Fig. 1.
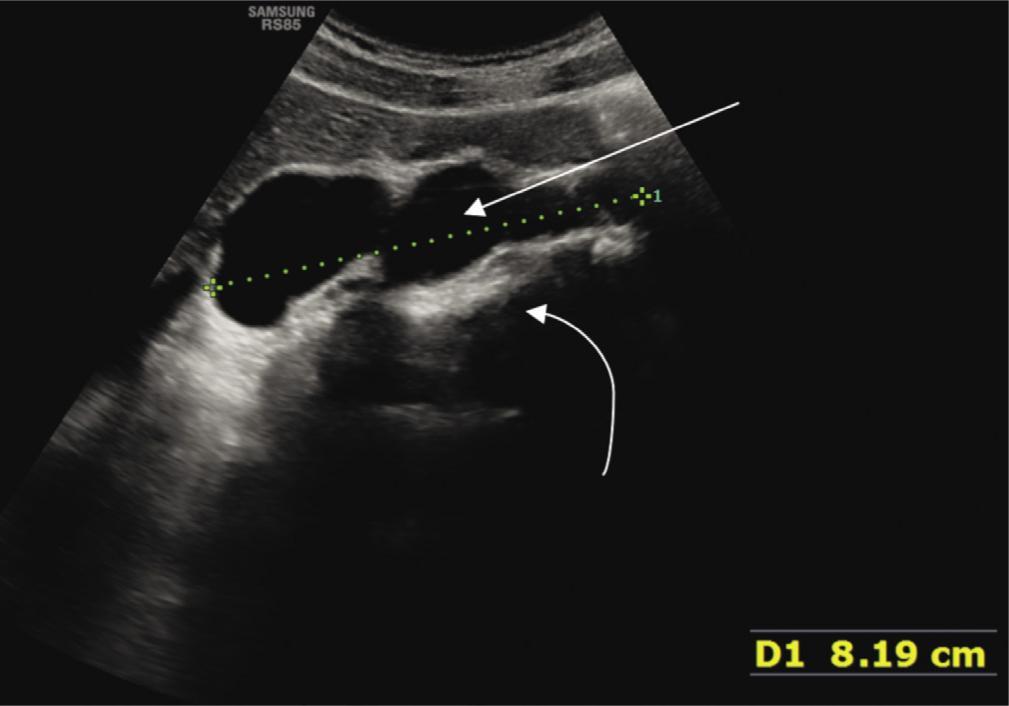
Fig. 2.
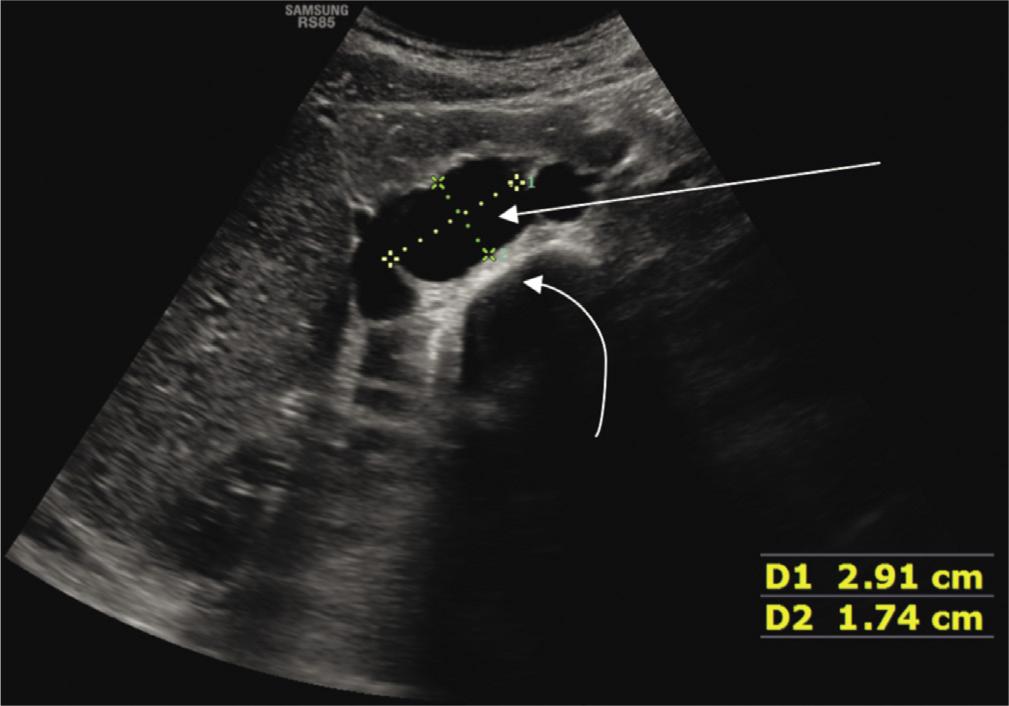
Fig. 3.
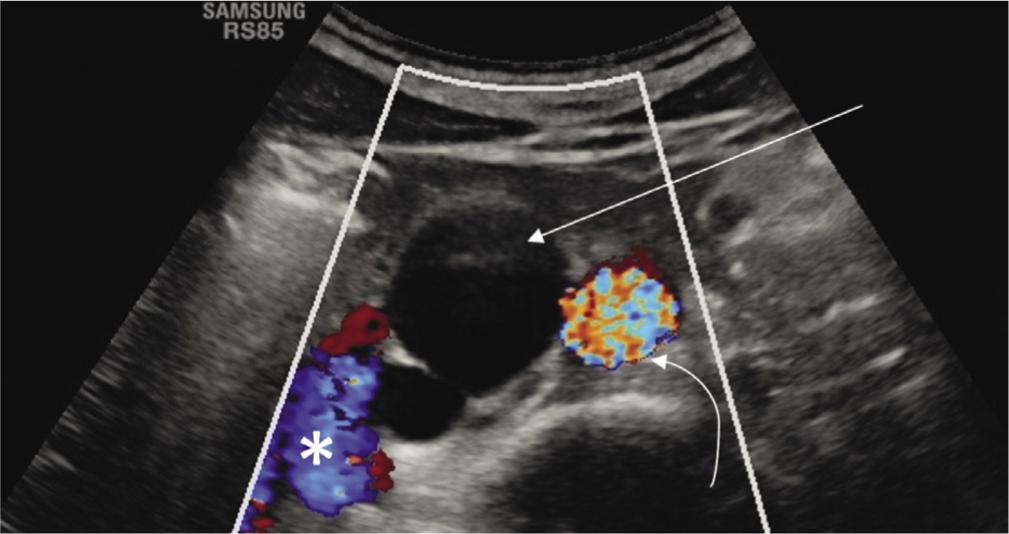
Fig. 4.

Fig. 5.
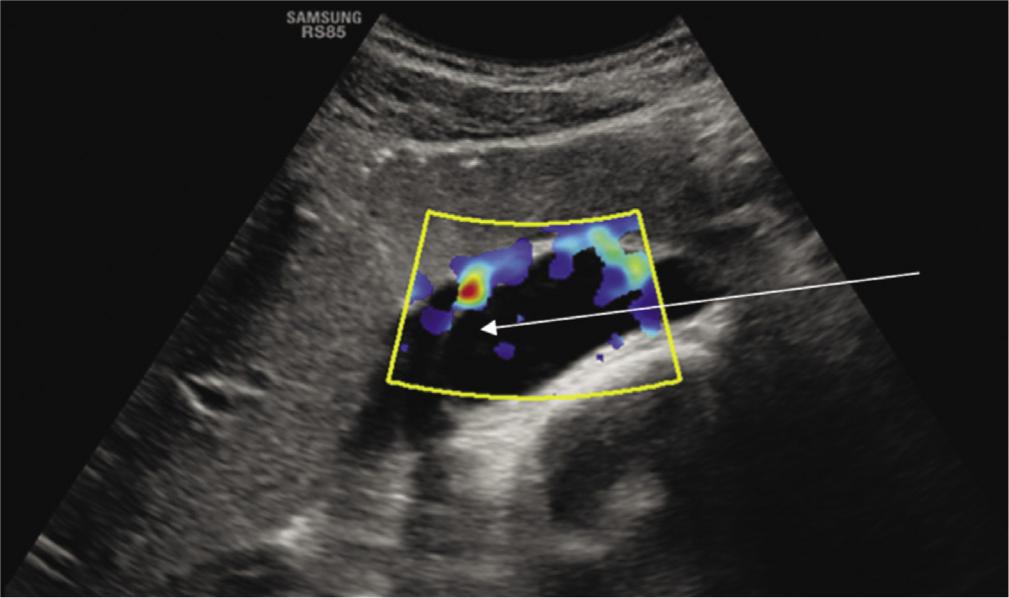
Fig. 6.
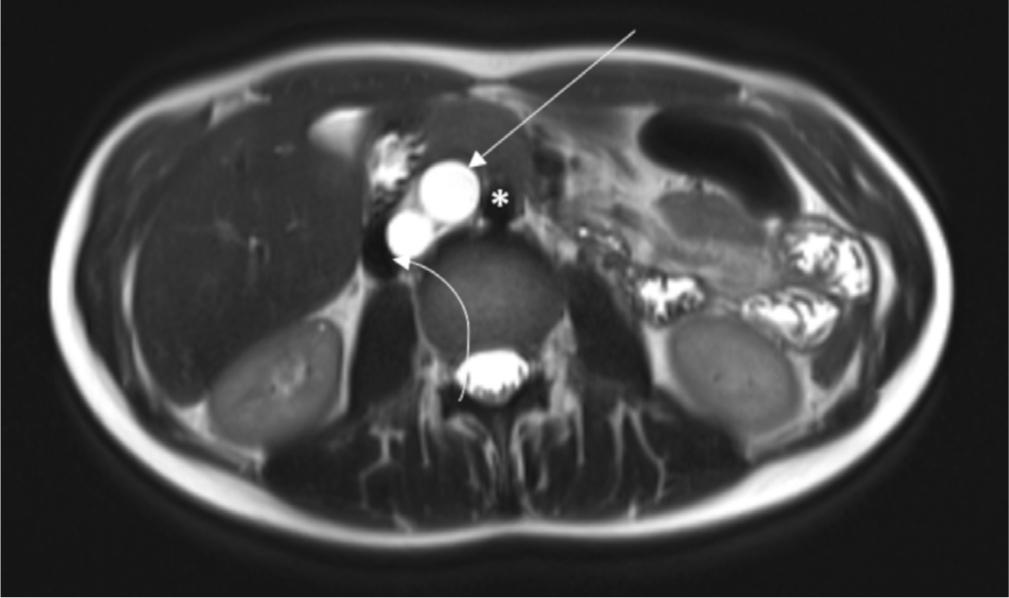
Fig. 7.
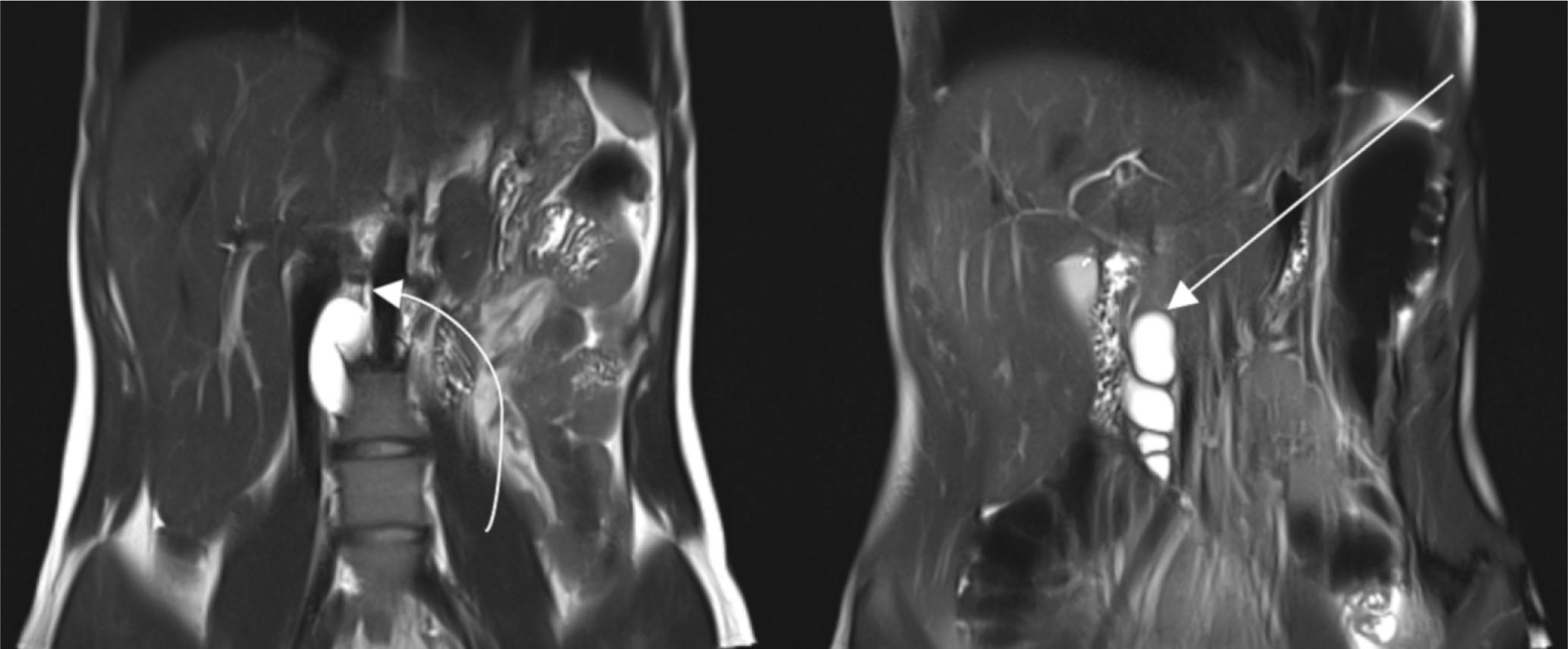
Fig. 8.
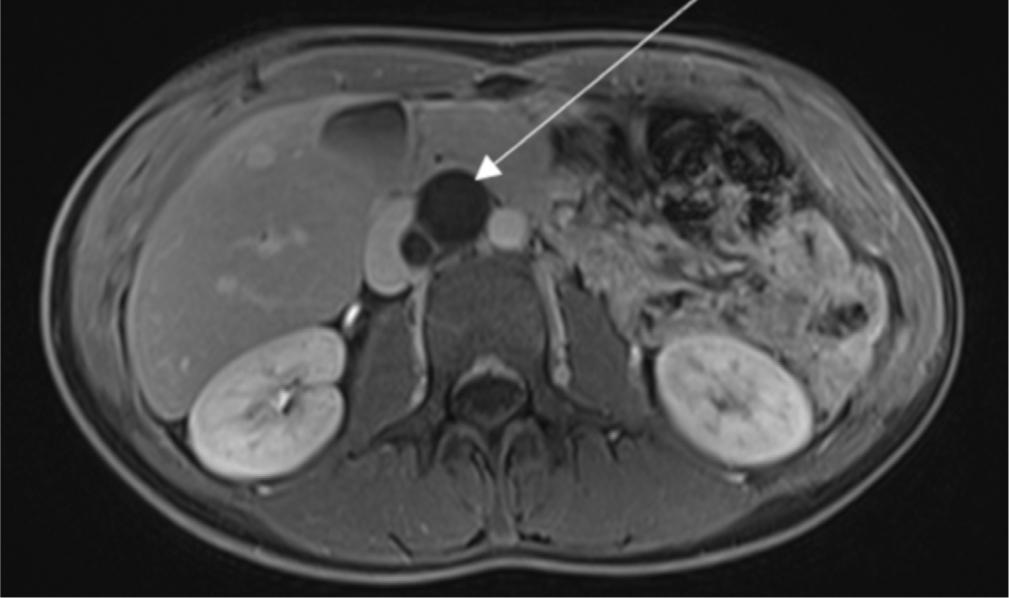
Fig. 9.
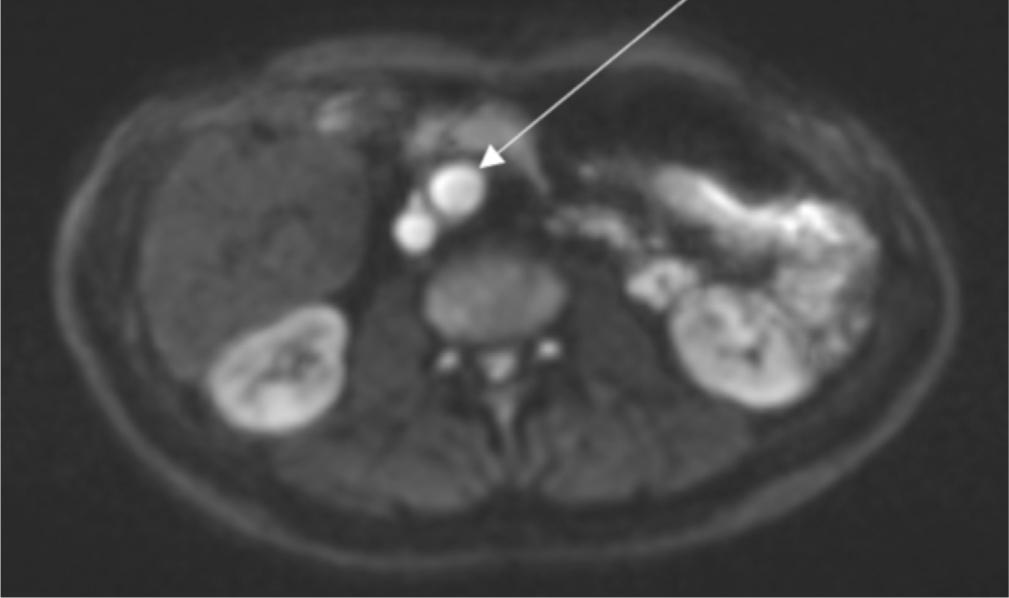
Differential diagnosis of cystic lesions in the retroperitoneal space
| Neoplastic lesions | Non-neoplastic lesions |
|---|---|
| lymphangioma | pancreatic pseudocyst |









| Neoplastic lesions | Non-neoplastic lesions |
|---|---|
| lymphangioma | pancreatic pseudocyst |
© 2022 Wojciech Łyczek, Bartosz Migda, Michał Kutyłowski, published by MEDICAL COMMUNICATIONS Sp. z o.o.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.