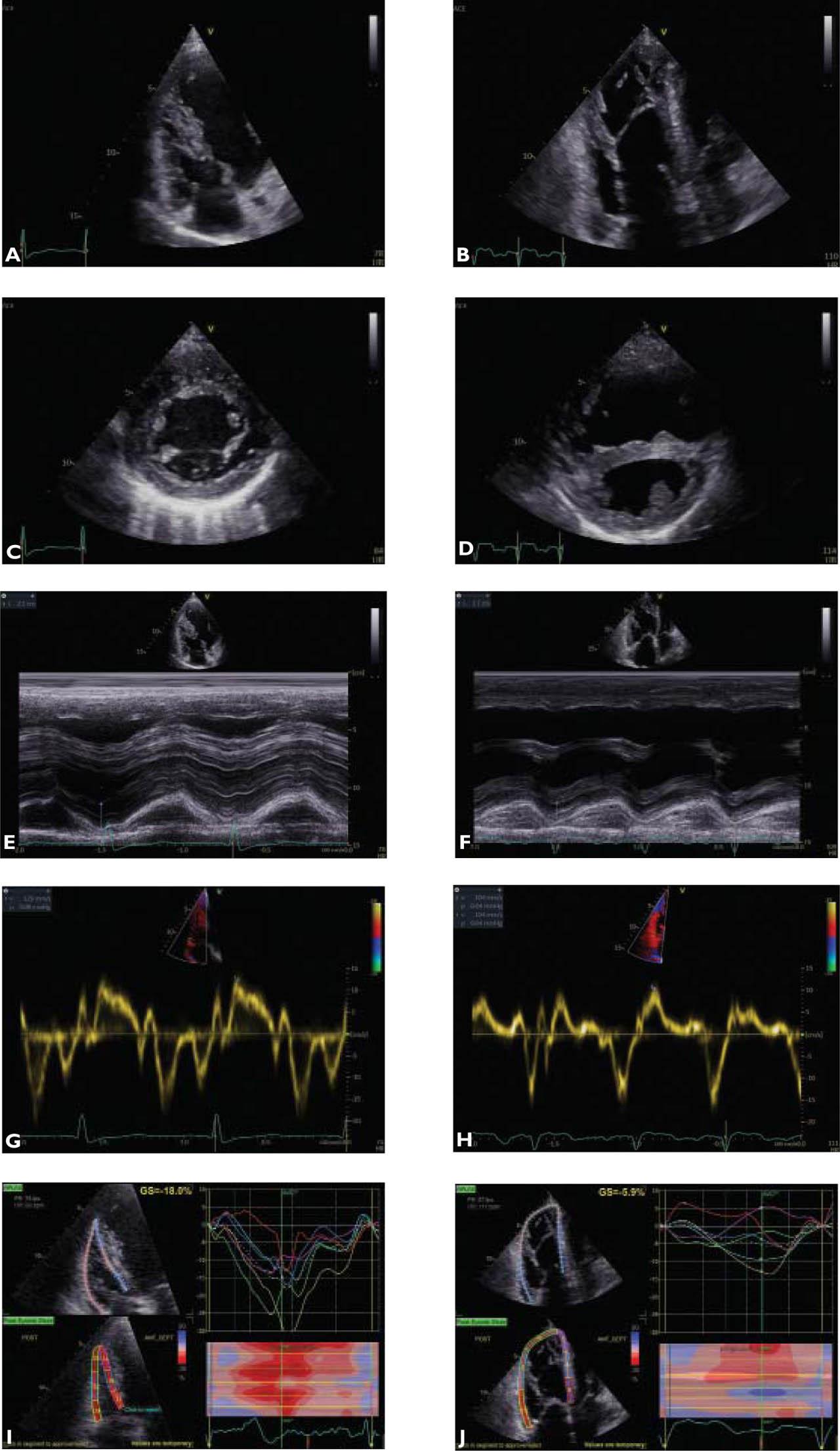
Diagnostic work-up in Eisenmenger Syndrome (adapted from [4])
| Clinical evaluation | Symptoms | Physical examination |
| ECG | Presence of sinus rhythm | Holter monitoring may be considered in case of syncope, palpitations, baseline ECG abnormalities |
| Non-invasive imaging | Chest X-ray | Position of cardiac apex (RV hypertrophy) |
| TTE | Systematic analysis of cardiac morphology and ventriculo-arterial connections | |
| TEE (unanswered questions on TTE) | Shunt description | |
| CMR (complex lesions/inadequate patient echogenicity) | Detailed description of cardiac morphology | |
| Non-invasive imaging | CT (specific indications) | Pulmonary artery diameters/calcification |
| Exercise testing | 6MWD | Systematic at baseline and follow-up visits |
| Cardiopulmonary exercise testing | Exercice capacity | |
| Cardiac catheterization | Confirmation of diagnosis and haemodynamic assessment–right atrial pressure, sPAP, mPAP, dPAP, capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary vascular resistances cardiac output, SVO2 %, pulmonary-to-systemic flow ratio | Differential diagnosis: ES, PAH with left-to-right shunt, iPAH, segmental PH |
| Biomarkers | Full blood count |