Figure 1
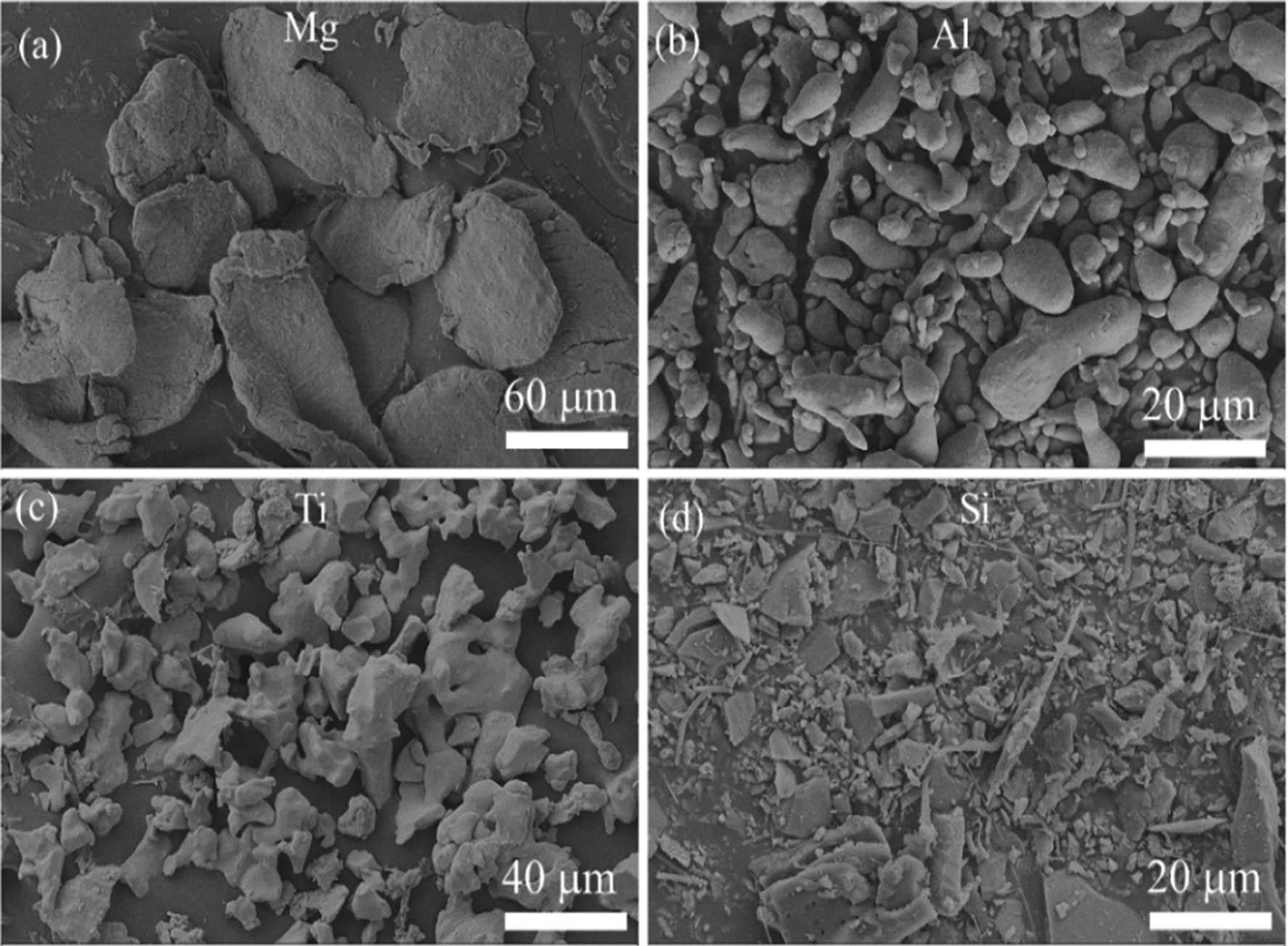
Figure 2
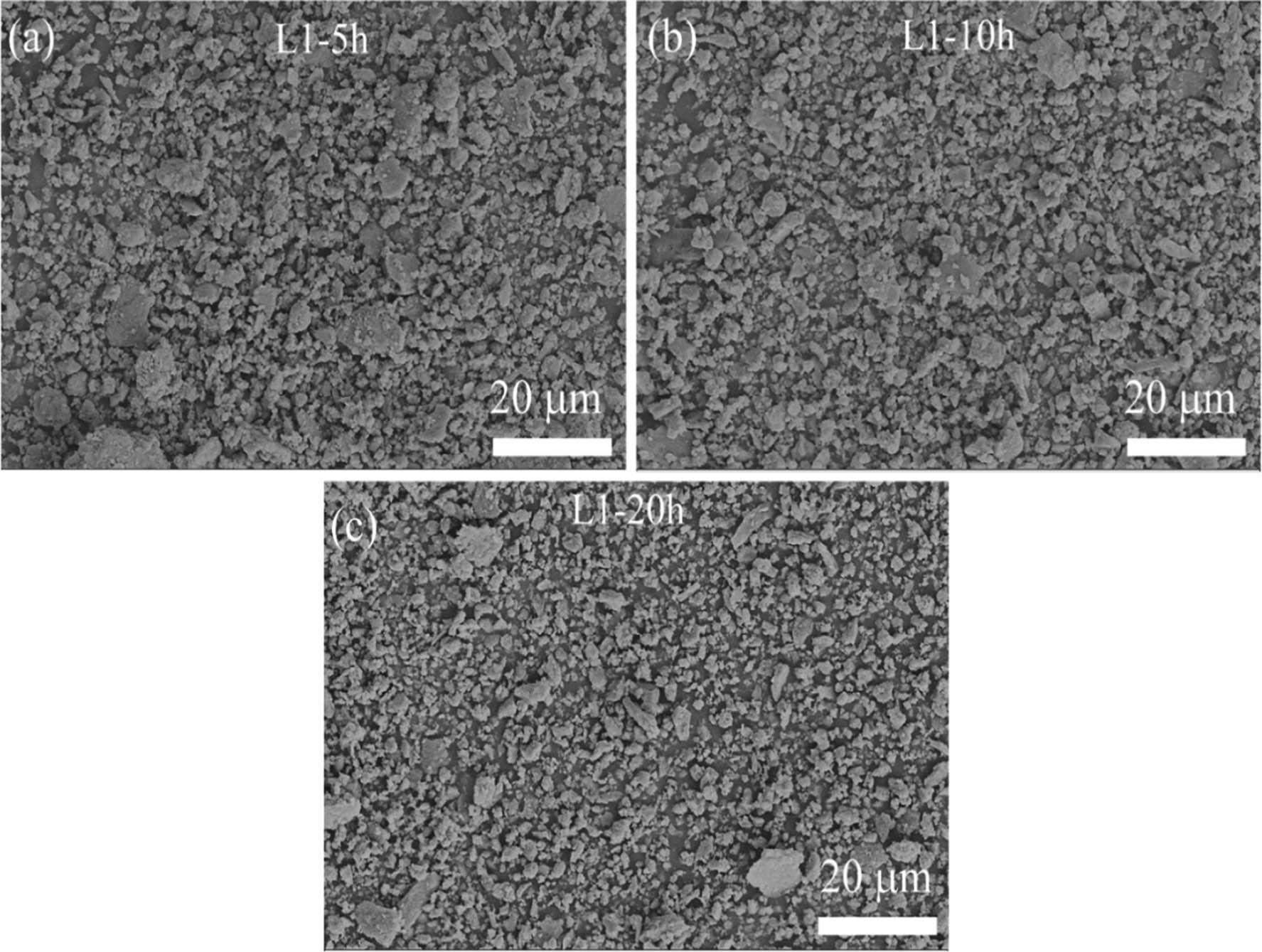
Figure 3
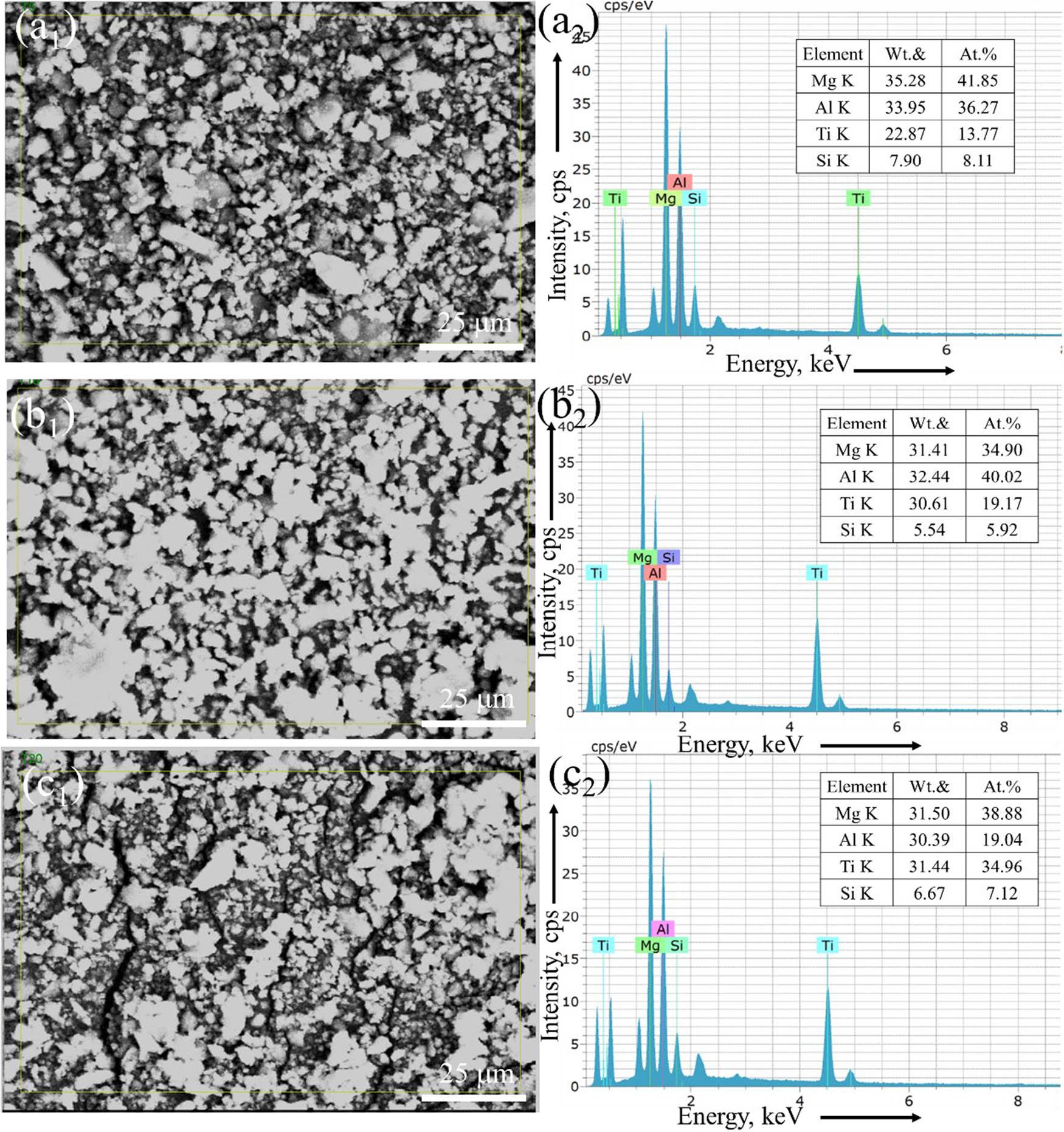
Figure 4
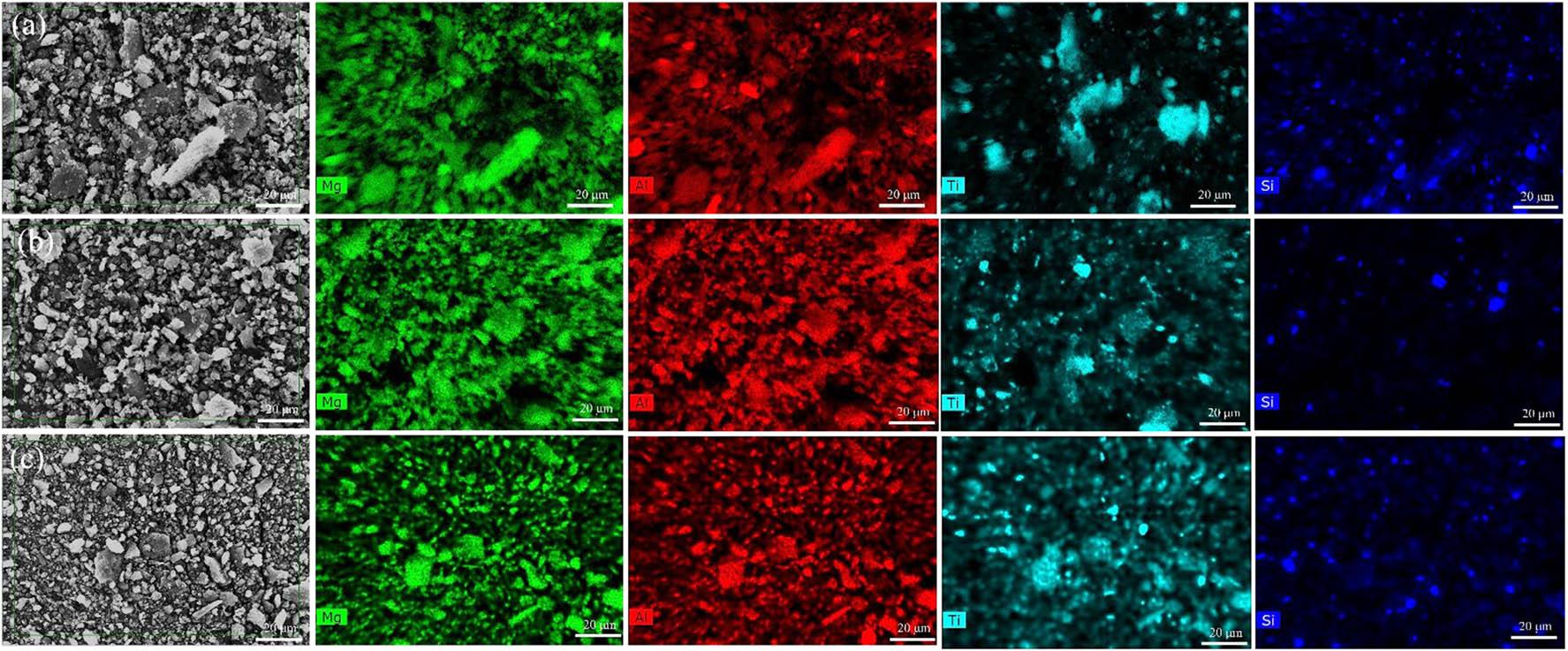
Figure 5

Figure 6
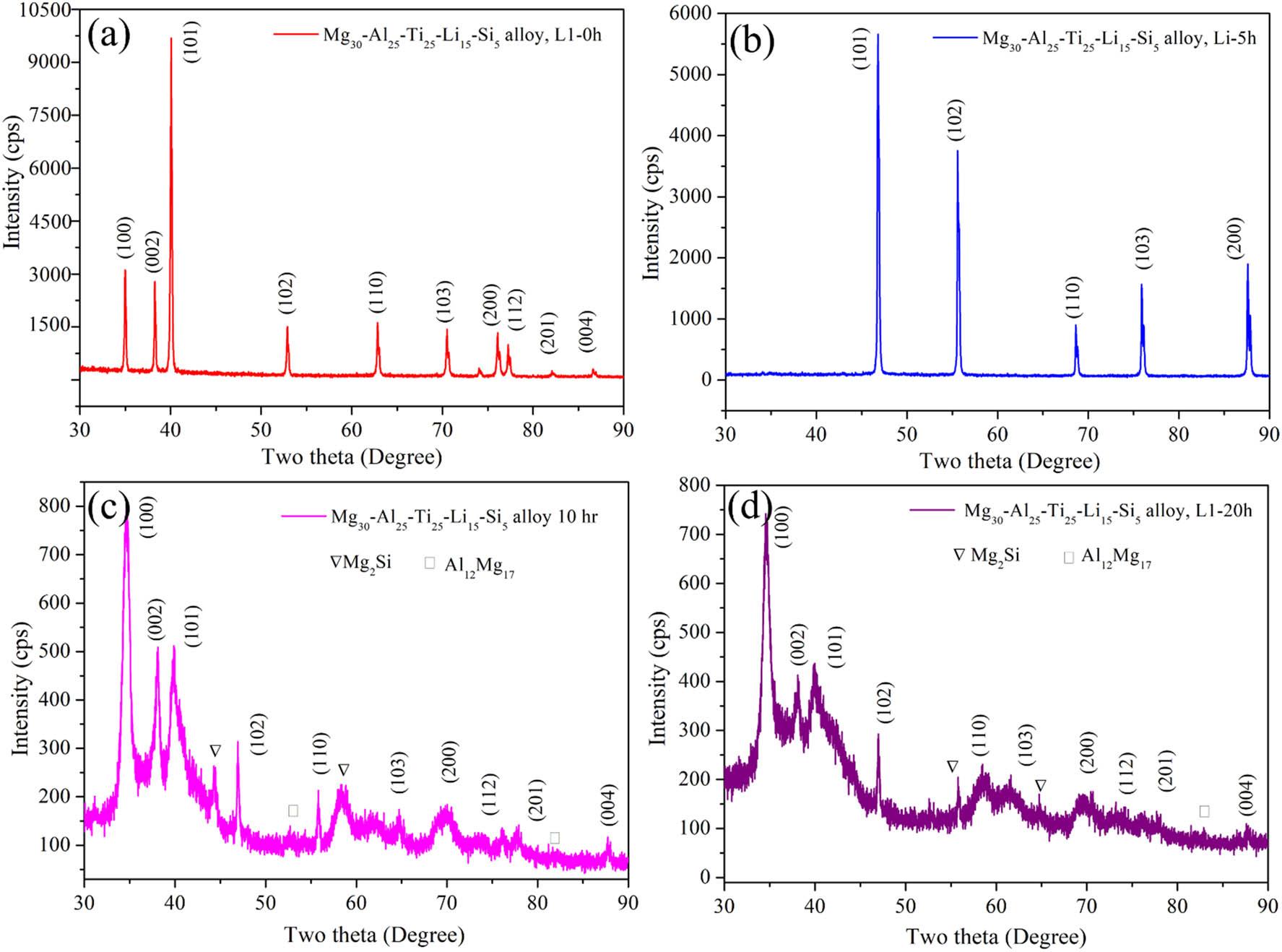
Figure 7
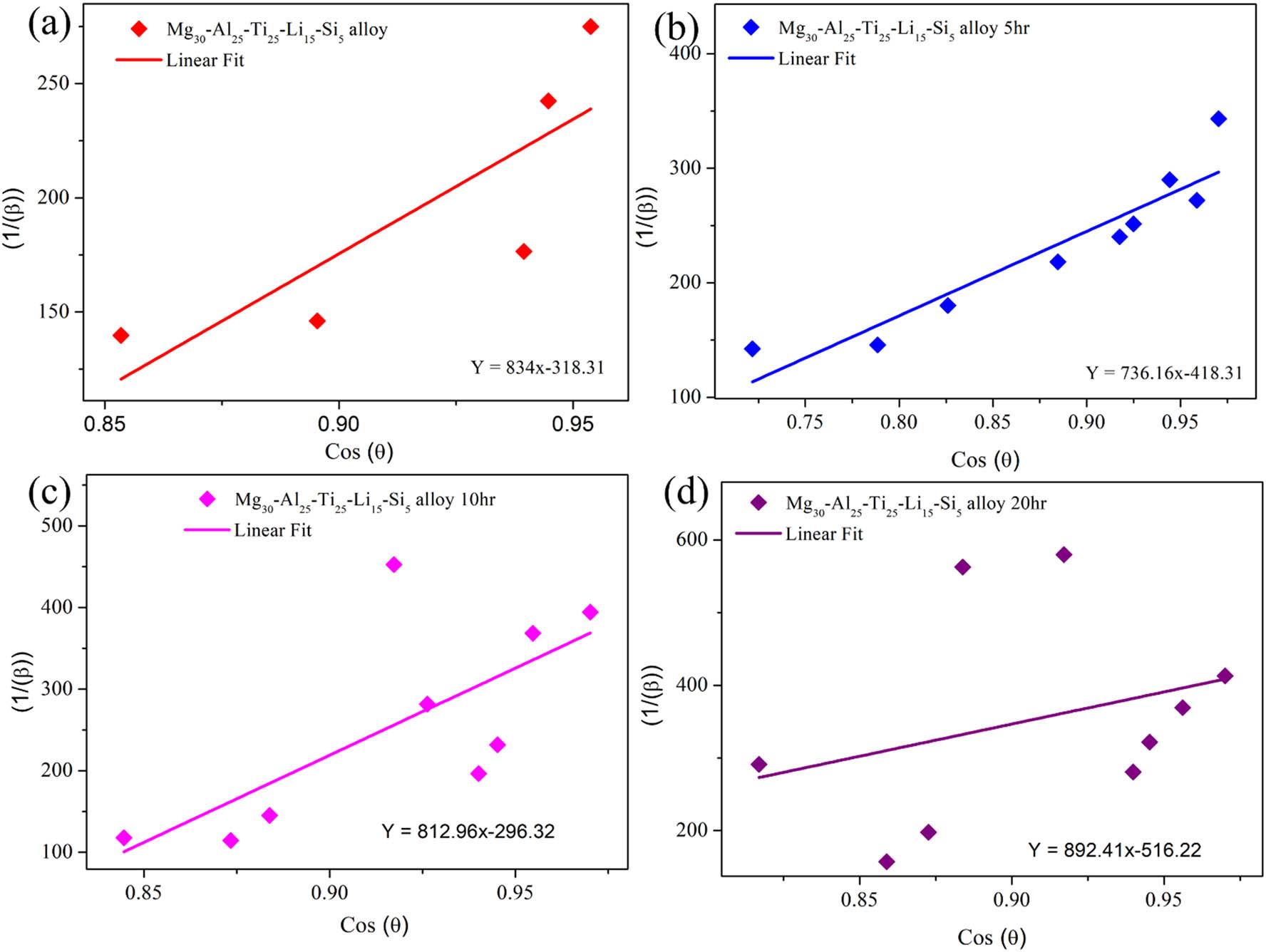
Figure 8
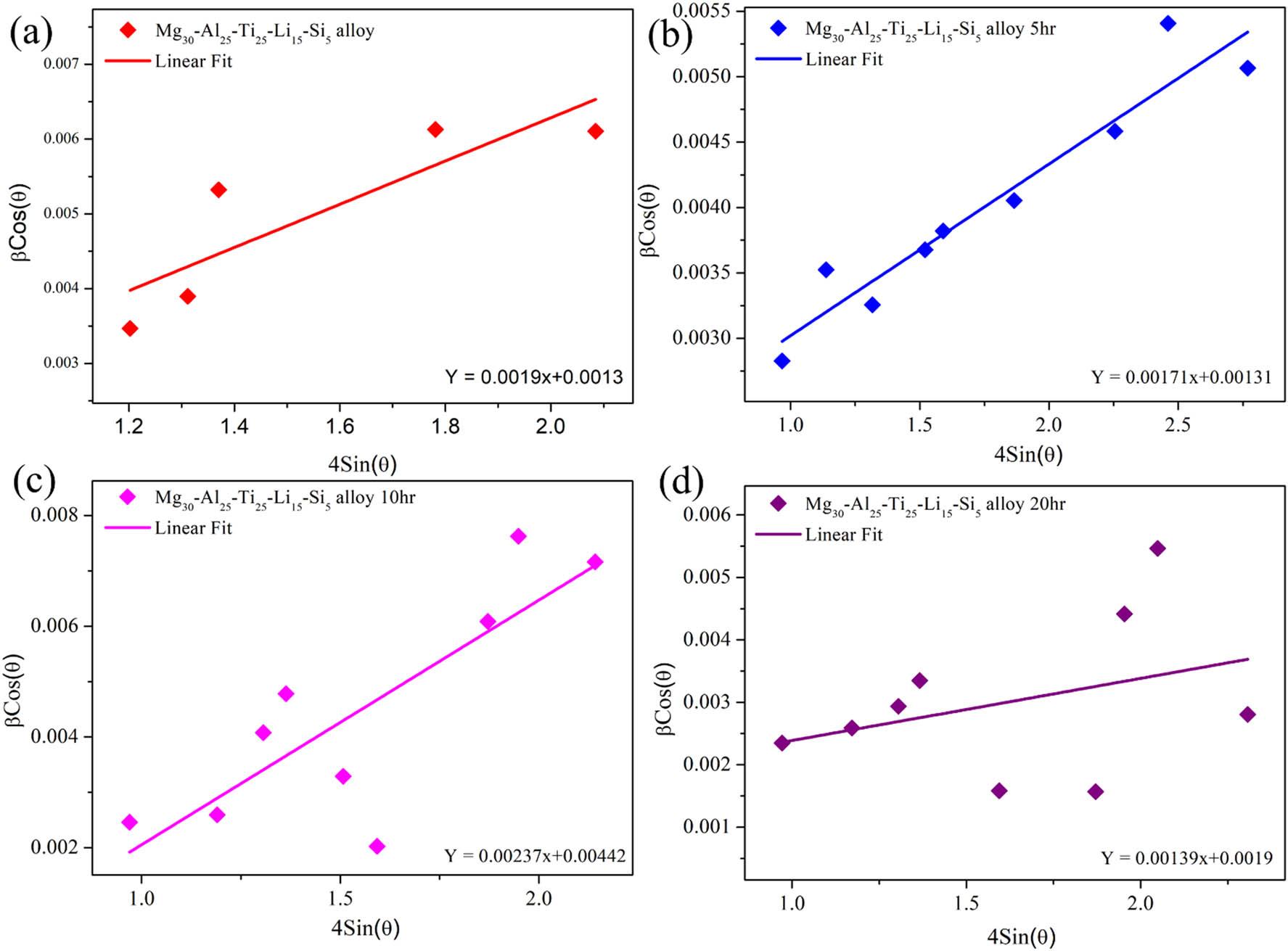
Figure 9
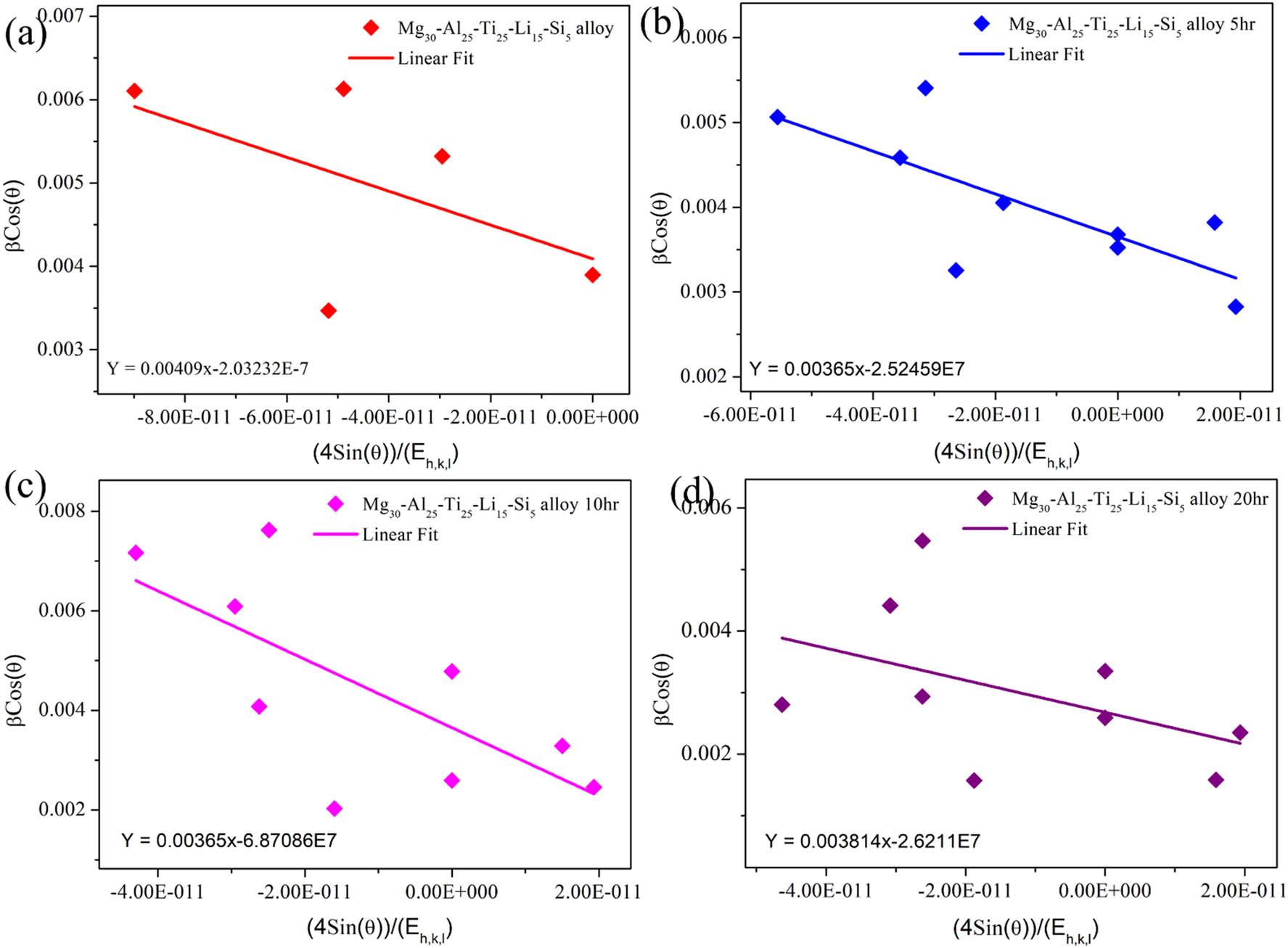
Figure 10
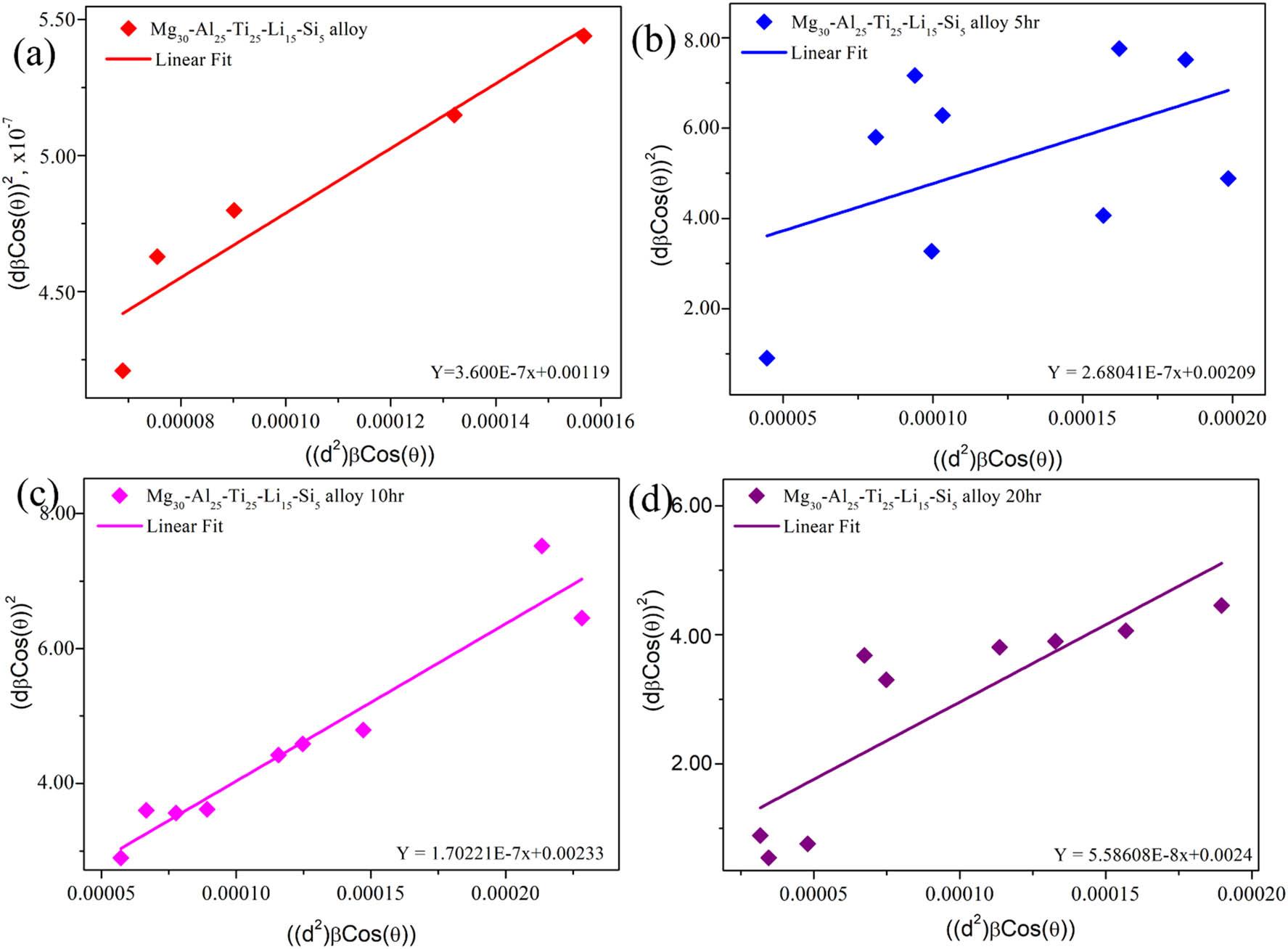
Figure 11
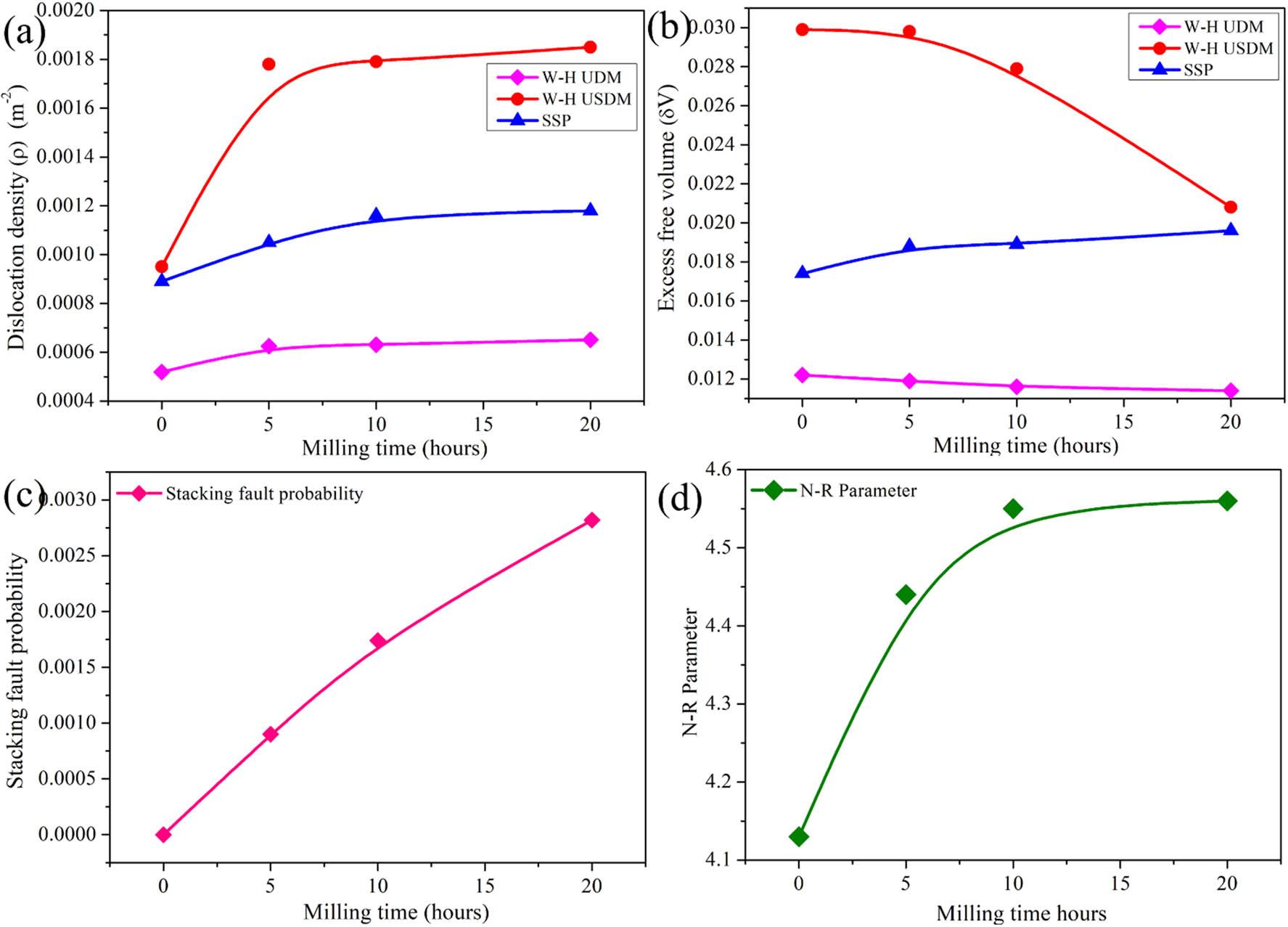
Figure 12
Figure 13
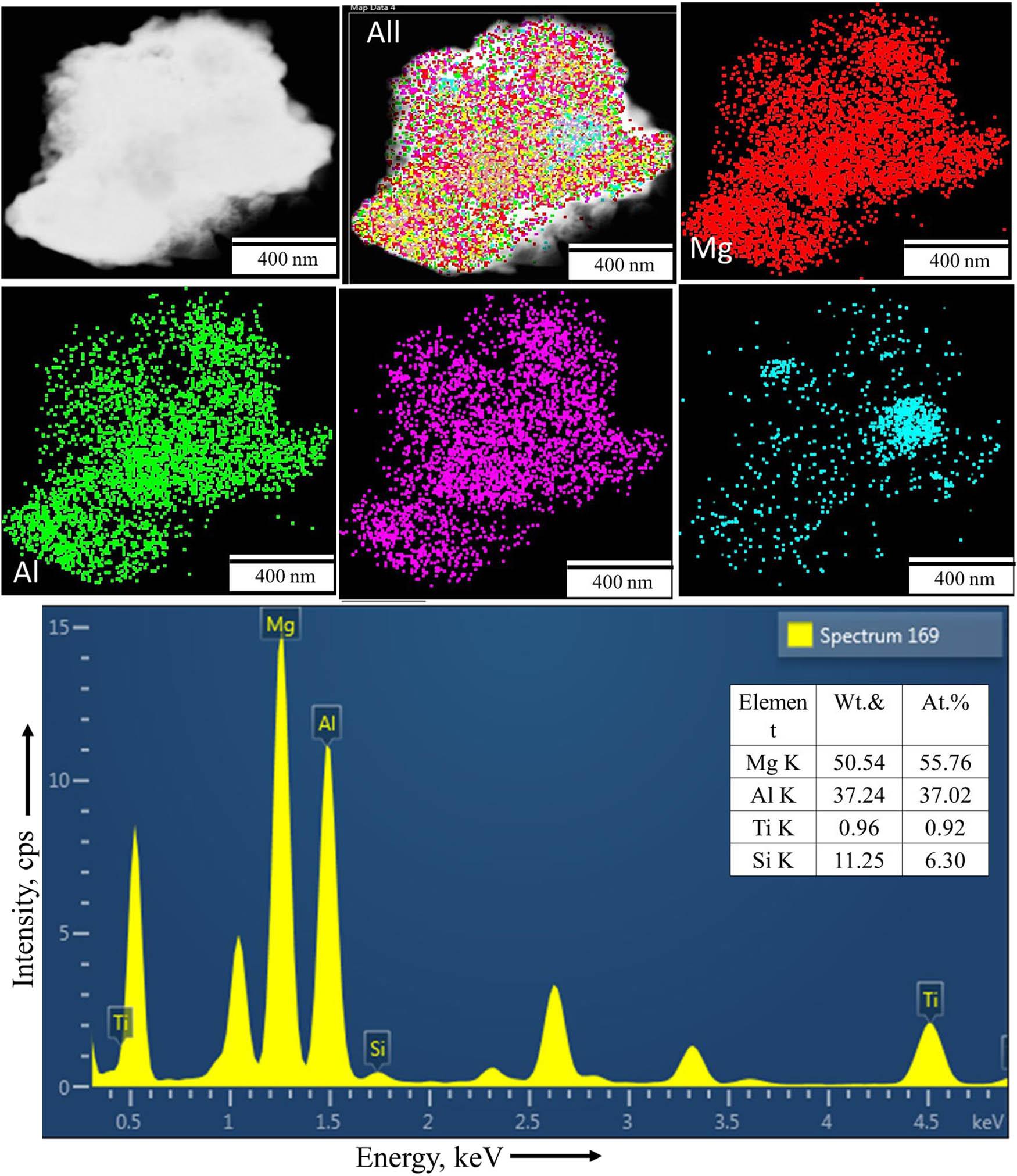
Figure 14
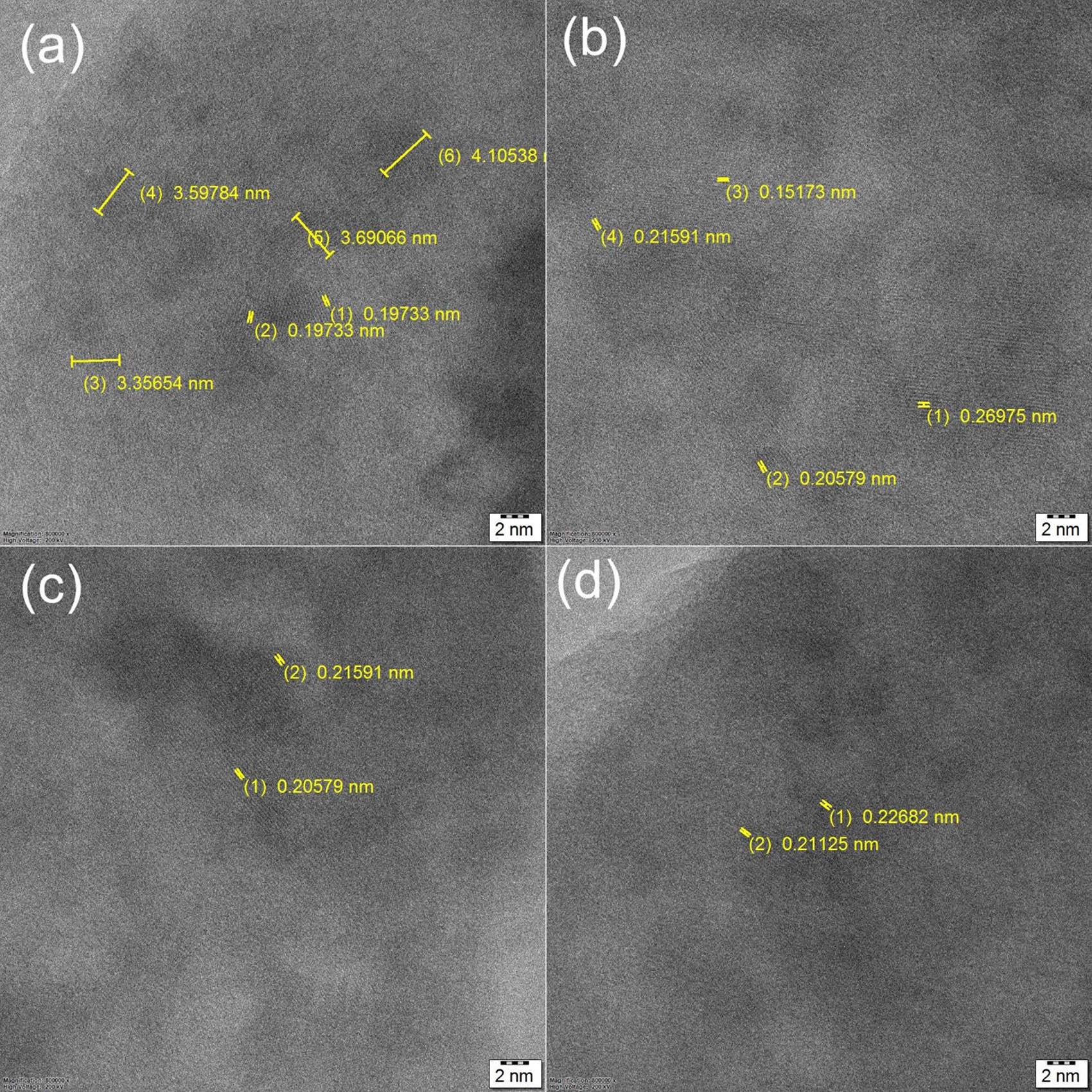
Figure 15
A list of low-density elements selected for the present study [14]_
| Element | Atomic number | Atomic radius (nm) | Melting temperature (K) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | 24 | 0.1249 | 923 | 1.74 |
| Al | 26 | 0.1241 | 933.3 | 2.70 |
| Ti | 13 | 0.1432 | 1,941 | 4.50 |
| Li | 27 | 0.1251 | 453.5 | 0.53 |
| Si | 14 | 0.1153 | 1,687 | 2.33 |
Chemical composition of the developed Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 LWHEA_
| Mg | Al | Ti | Li | Si | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt% | At% | Wt% | At% | Wt% | At% | Wt% | At% | Wt% | At% |
| 30 | 24.57 | 25 | 18.45 | 25 | 10.40 | 15 | 43.03 | 5 | 3.55 |
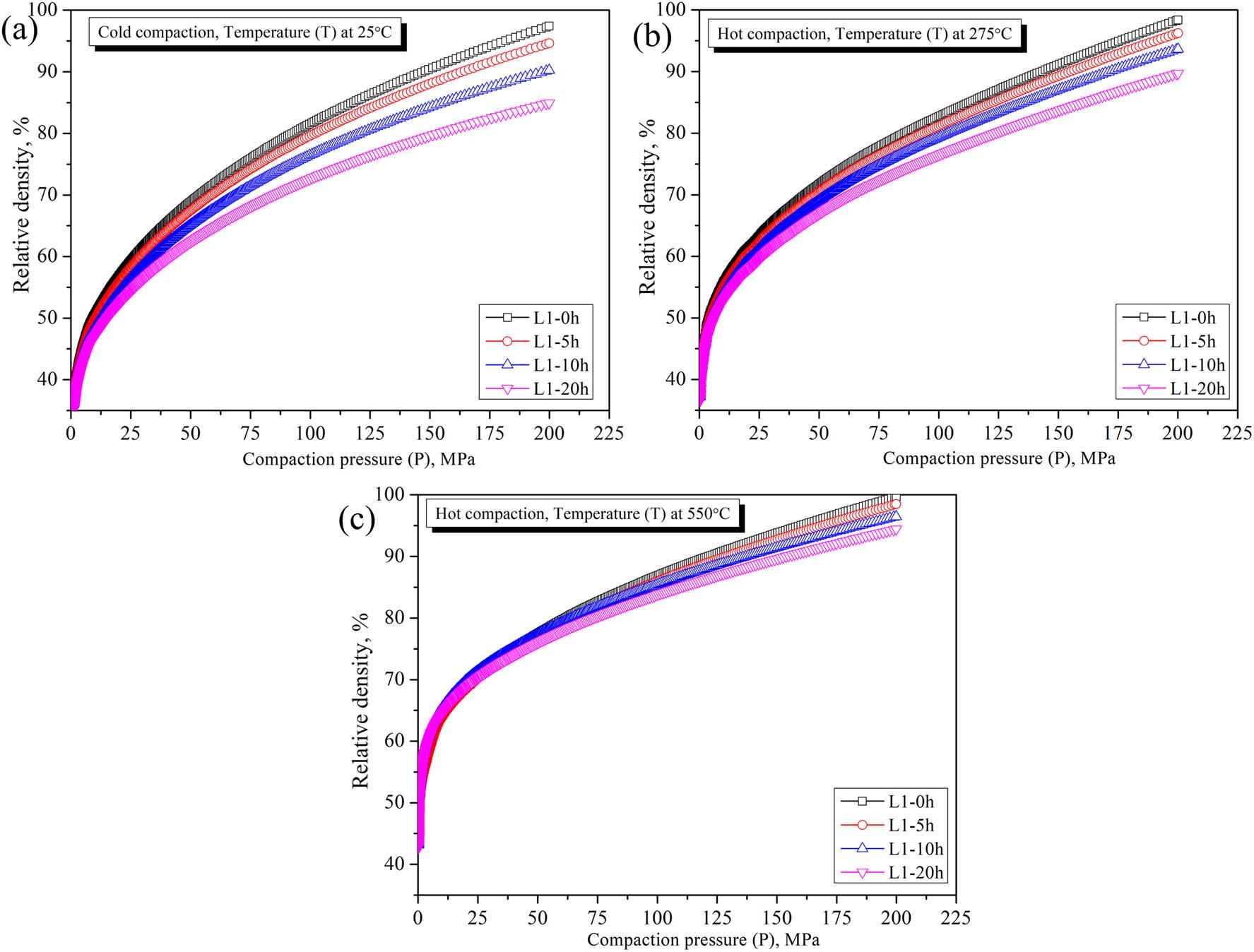
Variation in relative density in different stages during compaction (both cold and hot compaction) as a function of compaction pressure and temperature for Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 LWHEAs milled for different times (0, 5, 15, and 20 h)_
| Sample | T (°C) | P (MPa) | Compaction stages | RD (%) | Sample | T (°C) | P (MPa) | Compaction stages | RD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1-0 h | RT | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 56.81 | L1-5 h | RT | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 55.85 |
| 30 | 61.55 | 30 | 60.43 | ||||||
| 40 | 65.56 | 40 | 64.30 | ||||||
| 50 | 68.97 | 50 | 67.57 | ||||||
| 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 71.95 | 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 70.42 | ||||
| 70 | 74.71 | 70 | 73.07 | ||||||
| 80 | 77.15 | 80 | 75.40 | ||||||
| 90 | 79.55 | 90 | 77.69 | ||||||
| 100 | 81.70 | 100 | 79.74 | ||||||
| 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 86.38 | 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 84.19 | ||||
| 150 | 90.38 | 150 | 87.98 | ||||||
| 175 | 94.22 | 175 | 91.62 | ||||||
| 200 | 97.40 | 200 | 94.63 | ||||||
| 275 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 61.26 | 275 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 60.43 | ||
| 30 | 65.34 | 30 | 64.39 | ||||||
| 40 | 68.67 | 40 | 67.62 | ||||||
| 50 | 71.68 | 50 | 70.54 | ||||||
| 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 74.34 | 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 73.11 | ||||
| 70 | 76.80 | 70 | 75.49 | ||||||
| 80 | 78.83 | 80 | 77.45 | ||||||
| 90 | 80.85 | 90 | 79.40 | ||||||
| 100 | 82.66 | 100 | 81.15 | ||||||
| 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 87.05 | 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 85.38 | ||||
| 150 | 91.17 | 150 | 89.33 | ||||||
| 175 | 94.90 | 175 | 92.91 | ||||||
| 200 | 98.36 | 200 | 96.22 | ||||||
| 550 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 69.04 | 550 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 68.47 | ||
| 30 | 72.42 | 30 | 71.80 | ||||||
| 40 | 75.13 | 40 | 74.46 | ||||||
| 50 | 77.51 | 50 | 76.79 | ||||||
| 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 79.73 | 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 78.98 | ||||
| 70 | 81.79 | 70 | 81.00 | ||||||
| 80 | 83.56 | 80 | 82.72 | ||||||
| 90 | 85.26 | 90 | 84.51 | ||||||
| 100 | 86.93 | 100 | 86.03 | ||||||
| 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 90.48 | 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 89.64 | ||||
| 150 | 93.82 | 150 | 92.77 | ||||||
| 175 | 96.82 | 175 | 95.71 | ||||||
| 200 | 99.67 | 200 | 98.48 | ||||||
| L1-10 h | RT | 20 | Particle Rearrangement stage | 54.22 | L1-20 h | RT | 20 | Particle Rearrangement stage | 52.33 |
| 30 | 58.62 | 30 | 56.33 | ||||||
| 40 | 62.25 | 40 | 59.67 | ||||||
| 50 | 65.31 | 50 | 62.48 | ||||||
| 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 67.97 | 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 64.92 | ||||
| 70 | 70.43 | 70 | 67.16 | ||||||
| 80 | 72.59 | 80 | 69.12 | ||||||
| 90 | 74.72 | 90 | 71.04 | ||||||
| 100 | 76.61 | 100 | 72.75 | ||||||
| 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 80.71 | 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 76.44 | ||||
| 150 | 84.19 | 150 | 79.55 | ||||||
| 175 | 87.52 | 175 | 82.51 | ||||||
| 200 | 90.25 | 200 | 84.94 | ||||||
| 275 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 59.40 | L1-20 h | 275 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 57.80 | |
| 30 | 63.22 | 30 | 61.41 | ||||||
| 40 | 66.34 | 40 | 64.35 | ||||||
| 50 | 69.14 | 50 | 66.98 | ||||||
| 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 71.61 | 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 69.29 | ||||
| 70 | 73.89 | 70 | 71.43 | ||||||
| 80 | 75.77 | 80 | 73.18 | ||||||
| 90 | 77.64 | 90 | 74.92 | ||||||
| 100 | 79.30 | 100 | 76.47 | ||||||
| 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 83.34 | 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 80.22 | ||||
| 150 | 87.11 | 150 | 83.70 | ||||||
| 175 | 90.50 | 175 | 86.83 | ||||||
| 200 | 93.64 | 200 | 89.72 | ||||||
| 550 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 69.97 | L1-20 h | 550 | 20 | Particle rearrangement stage | 68.88 | |
| 30 | 72.89 | 30 | 71.71 | ||||||
| 40 | 75.29 | 40 | 74.03 | ||||||
| 50 | 77.39 | 50 | 76.06 | ||||||
| 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 79.33 | 60 | Elastic deformation stage | 77.94 | ||||
| 70 | 80.97 | 70 | 79.52 | ||||||
| 80 | 82.58 | 80 | 81.07 | ||||||
| 90 | 84.06 | 90 | 82.50 | ||||||
| 100 | 85.47 | 100 | 83.85 | ||||||
| 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 88.66 | 125 | Plastic deformation stage | 86.92 | ||||
| 150 | 91.46 | 150 | 89.61 | ||||||
| 175 | 94.06 | 175 | 92.10 | ||||||
| 200 | 96.48 | 200 | 94.42 |
Estimation of the size and strain for different milled time durations of Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 LWHEA powders_
| Sample/model | Parameter | Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 (0 h) | Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 (5 h) | Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 (10 h) | Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 (20 h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scherrer | Size (D) (nm) | 1422.14 | 1066.7100 | 719.3300 | 618.4100 |
| W-H UDM | Size (D) (nm) | 90.5700 | 89.0300 | 81.3200 | 73.7200 |
| Strain (ε) (%) | 0.0002 | 0.0013 | 0.0044 | 0.0097 | |
| W-H USDM | Size (D) (nm) | 47.0200 | 44.5000 | 34.5800 | 30.8000 |
| Strain (ε) (%) | 0.0004 | 0.0011 | 0.0032 | 0.0043 | |
| SSP | Size (D) (nm) | 98.0400 | 60.2200 | 54.1900 | 42.5300 |
| Strain (ε) (%) | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | 0.0010 | 0.0030 |
Properties of the elements used in the present study to develop the Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 alloy_
| Element | Atomic number | Atomic radius (nm) | Pauling electronegativity | VEC | Atomic weight | Melting temperature (K) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | 24 | 0.1249 | 1.660 | 6 | 51.9961 | 2,180 | 7.2 |
| Al | 26 | 0.1241 | 1.833 | 8 | 55.8450 | 1,811 | 7.9 |
| Ti | 13 | 0.1432 | 1.610 | 3 | 26.9815 | 933 | 2.7 |
| Li | 27 | 0.1251 | 1.880 | 9 | 58.9332 | 1,768 | 8.9 |
| Si | 14 | 0.1153 | 1.900 | 4 | 28.0855 | 1,687 | 2.3 |
Enthalpy of mixing ( H mix AB {H}_{\text{mix}}^{\text{AB}} ) between each pair of elements in the Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 developed alloy_
| Element | Mg | Al | Ti | Li | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Mg | −2 | 16 | 0 | −26 |
| Al | −2 | Al | −30 | −4 | −19 |
| Ti | 16 | −30 | Ti | 34 | −66 |
| Li | 0 | −4 | 34 | Li | −30 |
| Si | −26 | −19 | −66 | −30 | Si |
Physicochemical and thermodynamic properties for the Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 developed alloy powders via MA_
| Alloy code | Mixing enthalpy, ΔH mix (kJ/mol) | Entropy of mixing, ΔS mix (J/mol K) | Gibbs free energy, | Melting temperature, T m (K) | Thermodynamic parameter, Ω | Mean atomic radius, | Atomic size difference, δ (%) | Valency electron concentration, VEC | Difference in Pauling electronegativity, | Density, ρ (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1-0, L1-5, L1-10, and L1-20 | −0.4205 | 11.42 | −3,823 | 855.8 | 15.82 | 0.1504 | 5.93% | −0.4205 | 11.42 | 1.704 |
Ball milling processing parameters of the developed Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 LWHEA_
| Alloy code | Chemical composition | PBR | Milling speed | Milling time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1-0 | Mg30-Al25-Ti25-Li15-Si5 | 15:1 | 300 rpm | 0 (premixed Conditions) |
| L1-5 | 5 | |||
| L1-10 | 10 | |||
| L1-20 | 20 |