Figure 1.

Figure 2.
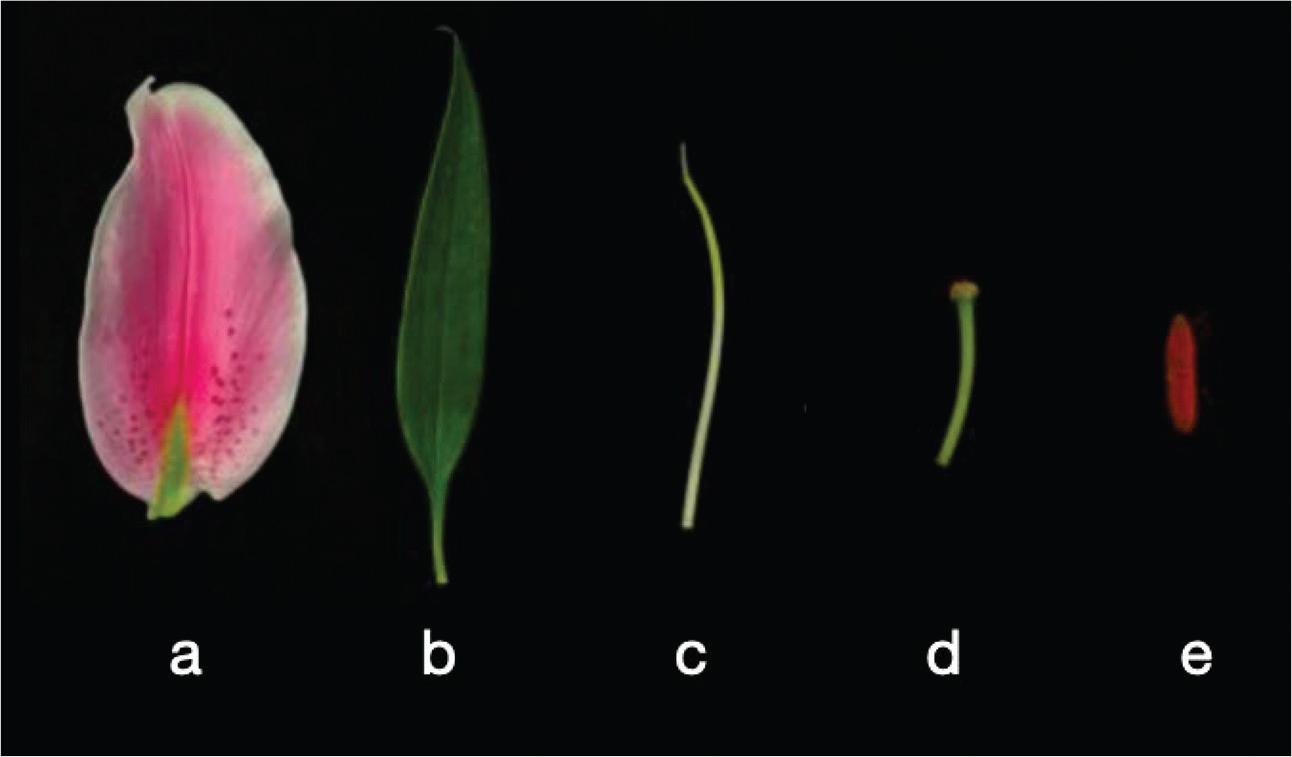
Figure 3.

Figure 4.
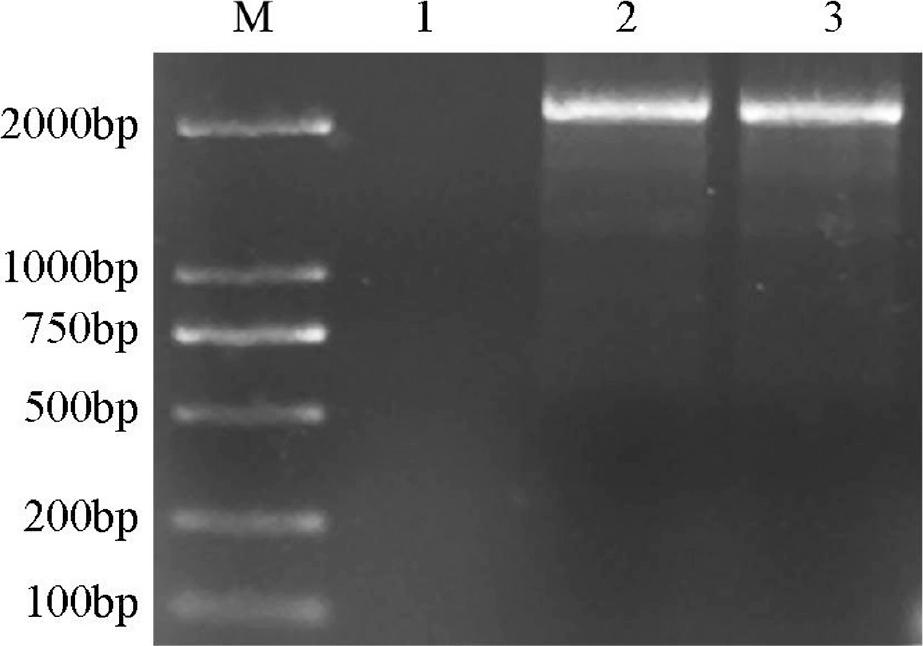
Figure 5.
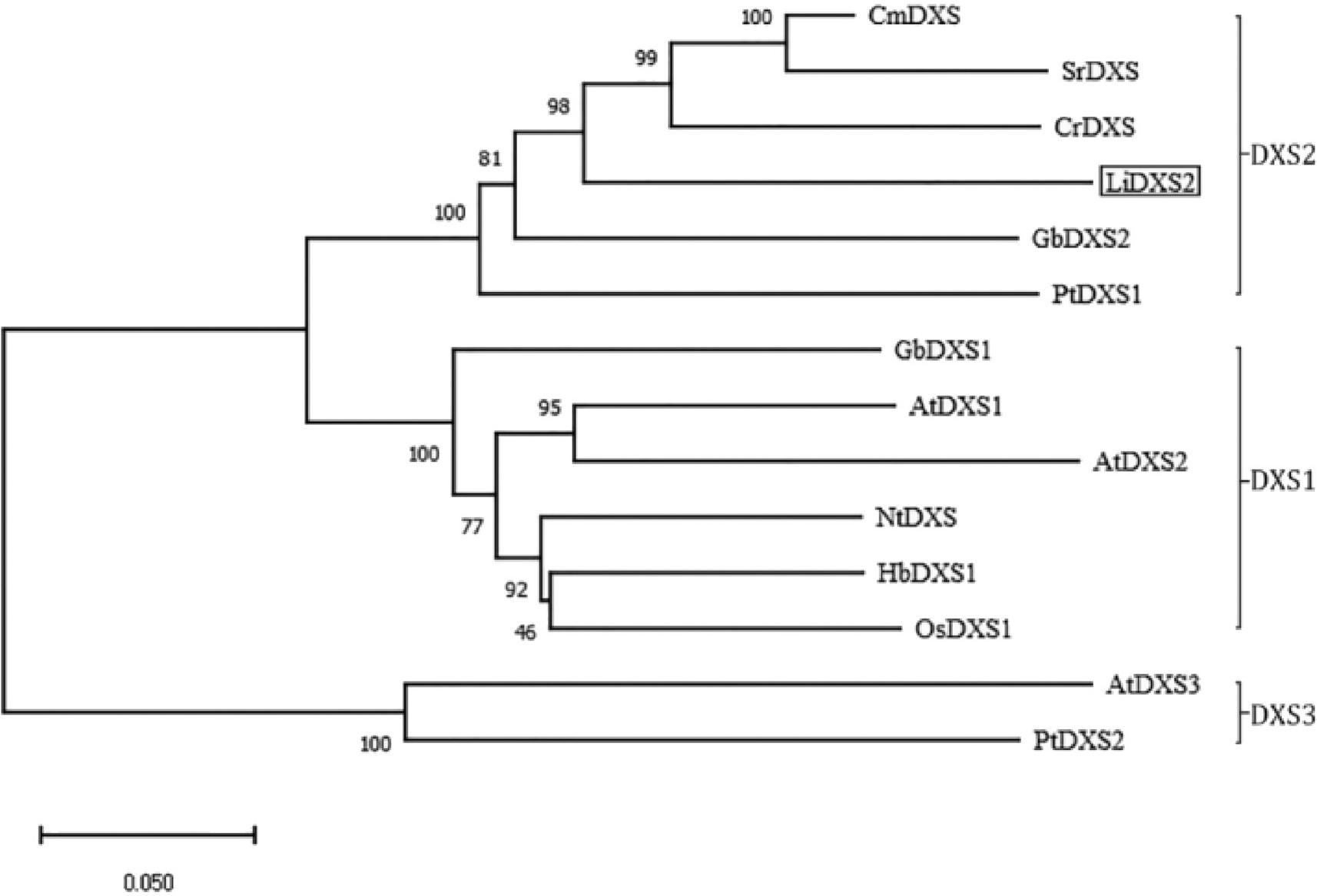
Figure 6.
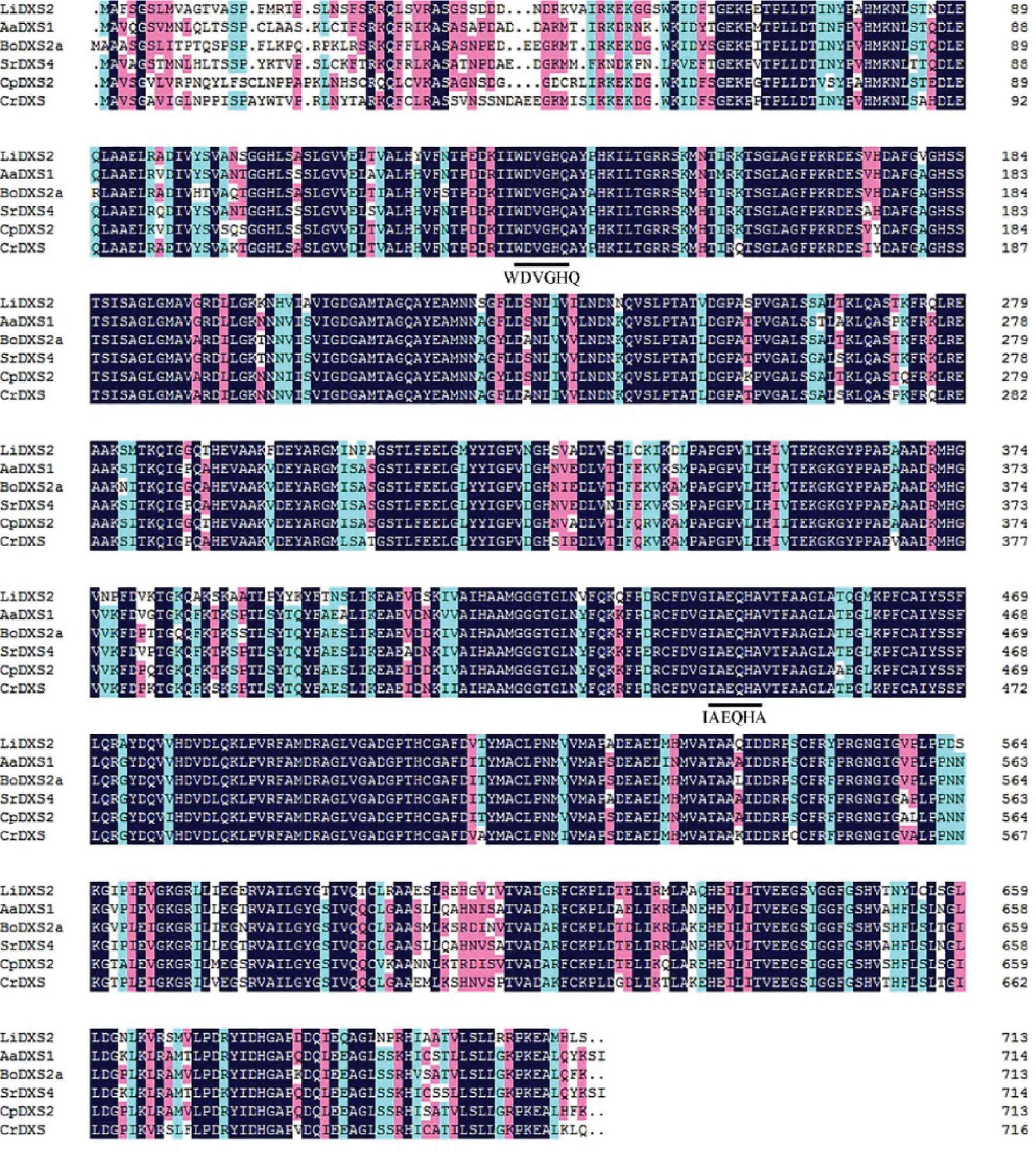
Figure 7.
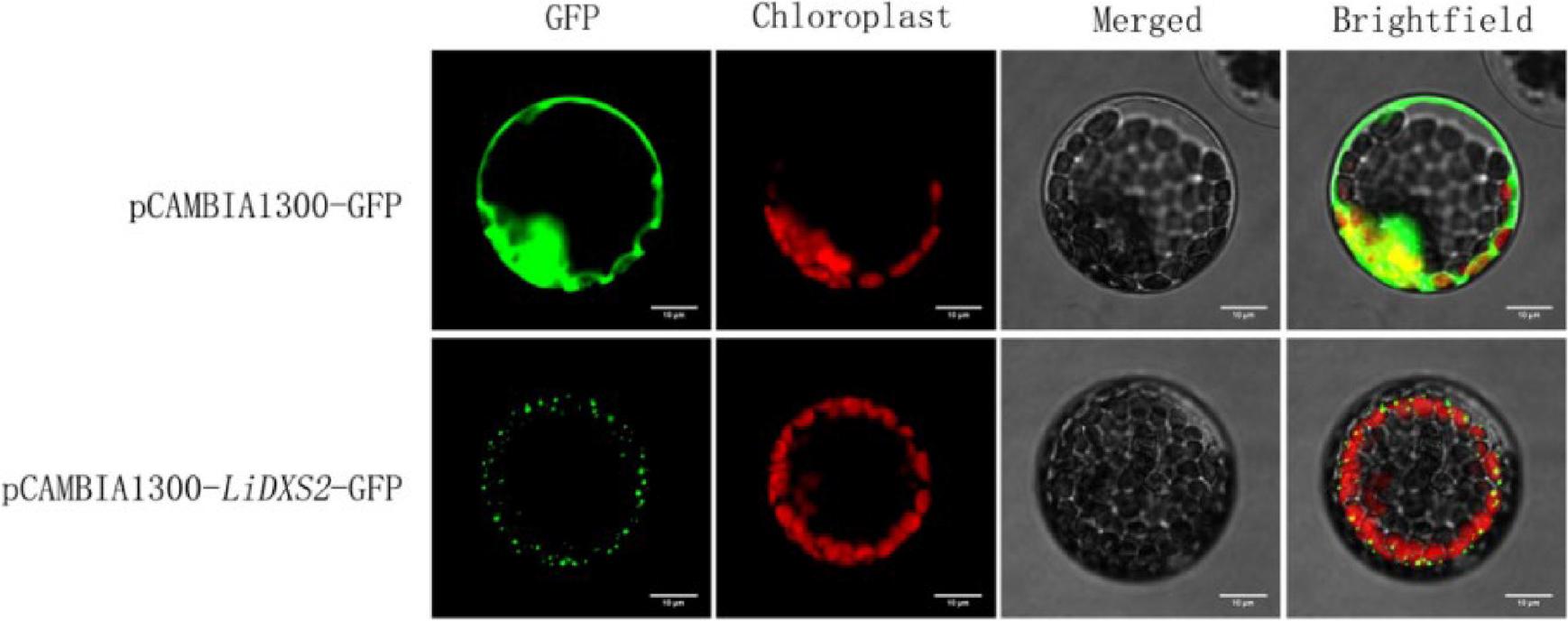
Figure 8.
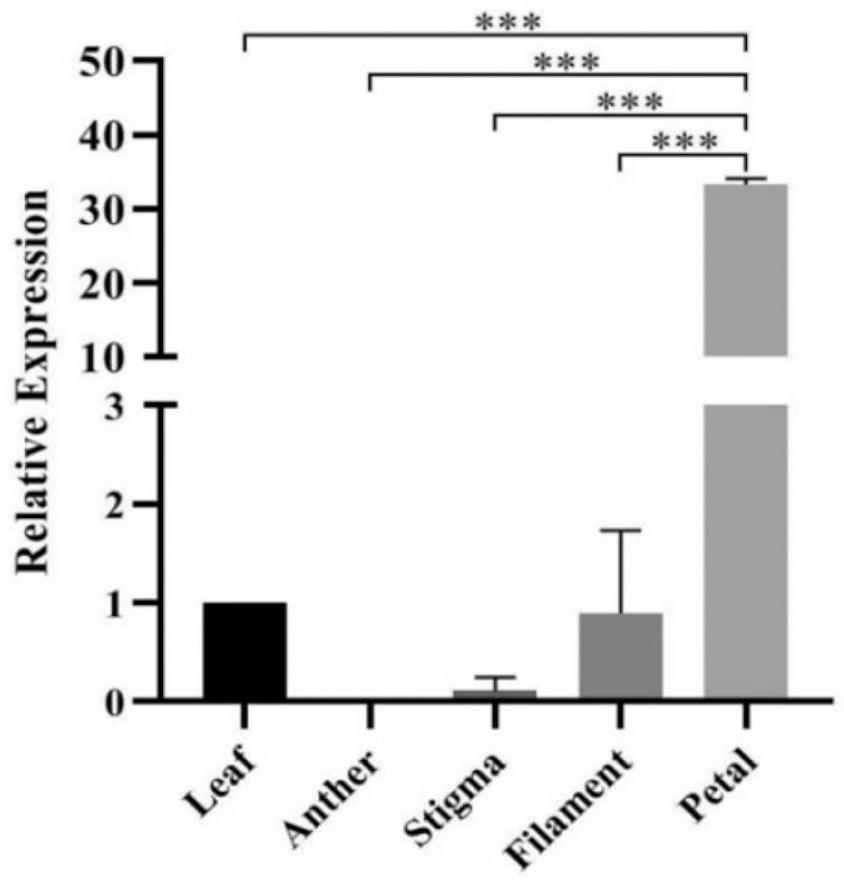
Figure 9.
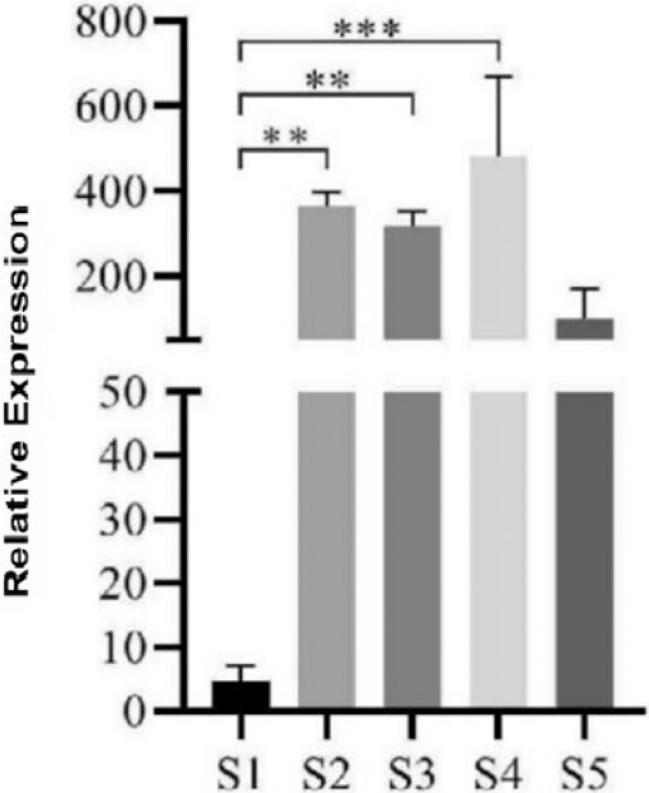
Figure 10.
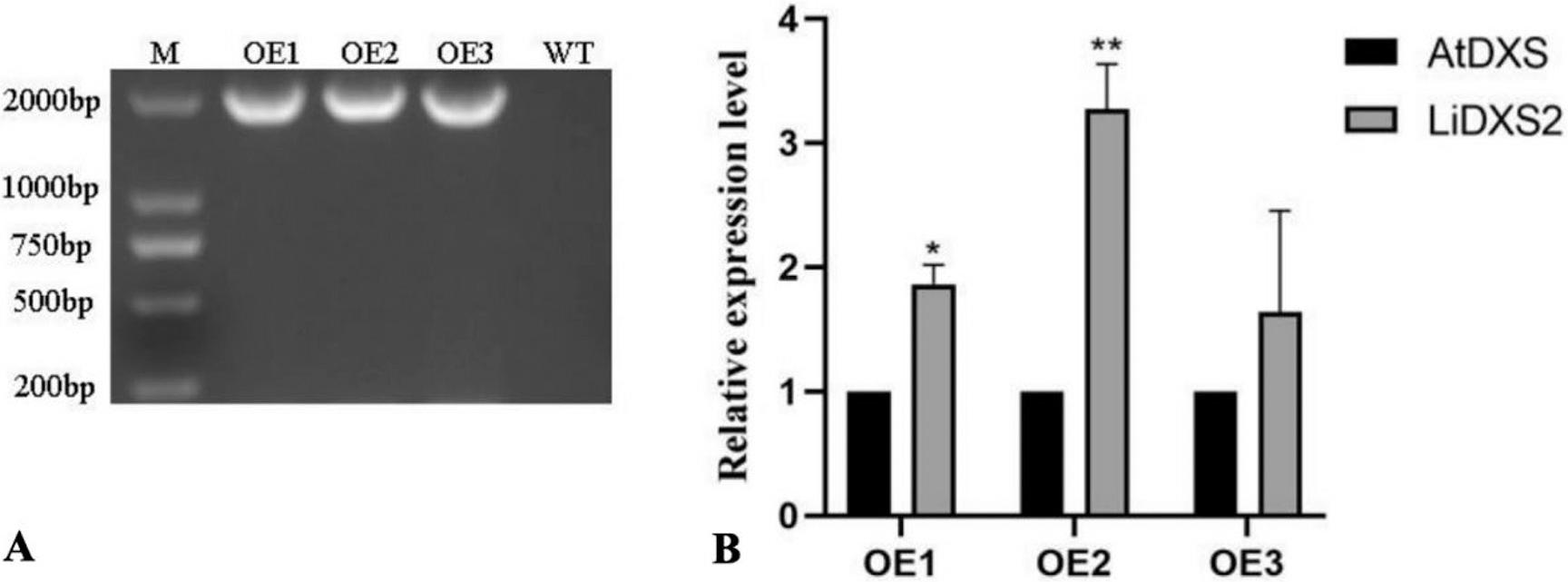
Figure 11.
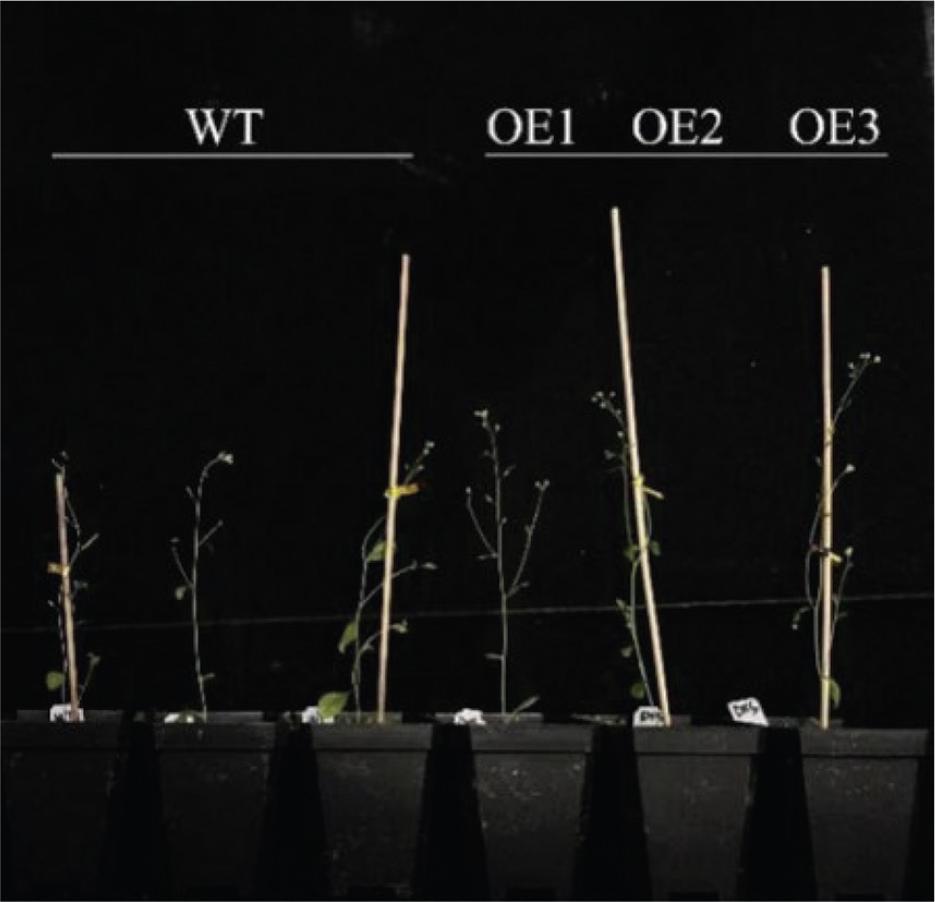
Figure 12.
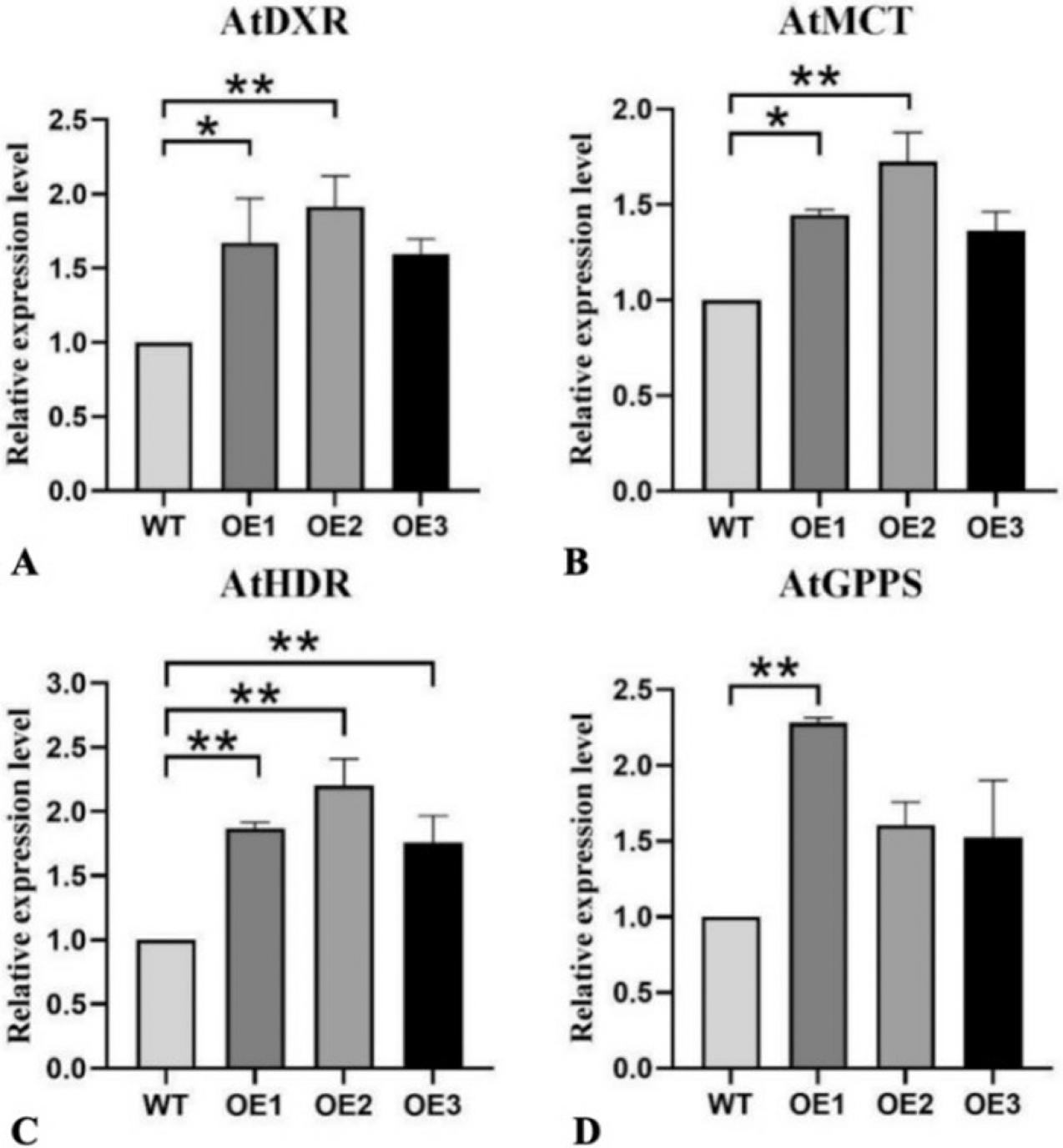
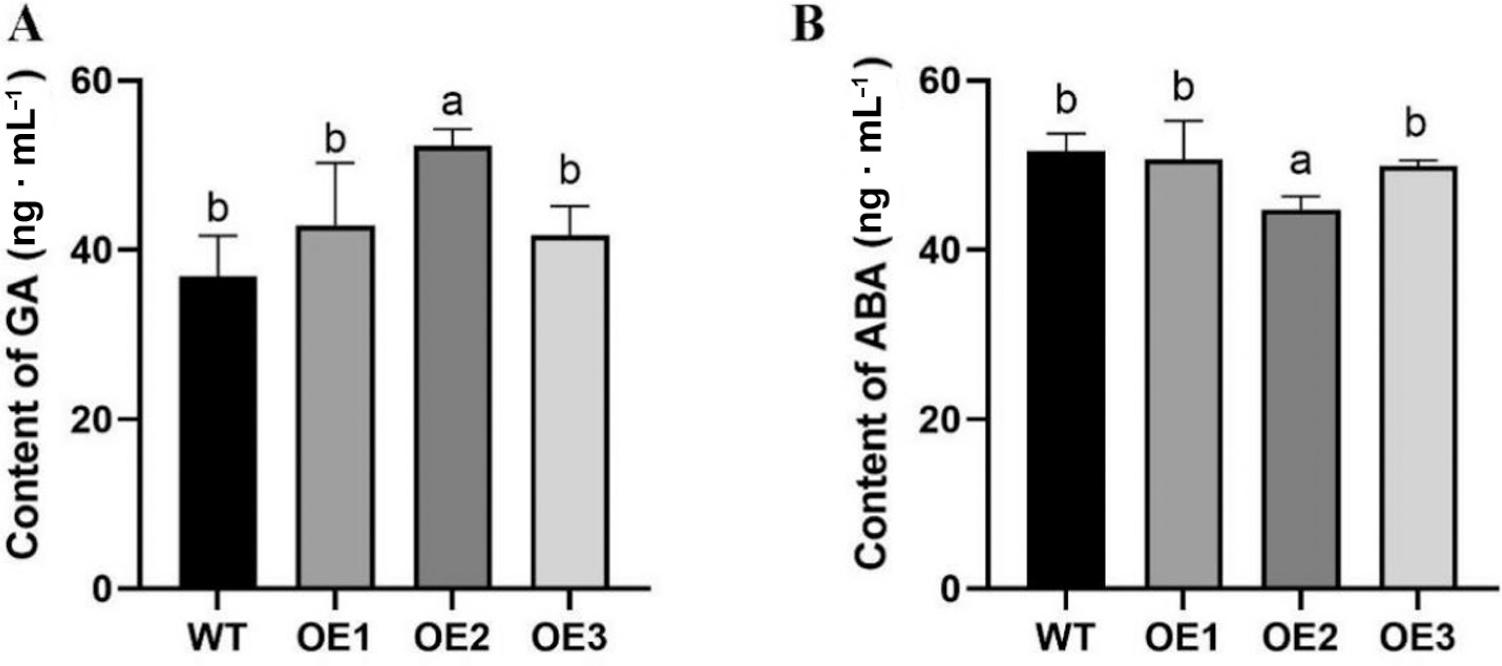
Figure 13.
Primers used for amplification and expression analysis of LiDXS2_
| Primers | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Actin-F | TGTGCTTTCCCTCTACGCCAGT |
| Actin-R | TCCCTCACGATTTCCCGCTCT |
| LiDXS2-F | ATGGCTTTCTCAGGCTCTCTC |
| LiDXS2-R | CTAGCTCAGATGCATGGCCT |
| egLiDXS2-F | CAGTCACCTGCAAAACAACATGGCTTTCTCAGGCTCTCT |
| egLiDXS2-R | CAGTCACCTGCAAAATACAGCTCAGATGCATGGCCTCTT |
| ecLiDXS2-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGGCTTTCTCAGGCTCTCTCA |
| ecLiDXS2-R | CGATCGGGGAAATTCGAGCTCCTAGCTCAGATGCATGGCCTCT |
| LiDXS2-qF | GGATGATAAACCCCGCTGG |
| LiDXS2-qR | CCCTTCCCTTTCTCCGTGA |
| AtDXR-F | GAGGTCATTGAAGCGCATTATT |
| AtDXR-R | GCCAAGTTACTTCAGAACAAGG |
| AtHDR-F | TTCAGATTGCATATGAAGCACG |
| AtHDR-R | GGTCGGGTTATGAATGATTTCG |
| AtGPPS-F | GAGCAGCGTTATAGTATGGACT |
| AtGPPS-R | CCATACTCAAAAGCTAACACGG |
| AtMCT-F | GAAATCGATGTGAACTCTGAGC |
| AtMCT-R | ACCATCTTTAAGGACCTTCTCG |
| AtActin-F | GAAGTCTTGTTCCAGCCCTCGTTTG |
| AtActin-R | GAACCACCGATCCAGACACTGTACT |