Fig. 1
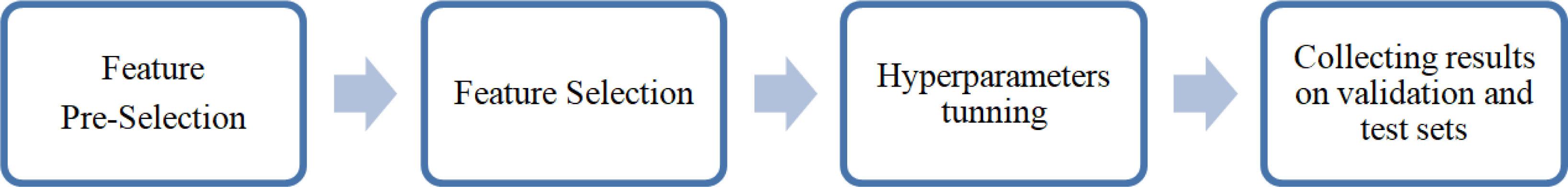
Fig. 2
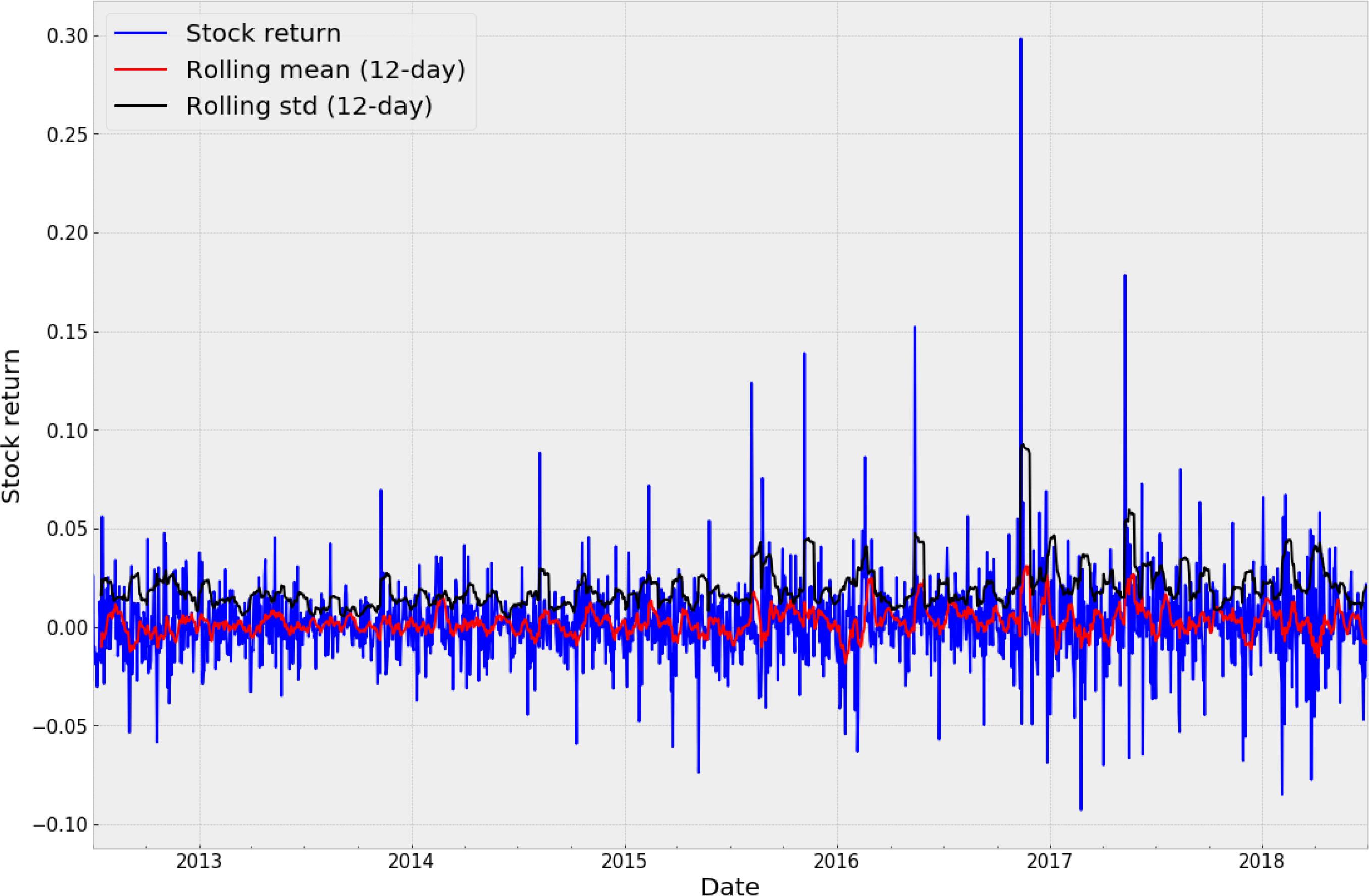
Fig. 3
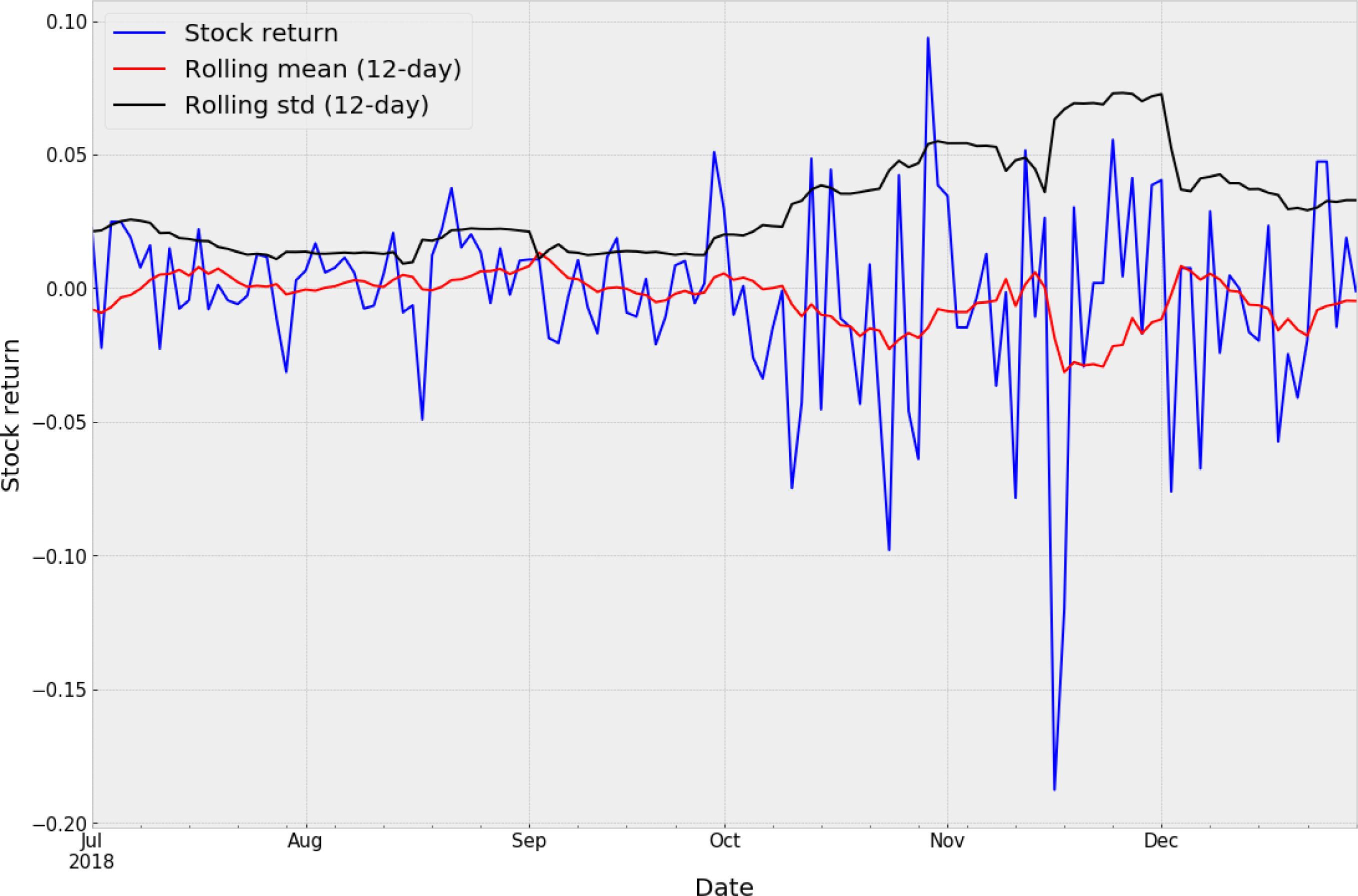
Fig. 4
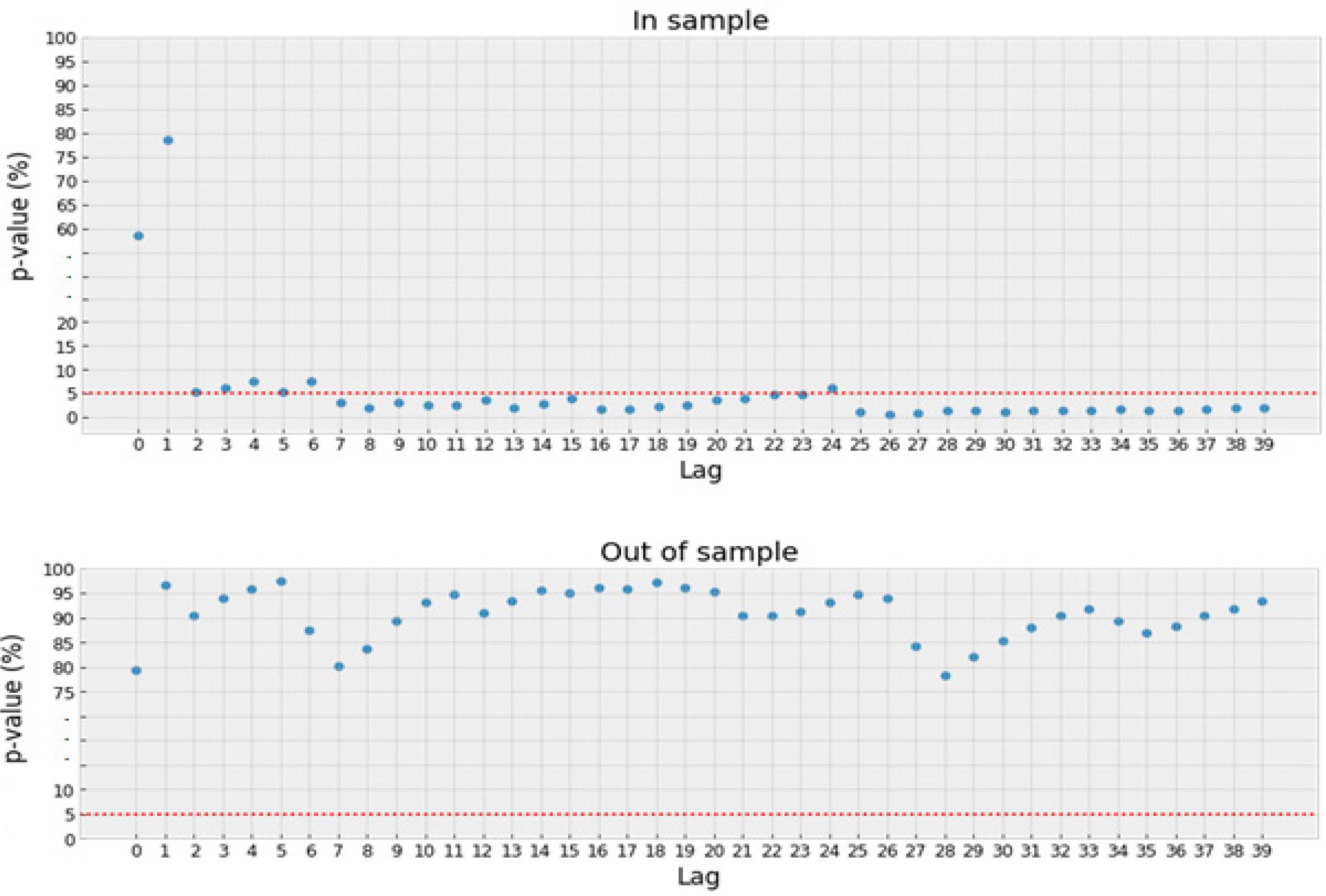
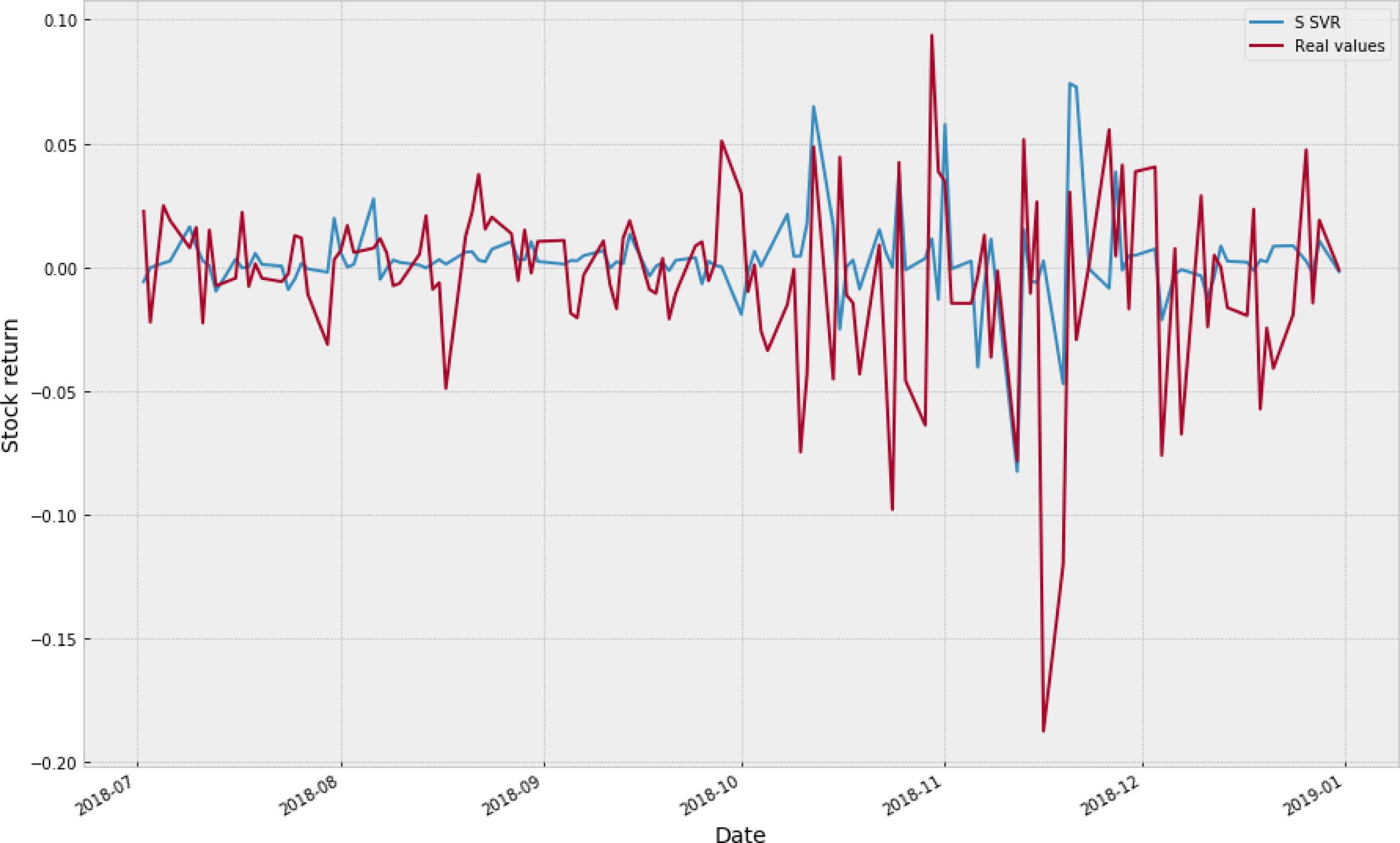
Fig. 5
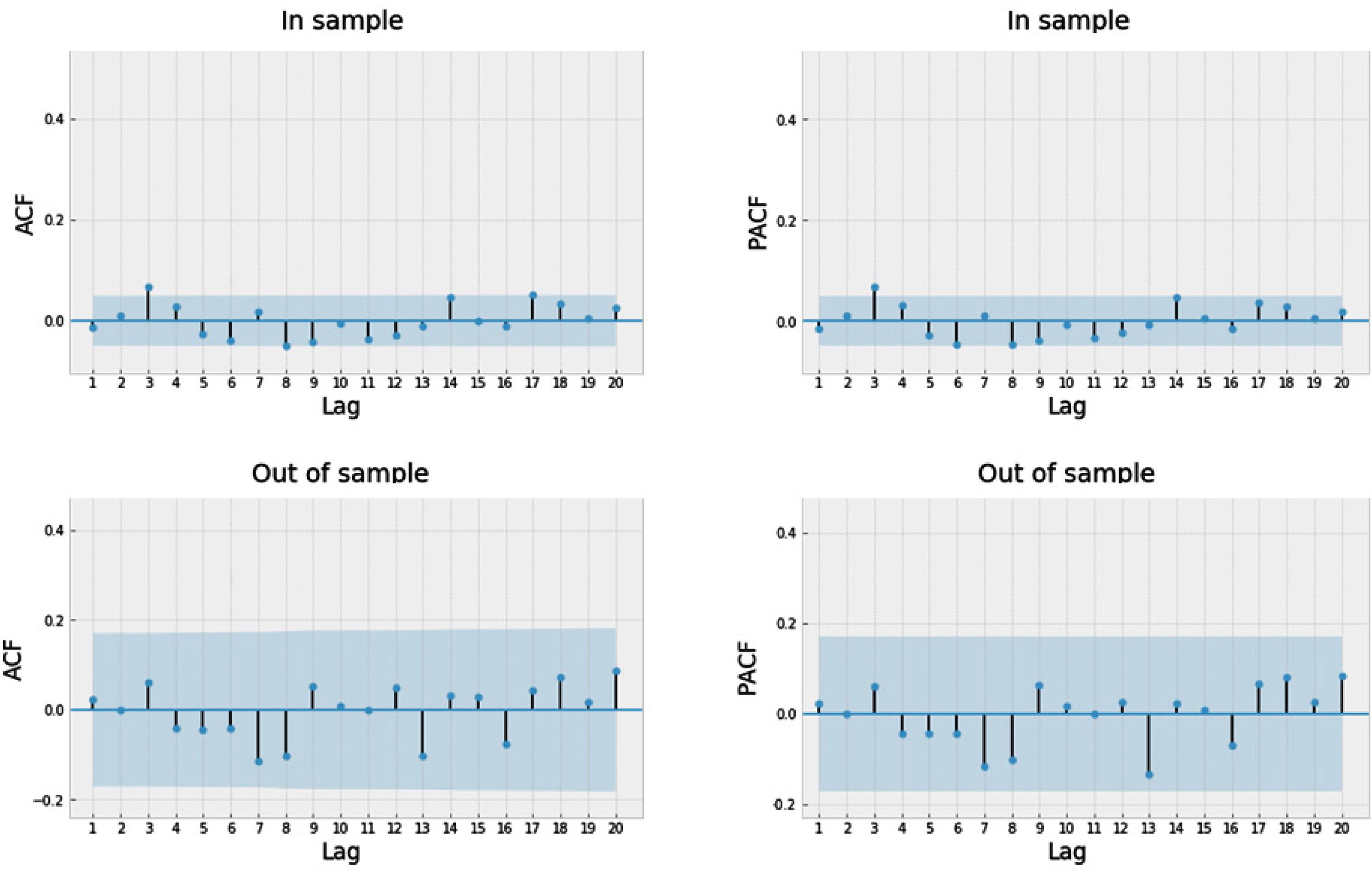
Fig. 6
Results of Augmented Dickey-Fuller test for in-sample set and out-of-sample set
| Test statistic (in sample) | p-value (in sample) | Test statistic (out of sample) | p-value (out of sample) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −11.01 | <0.0001 | −11.09 | <0.0001 |
Results of singular models on validation and test set (based on stationary variables)
| Model (number of attributes) | Set | Hyperparameters | RMSE | MAE | MedAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVR (20) | Validation | C=0.005206 | 0.026924 | 0.019478 | 0.014985 |
| SVR (20) | Test | C=0.005206 | 0.036014 | 0.024916 | 0.016682 |
| KNN (20) | Validation | Power of Minkowski metric=2 | 0.026328 | 0.020331 | 0.016199 |
| KNN (20) | Test | Power of Minkowski metric=2 | 0.039305 | 0.025935 | 0.017202 |
| XGBoost (27) | Validation | Max depth:7 | 0.027622 | 0.020678 | 0.016553 |
| XGBoost (27) | Test | Max depth:7 | 0.038848 | 0.027218 | 0.019782 |
| LGBM (43) | Validation | Number of leaves:58 | 0.025905 | 0.018803 | 0.014339 |
| LGBM (43) | Test | Number of leaves:58 | 0.038870 | 0.026283 | 0.016467 |
| LSTM (20) | Validation | H1 | 0.026565 | 0.019741 | 0.014537 |
| LSTM (20) | Test | H1 | 0.036705 | 0.024918 | 0.016772 |
Performance of ensemble models on test set (based on all models)
| Number of models | Models (weight) | RMSE | MAE | MedAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | S+NS SVR (0.504057), S+NS LightGBM (0.495943) | 0.03873 | 0.025882 | 0.017714 |
| 3 | S+NS SVR (0.337508), S+NS LightGBM (0.332075), S LightGBM (0.330417) | 0.038593 | 0.025959 | 0.017321 |
| 4 | S+NS SVR (0.255711), S+NS LightGBM (0.251594), S LightGBM (0.250338), S KNN (0.242357) | 0.038436 | 0.025665 | 0.017152 |
| 5 | S+NS SVR (0.206542), S+NS LightGBM (0.203217), S LightGBM (0.202202), S KNN (0.195756), S LSTM (0.192283) | 0.037734 | 0.025267 | 0.016599 |
| 6 | S+NS SVR (0.173976), S+NS LightGBM (0.171176), S LightGBM (0.170321), S KNN (0.164891), S LSTM (0.161965), S SVR (0.157671) | 0.03681 | 0.024751 | 0.01743 |
| 7 | S+NS SVR (0.150427), S+NS LightGBM (0.148006), S LightGBM (0.147266), S KNN (0.142572), S LSTM (0.140042), S SVR (0.136329), S+NS KNN (0.135359) | 0.036871 | 0.024897 | 0.016953 |
| 8 | S+NS SVR (0.133177), S+NS LightGBM (0.131034), S LightGBM (0.130379), S KNN (0.126223), S LSTM (0.123983), S SVR (0.120696), S+NS KNN (0.119837), S XGBoost (0.114672) | 0.036746 | 0.024681 | 0.01647 |
| 9 | S+NS SVR (0.119825), S+NS LightGBM (0.117896), S LightGBM (0.117307), S KNN (0.113568), S LSTM (0.111553), S SVR (0.108595), S+NS KNN (0.107822), S XGBoost (0.103175), S+NS XGBoost (0.100259) | 0.036898 | 0.024757 | 0.01645 |
| 10 | S+NS SVR (0.109125), S+NS LightGBM (0.107368), S LightGBM (0.106832), S KNN (0.103426), S LSTM (0.101591), S SVR (0.098897), S+NS KNN (0.098193), S XGBoost (0.093961), S+NS XGBoost (0.091305), S+NS LSTM (0.089302) | 0.036899 | 0.024915 | 0.016466 |
Performance of best models on test set (ensemble and primary models)
| Metric | Best stationary ensemble model | Best stationary + non-stationary ensemble model | Best ensemble model based on all models | Best stationary model – SVR | Best stationary + non-stationary model − LGBM | Naive model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.036106 | 0.038053 | 0.036746 | 0.036014 | 0.037284 | 0.050244 |
| MAE | 0.024094 | 0.026068 | 0.024681 | 0.024916 | 0.026295 | 0.034908 |
| MedAE | 0.015307 | 0.016645 | 0.01647 | 0.016682 | 0.017959 | 0.022378 |
Performance of ensemble models on test set (models based on stationary and non-stationary variables)
| Number of models | Models (weight) | RMSE | MAE | MedAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | SVR (0.504057), LightGBM (0.495943) | 0.038730 | 0.025882 | 0.017714 |
| 3 | SVR (0.346773), LightGBM (0.341191), KNN (0.312036) | 0.038314 | 0.026003 | 0.016682 |
| 4 | SVR (0.268786), LightGBM (0.264459), KNN (0.241861), XGBoost (0.224895) | 0.038301 | 0.025793 | 0.016876 |
| 5 | SVR (0.220323), LightGBM (0.216777), KNN (0.198253), XGBoost (0.184346), LSTM (0.180301) | 0.038053 | 0.026068 | 0.016645 |
Performance of models on test set (based on stationary and non-stationary variables)
| Metric | SVR | KNN | XGBoost | LSTM | LGBM | Best ensemble model | Naive model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.041904 | 0.039313 | 0.040685 | 0.039593 | 0.037284 | 0.038053 | 0.050244 |
| MAE | 0.025875 | 0.026863 | 0.026906 | 0.028891 | 0.026295 | 0.026068 | 0.034908 |
| MedAE | 0.017279 | 0.018946 | 0.016939 | 0.020576 | 0.017959 | 0.016645 | 0.022378 |
Performance of ensemble models on test set (models based on stationary variables)
| Number of models | Models (weight) | RMSE | MAE | MedAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | LightGBM (0.508099), KNN (0.491901) | 0.038571 | 0.025784 | 0.017147 |
| 3 | LightGBM (0.342575), KNN (0.331655), LSTM (0.32577) | 0.037403 | 0.025111 | 0.015704 |
| 4 | LightGBM (0.260092), KNN (0.251801), LSTM (0.247333), SVR (0.240775) | 0.036181 | 0.024366 | 0.01599 |
| 5 | LightGBM (0.211671), KNN (0.204923), LSTM (0.201287), SVR (0.19595), | 0.036106 | 0.024094 | 0.015307 |
Results of singular models on validation and test set (based on stationary and non-stationary variables)
| Model (number of attributes) | Set | Hyperparameters | RMSE | MAE | MedAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVR (27) | Validation | C=0.005317, epsilon=0.092179 | 0.025632 | 0.019126 | 0.015488 |
| SVR (27) | Test | C=0.005317, epsilon=0.092179 | 0.041904 | 0.025875 | 0.017279 |
| KNN (40) | Validation | Power of Minkowski metric=1 | 0.027021 | 0.020110 | 0.013813 |
| KNN (40) | Test | Power of Minkowski metric=1 | 0.039313 | 0.026863 | 0.018946 |
| XGBoost (74) | Validation | Max depth:3 | 0.028021 | 0.021604 | 0.020396 |
| XGBoost (74) | Test | Max depth:3 | 0.040685 | 0.026906 | 0.016939 |
| LGBM (80) | Validation | Number of leaves:32 | 0.025840 | 0.019361 | 0.014083 |
| LGBM (80) | Test | Number of leaves:32 | 0.037284 | 0.026295 | 0.017959 |
| LSTM (20) | Validation | H2 | 0.028334 | 0.021702 | 0.018201 |
| LSTM (20) | Test | H2 | 0.039593 | 0.028891 | 0.020576 |
Hyperparameters tuning algorithm_
| 1. | For each pair of sets (Xi,Yi) ∈ S={(train, validation1), (train ∪ validation1, validation2), (train ∪ validation1∪ validation2, validation3)} next operations will be performed: |
| a. | the possibly largest group of hyperparameters will be selected according to best practice mentioned in literature, |
| b. | one-step-ahead prediction will be done, providing Xi as train set and Yi as test set, and then one model with the lowest RMSE will be chosen, with parameters Hi. |
| As a result, set {H1, H2, H3} is obtained. | |
| 2. | For Hi will be executed three predictions on each pair from S. In effect 3 RMSE will be received, from which the average will be calculated – Ai. As a result, set {A1, A2, A3} is obtained. |
| 3. | Hj will be chosen, where Aj = min{A1, A2, A3}. It is the best set of hyperparameters, which is believed to assure stable fit in future forecasts. |
Performance of models on test set (based on stationary variables)
| Metric | SVR | KNN | XGBoost | LSTM | LGBM | Best ensemble | Naive model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.036014 | 0.039305 | 0.038848 | 0.036705 | 0.038870 | 0.036106 | 0.050244 |
| MAE | 0.024916 | 0.025935 | 0.027218 | 0.024918 | 0.026283 | 0.024094 | 0.034908 |
| MedAE | 0.016682 | 0.017202 | 0.019780 | 0.016772 | 0.016467 | 0.015307 | 0.022378 |
