Fig. 1
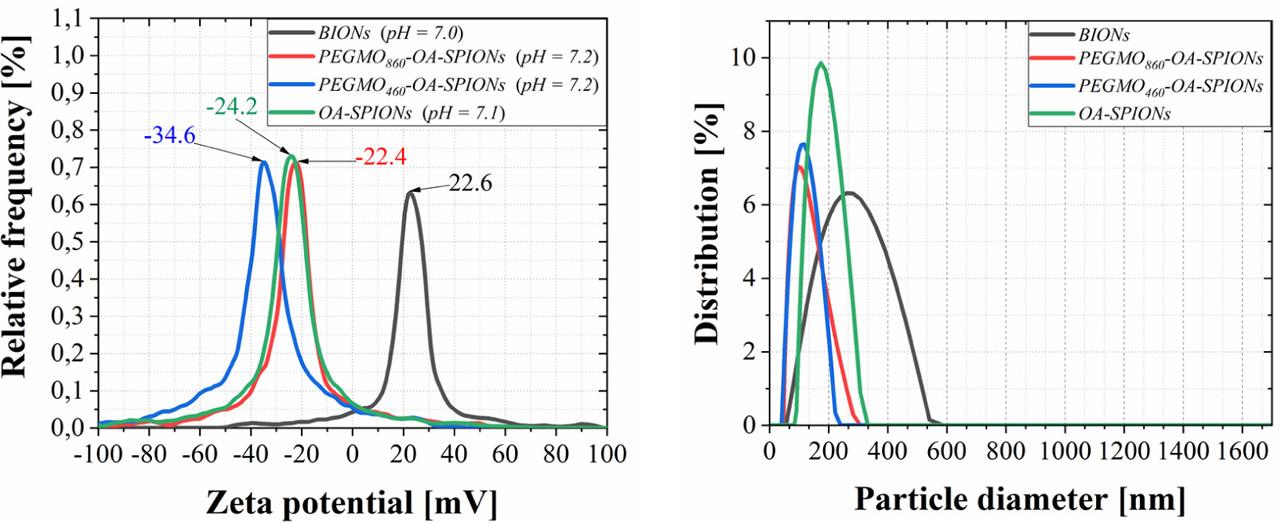
Fig. 2
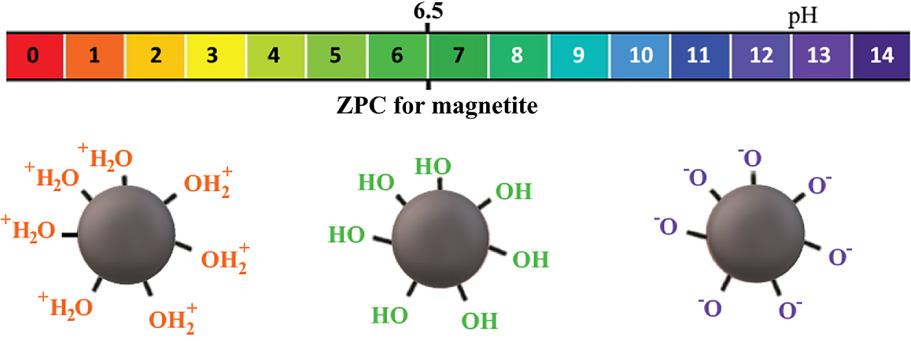
Fig. 3
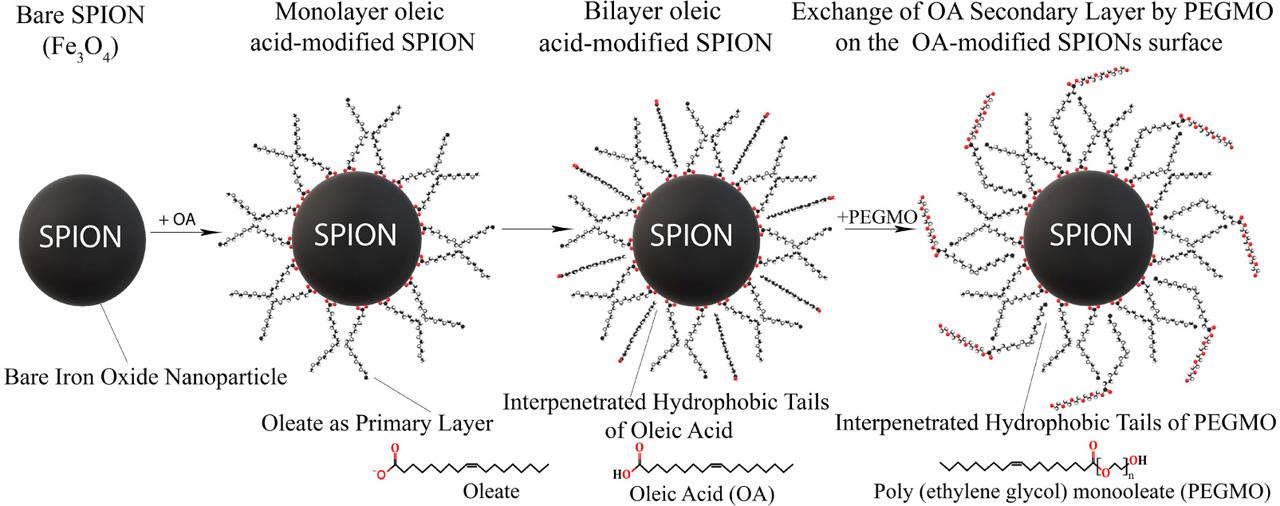
Fig. 4
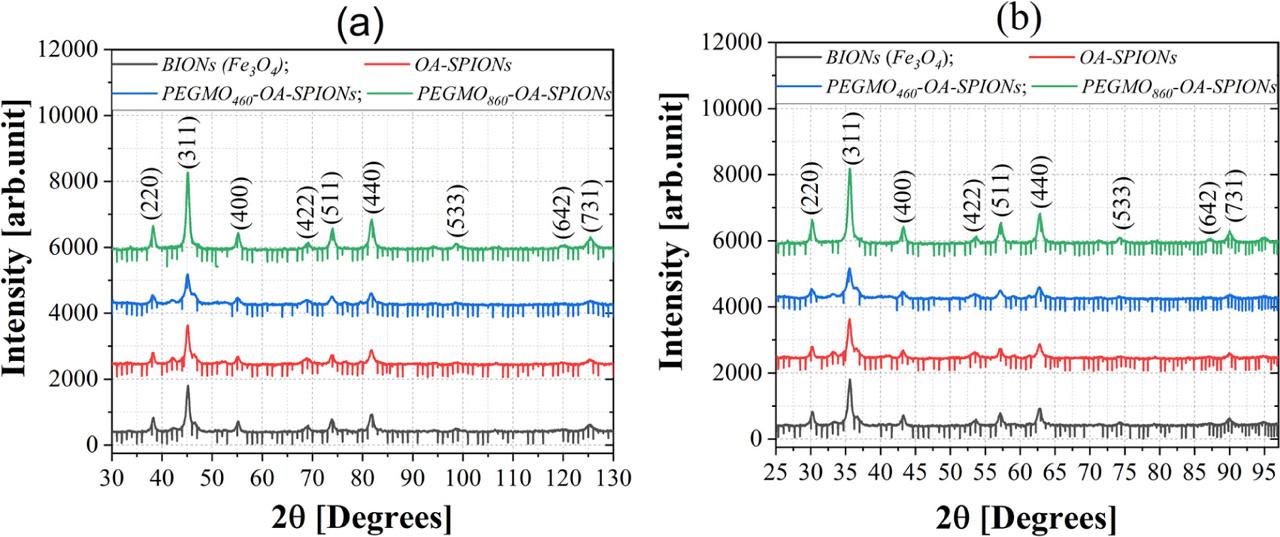
Fig. 5
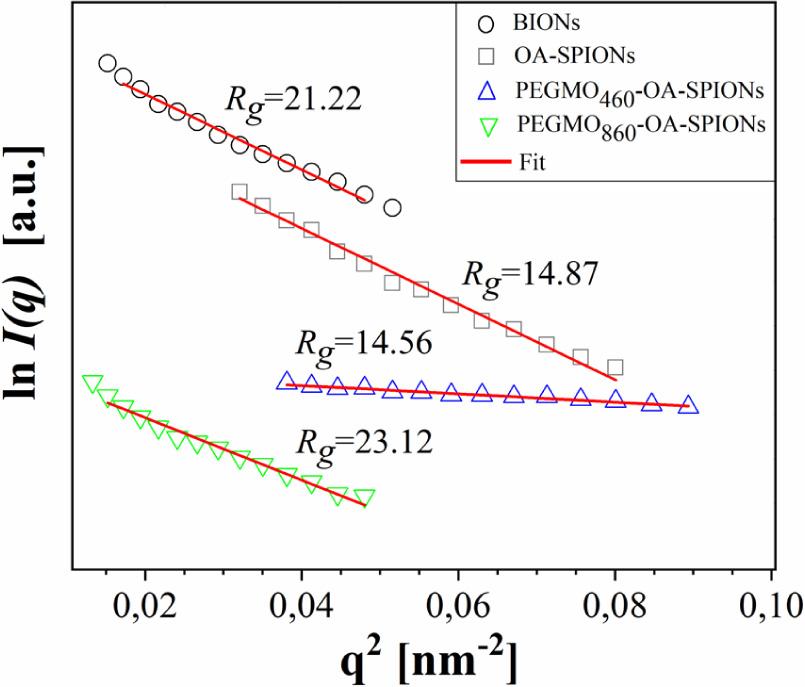
Fig. 6
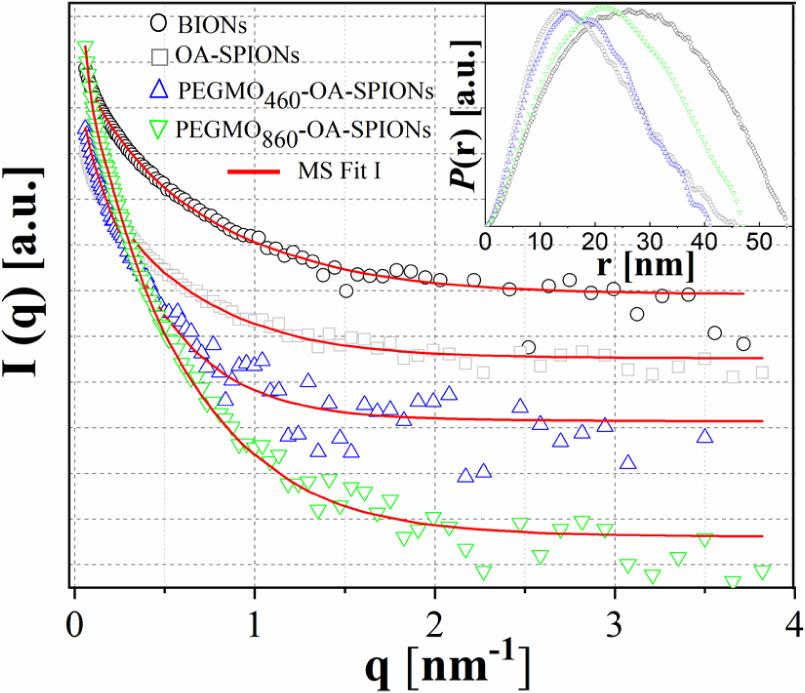
Fig. 7
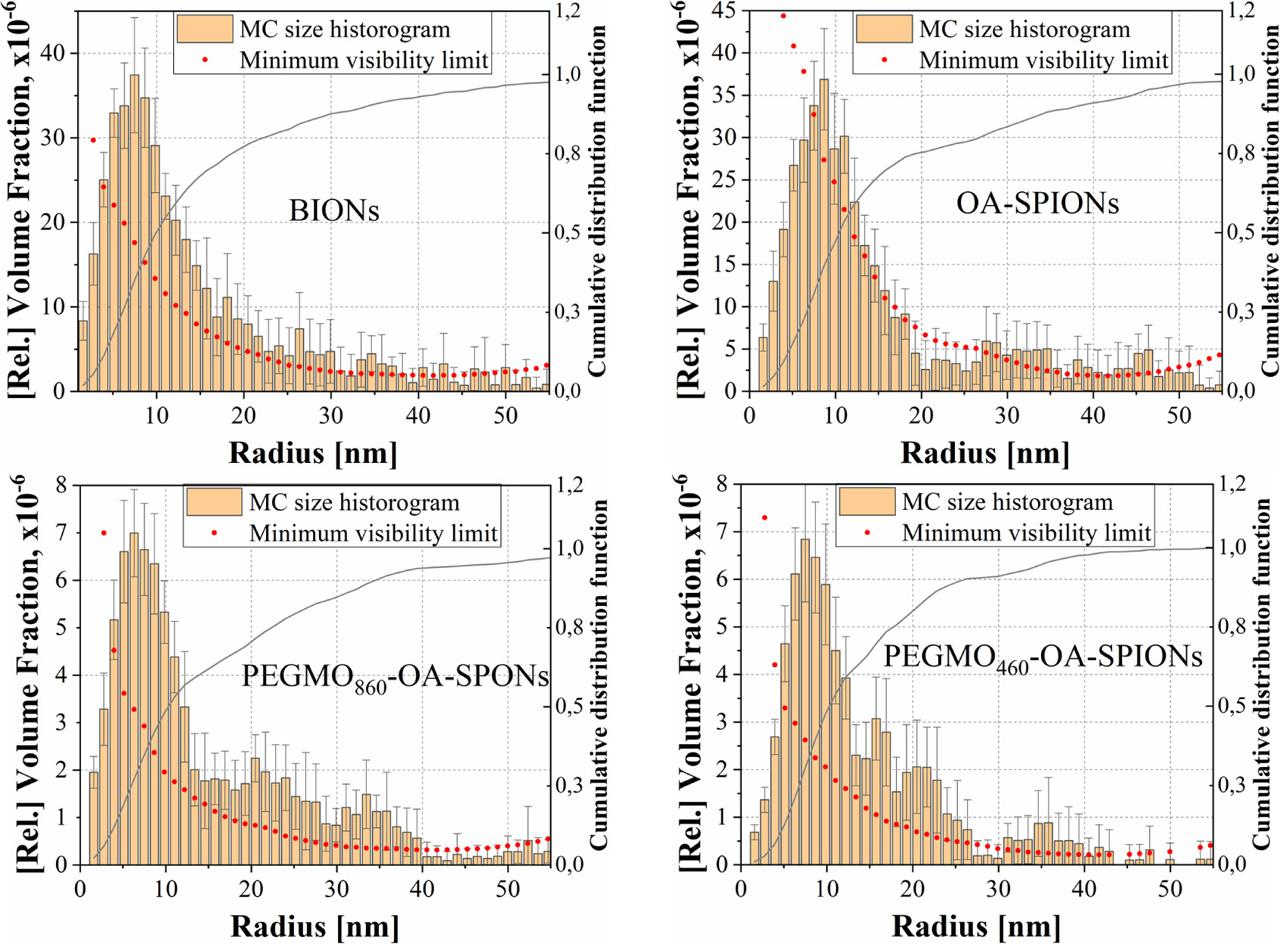
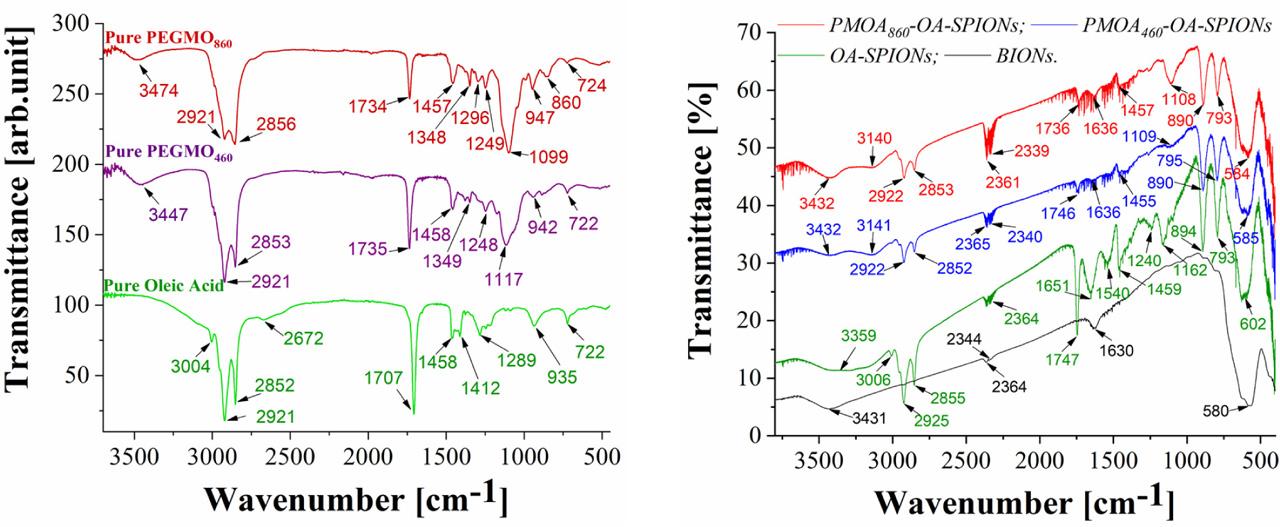
Fig. 8
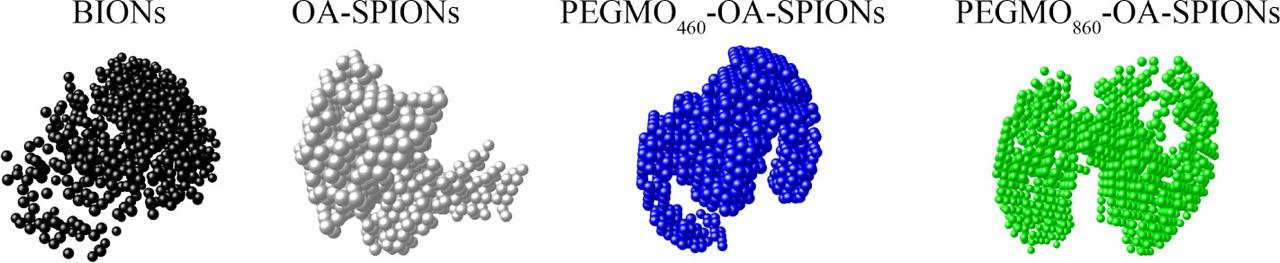
Fig. 9
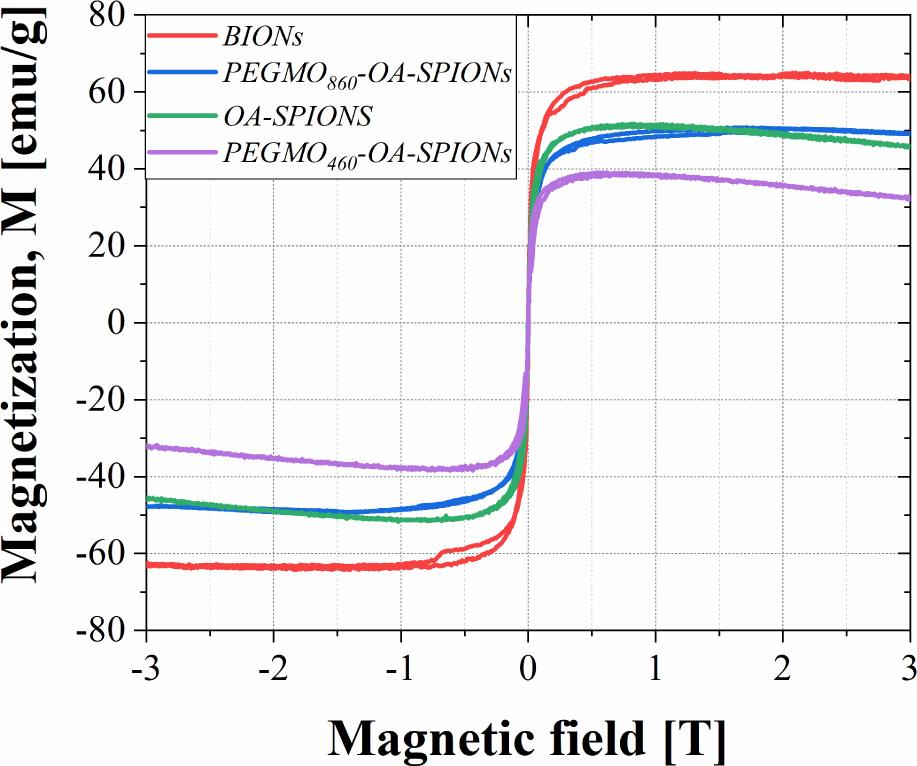
Fig. 10
Nanoparticles average size obtained by SAXS measurement_
| Sample | Average radius of nanoparticles obtained by SAXS (nm) |
|---|---|
| BIONs | 14.6 |
| OA–SPIONs | 15.8 |
| PEGMO460–OA–SPIONs | 14.0 |
| PEGMO860–OA–SPIONs | 15.5 |
Saturation magnetization of the samples_
| Samples | Saturation magnetization Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|
| BIONs (Fe3O4) | 64.6 (Ha = 1.07 T) |
| OA-SPIONs | 51.1 (Ha = 1.07 T) |
| PEGMO460-OA-SPIONs | 39.0 (Ha = 1.00 T) |
| PEGMO860-OA-SPIONs | 48.9 (Ha = 1.07 T) |
ELS and DLS Experimental results of samples_
| Samples | Measurement temperature °C | Mean value of potential (mV) | Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) | Polydispersity index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIONs | 20 | 21.7 | 225 | 20.6 |
| OA-SPIONs | 20 | −24.2 | 182 | 22.0 |
| PEGMO860-OA-SPIONs | 20 | −23.3 | 101 | 19.5 |
| PEGMO460-OA-SPIONs | 20 | −34.5 | 110 | 23.2 |
Average crystallite size of the samples calculated by Scherrer formula_
| Sample | Average size of crystallite estimated by XRD (Fe Kα; λ = 1.937Å) (nm) | Crystalline lattice parameter (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| BIONs | 20.0 | 8.3755 |
| OA–SPIONs | 21.8 | 8.3755 |
| PEGMO460–OA–SPIONs | 21.0 | 8.3725 |
| PEGMO860–OA–SPIONs | 23.1 | 8.3725 |