Fig. 1
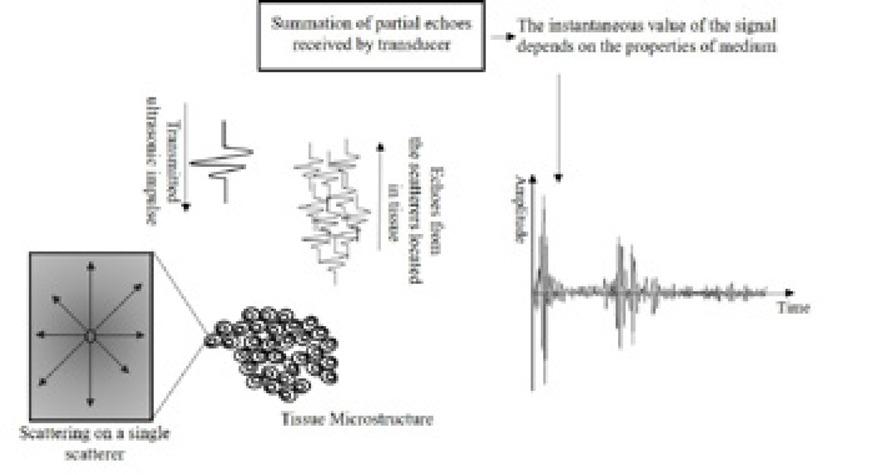
Fig. 2
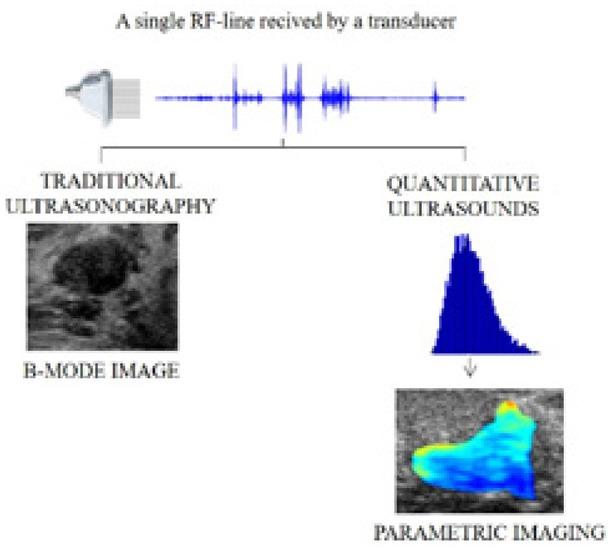
Fig. 3
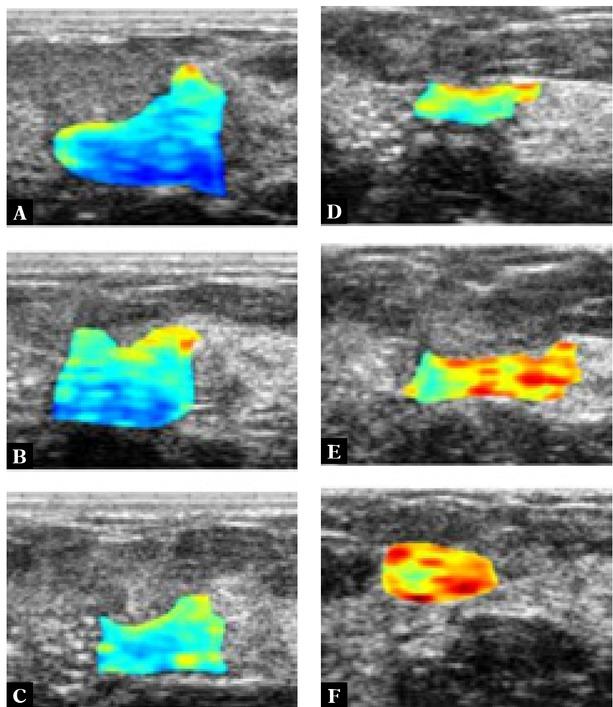
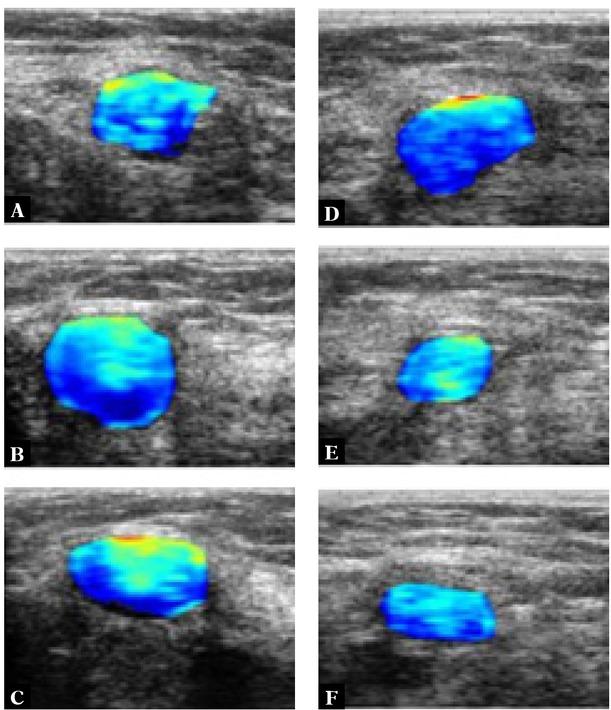
Fig. 4
Characteristics of the ultrasonic parameters discussed in the article
| Determination method | Parameter name and definition | Tissue features affecting its value |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral parameters – determined directly from the signal spectrum in the frequency range corresponding to the transducer frequency band | Mid-band fit (MBF) [dB] | Size, shape, quantity, and elastic properties of scatterers |
| 0-MHz intercept (SI) [dB]: | Size, shape, quantity, and elastic properties of scatterers | |
| Spectral slope (SS) [dB/MHz]: | Size, shape of scatterers | |
| Backscatter scattering parameters – determined on the basis of the backscattering coefficient in the frequency range corresponding to the transducer frequency band | Average scatterer diameter (ASD) [μm] | Average size of the scatterers (e.g., single cells or clusters of cells) |
| Average acoustic concentration (AAC) [dB/cm3] | Spatial density, organization, elastic properties of scatterers | |
| Integrated backscatter coefficient (IBC) [dB] | Size (AND), shape, quantity, organization, and elastic properties of scatterers | |
| Statistical properties | ||
| First-order statistical properties of the RF echo envelope – basic concept relies on modeling the magnitude of speckle with probability density functions, shape parameters of the K homodyne distribution | ENS – effective numbers of scatterers the scatterer clustering parameter | Quantity, organization, and elastic properties of scatterers |
| k– the structure parameter | Size, elastic properties of diffusing structures | |