Figure 1:
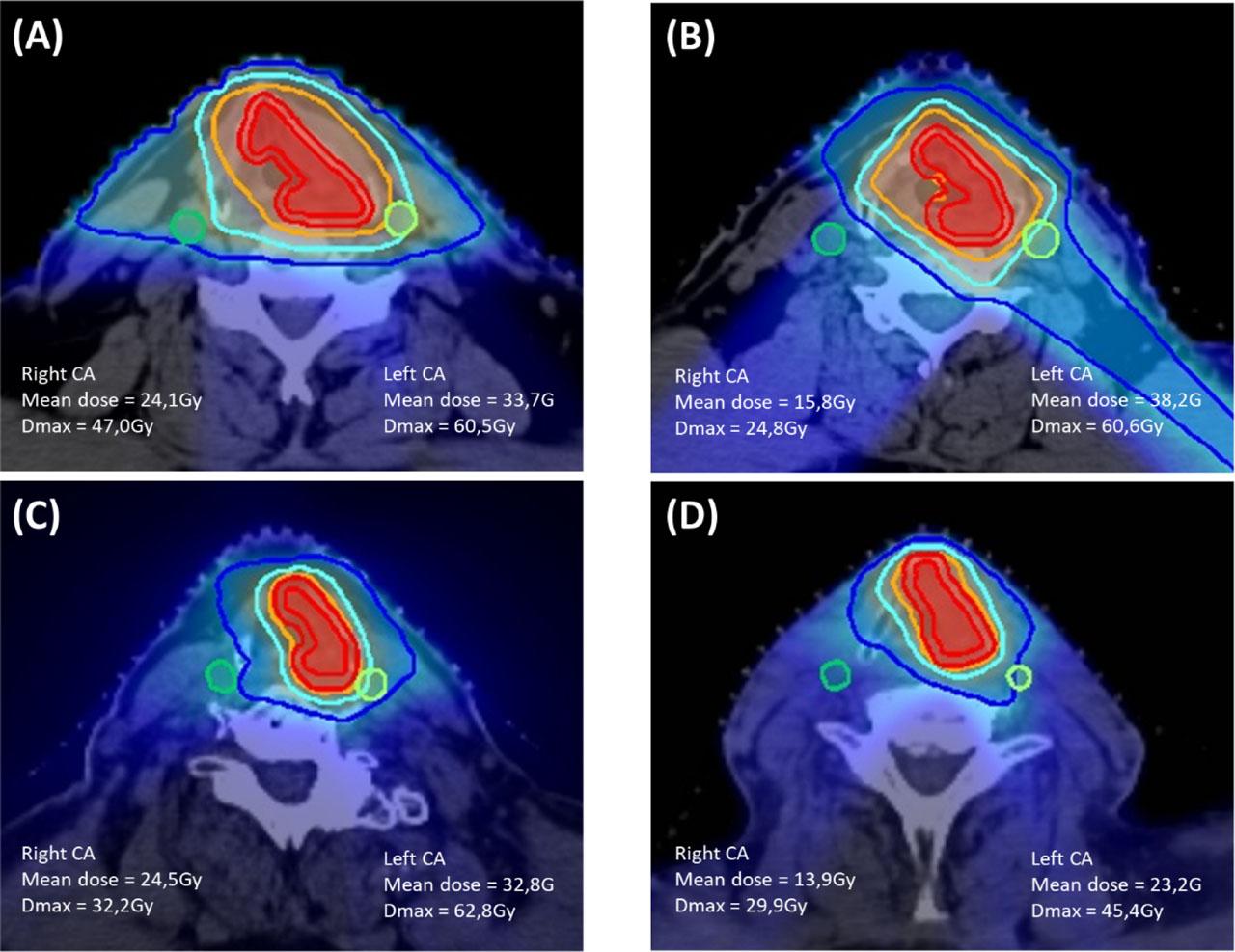
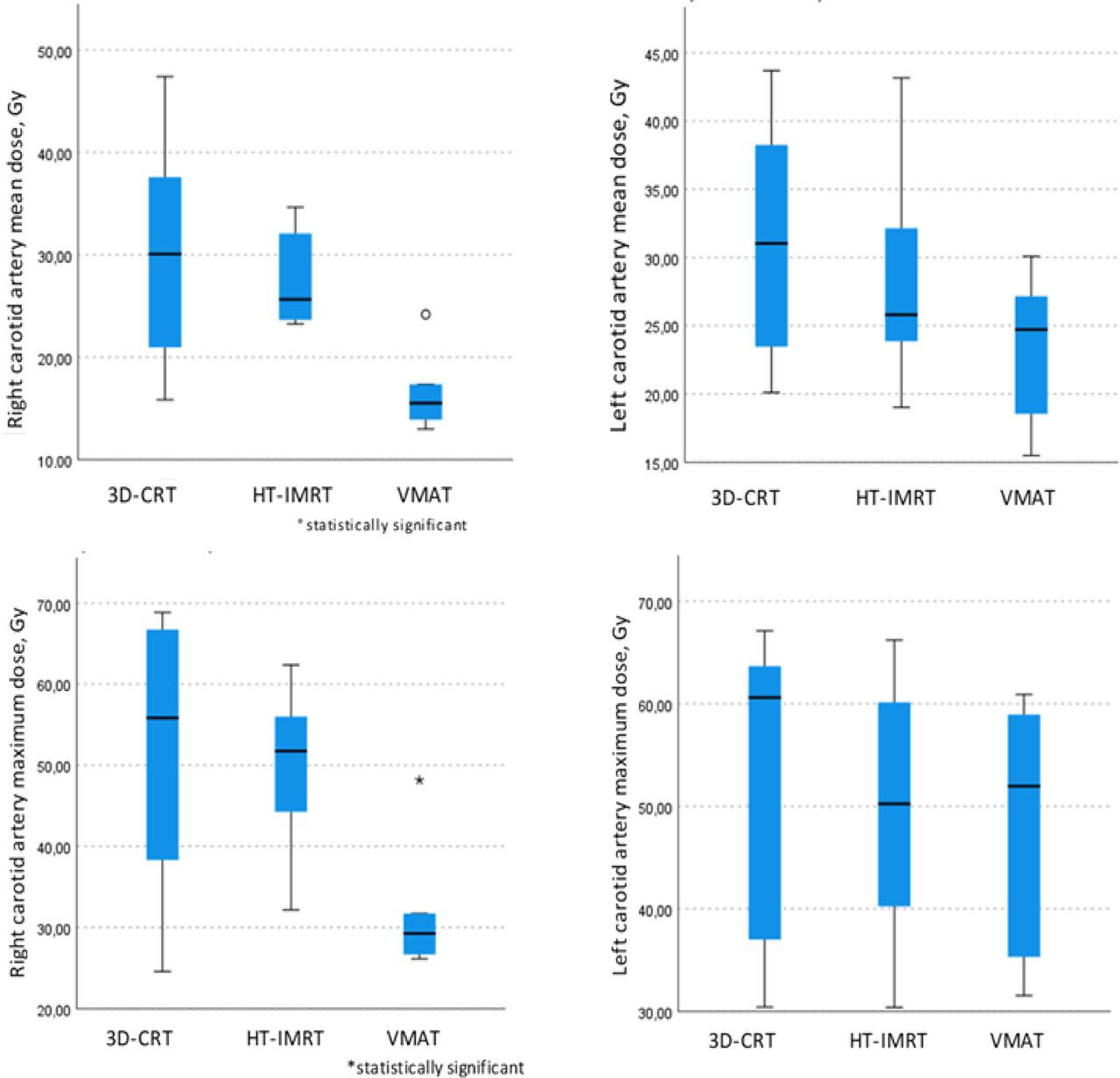
Figure 2:
Summary of the patients’ demographics and disease and treatment characteristics for the three different radiotherapy techniques utilized in this study_
| Characteristics | Treatment technique | Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D-CRT (n = 14) (%) | HT-IMRT (n = 8) (%) | VMAT (n = 6) (%) | ||
| Sex | p = 0.7 | |||
| Female | 1 (7.1) | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Male | 13 (92.9) | 7 (87.5) | 6 (100.0) | |
| Age at diagnosis | p = 0.1 | |||
| <60 years | 3 (21.4) | 1 (12.5) | 4 (66.7) | |
| ≥60 years | 11 (78.6) | 7 (87.5) | 2 (33.3) | |
| Performance status | p = 0.1 | |||
| ECOG 0 | 14 (100.0) | 6 (75.0) | 6 (100.0) | |
| ECOG 1 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (25.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Prognostic stage groups | p = 0.3 | |||
| Stage 0 | 2 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Stage I | 11 (78.6) | 5 (63.5) | 4 (66.7) | |
| Stage II | 1 (7.1) | 3 (37.5) | 2 (33.3) | |
| Tumor location/target treatment volume | p = 0.4 | |||
| Both vocal cords | 4 (28.6) | 3 (37.5) | 1 (16.7) | |
| Right vocal cord | 4 (28.6) | 2 (25.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Left vocal cord | 6 (42.9) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (83.3) | |
| Mean ± SD total radiation dose (Gy) | 64.9 ± 1.7 | 62.4 ± 5.4 | 64.4 ± 1.5 | p = 0.2 |
| Mean ± SD no. of fractions received | 31.2 ± 2.5 | 29.3 ± 4.3 | 29.8 ± 2.5 | p = 0.3 |
| Mean ± SD dose per fraction (Gy) | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | p = 0.4 |
Comparison of dosimetric characteristics among the three treatment techniques_
| Parameter | Treatment technique | Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D-CRT (n = 14) | HT-IMRT (n = 8) | VMAT (n = 6) | ||
| Right carotid artery | ||||
| Mean dose, Gy (range) | 30.9 (15.8–47.4) | 27.6 (23.2–34.6) | 16.6 (13.0–47.4) | p = 0.01 |
| Dmax, Gy (range) | 51.7 (24.6–68.9) | 49.9 (32.2–62.4) | 31.9 (26.1–48.2) | p = 0.02 |
| Mean volume delineated, ml (range) | 5.0 (3.6–6.4) | 3.9 (2.8–5.8) | 4.2 (2.6–6.5) | p = 0.1 |
| Left carotid artery | ||||
| Mean dose, Gy (range) | 31.0 (20.1–43.7) | 28.2 (19.0–43.2) | 23.4 (15.5–30.1) | p = 0.1 |
| Dmax, Gy (range) | 54.0 (30.4–67.1) | 49.7 (30.4–66.2) | 48.4 (31.5–60.9) | p = 0.6 |
| Mean volume delineated, ml (range) | 4.7 (3.1–6.2) | 4.0 (3.0–5.8) | 4.0 (2.5–5.6) | p = 0.3 |