Fig. 1.
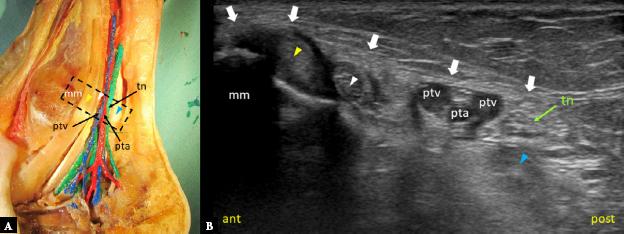
Fig. 2.
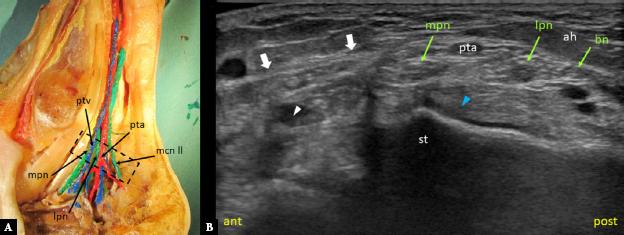
Fig. 3.
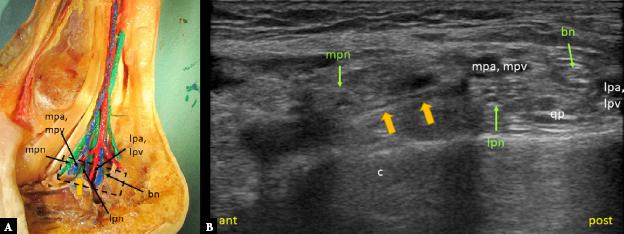
Fig. 4.

Fig. 5.
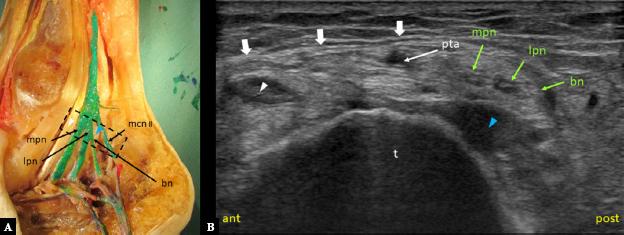
Fig. 6.

Fig. 7.
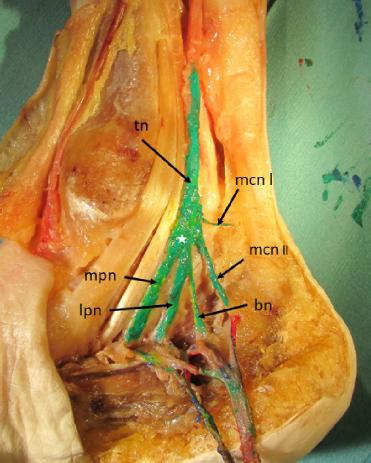
Fig. 8.
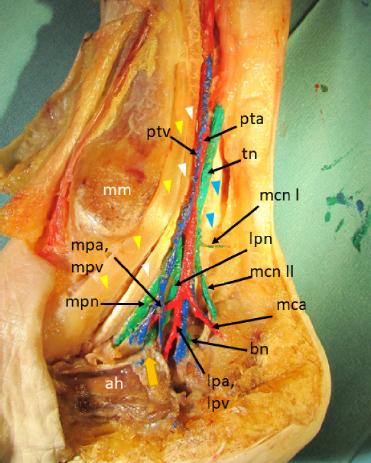








© 2023 Nežka Harej, Vladka Salapura, Erika Cvetko, Žiga Snoj, published by MEDICAL COMMUNICATIONS Sp. z o.o.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.