Figure 1:
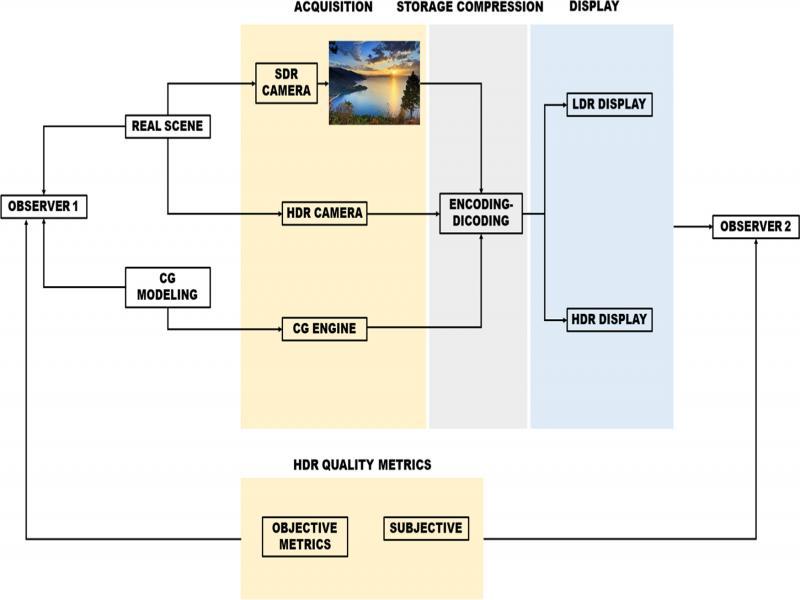
Figure 2:
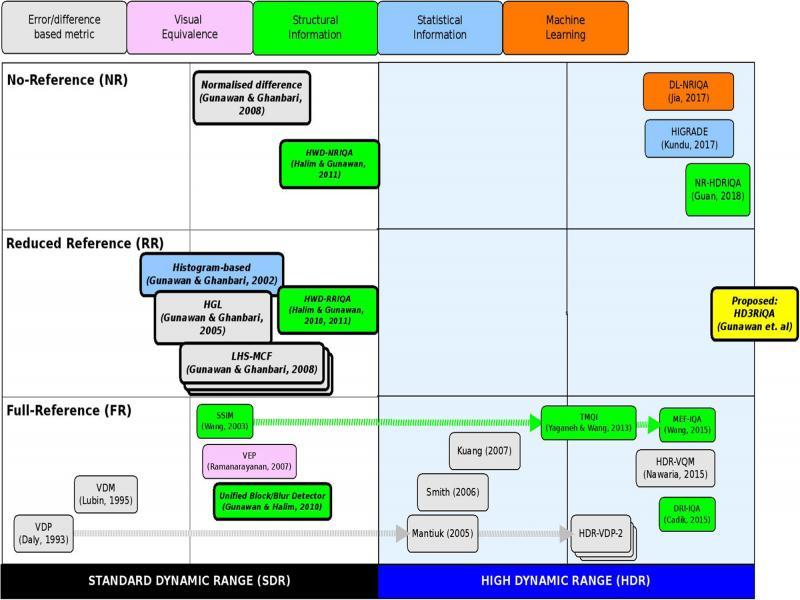
Figure 3:
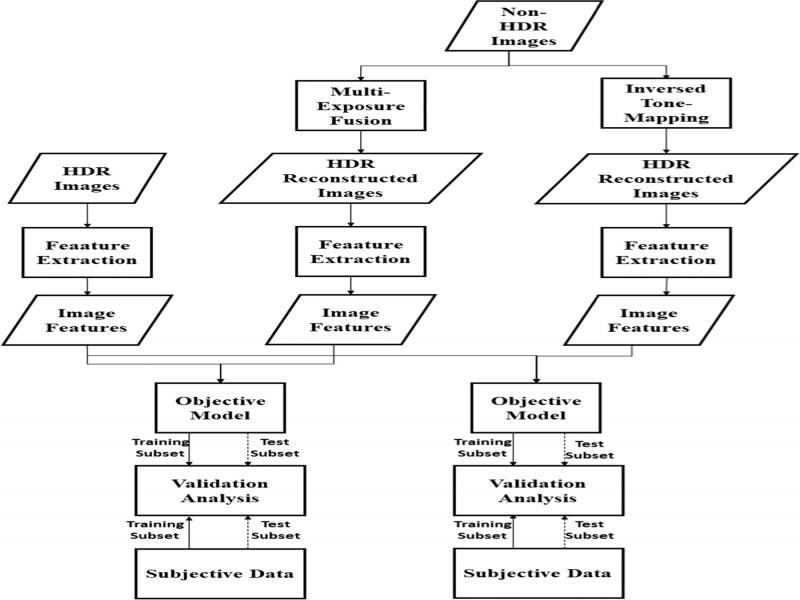
Figure 4:
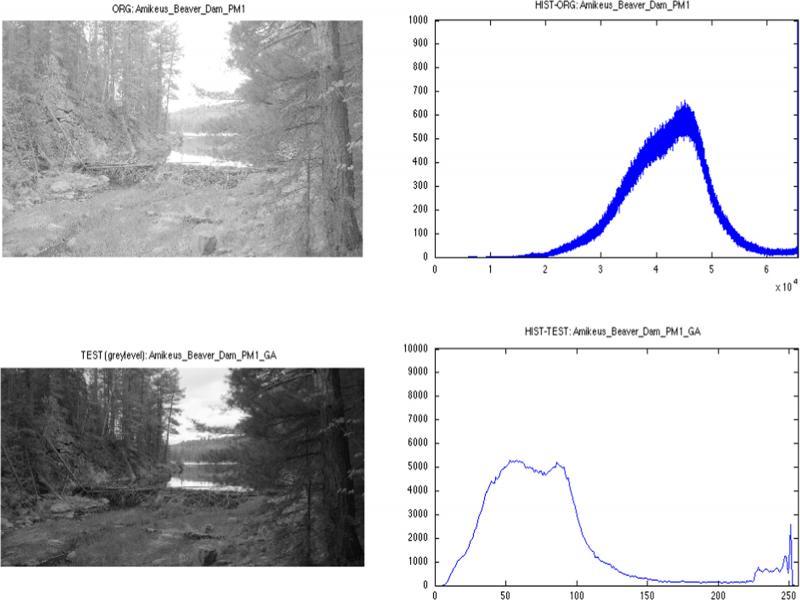
Figure 5:
Summary of MEF-based HDR images_
| Paper | Method | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ma et al. (2015) | Multi-exposure fusion algorithm | Well correlates with subjective judgments and significantly outperforms the existing IQA models for general image fusion | Cannot apply on a various image content |
| Rovid et al. (2007) | Gradient-based synthesized multiple exposure | Produces good quality HDR images from a series of poor quality photos taken by various exposures | Cannot apply on a colored image |
| Varkonyi-Koczy et al. (2008) | New multiple exposure time image synthesization technique | High-quality color HDR image which contains the maximum level of details and RGB color information | The current implementation of the proposed method is limited to process static scenes |
| Gu et al. (2012) | Fused gradient field | This method is efficient and effective | Existing algorithms can only be used for small movements |
| Li et al. (2012) | New quadratic optimization | Can enhance fine detail to produce sharper images as existing high dynamic range imaging schemes | Saturation images sometimes reduced by using both proposed exposure fusion schemes |
| Song et al. (2012) | New probabilistic exposure fusion scheme | New approach is advantageous compared with representative existing tone mapping operators | Rating and ranking are not suitable because both are too complex for an observer |
| Shen et al. (2013) | A novel fusion algorithm based on perceptual quality measures | Experiments demonstrated better performance of proposed algorithm compared to other methods | It is relatively difficult to extend these metrics to cases with several image sources |
| Goshtasby (2005) | Fuse multi-exposure images of a static scene taken by a stationary camera | It has no side effect and the local color and contrast in the input will not change | Select images to be mixed, the right size must be used to fuse the image |
| Mertens et al. (2009) | Fuse a bracket exposure sequence | Comparable to the existing tone mapping operator | Unoptimized implementation of software performs fusion of exposure within seconds |
| Yun et al. (2012) | Single exposure-based image fusion using multi-transformation | Shows a more visually pleasing output with the perceptually increased dynamic range | – |
| Huang et al. (2018a, b) | A new color multi-exposure image fusion | Successfully producing a better color display from the image blends and more texture details than other existing exposure fusion techniques | Based on the proposed approach, MEF cannot yet combine dynamic multi-exposure images and eliminate them |
| Kinoshita et al. (2018) | A new multi-exposure image fusion method based on exposure compensation | Better than other methods in terms of TMQI, statistical naturalness and discrete entropy | It is unclear how to determine appropriate exposure values, which are difficult to set at the time of photography |
Summary of contour detection methods_
| Paper | Method | Advantage | Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al. (2018a, b) | False contour candidate in HEVC | Detecting very noticeable, remove and preseving texture and details | false remove false contour in larger sized |
| Ahn and Kim (2005) | Flat-region and bit-depth extension | Removes false contour effectively and preserving sharpness | Cannot remove the local holelike pattern effectively |
| Lokmanwar and Bhalchandra (2019) | Gaussian filter and spectral clustering | Enhancing peak level and smoothing direction | Contour detection only generates only around a strong boundary |
| Manno-Kovacs (2019) | MHEC (Harris for edge and corners) point set | Handle complex contour, ability for multiple object detection | Iterative active contour still slower than other method |
| Chua and Shen (2017) | CNN patch-level measurement | No need precisely predict boundary pixel | At large texture regions still erroneous |
Summary of several HDR IQA methods_
| Authors | Methods | Databases | Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mantiuk et al. (2011) | Full-reference error metrics | LIVE, TID2008 | HDR-VDP-2 |
| Yeganeh and Wang (2013) | Full-reference, tone-mapped images, multi-scale SSIM | Own dataset (Yeganeh and Wang, 2013) | TMQI |
| Ma et al. (2015) | Full-reference, MEF images | Own dataset (Ma et al., 2015) | MEF-IQA |
| Kundu et al. (2017a, b) | No-reference, natural scene statistics | ESPL-LIVE | HIGRADE |
| Jia et al. (2017) | No-reference, DL, convolutional neural networks with saliency maps | LIVE and CSIQ (SDR) | DL-NRIQA |
| Guan et al. (2018) | No-reference, tensor space, image manifold | Publicly available dataset | TDML with SVR-based |
| Ravuri et al. (2019) | Convolutional neural nets, SVM, tone mapping, deep no-reference tone-mapped image quality assessment, NRIQA | ESPL-LIVE and Yeganeh | RcNet |
| Yue et al. (2020) | Feature extraction; support vector machines; tone-mapped HDR; multi-exposure fused images; no-reference (NR); colorfulness, exposure, naturalness | Publicly available dataset | SVM-based features |
| Duan et al. (2020) | Local dimming algorithms, image contrast ratio, subjective, objective | Fairchild’s | BLD algorithms |
| Fang et al. (2020) | MEF algorithms; objective quality model; reduced ghosting artifacts; Heuristic algorithms; structural similarity | Own dataset and Mantiuk’s MEF deghosting images | MEF-SSIM_d |
| Kim and Kim (2020) | Convolutional neural nets; learning-based RTM scheme; low-complexity reverse tone mapping | Own dataset | RTM Scheme, HDR-VQM |
| Jiang et al. (2020) | Entropy; feature extraction; support vector machines; colorfulness index; tone mapping operators; luminance partition; NRIQA | TMID and ESPL-LIVE | SVR-based |
| Ellahi et al. (2020) | HMM, TMO, FR | ETHyma | HMM-based similarity measure |
| Krasula et al. (2020) | TMO, FR, NR, feature naturalness, structural similarity, and feature similarity | Yeganeh, Cadik, and TMIQD | FFTMI, based on SS-II, FN, and FSITM |
| Wang et al. (2021) | NRIQA, tone-mapped images | TMID and ESPL-LIVE | SVR-based with RBF kernel |
| Fang et al. (2021) | NRIQA, tone-mapped images, gradient, chromatics, statistics | ESPL-LIVE | VQGC |
Summary of ITMO-based HDR images_
| Paper | Method | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Larson et al. (1997) | Tone reproduction curves (TRC) | Performs well on a wide category of images | Produced a visual accurate images but not enhanced images |
| Reinhard et al. (2002) | Zone system and Automatic dodging and burning | Well-suited on a across-the-board of HDR images | This method only brought textured areas within range which is categorized simple |
| Durand and Dorsey (2000) | Extended version of Ferwerda et al. (1996) | Solve interesting problem in TMO | This system is slower than its state-of-the-art method |
| Fattal et al. (2002) | A gradient-based tone mapping operator | Able to compress a very wide dynamic range, present every details and less common noise or artifacts | Does not enhance global features |
| Mantiuk et al. (2006) | Contrast mapping and contrast equalization | Provide a high visual quality output with appealing brighness and contrast even no artifacts | Does not run in real-time application and does not include color in information |
| Qiu et al. (2006) | Optimized tone reproduction curve (TRC) | More simple than the previous, faster in time consuming and easier to implement | Weak at destroying spatial details |
| Eilertsen et al. (2015) | A real-time noise TMO | Minimize the contrast disortions, control the perceptibility of noises and adjust to a provide and shifting light, also can be apply in real-time | Lack in scenery creation and best subjective score |
| Rana et al. (2019) | SVR | Gained a consistent result under complex real-world ilumination transitions | The execution time are the longest among the-state-of-the-art |
| El Mezeni and Saranovac (2018) | Local tone mapping | Present details and good local and global contrast of proceed images also better result in overall image quality | Produce a little amount of noise |
Summary of several subjective assessment methods_
| Paper | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| van Dijk et al. (1995) | Category scaling | Numerical category scaling techniques provide an efficient and valid way to get a compression ratio versus a quality curve and to assess the image quality perceived in a much smaller way |
| Th. Alpert (CCETT) and J.-P. Evain (EBU) (Alpert and Evain, 1997) | SSCQE and DSCQE | SSCQE to evaluate subjective quality, while the DCSQE is used to maintain image quality and information transmitted |
| Sheikh et al. (2006) | Double stimulus | The experiment used a double-stimulus methodology to measure quality more accurately for realignment purposes |
| Redi et al. (2010) | SS and QR | Single stimulus (SS) method presents several weaknesses. Quality ruler (QR) method is worth implementing efforts from the point of view of consistency and repetition of scores |
| Mantiuk et al. (2012) | Force-choice pairwise comparison | The forced-choice pairwise comparison method results in the smallest measurement variance and thus produces the most accurate results. This method is also the most time-efficient, assuming a moderate number of compared conditions |
| Persson (2014) | QR | The difference in assessment in the study seemed to be significantly dependent on the perceived similarity between the ruler image and the test image |
| Nuutinen et al. (2016) | Dynamic reference | The DR method is very suitable for experiments that require very accurate results in a short time because the DR method is more accurate than the ACR method and faster than the PC method |
| Zhu et al. (2018a, b) | AIT inspired MOS and PC | Using arrow’s impossibility theorem (AIT) proves that the meeting between unanimity and independence of irrelevant alternatives (IIA) will produce an ‘important subject’, which in fact determines the final rating of image quality |