FIGURE 1.
FIGURE 2.
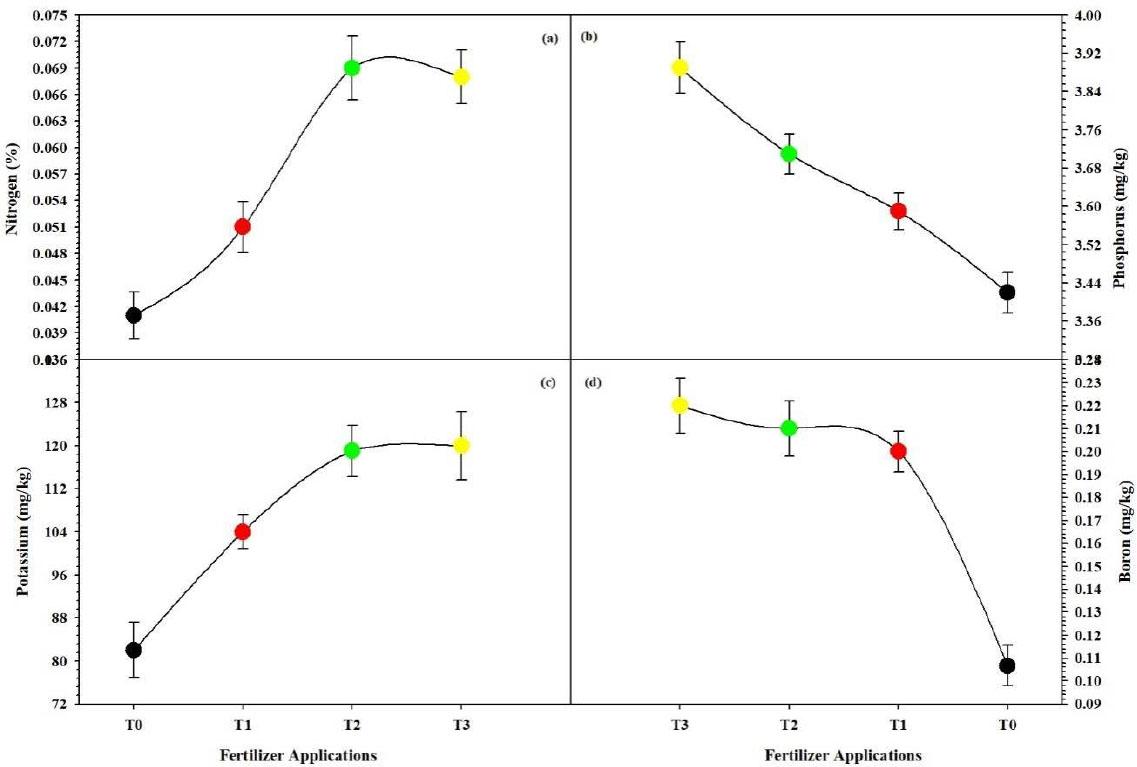
FIGURE 3.
![Triplicates mean that with the standard different plant growth characteristics (plant height [cm], spike length [cm], pedicel length [cm], and leaf area [cm]) under different applications of both fertilizers (potassium and boron) were significantly different (p ≤ 0.05)
Source: own work.](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/68debd8c81e1b934196924a1/j_srees.9875_fig_003.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251203%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251203T160011Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=230fe38857ef4fa49ac25577445b1ad696dd50bb4ea0447097e9fa5d7a1f336f&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
FIGURE 4.
![The triplicates mean that with the standard of different yield parameters: grain weight per spike weight [g], grain weight per thousand-grain weight [g], and biological yield [kg·ha−1], the results are significant (p ≤ 0.05) under different application of both fertilizers (potassium and boron)
Source: own work.](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/68debd8c81e1b934196924a1/j_srees.9875_fig_004.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251203%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251203T160011Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=7df8f6ba8baf2dd6f756f8731eb2d5a0125ae4378583b4422e5c262a8e5aab45&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
FIGURE 5.

FIGURE 6.

FIGURE 7.
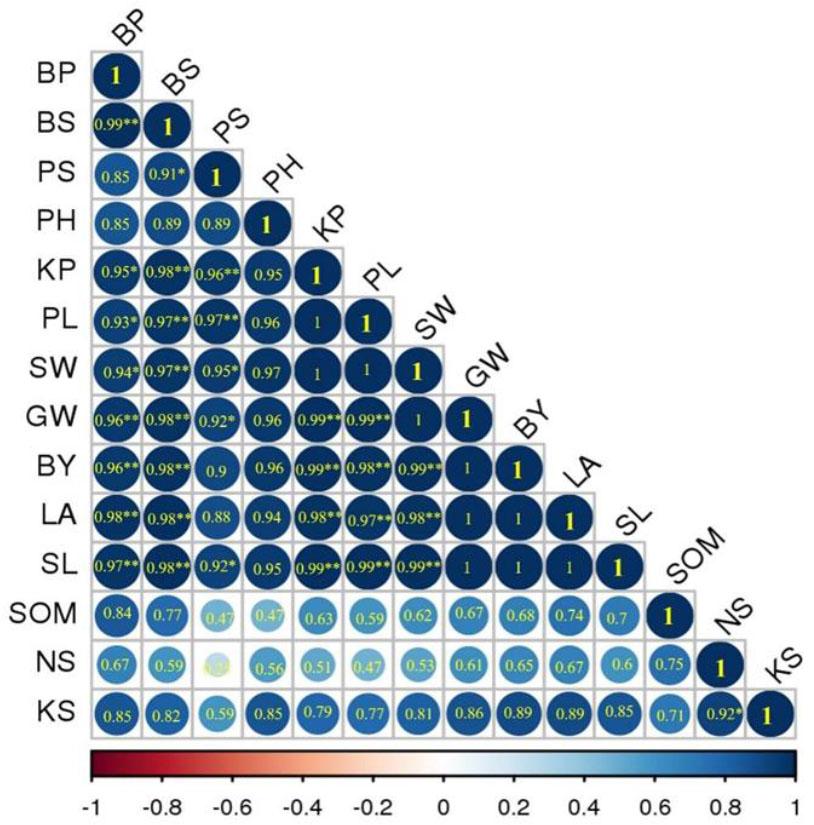
Soil basic characteristics before sowing seed
| Parameter | Mean | CV | LSD | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity [dS·m−1] | 0.49 ±0.02 | 5.74 | 0.02 | 0.47 |
| pH | 8.02 ±0.10 | 2.39 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| Organic matter [%] | 0.29 ±0.04 | 3.18 | 5.10 | 0.02 |
| Nitrogen [%] | 0.07 ±0.01 | 1.14 | 5.95 | 0.00 |
| Phosphorus [mg·kg−1] | 1.62 ±0.39 | 11.5 | 0.24 | 0.00 |
| Potassium [mg·kg−1] | 87.6 ±4.12 | 0.57 | 0.39 | 0.00 |
| Boron [mg·kg−1] | 0.16 ±0.01 | 6.17 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
