Figure 1:

Figure 2:
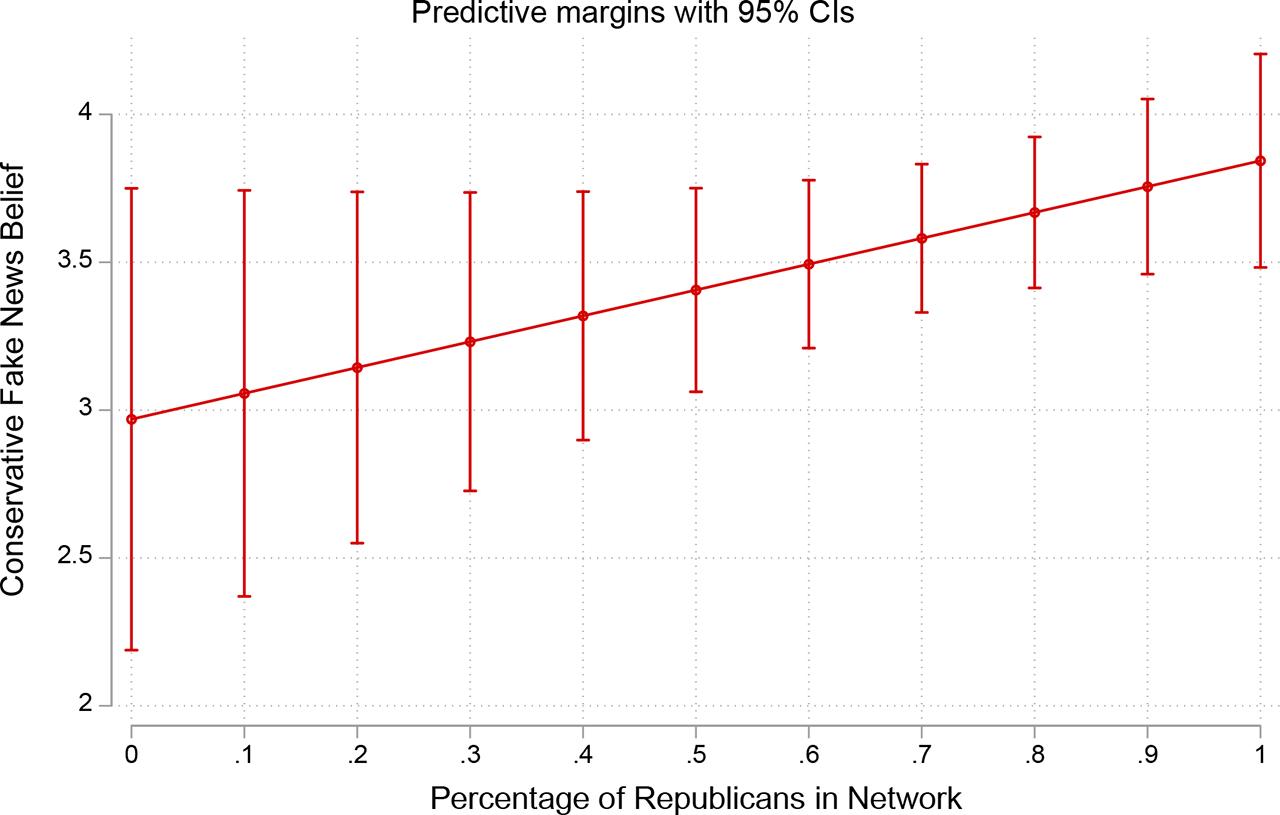
Figure 3:
Summary of hypotheses results_
| Hypothesis | Result |
|---|---|
| H1: Homogeneity increases importance of political identity. | ✓ |
| H2: Homogeneity increases ingroup evaluation. | ✓ |
| H3a: Homogeneity increases political rumor bias. | PS: Only for helping rumor |
| H3b: Homogeneity increases sharing political rumor bias. | PS: Only for helping rumor |
| H4a: Homogeneity increases fake headline bias. | PS: Only for Republicans |
| H4b: Homogeneity increases sharing fake headline bias. | PS: Only for Republicans |
| H5a: Cognitive reflection not related to rumor belief. | ✓ |
| H5b: Cognitive reflection not related to rumor sharing. | ✓ |
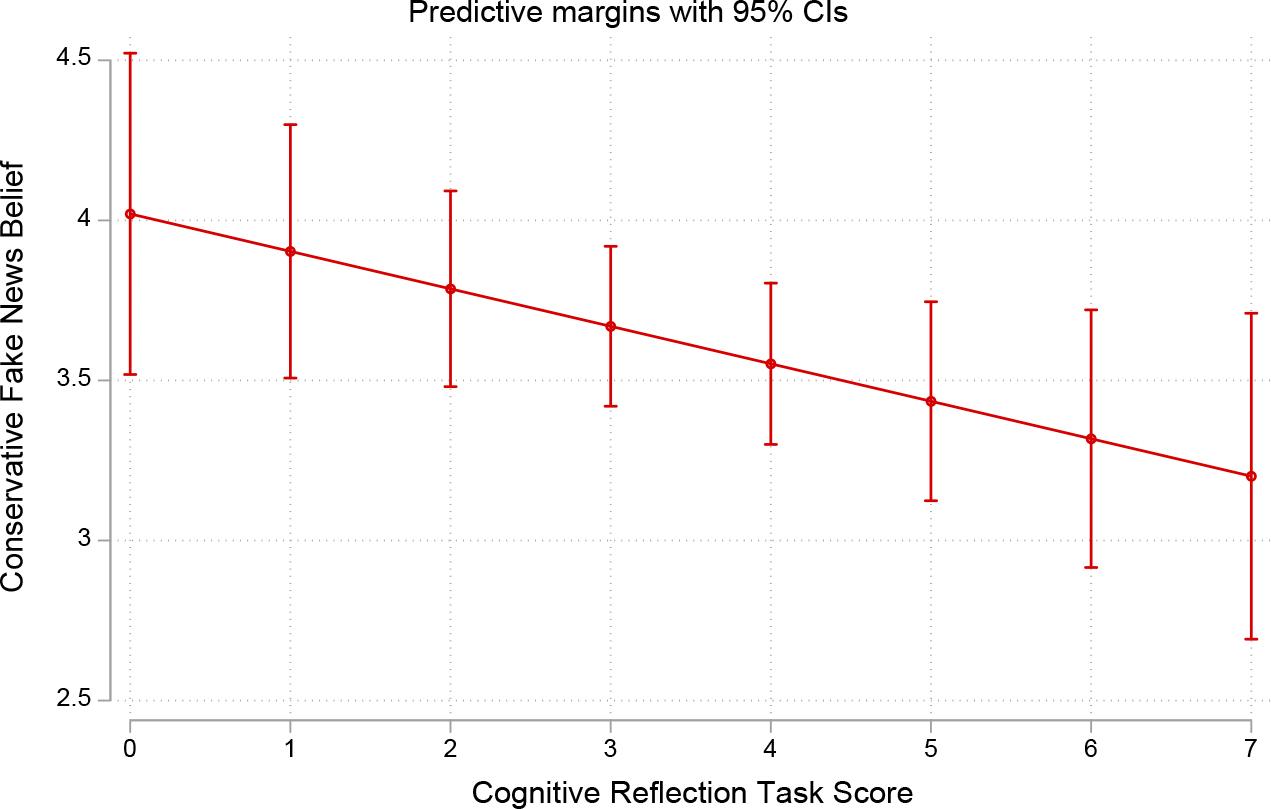
| H6a: Cognitive reflection predicts fake news belief. | PS: Only for Republicans |
| H6b: Cognitive reflection predicts fake news sharing. | PS: Only for Republicans |
Hypothesis summary list_
| Hypothesis |
|---|
| H1: Homogeneity increases importance of political identity. |
| H2: Homogeneity increases ingroup evaluation. |
| H3a: Homogeneity increases political rumor bias. |
| H3b: Homogeneity increases sharing political rumor bias. |
| H4a: Homogeneity increases fake headline bias. |
| H4b: Homogeneity increases sharing fake headline bias. |
| H5a: Cognitive reflection not related to rumor belief. |
| H5b: Cognitive reflection not related to rumor sharing. |
| H6a: Cognitive reflection predicts fake news belief. |
| H6b: Cognitive reflection predicts fake news sharing. |
The influence of network homogeneity on fake news headlines (Democrats and Republicans)_
| Liberal fake news | Share liberal fake news | Conservative fake news | Share conservative fake news | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network homogeneity | −0.257 (−1.19) | 0.147 (0.54) | 0.465~1.69 | 0.012 (0.04) |
| Number of alters | 0.07 (0.99) | 0.078 (0.88) | 0.001 (0.01) | −0.116 (−1.23) |
| Higher liberalism | 0.075 (1.36) | 0.024 (0.35) | −0.168* (−2.14) | −0.064 (−0.74) |
| Constant | 3.52** (5.67) | 2.55** (3.25) | 4.064 (7.43) | 3.48** (5.70) |
| N | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 |
The influence of network homogeneity on political rumor likelihood and sharing_
| Ingroup helping rumor belief | Outgroup bullying rumor belief | Share ingroup helping rumor | Share outgroup bullying rumor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network homogeneity | 0.191~(1.74) | 0.055 (0.47) | 0.256* (2.52) | 0.081 (0.72) |
| Number of alters | −0.001 (−0.02) | 0.007 (0.20) | 0.037 (1.15) | −0.005 (−0.14) |
| Higher liberalism | −0.034 (−1.18) | −0.021 (−0.66) | −0.059* (−2.17) | −0.064 (−2.14) |
| Democrat identification | 0.133 (0.73) | 0.289 (1.46) | 0.201 (1.19) | 0.359~(1.92) |
| Constant | 0.614** (2.75) | 0.453~(1.88) | 0.288 (1.39) | 0.670** (2.93) |
| N | 214 | 214 | 214 | 214 |
Homogeneity predicts political identity importance_
| Political identity importance | |
|---|---|
| Network homogeneity | 0.527** (3.28) |
| Number of alters | 0.011 (0.23) |
| Higher liberalism | 0.038 (0.89) |
| Democrat identification | 0.214 (0.80) |
| Constant | 2.392** (7.32) |
| N | 214 |
The influence of network homogeneity on political group ratings_
| Ingroup evaluation | Outgroup evaluation | |
|---|---|---|
| Network homogeneity | 0.581** (2.69) | −0.670** (−2.61) |
| Number of alters | 0.105 (1.53) | 0.035 (0.43) |
| Higher liberalism | −0.096~(1.66) | −0.058 (−0.84) |
| Democrat identification | 0.625~(1.74) | −0.286 (−0.67) |
| Constant | 1.295** (2.95) | −0.931~(−1.78) |
| N | 214 | 214 |
Cognitive reflection predicts fake news headline belief in Republicans_
| Liberal fake news | Share liberal fake news | Conservative fake news | Share conservative fake news | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRT scores | −0.026 (−0.46) | −0.083 (−1.15) | −0.115~(−1.82) | −0.040 (−0.57) |
| Higher liberalism | 0.068 (1.23) | 0.038 (0.56) | −0.190* (−2.44) | −0.077 (−0.88) |
| Constant | 3.90 (7.44) | 3.20 (4.90) | 4.72** | 3.11 |
| 11.95 | 7.00 | |||
| N | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 |
Cognitive reflection does not predict political rumors likelihood_
| Ingroup helping rumor | Outgroup bullying rumor | Share ingroup helping rumor | Share outgroup bullying rumor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRT scores | −0.19 (−0.71) | −0.011 (−0.37) | 0.020 (0.79) | 0.016 (0.59) |
| Higher liberalism | −0.012 (−0.76) | 0.019 (1.06) | −0.029~(−1.86) | −0.165 (−0.97) |
| Constant | 0.690 (4.69) | 0.443 (2.80)** | 0.411** (2.98) | 0.495 (3.28) |
| N | 214 | 214 | 214 | 214 |