Figure 1:
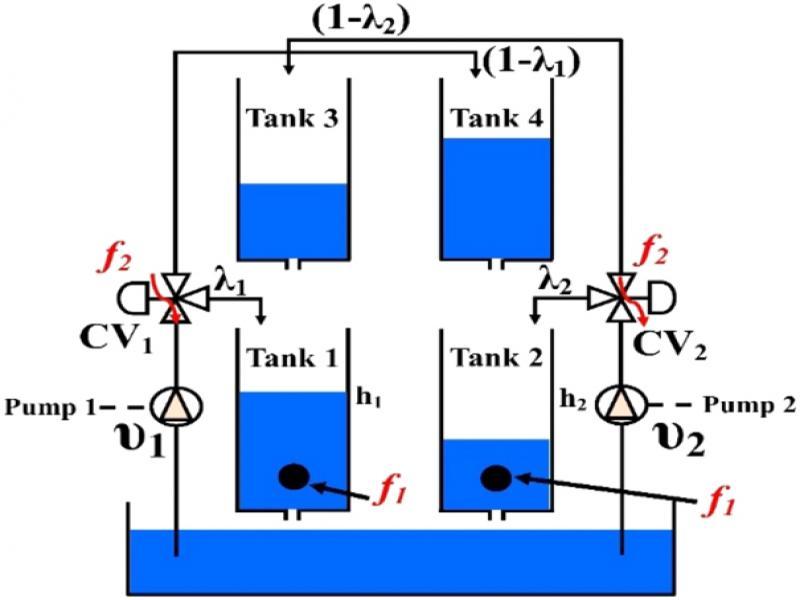
Figure 2:
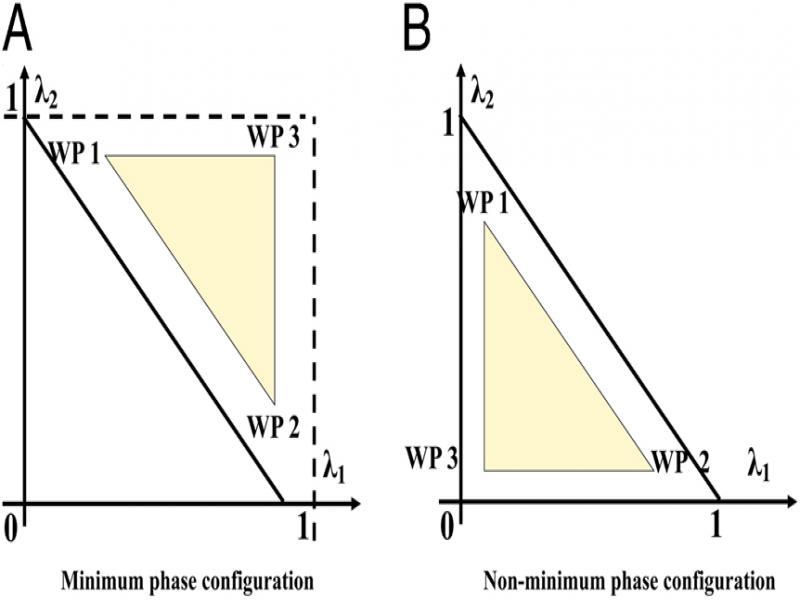
Figure 3:
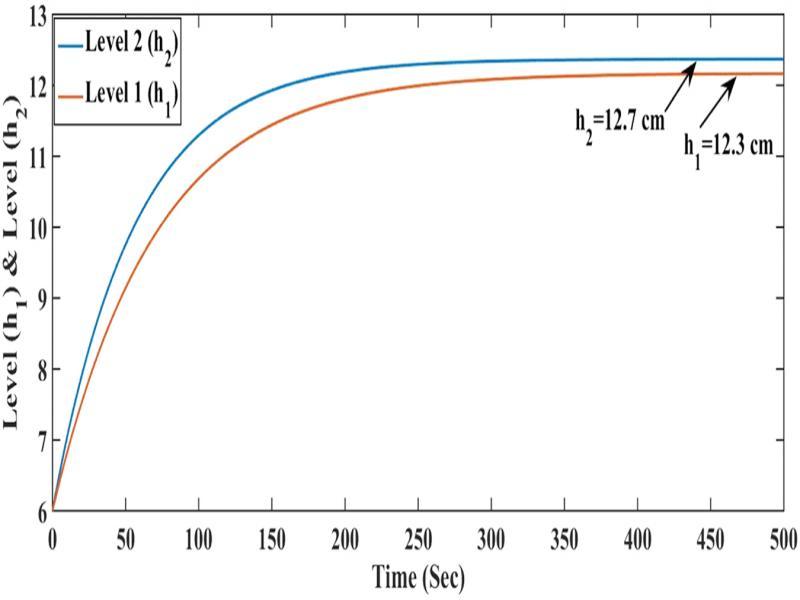
Figure 4:
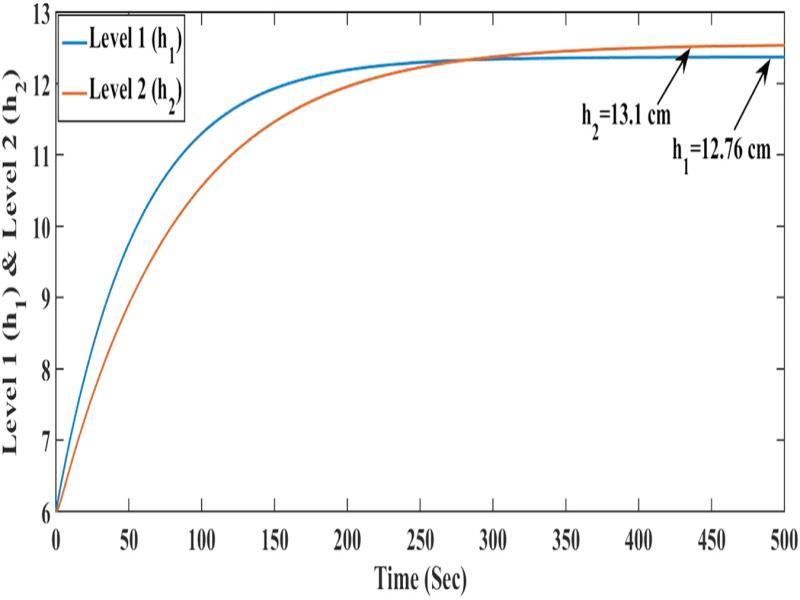
Figure 5:
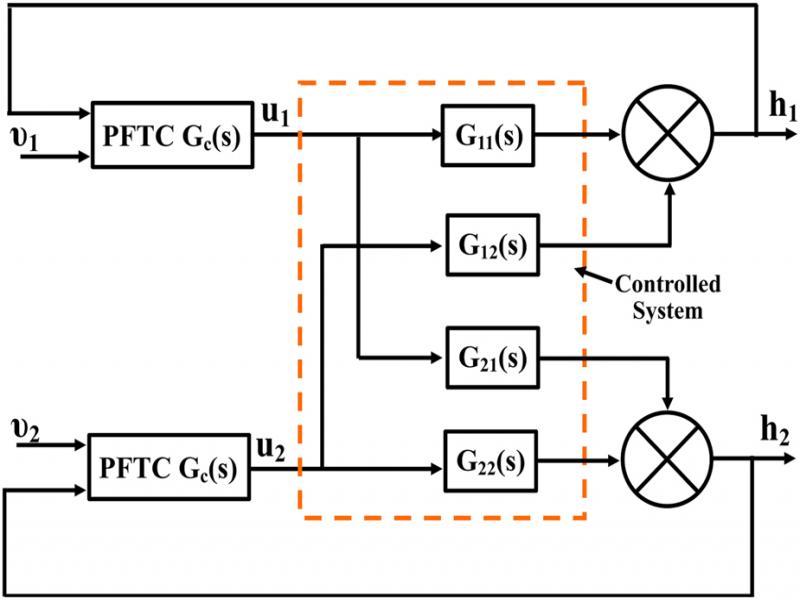
Figure 6:
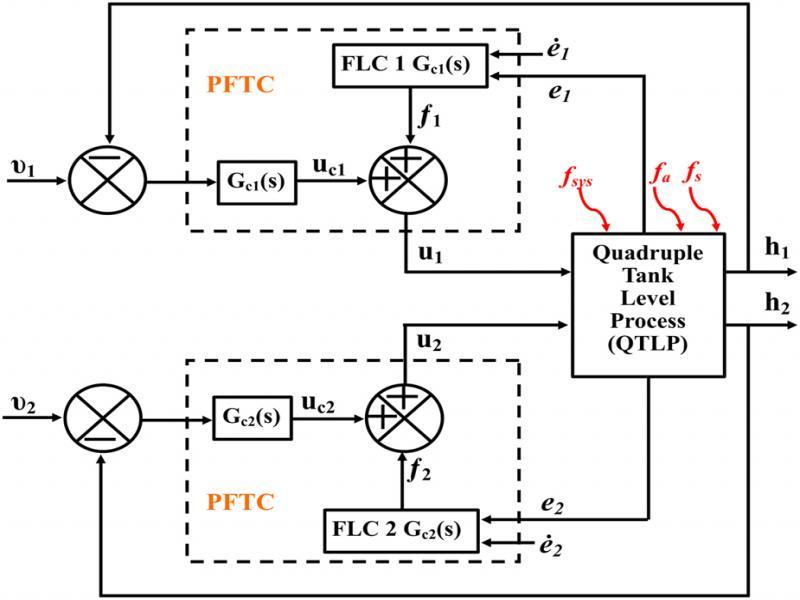
Figure 7:
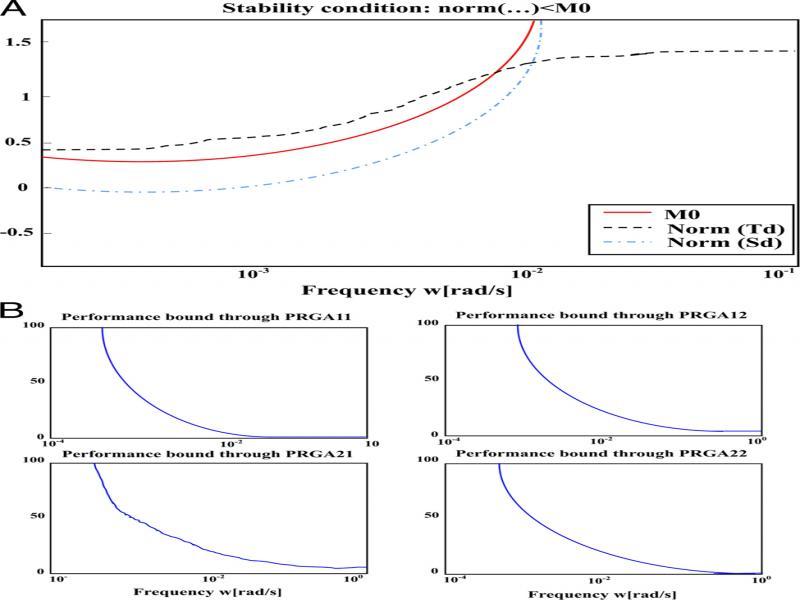
Figure 8:
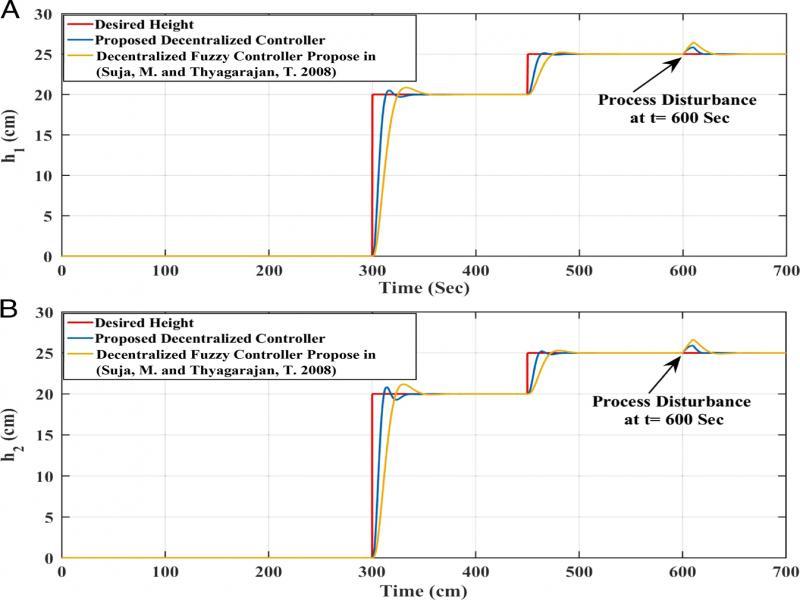
Figure 9:
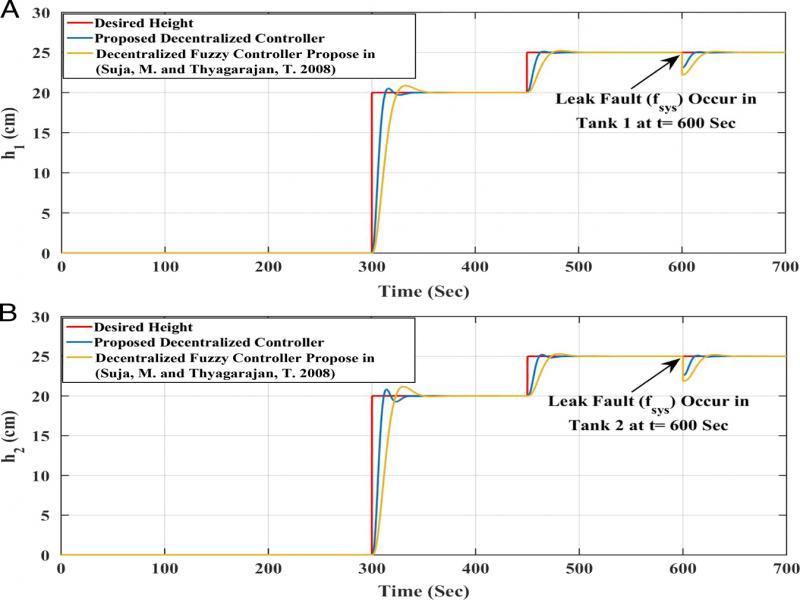
Figure 10:
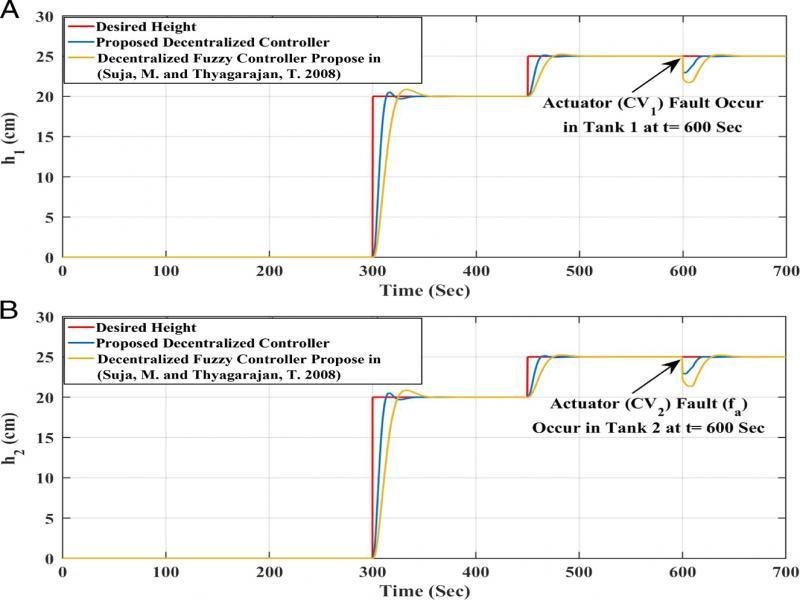
Figure 11:
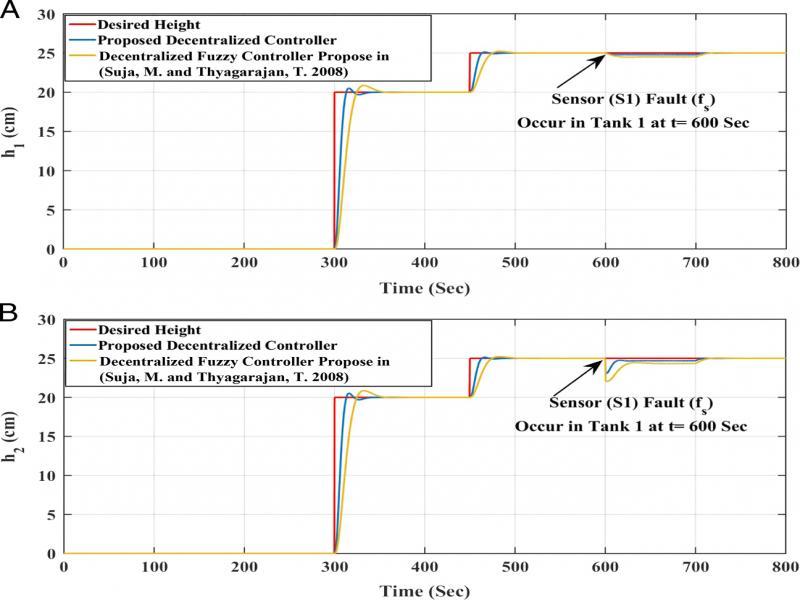
Figure 12:
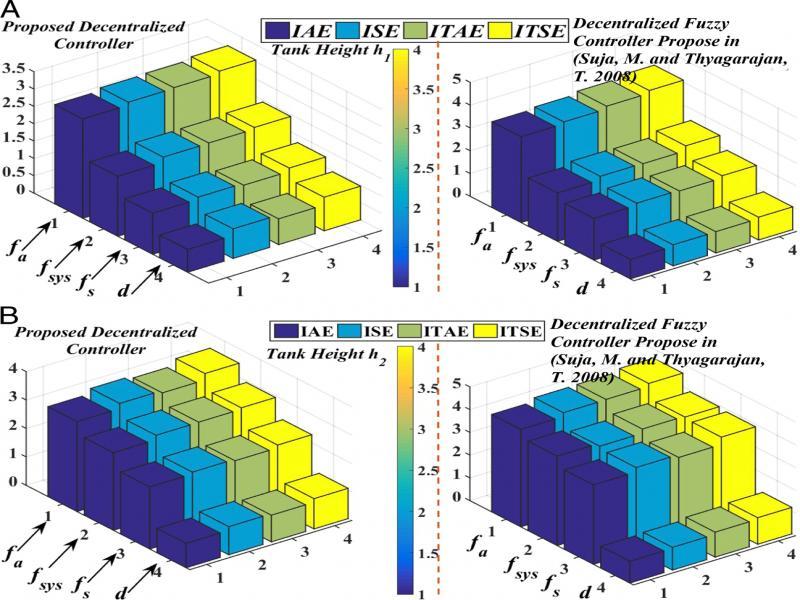
Figure 13:
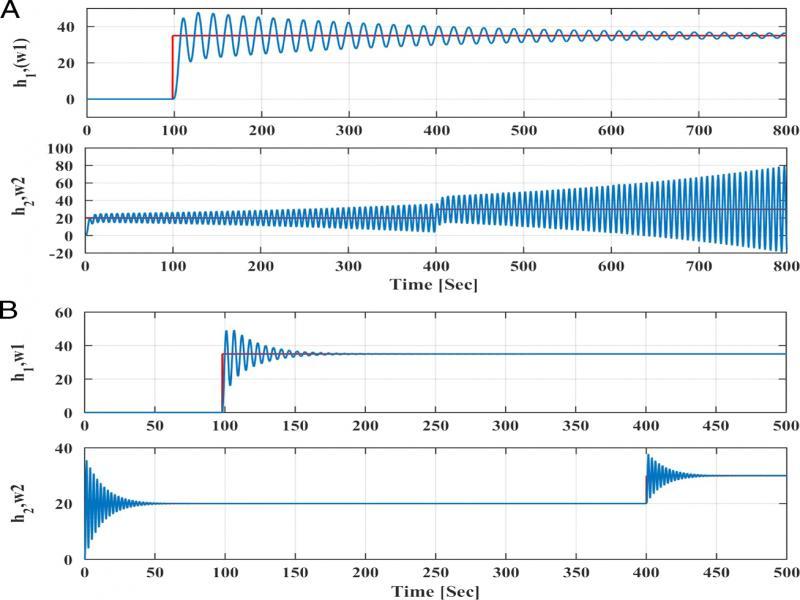
Figure 14:
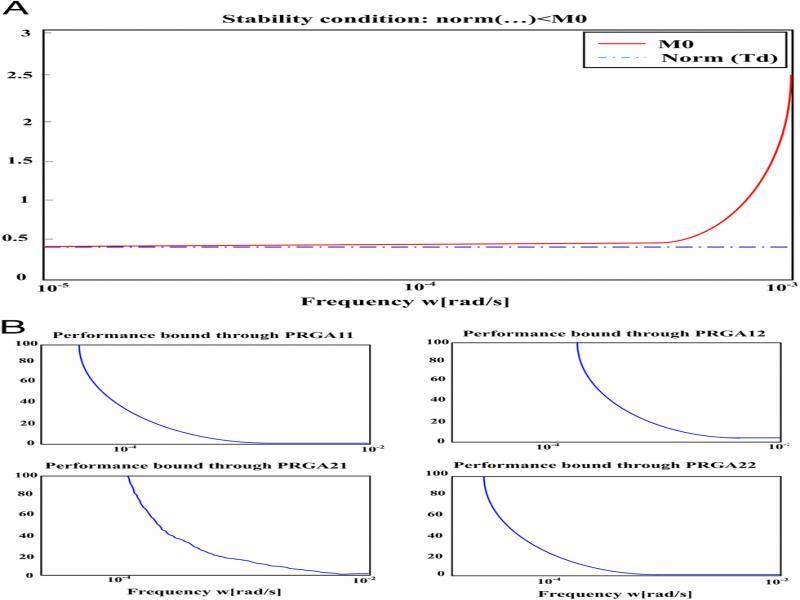
Figure 15:
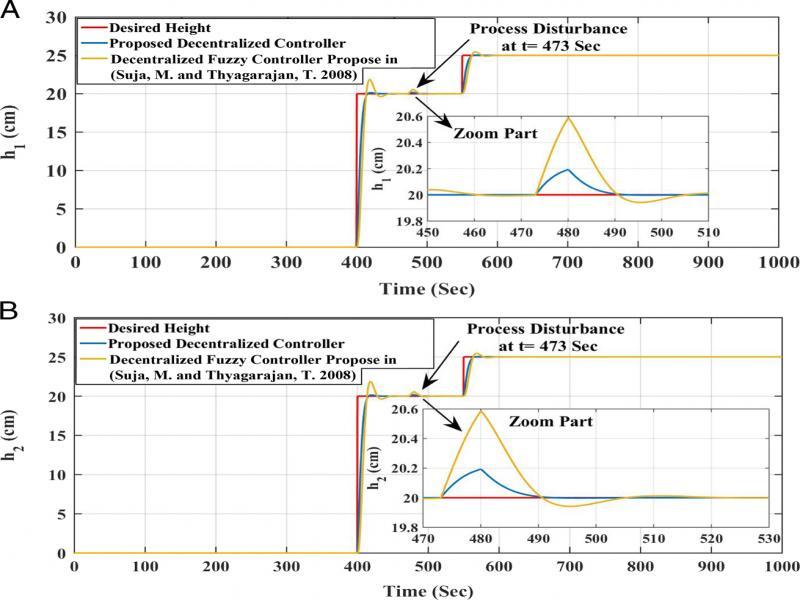
Figure 16:
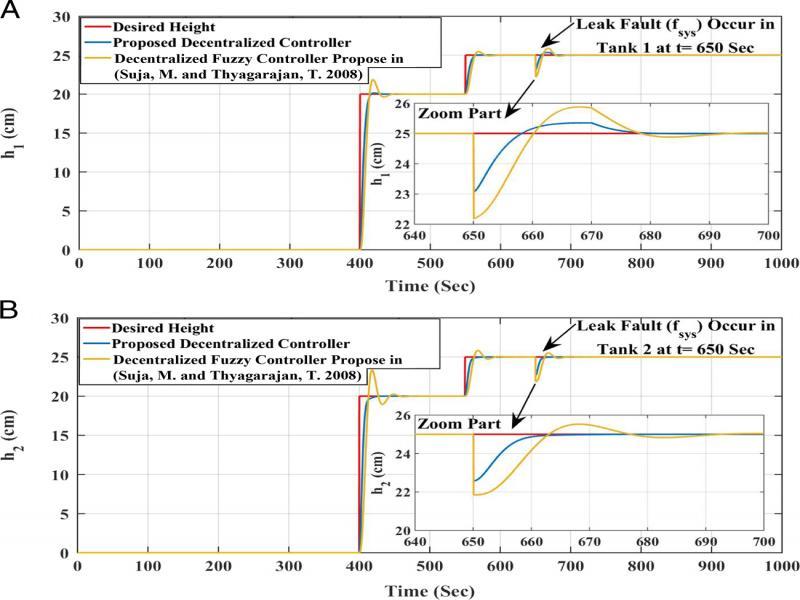
Figure 17:
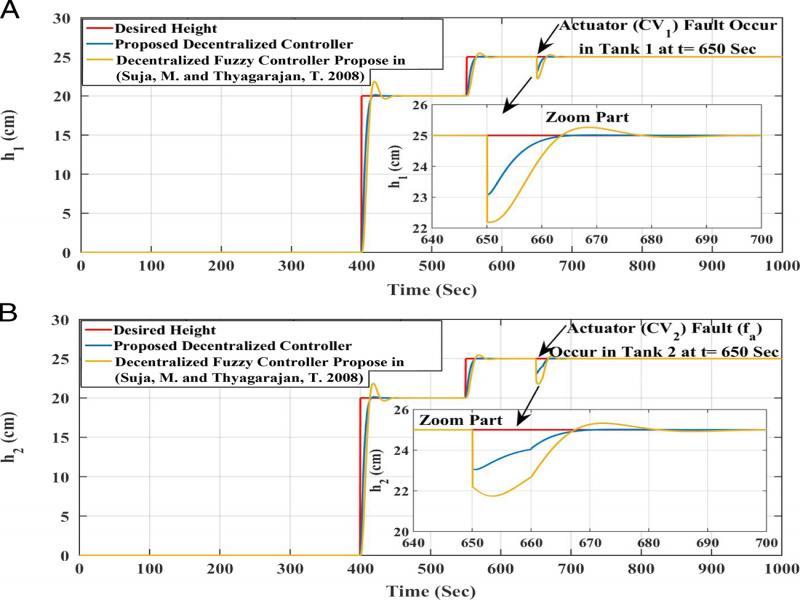
Figure 18:
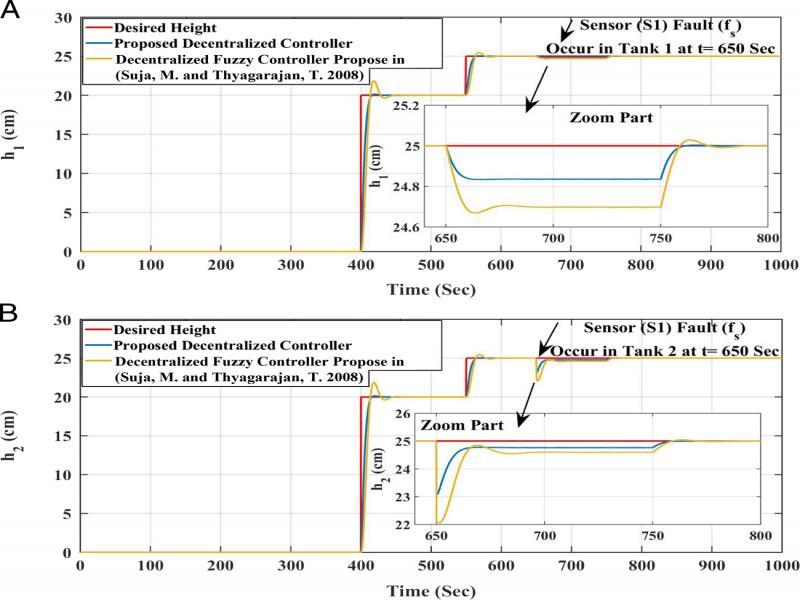
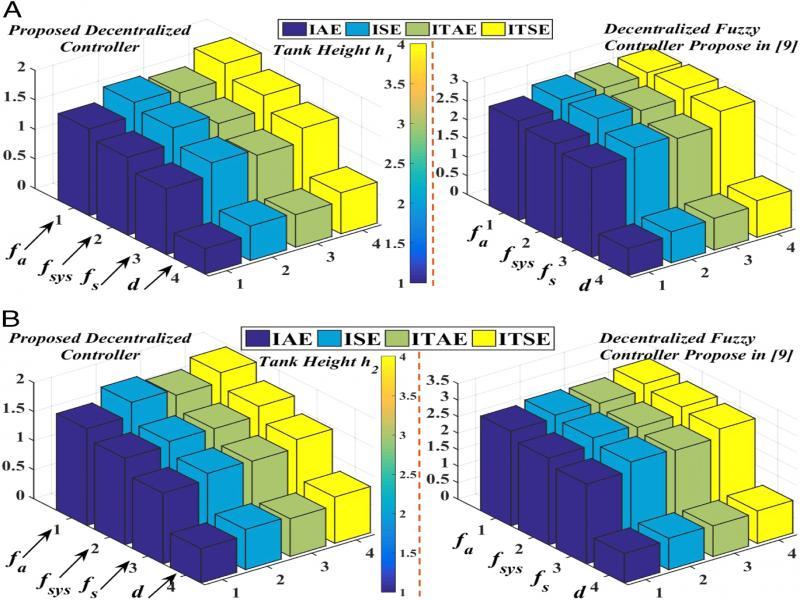
Figure 19:
Parameters for FLC_
| Parameter | Parameter value |
|---|---|
| No. of input variables | 2 |
| No. of output variables | 1 |
| No. of linguistic variables per MF | 7 |
| No. of rules | 49 |
| Membership function (MF) | Triangular |
| Defuzzification methods | Center of gravity method |
Parameters of the quadruple tank level process_
| Sr. no. | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Area of the tanks A1, A3, A2, and A4 | 32 cm2 |
| 2 | Area of outlet pipes a1 and a3 | 0.071 cm2 |
| 3 | Area of outlet pipes a2 and a4 | 0.057 cm2 |
| 4 | Constant k | 0.50 V/cm |
| 5 | Gravitational constant g | 981 cm/s2 |
Operating parameters of minimum phase and non-minimum phase system_
| Parameters | Operating point minimum phase | Operating point non-minimum phase |
|---|---|---|
|
| 12.76, 13.1 | 12.3, 12.7 |
|
| 2.1, 1.8 | 5.1, 5.7 |
|
| 3.33, 3.36 | 3.14, 3.31 |
| k1, k2 | 3.33, 3.38 | 3.14, 3.33 |
| λ1, λ2 | 0.7, 0.6 | 0.43, 0.34 |
Rule base for type-1 FLC 2 loop 2_
| f2, e2 and ė2 | NB | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NB | NB | NB | NM | NS | NS | ZR |
| NM | NB | NB | NM | NS | NS | ZR | PM |
| NS | NB | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB |
| ZR | NM | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB |
| PS | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB | PB |
| PM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PM | PB | PB |
| PB | ZR | PS | PM | PB | PB | PB | PB |
Rule base for type-1 FLC 1 loop 1_
| f1, e1 and ė1 | NB | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NB | NB | NB | NM | NS | NS | ZR |
| NM | NB | NB | NM | NS | NS | ZR | PM |
| NS | NB | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB |
| ZR | NM | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PM | PB |
| PS | NM | NS | ZR | PS | PS | PM | PB |
| PM | NS | ZR | PS | PS | PM | PB | PB |
| PB | ZR | PS | PS | PM | PB | PB | PB |