FIGURE 1.
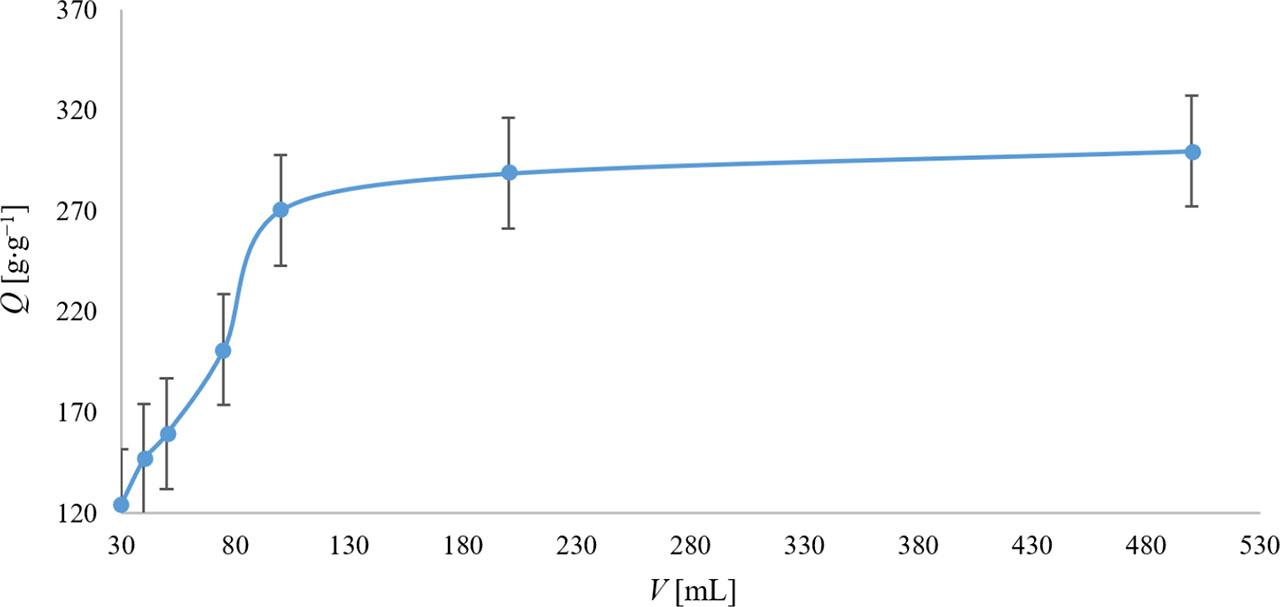
FIGURE 2.
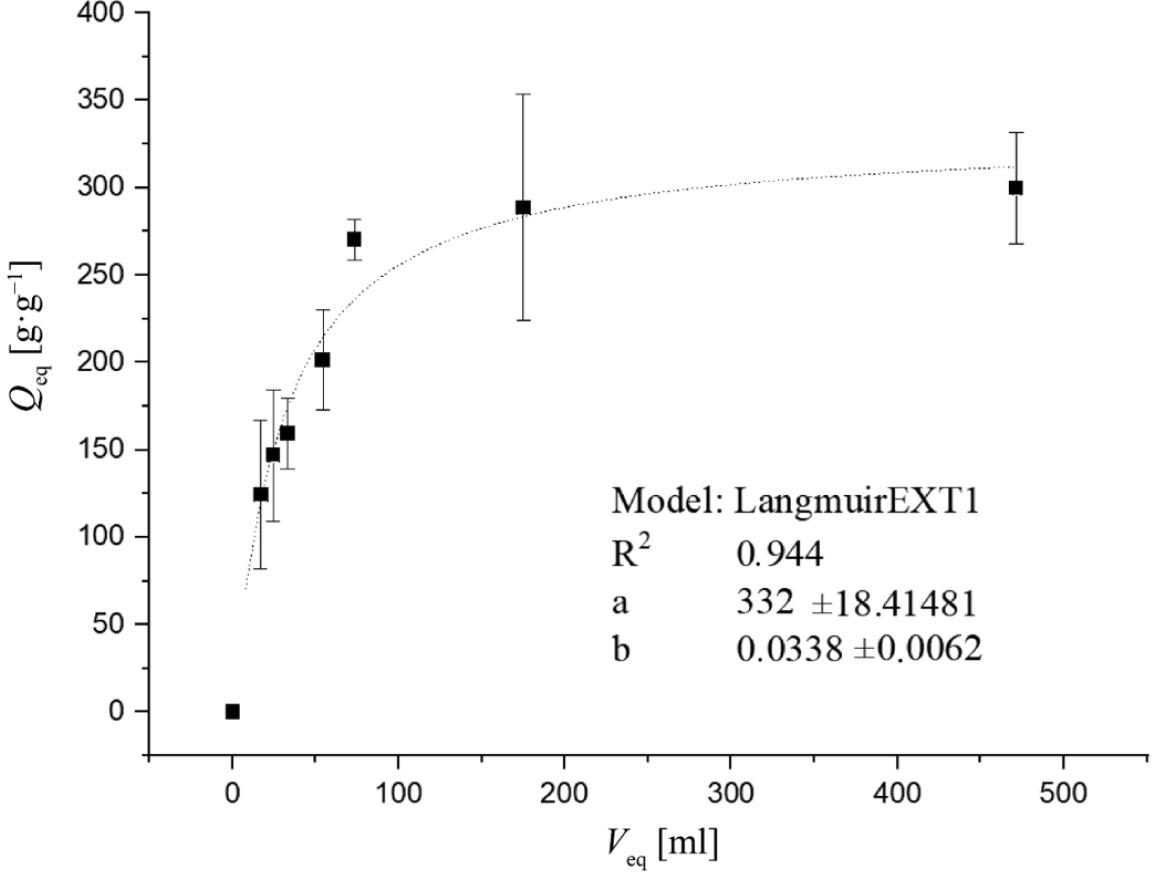
FIGURE 3.
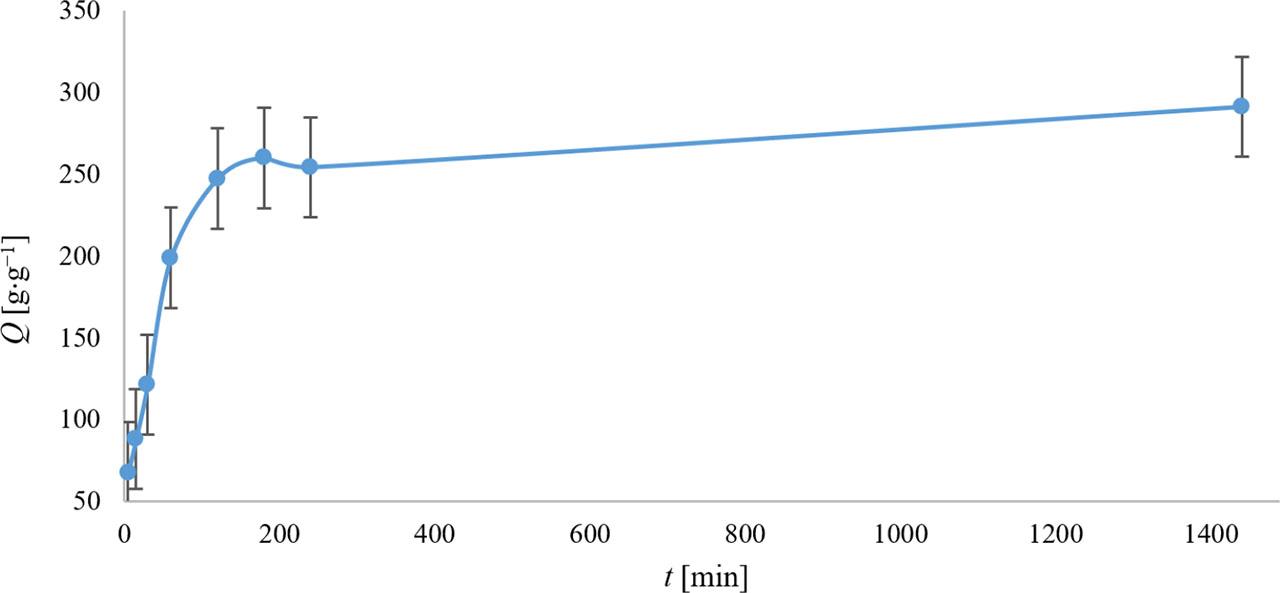
FIGURE 4.

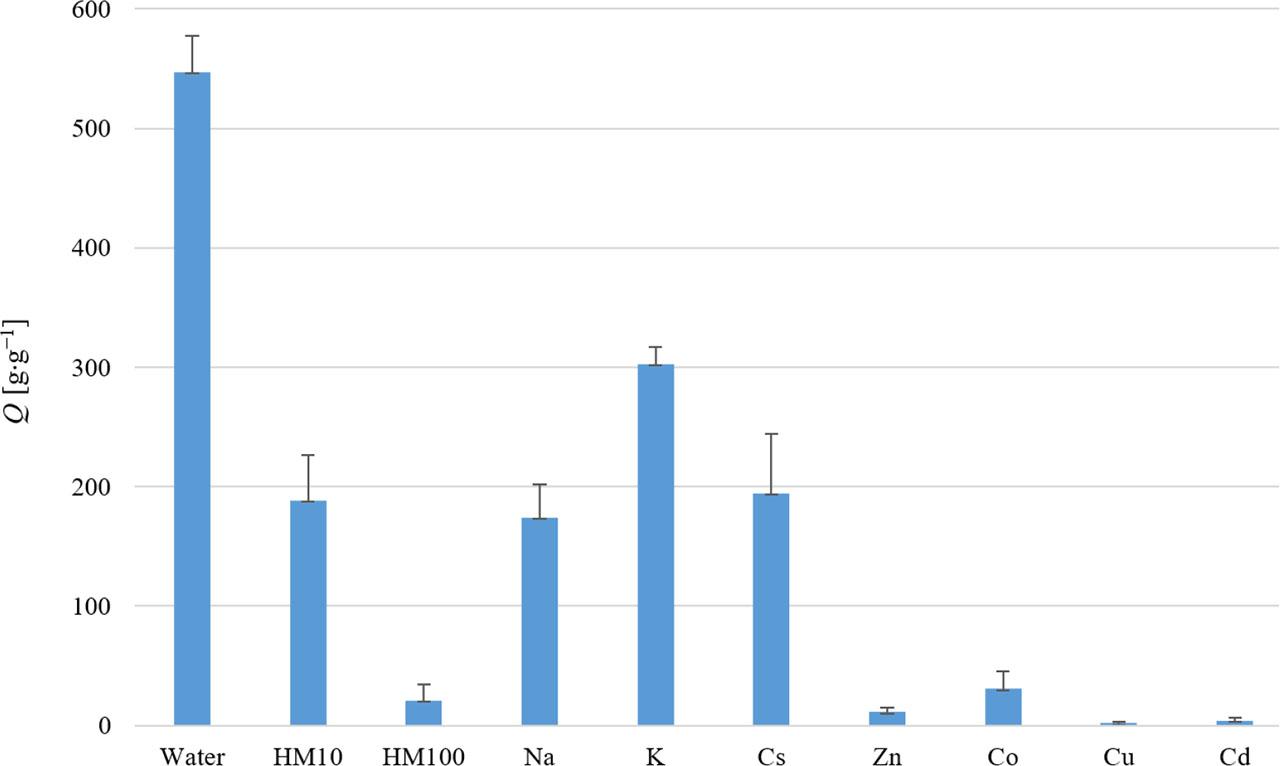
FIGURE 5.





© 2025 Lenka Vavrincová, Vanda Adamcová, Linda Machalová, Martin Valica, Šimon Rezbárik, Miroslav Horník, published by Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW Press
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License.