Figure 1:
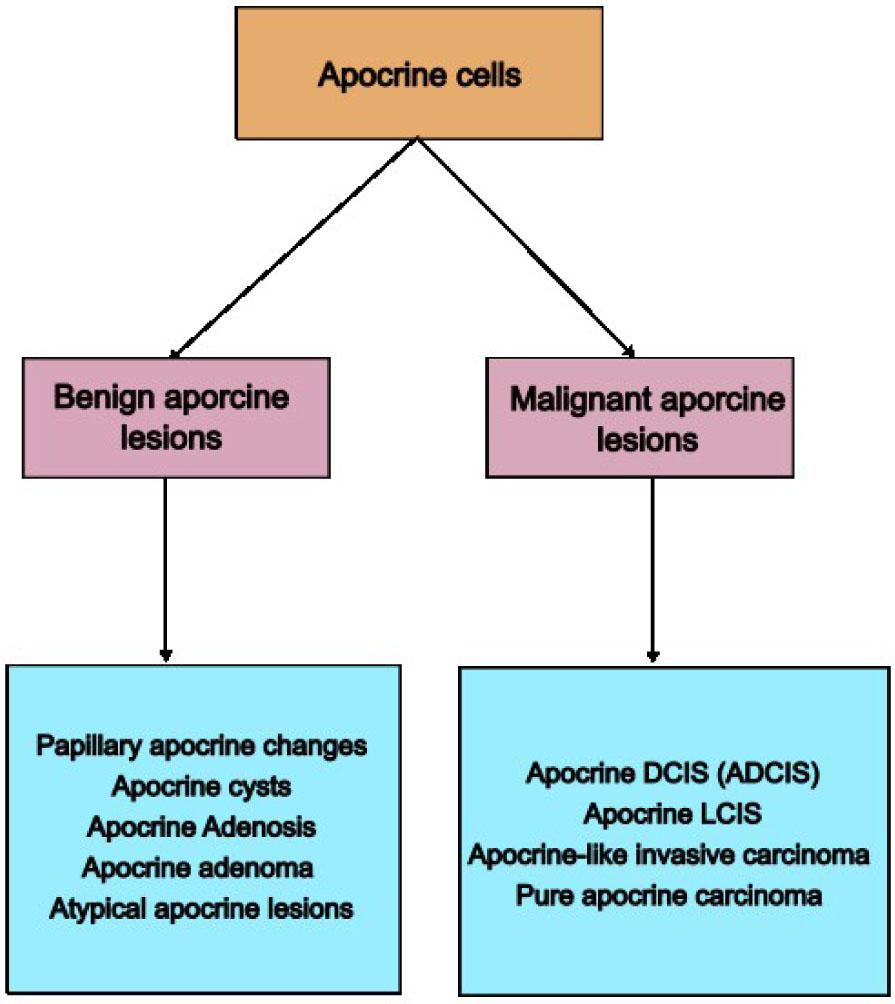
Figure 2:
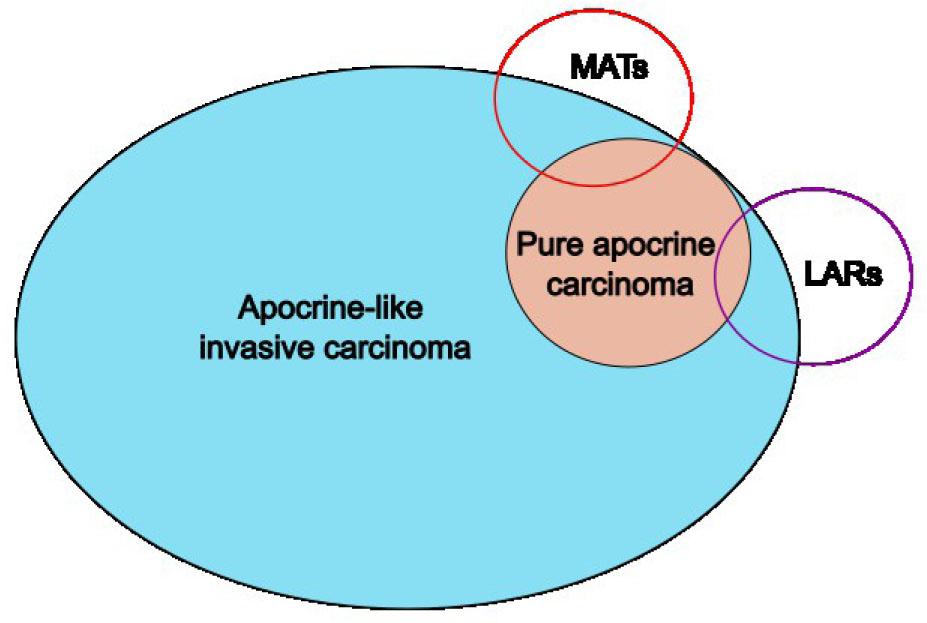
Figure 3:
![The Cross-talk of AR and ErbB2 pathways In Naderi's study, the function of ERK1/2, testosterone, and Heregulin can be suppressed by both AR and ErbB2 pathways. Anti-ErB2 and anti-androgen therapy can inhibit the function of testosterone and ErbB2 and further cause the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, followed by negative regulation of cell growth. [52]](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/6471cdf2215d2f6c89db169a/j_fco-2023-0007_fig_003.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251205%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251205T193923Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=94c7c5adcf558754300388d2c1b6b67c0892dd5cacd5bba82f11bfe473ebbc71&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
Treatment recommendation from the literature review_
| CLASSIFICATION | INTERVENTION |
|---|---|
| ATYPICAL APOCRINE LESIONS (AA) | No intervention +− Core needle biopsy |
| APOCRINE DCIS (ADCIS) | Mastectomy or conservative surgery +/− adjuvant radiation therapy |
| APOCRINE CARCINOMA | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy + surgery +/− radiation therapy + anti-androgen therapy (if AR+) + anti-HER2 antibodies (if HER2+) +/− PI3 kinase inhibition and CDK4/6 inhibitors (if biomarkers detected) |
Immunohistology characteristics of ADCIS and pure apocrine carcinoma_
| IMMUNOHISTOLOGY MARKERS | PURE APOCRINE CARCINOMA | ADCIS | INVOLVING PATHWAY |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER, PR (−), AR (+) | 100% strictly match to AR (+,) ER(−), PR (−) criteria | >90% | AR pathway |
| HER-2 | 1/3 positive, 2/3 negative | 47.1% | HER2 signaling pathway |
| GCDFP-15 | 75% | 96.4% | AR pathway |
| AMACR | > 90% | > 90% | Oxidative degradation pathways |
| ER-A36 | 94.7% | 94.7% (classified with pure apocrine carcinoma) | MAPK/ERK signaling pathway EGFR/Src/ERK signaling pathway |
| PIK3CA | >80% | 100% | PI3K/mTOR pathway |
| P53 | 46–50% | 61.8% | PI3K/mTOR/p53 pathway |
| PD-L1 | 10–40% | N/A | PD-1/PD-L1 pathway |
| AR-V7 | 57% | N/A | AR pathway |