Figure 1

Figure 2
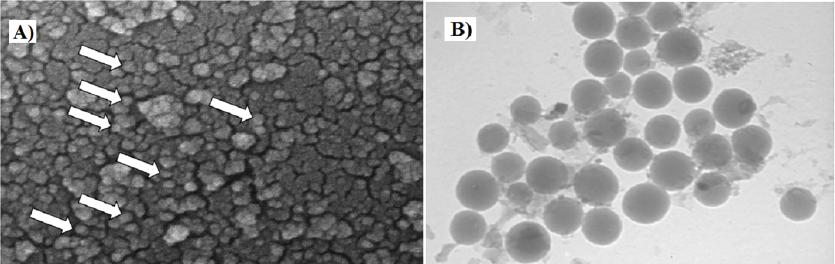
Figure 3

Figure 4

Figure 5

Figure 6
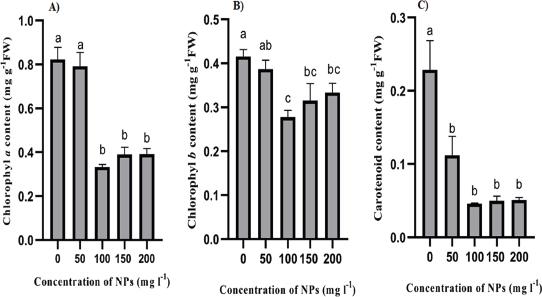
Figure 7

Figure 8
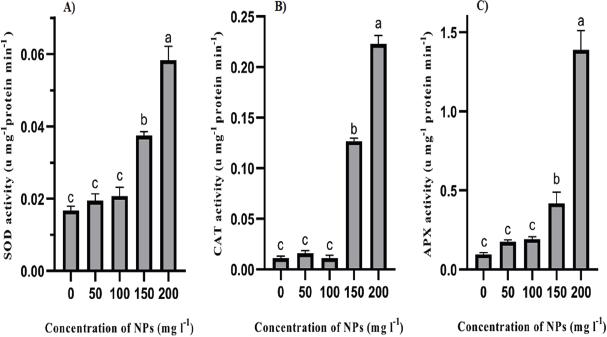








© 2023 Hanifeh Akbarian Kalehjahi, Morteza Kosari-Nasab, Mojtaba Amini, Ali Movafeghi, published by University of Gdańsk
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.