Fig 1.
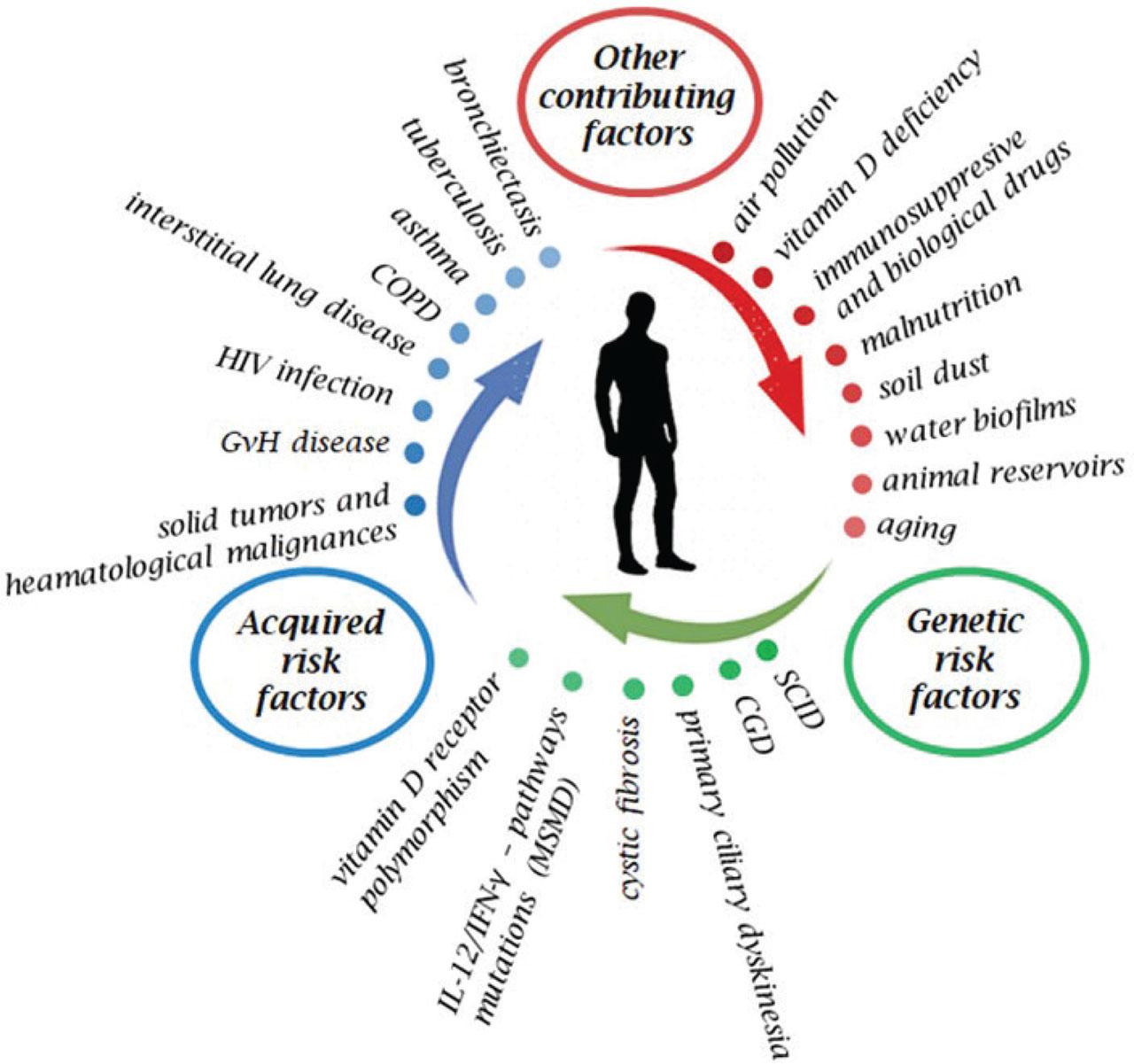
Fig 2.

Short characteristics of NTM groups [based on Runyon (1959); Herdman and Steele (2004); Salvana et al_ (2007); Abdalla et al_ (2009); Tortoli (2014); Koh (2017); Tortoli et al_ (2017); Sharma and Upadhyay (2020)]
| Classification | Growth rate | Characteristics | Common examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Slow-growing | Photochromogenic: Develop pigment when exposed to light. | Mycobacterium kansasii, Mycobacterium marinum |
| Group 2 | Slow-growing | Scotochromogenic: Produce pigment in both light and darkness. | Mycobacterium scrofulaceum, Mycobacterium szulgai, Mycobacterium gordonae |
| Group 3 | Slow-growing | Non-photochromogenic: Do not produce pigments. | MAC, Mycobacterium ulcerans |
| Group 4 | Fast-growing | May or may not produce colored colonies. | Mycobacterium fortuitum, Mycobacterium abscessus, Mycobacterium chelonae |