Figure 1:

Figure 2:

Figure 3:

Figure 4:
SEs’ growth challenges_
| Growth challenges | SEs | SEs’ advisors | SEs’ partners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not enough expertise on how to grow the business | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Not enough personnel with the requisite skills and experience | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Not enough money for investment in growth | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Not enough demand for services/products | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Not enough active commitment from board members | 5 | 5 | 5 |
A summary of the respondents’ origin_
| Country | SEs | SEs’ advisors | SEs’ partners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greece | 25 | 5 | 5 |
| Ireland | 25 | 5 | 4 |
| Italy | 25 | 5 | 4 |
| Slovenia | 19 | 5 | 7 |
| Total | 94 | 20 | 20 |
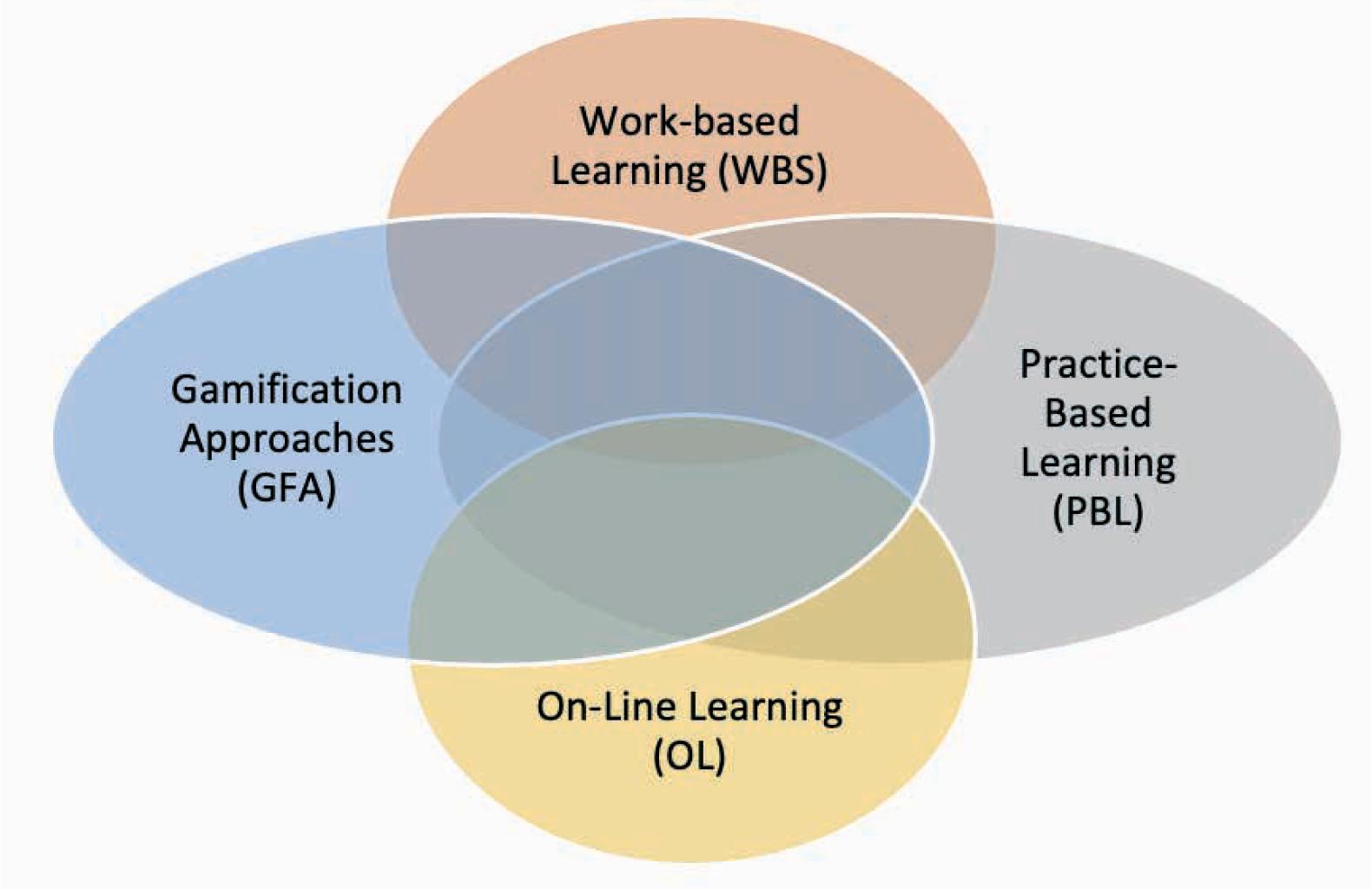
An overview of SocialB’s Modules and Learning Units_
| Modules | Learning Units |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction to SE | Unit 1 – History and evolution of SE in Europe |
| 2. Project Design and Management | Unit 5 – EU projects – EU opportunities for the development and funding of SEs |
| 3. Human resources | Unit 9 – The role of human resource management |
| 4. Social impact assessment | Unit 13 – Introduction to Social Impact Assessment |
| 5. Financial and Sustainability for SE | Unit 17 – Strategic planning and the life cycle of SEs |
| 6. Growth Strategies, Marketing and Fundraising for SE | Unit 21 – Growth strategies and long-term profitability of SE projects |
SEs’ growth areas_
| SEs’ growth areas |
|---|
| Employing more paid staff |
| Generating more income through securing grants/government funding |
| Expanding new products and services to the existing customer base |
| Growth of geographic spread of the organisation’s services/goods |
| Generating more income through the trading of goods/services |
| Including new target groups and widening our customer base |
| Using resources innovatively to expand services/product range |
| Franchising strategy and/or operational partnerships |
The operational aspects of SEs’ management function_
| Operational aspects of SEs’ management function |
|---|
| Insufficient paid staff resources & funding to recruit required staff |
| Meeting/responding to increased demand for services/goods they provide |
| Unsustainability due to low level of income generated for services/goods we provide |
| Lack of marketing expertise, to connect with customers/target group |
| Over-reliance on statutory funding (grants, state funding programmes, etc.) |
| Availability of appropriate, accessible training for staff |
| Lack of skills and experience within the organisation to develop and expand services and income |
| Lack of opportunities for networking with critical stakeholders and other SE organisations that share the same social vision |
| Limited involvement in the development of future direction and planning |
| Lack of market knowledge and competitiveness |
| Quality management procedures |
| Speed of decision-making |
| Over-reliance on volunteers |
Training and learning methods/Barriers to training participation_
| Training and learning methods |
|---|
| In-class Training (face-to-face) |
| Work-based Learning |
| Online Training – own time |
| Online Training – class |
| Blended learning |
| Seminars – guest SEs |
| Shadowing SE staff |
| One-to-one Mentoring & Homework |
| Barriers to training participation |
| Lack of accessible/available training courses on relevant subjects |
| Lack of basic skills, training and knowledge in relevant subjects |
| Lack of staff capacity |
| Unavailability of funding to pay for further training |
| Lack of available time |
| Lack of learning culture |
A priority list of skills and expertise needs for SEs_
| Skills and expertise needs | Priority 1 Skills Needs | Priority 2 Skills Needs | Priority 3 Skills Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expertise in how to maintain sustainability and growth | √ | ||
| Financial planning and management, including risk management, internal auditing, etc. | √ | ||
| Communication, sales & marketing skills | √ | ||
| Soft skills, e.g. interpersonal skills, listening, etc. | √ | ||
| Developing and motivating staff | √ | ||
| Fundraising and funding from different resources | √ | ||
| Business & Strategic Planning | √ | ||
| Project Management skills | √ | ||
| Procurement and how to win contracts | √ | ||
| Skills to monitor & assess Social Impact | √ | ||
| IT and online communications technology (ICT) | √ | ||
| Governance and leadership for SEs | √ | ||
| Networking with stakeholders, collaborative partnerships, and alliances | √ | ||
| Gaining and sustaining community buy-in and market acceptance | √ | ||
| Managing multiple bottom lines | √ |
The phases of the study_
| Phases | Goals |
|---|---|
| Phase 1 (desk research: existing data collection) | Compile data about the respondents’ organisations, board structure, operational structure, and training needs |
| Phase 2 (qualitative: semi-structured interviews) | Identify key challenges in the SE field of management, growth and sustainability |
| Phase 3 (quantitative: quastionnaire) | Identify appropriate learning and training needs and associated access pathways for SEs relating to management, growth and sustainability issues |
Skill areas_
| Skill areas |
|---|
| Expertise in how to maintain sustainability and growth |
| Financial planning and management, including risk management, internal auditing, etc. |
| Communication, sales & marketing skills |
| Soft skills, e.g. interpersonal skills, listening, etc. |
| Developing and motivating staff |
| Fundraising and funding from different resources |
| Business & Strategic Planning |
| Project Management skills |
| Procurement and how to win contracts |
| Skills to monitor & assess Social Impact |
| IT and online communications technology (ICT) |
| Governance and leadership for social enterprises |
| Networking with stakeholders, collaborative partnerships, and alliances |
| Gaining and sustaining community buy-in and market acceptance |
| Managing multiple bottom lines |
A summary of the survey’s key topics
| Survey’s key issues |
|---|
| 1. Challenges in SEs’ Management Function |
| 2. Perceptions in SEs’ Sustainability |
| 3. Perceptions in SEs’ Growth |
| 4. Perceptions in SEs’ Skills and Expertise Areas |
| 5. SEs’ Training Preferences and Challenges |
Aggregate ranking of growth areas amongst the three cohorts_
| Growth areas | SEs | SEs’ advisors | SEs’ partners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employing more paid staff | 6 | 3 | 4 |
| Generating more income through securing grants/government funding | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Expanding new products and services to the existing customer base | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Growth of geographic spread of the organisation’s services/goods | 5 | 5 | 7 |
| Generating more income through the trading of goods/ services | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Including new target groups and widening our customer base | 4 | 6 | 5 |
| Using resources innovatively to expand services/ product range | 7 | 7 | 6 |
| Franchising strategy and/or operational partnerships | 8 | 8 | 8 |
SEs’ sustainability: definitions and challenges_
| SEs’ sustainability |
|---|
| Definitions (SEs are sustainable when they […]) |
| Can be financially viable and serve their social objectives |
| Make a profit, or break even, at a minimum, without support from external funding and grants |
| Retain ongoing support from the community for their mission |
| Do no harm to the environment |
| Challenges |
| Not enough strategic expertise on how to become sustainable |
| Not enough personnel with the right skills |
| Not enough demand for our services/products |
| The costs of running our organisation are too high |
| Over-reliance on statutory funding - grants, state funding programmes, etc. |
| Other |
Challenges’ priority for SEs’ management function per cohort_
| Challenges for SEs’ Management Function | Priority | |
|---|---|---|
| SEs | SEs’ advisors & partners* | |
| Insufficient paid staff resources & funding to recruit required staff | 1 | 1 |
| Meeting/responding to increased demand for services/ goods they provide | 2 | 6 |
| Unsustainability due to low level of income generated for services/goods they provide | 3 | 4 |
| Lack of marketing expertise to connect with customers/target group | 4 | 5 |
| Over-reliance on statutory funding (grants, state funding programmes, etc.) | 5 | 8 |
| Availability of appropriate, accessible training for staff | 6 | 10 |
| Lack of skills and experience within the organisation to develop and expand services and income | 7 | 2 |
| Lack of opportunities for networking with critical stakeholders and other SE organisations that share the same social vision | 8 | 9 |
| Limited involvement in the development of future direction and planning | 9 | 3 |
| Lack of market knowledge and competitiveness | 10 | 7 |