FIGURE 1.
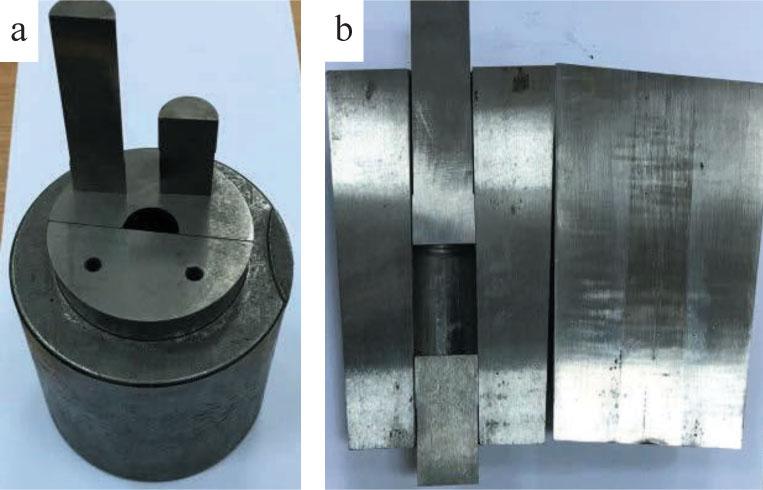
FIGURE 2.

FIGURE 3.
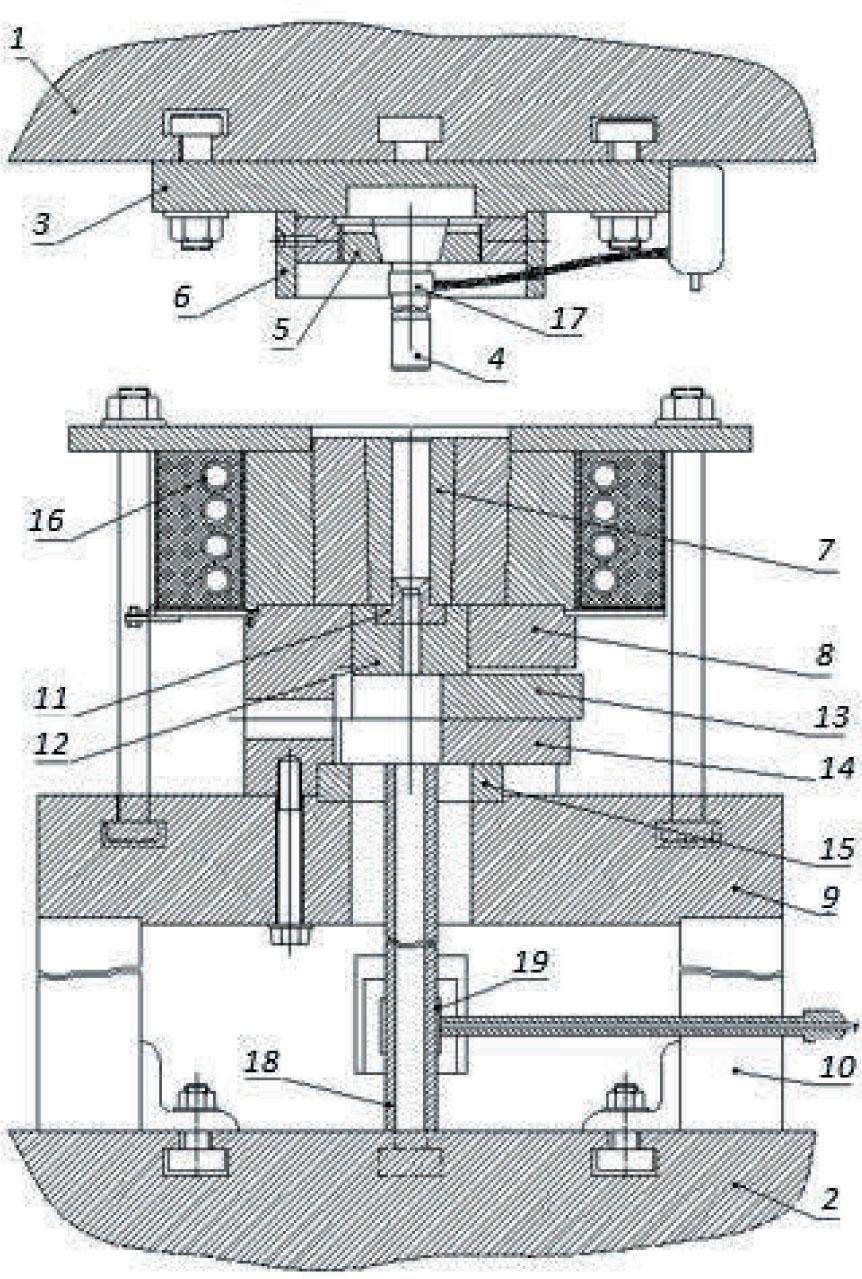
FIGURE 4.

FIGURE 5.
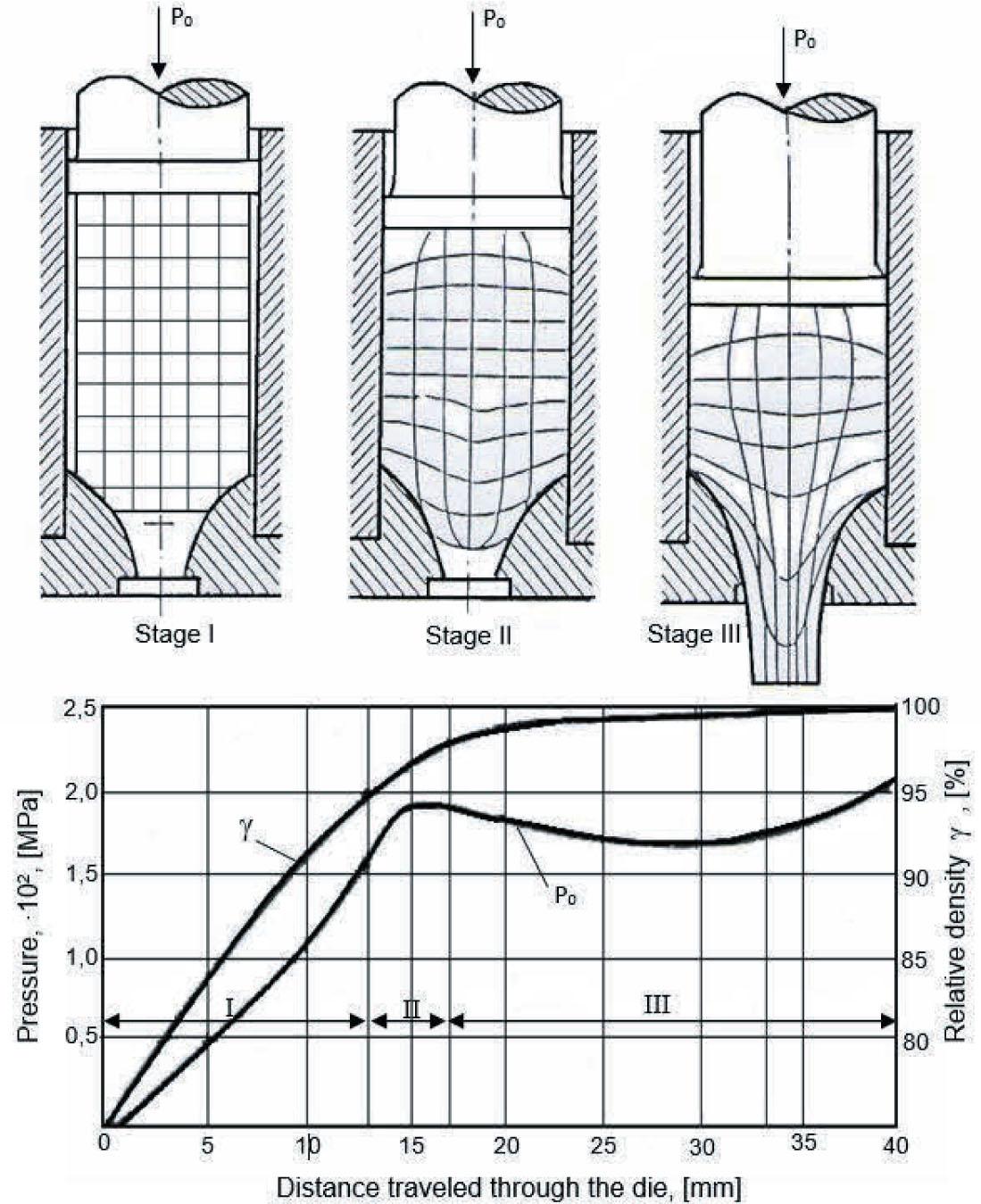
FIGURE 6.
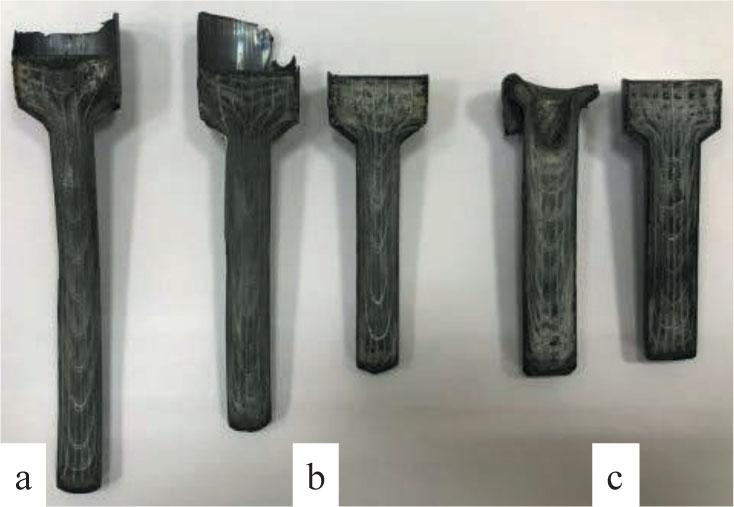

FIGURE 7.
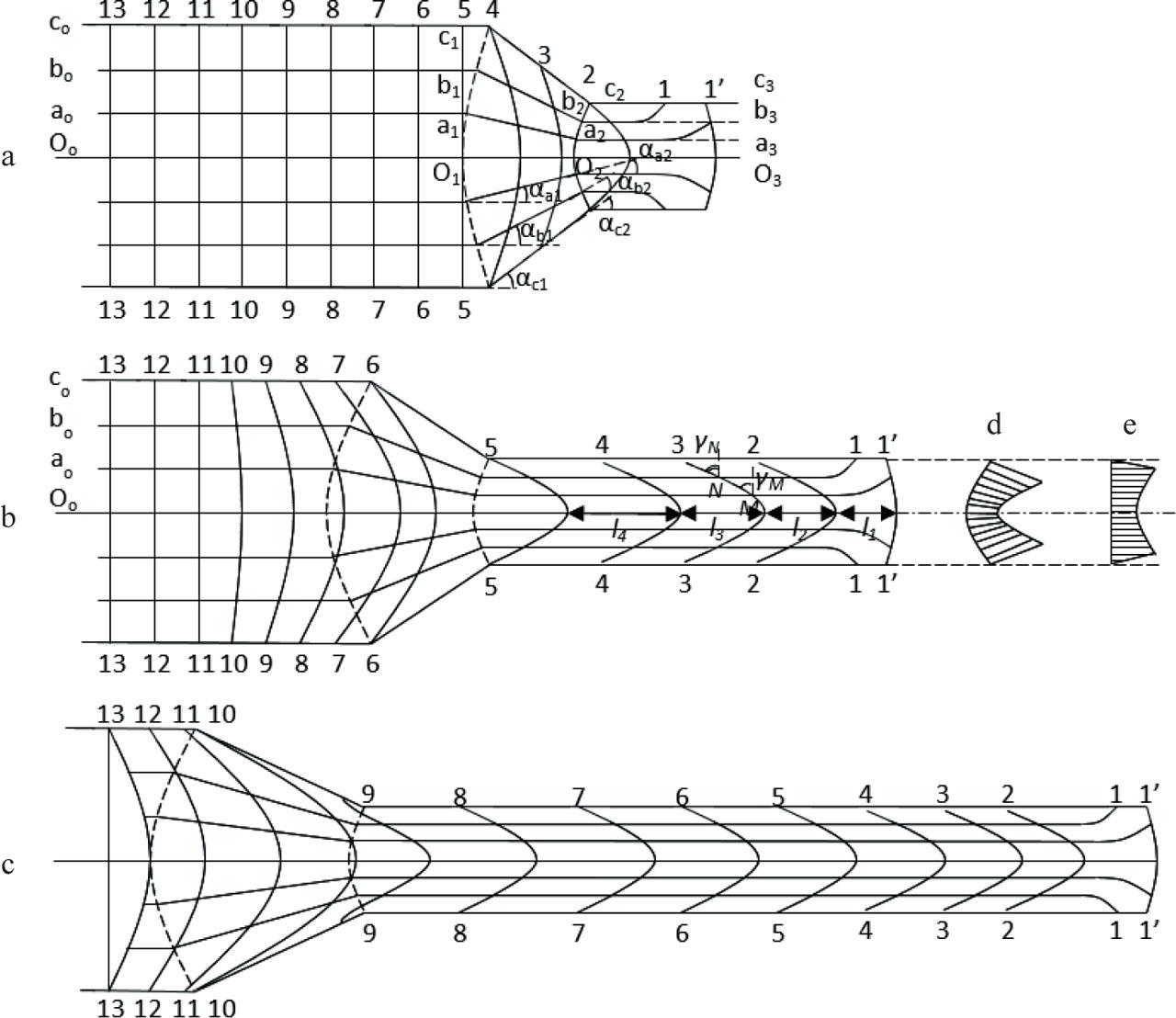
FIGURE 8.
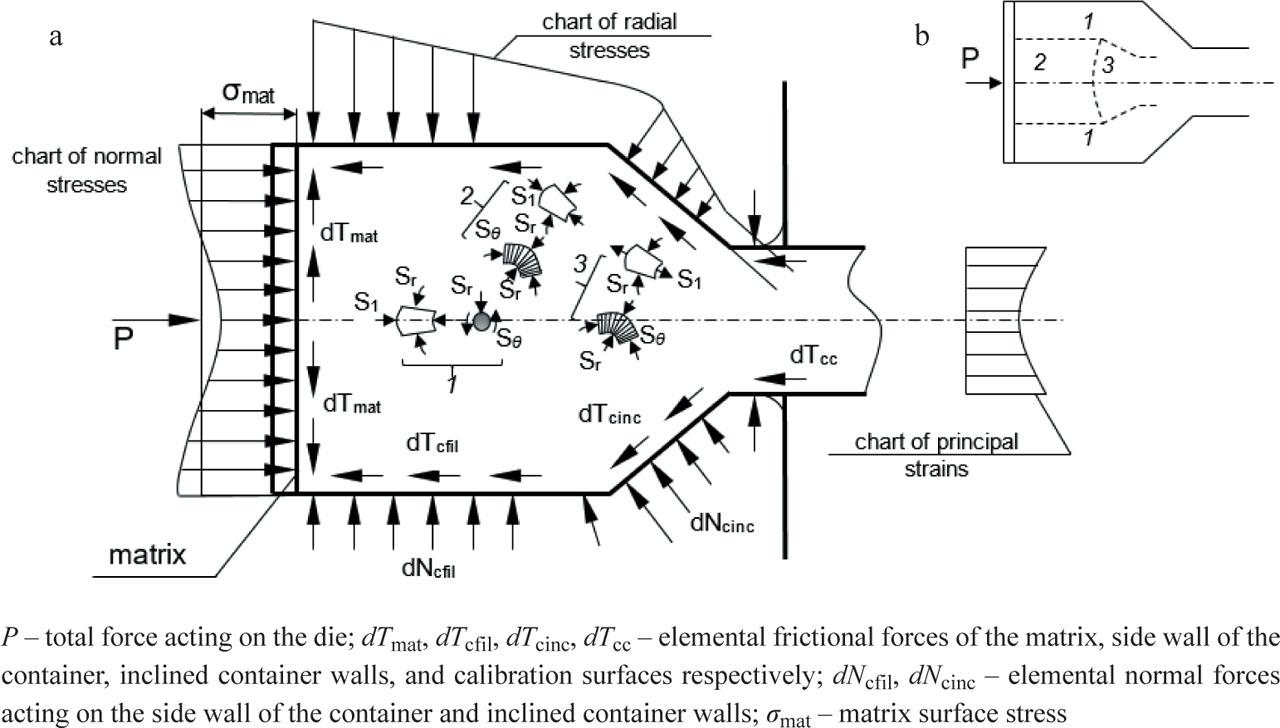
FIGURE 9.
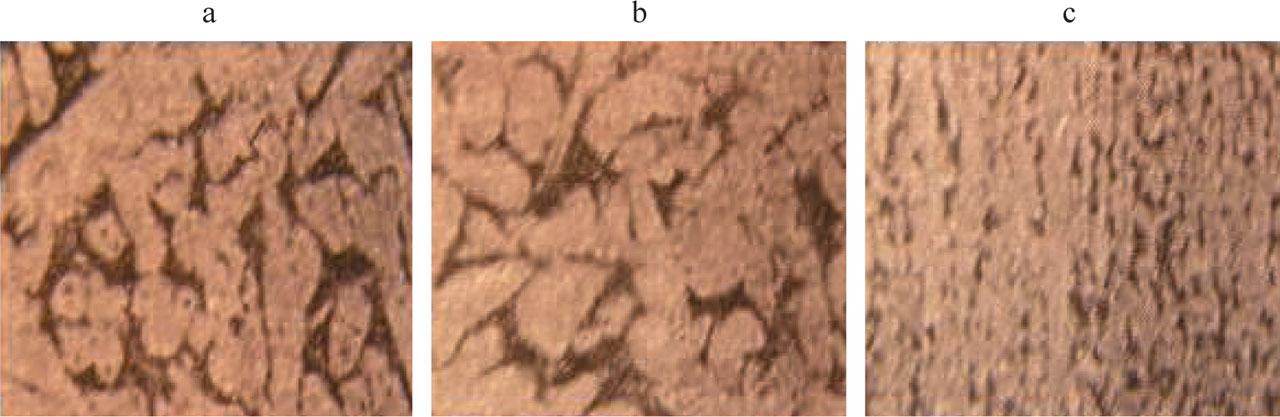
FIGURE 10.
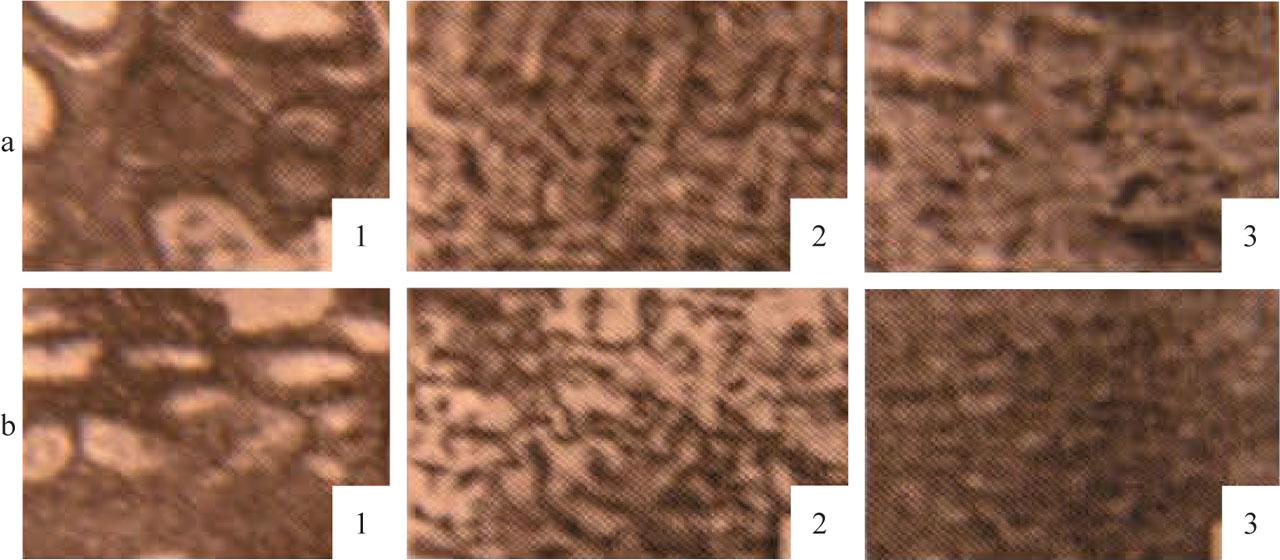
The composition and physical properties of the used aluminum powder
| Al content [%] | Al2O3 content [%] | Fe content [%] | Humidity [%] | Bulk density [g·cm−3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 93.8 | 6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.9 |
The composition and physical properties of the used copper powder
| Cu content [%] | Fe content [%] | Pb content [%] | As content [%] | Sb content [%] | Bi content [%] | Bulk density [g·cm−3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.5 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 2.5 |
