Fig. 1
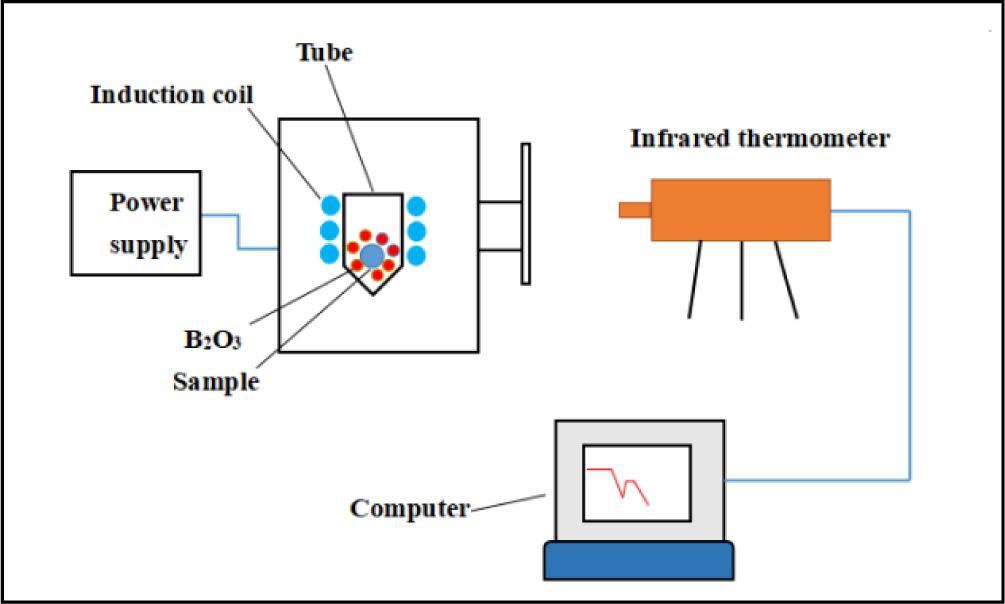
Fig. 2
![Microstructure of Cu55Ni45 alloy under different undercooling degrees. [(A) ΔT = 47 K, (B) ΔT = 68 K, (C) ΔT = 70 K, (D) ΔT = 91 K, (E) ΔT = 187 K, (F) ΔT = 227 K, (G) ΔT = 272 K, (H) ΔT = 284 K].](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/64725287215d2f6c89dc41c3/j_msp-2021-0027_fig_002.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251204%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251204T124445Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=bf8b3857c7b7e66953eb6ff78919aec0e8c9ae5439d374a15aab650e5a5eedbd&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
Fig. 3
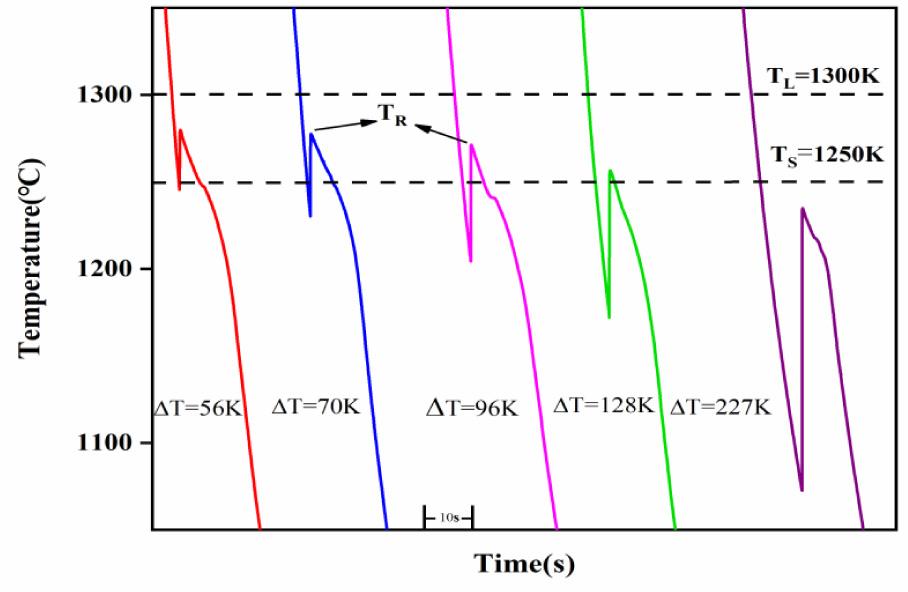
Fig. 4
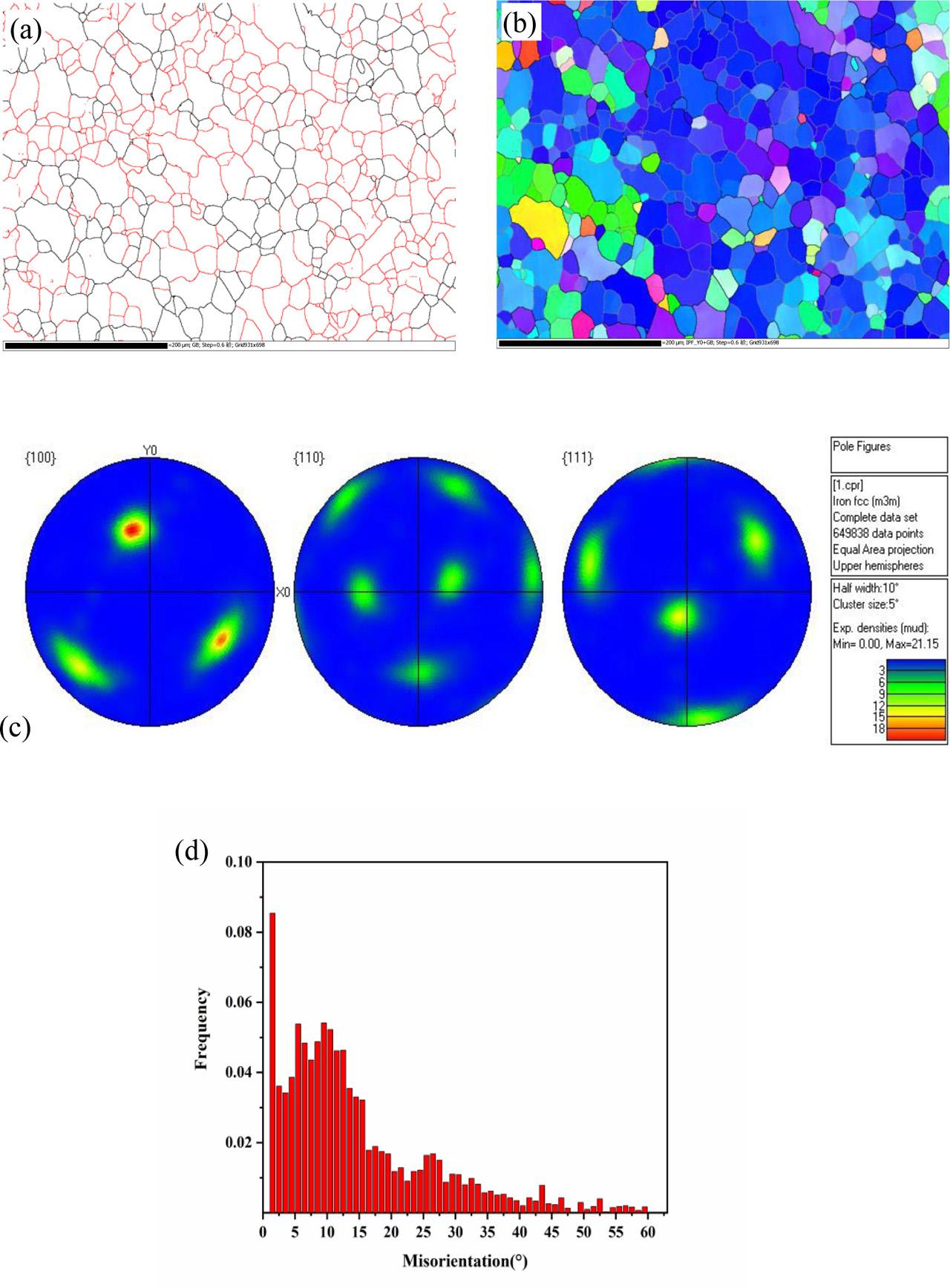
Fig. 5
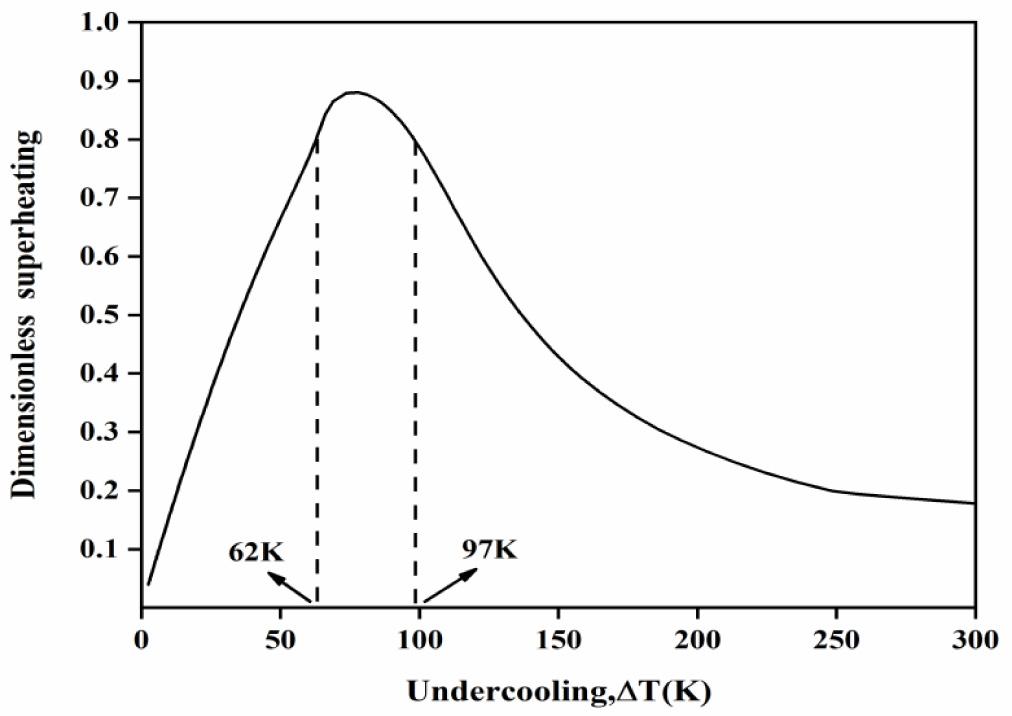
Fig. 6
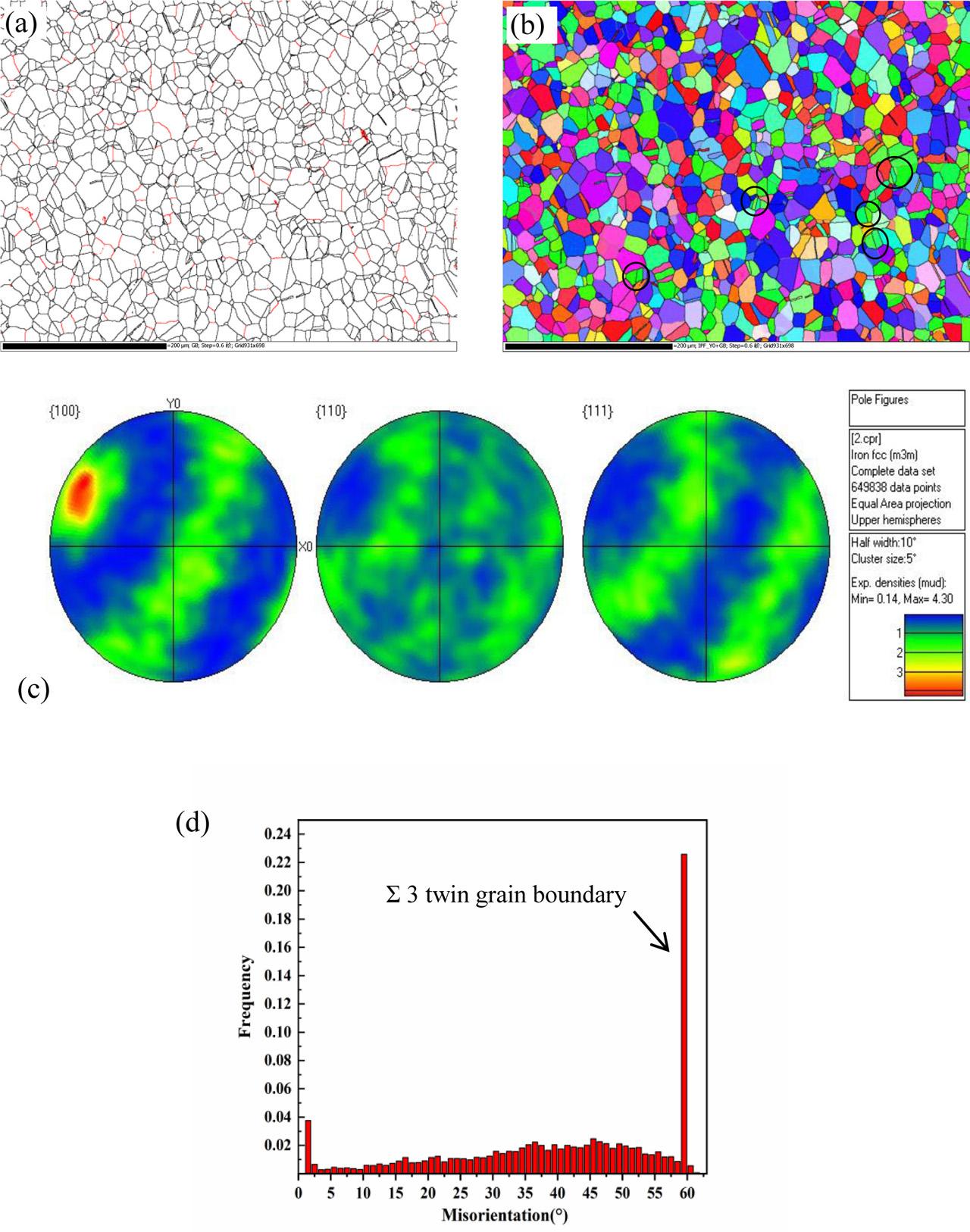
Fig. 7
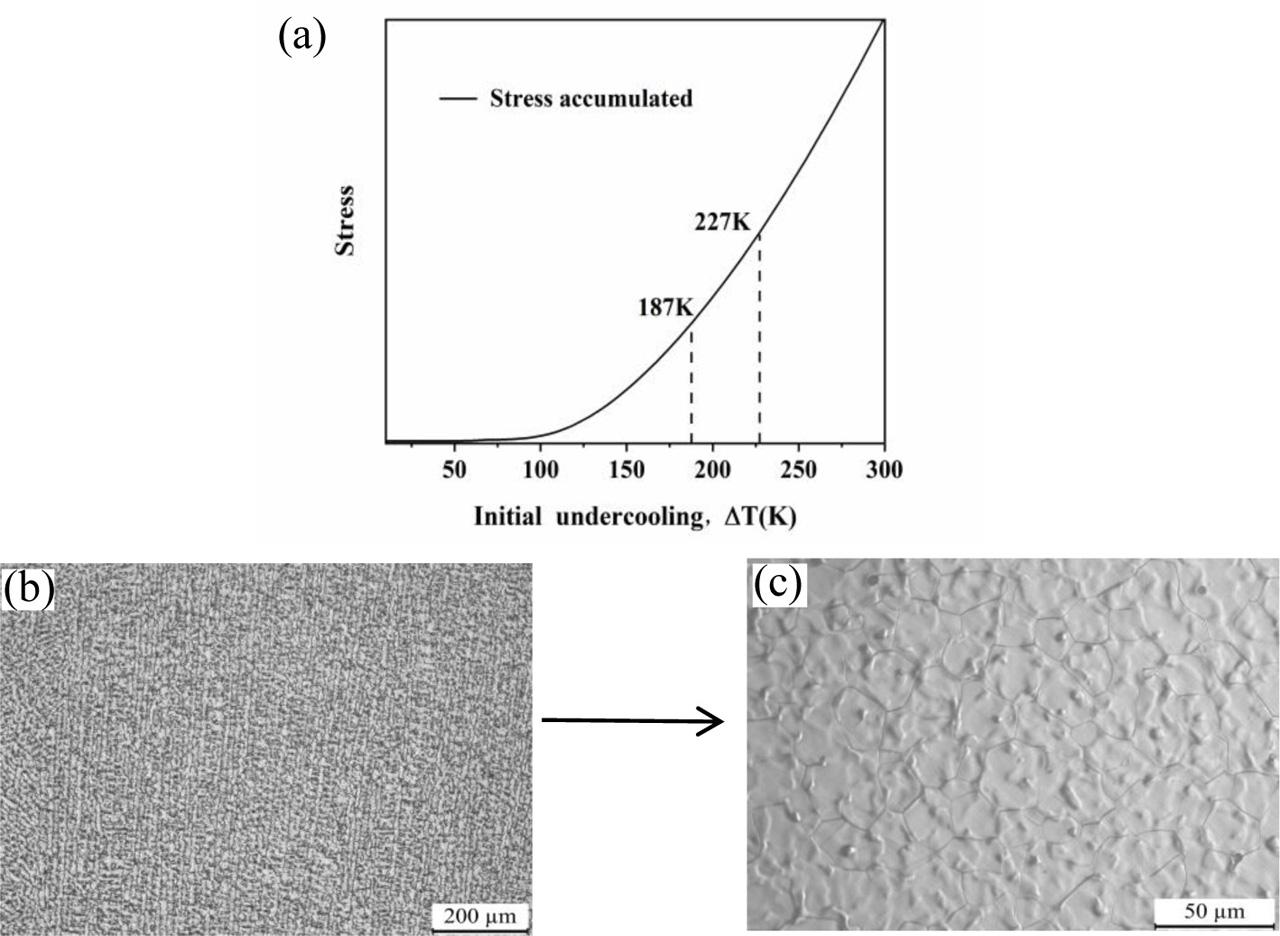
Fig. 8
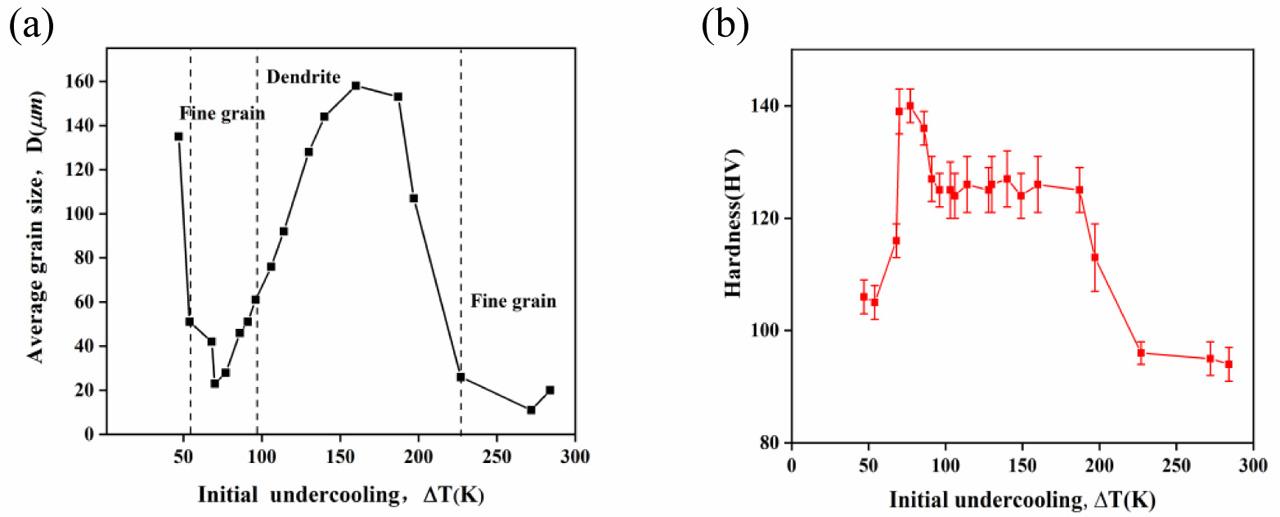

![Microstructure of Cu55Ni45 alloy under different undercooling degrees. [(A) ΔT = 47 K, (B) ΔT = 68 K, (C) ΔT = 70 K, (D) ΔT = 91 K, (E) ΔT = 187 K, (F) ΔT = 227 K, (G) ΔT = 272 K, (H) ΔT = 284 K].](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/64725287215d2f6c89dc41c3/j_msp-2021-0027_fig_002.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251204%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251204T124445Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=bf8b3857c7b7e66953eb6ff78919aec0e8c9ae5439d374a15aab650e5a5eedbd&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)






© 2021 Hongfu Wang, Cheng Tang, Hongen An, Yuhong Zhao, published by Wroclaw University of Science and Technology
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.