Figure 1
Figure 2
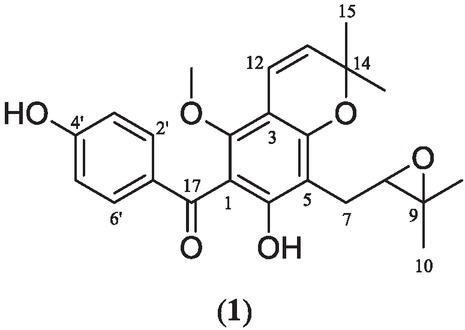
Figure 3
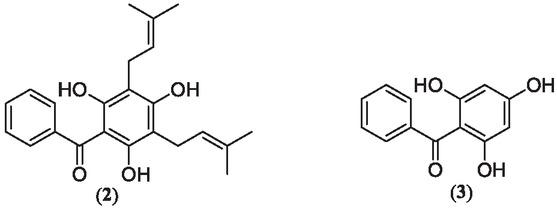
Figure 4
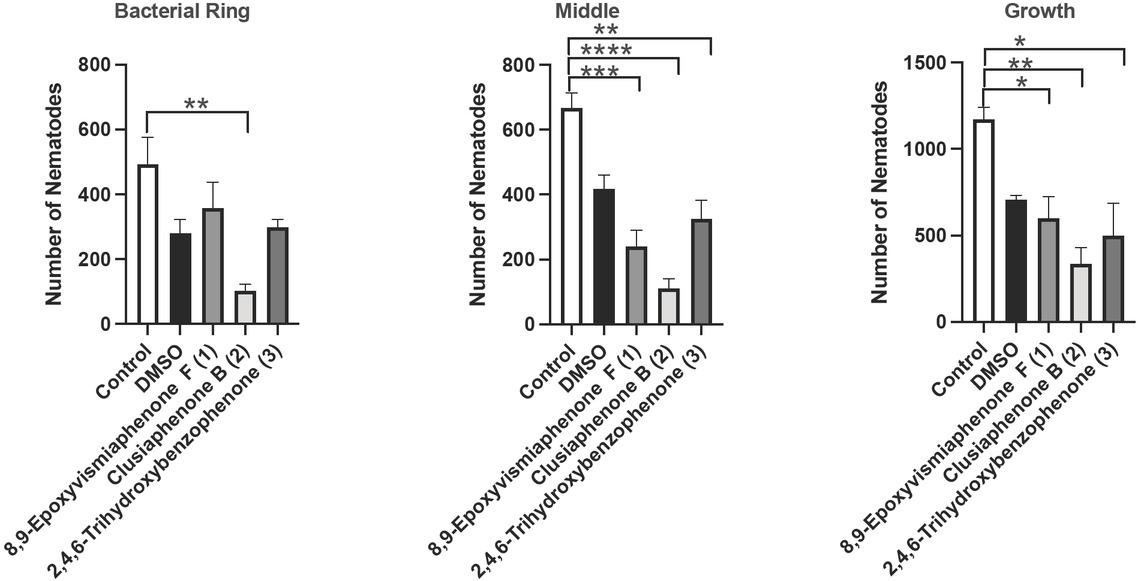
Figure 5
1H and 13C NMR data for 8,9-epoxyvismiaphenone F (1) in CDCl3_
| Position | δC | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 107.5 | |
| 2 | 160.3 | |
| 3 | 103.8 | |
| 4 | 153.1 | |
| 5 | 110.4 | |
| 6 | 152.9 | |
| 7a | 26.0 | 2.65 (dd, 17.3, 5.6) |
| 7b | 2.90 (dd, 17.3, 5.2) | |
| 8 | 69.0 | 3.70 (dd, 5.2, 5.6) |
| 9 | 77.6 | |
| 10 | 21.6 | 1.10 (s) |
| 11 | 24.2 | 1.2 (s) |
| 12 | 116.8 | 6.50 (d, 9.9) |
| 13 | 127.4 | 5.52 (d, 9.9) |
| 14 | 77.6 | |
| 15 | 28.0 | 1.44 (s) |
| 16 | 28.1 | 1.44 (s) |
| 17 | 193.9 | |
| 1′ | 131.6 | |
| 2′ | 132.1 | 6.80 (d, 8.8) |
| 3′ | 115.2 | 7.75 (d, 8.8) |
| 4′ | 160.3 | |
| 5′ | 115.2 | 7.75 (d, 8.8) |
| 6′ | 132.1 | 6.80 (d, 8.8) |
| OCH3 | 63.4 | 3.67 (s) |