Figure 1.
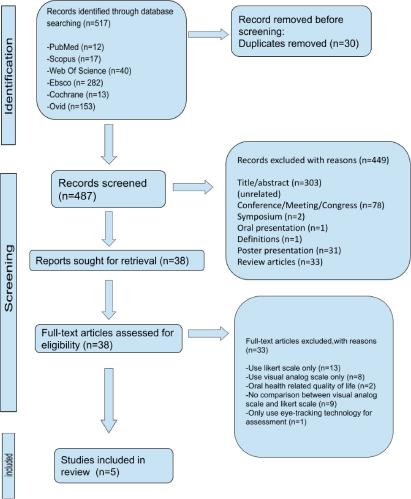
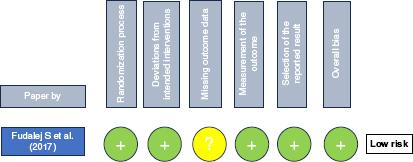
Figure 2.
Summary of research outcomes
| Study | Title | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Aşik & Kök (2021)13 | Perception of dental midline deviation and smile attractiveness by eye-tracking and aesthetic ratings | The ICC was 0.805 for the VAS, and 0.760 for the Likert Scale No statistically significant difference between the genders VAS and Likert scores were consistent with the eye-tracking data. No statistically significant difference between the age groups. |
| Hatch et al. (2017)12 | Effects of objective 3D measures of facial shape and symmetry on perceptions of facial attractiveness | The test-retest reliability for overall facial attractiveness ratings was 0.69 on the Likert-scale and 0.75 on the VAS. |
| Dourado et al. (2021)8 | Likert scale vs visual analog scale for assessing facial pleasantness | Intra examiner errors were 0.70 and 0.69 for the Likert scale and VAS, respectively. |
| Eslamipour et al. (2017)14 | Correlation coefficients of three self-perceived orthodontic treatment need indices | The intraclass coefficient for each examiner was over 0.9. |
| Fudalej et al. (2017)15 | Comparison of three methods of rating nasolabial appearance in cleft lip and palate | The VAS method was in turn more reproducible than Likert scale. |
Risk of bias (RoB) with STROBE checklist
| STROBE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | Study | Score | Paper |
| Perception of dental midline deviation and smile attractiveness by eye-tracking and aesthetic ratings | Aşik & Kök (2021)13 | 78.5% | Good |
| Effects of objective 3D measures of facial shape and symmetry on perceptions of facial attractiveness | Hatch et al. (2017)12 | 75.3% | Good |
| Likert scale vs visual analog scale for assessing facial pleasantness | Dourado et al. (2021)8 | 85.18% | Excellent |
| Correlation coefficients of three self-perceived orthodontic treatment need indices | Eslamipour et al. (2017)14 | 85.18% | Excellent |
Eligibility criteria
| Criteria | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Laypeople and/or dental clinicians | |
| Intervention | Likert Scale and VAS used in assessing facial aesthetic | |
| Outcome measures | 1.Validity and/or reliability of both scale | |
| Study design | Randomized controlled trial, cross sectional study | Reviews, case reports, letters to editor, and all other non-peer-reviewed articles |
| Others | All language article |
Study methodology, population, intervention characteristics, and outcome measure(s)
| Study | Study Methodology | Study Population | Intervention Charateristics | Outcome Measure(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fudalej et al. (2017)15 | Randomized controlled trial | Eight junior orthodontic residents without any experience in treatment of CLP. | Extra-oral images of 60 non-syndromic complete unilateral cleft lip and palate (CLP) patients were taken from the frontal and profile views and were cropped. | Reliability was measured by using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) in assessing nasolabial appearance. |
| Asik & Kök (2021)13 | Cross-sectional | 195 participants (52 laypersons, 50 patient’s - relatives, 51dentists, and 42 orthodontists) from the Necmettin Erbakan University Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Orthodontics. | Photographs of a female frontal posed smile were cropped to include only mouth and teeth produced a base image. Dental midline was adjusted 1, 2, 3, and 4mm to the left and right sides using Adobe Photoshop CC 2014 software resulting in 8 modified smile images. | Effect of dental midline deviation on the perception of smile aesthetics by orthodontist, dentists, patient relatives, and layperson. |
| Hatch et al. (2017)12 | Cross-sectional | Ten university students and staff (5 females and 5 males) identified from convenience sampling approach | Frontal and lateral views of images of 313 adults in Iowa were presented to the raters. | Reliability of both scales by using test-retest reliability in measuring overall facial attractiveness. |
| Dourado et al. (2021)8 | Cross-sectional | 90 evaluators divided into 3 groups equally: Lay people (20-67 years old) | Evaluation on facial pleasantness was done on 10 adult patients’ photographs that underwent orthodontic treatment for different facial discrepancies compiled in an album. | Reliability of Likert scale and VAS was measured through intra examiner error analysis. |
| Eslamipour et al. (2017)14 | Cross-sectional | 993 freshman students from Isfahan University were randomly selected and examined to assess the dental health component (DHC) index of the Index of orthodontic treatment need (IOTN) Examination was done by two examiners. | Questionnaire divide into three sections: Demographic, index of oral aesthetic subjective index scale (OASIS) using 7-point Likert scale, VAS and IOTN. | Determination of most reliable self-perceived indices by using intraclass coefficients. |