Fig. 1.
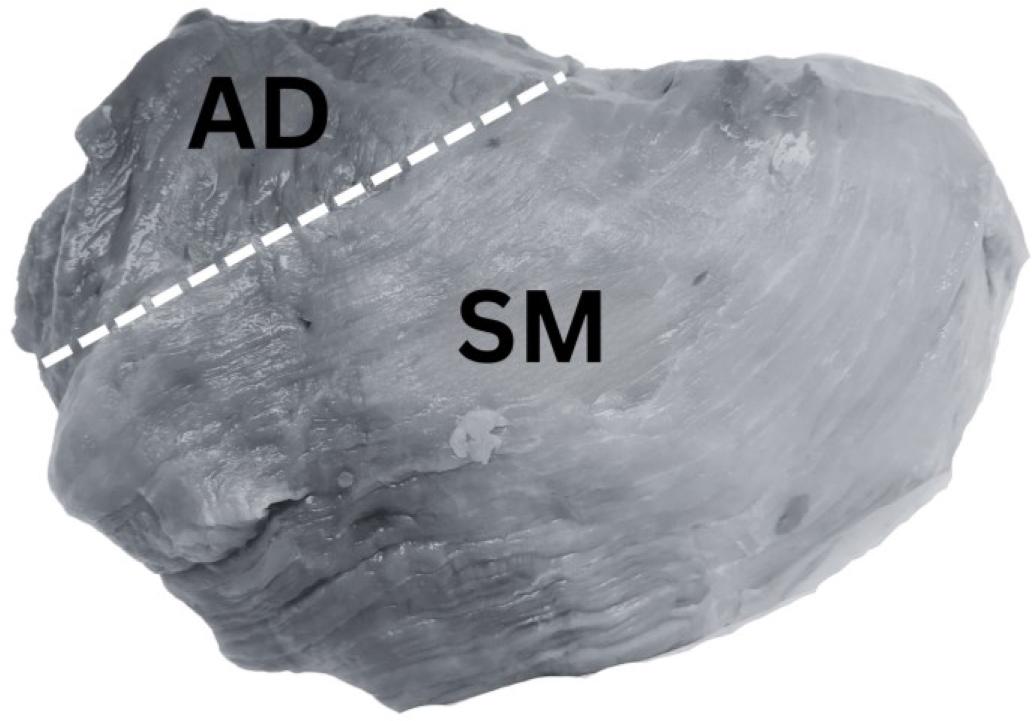
Fig. 2.
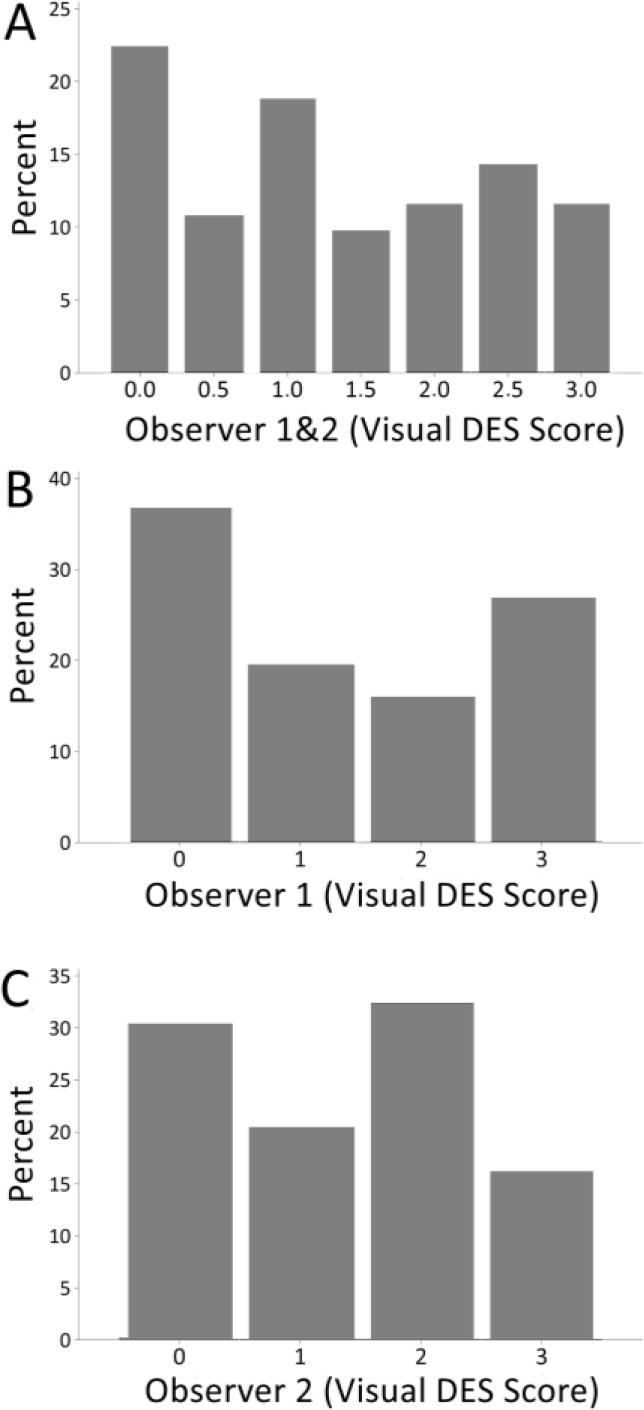
Fig. 3.
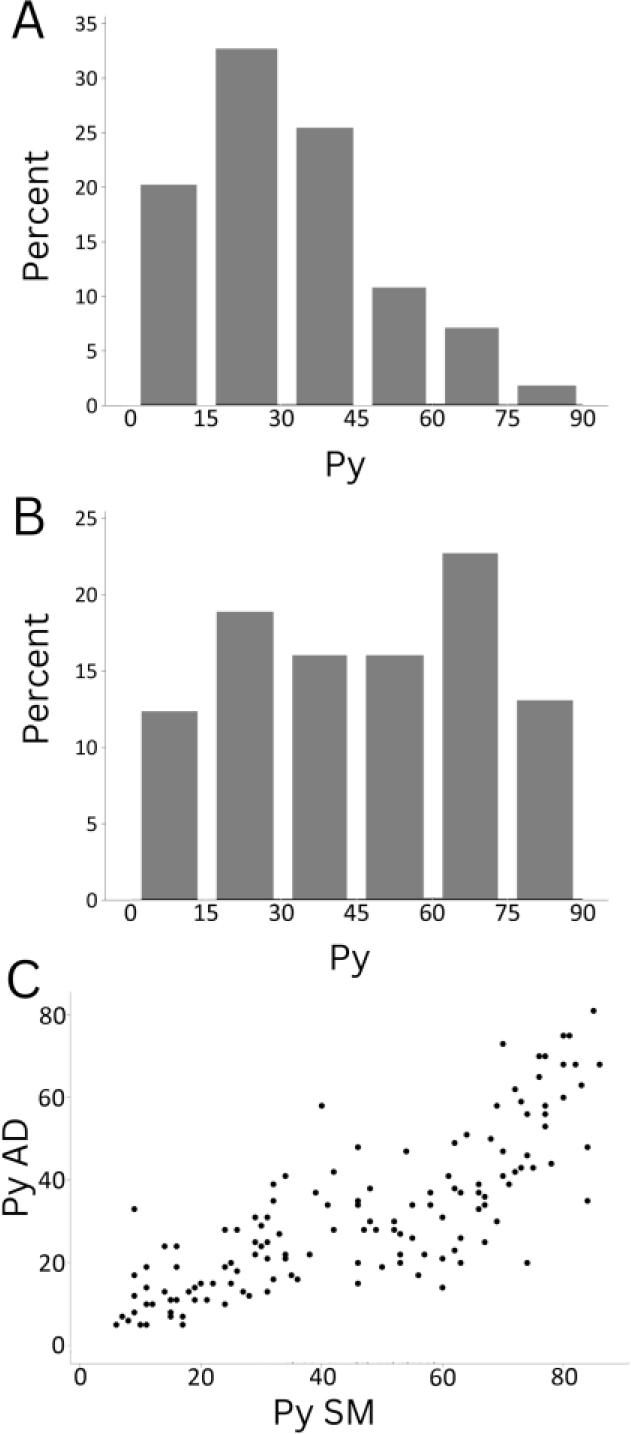
Fig. 4.
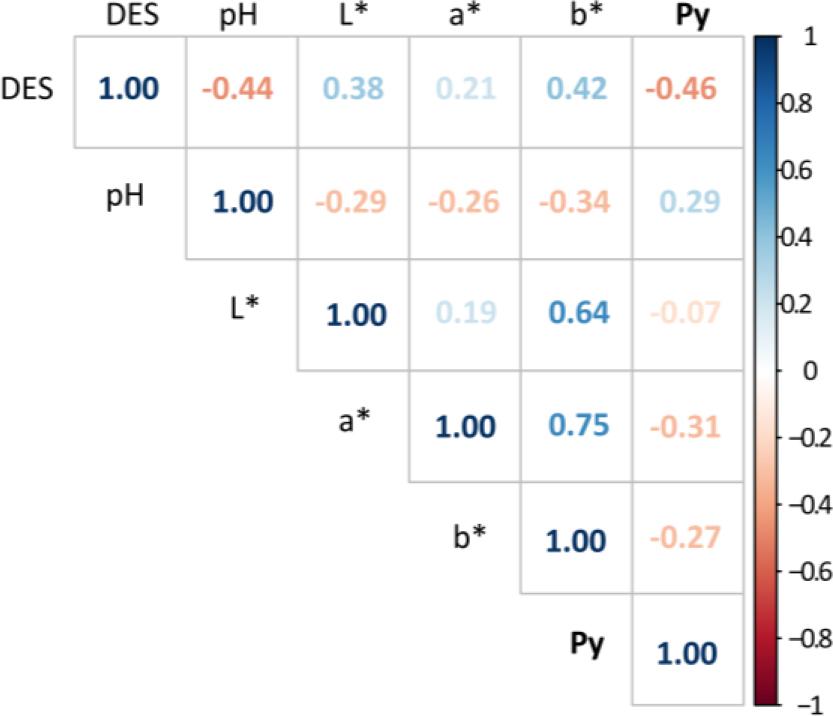
Estimated coefficients of the model statistics with P values_
| Estimate | SE | tSTAT | P - Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | −82.022 | 74.573 | −1.0999 | 0.274 |
| pHu | 17.343 | 13.121 | 1.3217 | 0.189 |
| L* | 2.3323 | 1.5671 | 1.4883 | 0.139 |
| a* | 0.85357 | 0.38534 | 2.2151 | 0.029 |
| b* | 0.21135 | 0.089393 | 2.3643 | 0.02 |
| Py | −0.83391 | 0.27336 | −3.0506 | 0.003 |
| pHu x L* | −0.54006 | 0.2669 | −2.0235 | 0.045 |
| pHu x Py | 0.11651 | 0.045719 | 2.5484 | 0.012 |
| L* x Py | 0.0033977 | 0.0011399 | 2.9807 | 0.003 |
| L*2 | 0.0054231 | 0.0029521 | 1.837 | 0.069 |
| a*2 | −0.035111 | 0.013828 | −2.5392 | 0.012 |
The four-rank visual DES scoring scheme for destructured ham cuts, including the semimembranosus and adductor muscle_ Scoring was based on evaluating structural disintegration and visual color (adapted from [19, 24])_
| Score | ||||
| Visual colour | Reddish (> 3) | From pale to reddish (1 - 3) | Very pale (1 - 2) | |
| Muscle structure defect | Compact fibre structure | Absence of fibrillar structure in the affected area Destructured meat | Absence of fibrillar structure in the affected area Soft and doughy, destructured meat Fluid exudate | |
| Area affected | None | Small areas on the surface with single patches of destructured zones | More than 50% of both muscle areas Lesions beneath the surface | |
| Observations | No visible defects | Small, pale areas on the surface | Lesion less than approx. 2cm in depth | Lesion more than approx. 2cm in depth |