Figure 1
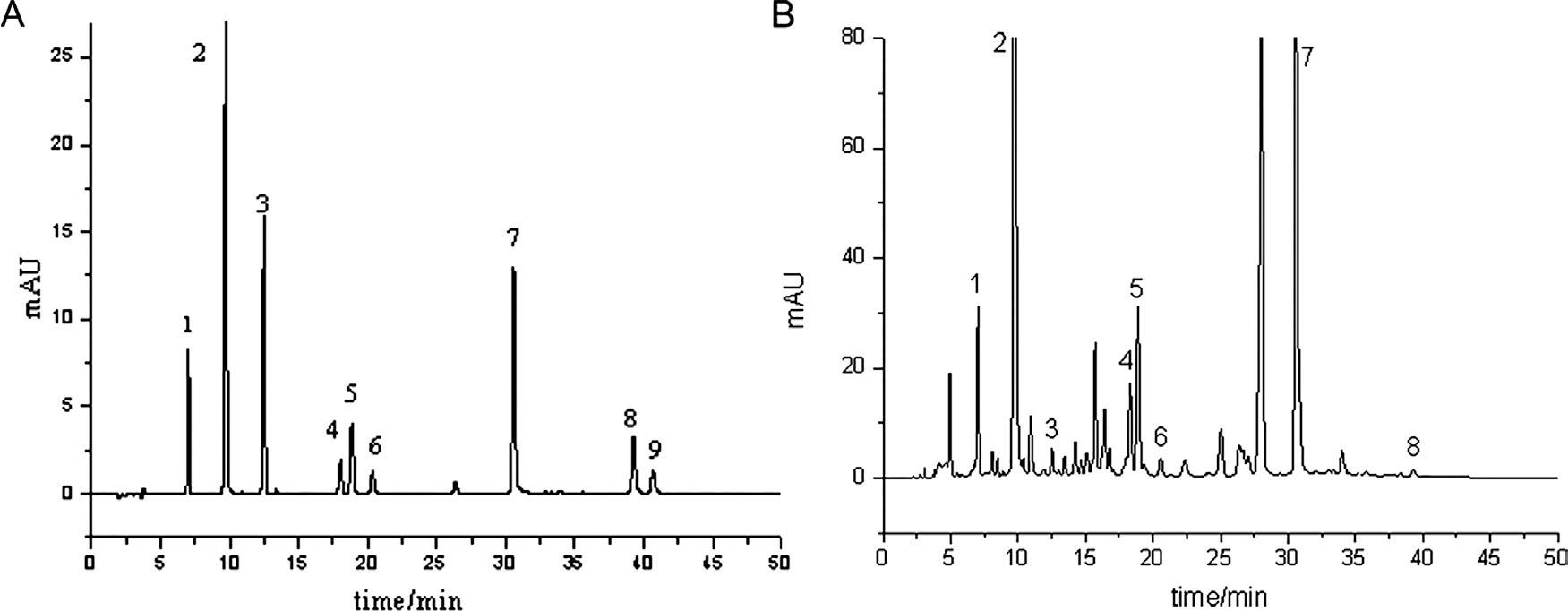
Figure 2
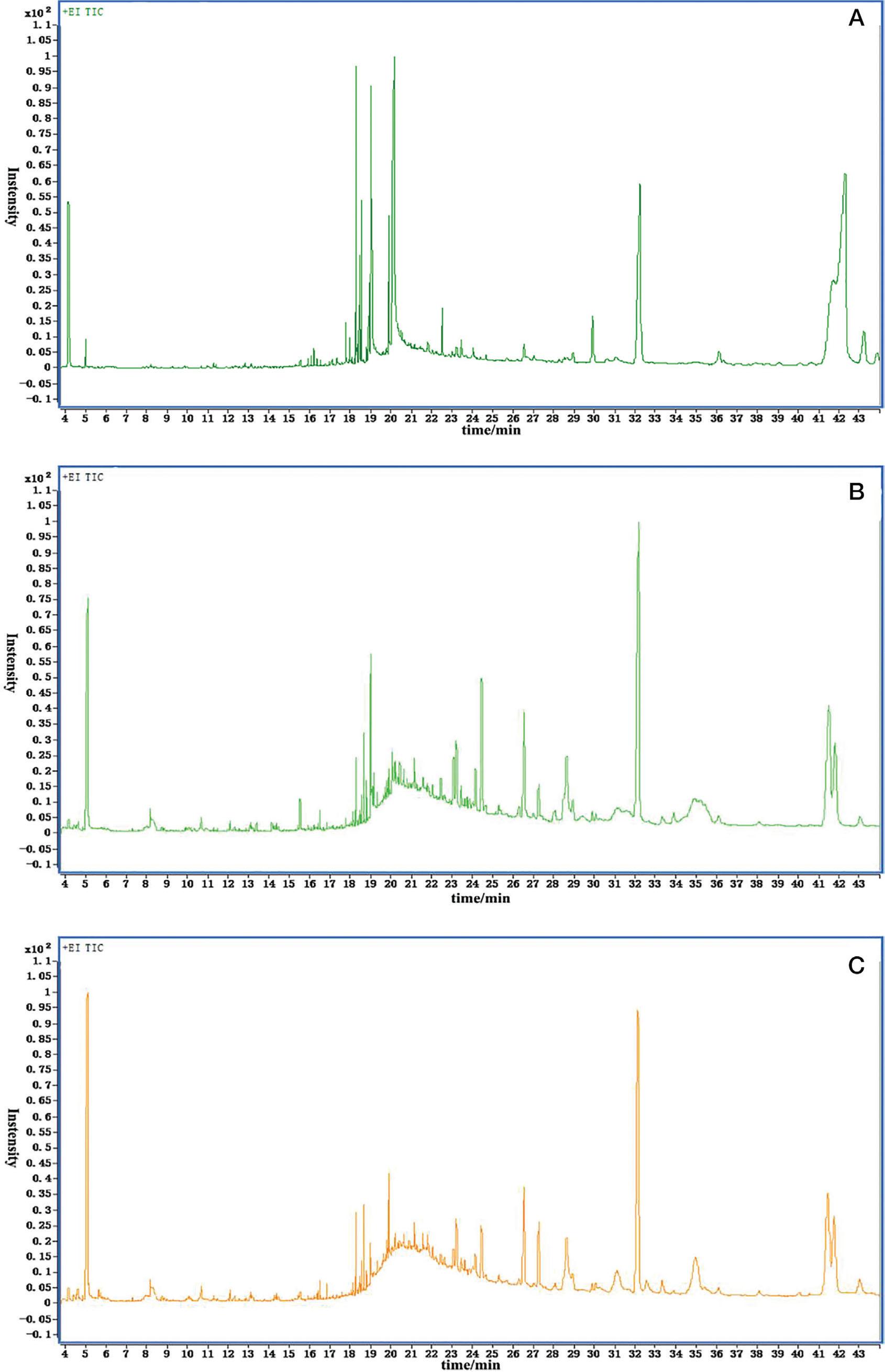
Figure 3
The contents of nine components in L_ japonica Thunb leaves (LE), green buds (GB), and flowers (FL)
| Compound | Content/mg/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LE* | GB | FL | |
| Galuteolin | 1.80 | 0.03 | 0.045 |
| Neochlorogenic acid | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.40 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 17.75 | 24.91 | 16.96 |
| Isochlorogenic acid C | 140.47 | 112.20 | 120.09 |
| Caffeic acid | 0.011 | 0.03 | 0.018 |
| Rutin | 13.82 | 0.95 | 2.50 |
| Hyperoside | – | – | – |
| Luteolin | 0.17 | 0.066 | 0.074 |
| Quercetin | – | – | – |
Total flavonoids in L_ japonica Thunb leaves (LE), green buds (GB), and flowers (FL) (n = 3)
| LE* | GB | FL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 6.68 | 7.38 | 6.35 |
| RSD % | 0.63 | 0.41 | 1.42 |
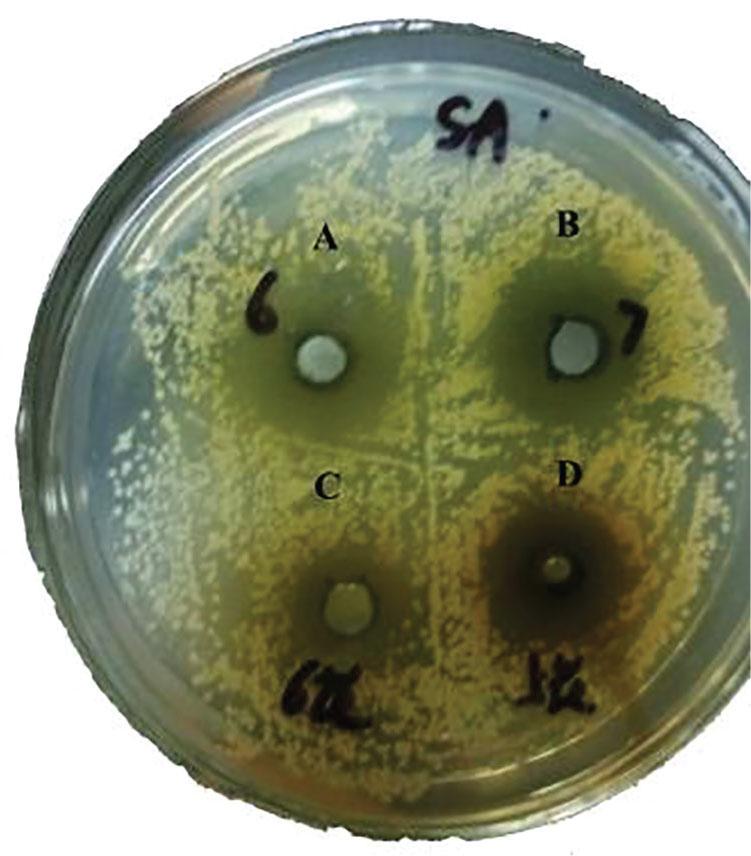
Bacteriostatic results of L_ japonica Thunb leaves (LE), green buds (GB), and flowers (FL)
| Samples | Concentration (g/mL) | Diameters of the inhibition zone (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | RSD/% | ESBL-SA | RSD/% | EC | ESBL-EC | ||
| LE* | 1.0 | 13 | 0.78 | 14 | 0.74 | – | – |
| GB | 1.0 | 11 | 1.17 | 13 | 0.43 | – | – |
| FL | 1.0 | 12 | 0.45 | 11 | 1.30 | – | – |
Volatile components in L_ japonica Thunb leaves (LE), green buds (GB), and flowers (FL)
| Compound | Content/%* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE† | GB | FL | ||
| 1 | 1,4-Eicosadiene1 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.42 |
| 2 | Tricosane | – | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| 3 | (Z)-9-Octadecenamide | – | 0.37 | – |
| 4 | 3-Ethyl-5-(2-ethylbutyl)-octadecane | – | 1.42 | – |
| 5 | Heptacosane | – | 6.70 | 7.59 |
| 6 | Tetratriacontane | 6.79 | 4.79 | – |
| 7 | Nonacosane | 10.11 | 30.71 | 32.82 |
| 8 | Tetratetracontane | – | 0.62 | – |
| 9 | Triacontane | 8.33 | 14.60 | 19.67 |
| 10 | 17-Pentatriacontene | 17.67 | 7.24 | 7.24 |
| 11 | Squalene | 8.72 | 0.52 | 0.66 |
| 12 | Pentacosane | – | – | 1.85 |
| 13 | Hexadecanamide | – | – | – |
| 14 | 9-Octadecene,1,1-[1,2-ethanediylbis(oxy)] bis-(Z,Z)- | – | – | – |
| Hydrocarbons/% | 66.07 | 67.94 | 70.75 | |
| 15 | 2-Heptadecanone | – | 1.49 | 1.59 |
| 16 | Bacteriochlorophyll-c-stearyl | 0.41 | – | – |
| 17 | 6,10,14-Trimethyl-2-pentadecanone | 0.17 | – | – |
| 18 | 2-Nonadecanone | – | 0.33 | – |
| 19 | Phytol | 1.85 | 1.90 | 0.52 |
| 20 | (Z)-Ethanol, 2-(9-octadecenyloxy)- | – | 0.20 | – |
| 21 | γ-Sitosterol | 6.92 | 6.58 | 8.35 |
| 22 | (Z,Z,Z)-9,12,15-Octadecatrien-1-ol | – | – | – |
| 23 | Stigmasterol | – | – | – |
| 24 | Trans-Geranylgeraniol | – | – | 0.37 |
| 25 | 14,16-Hentriacontanedione | – | – | 6.74 |
| Alcohol ketones/% | 9.35 | 10.50 | 17.57 | |
| 26 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | – | 0.75 | 3.76 |
| 27 | Phytol, acetate | 3.56 | 1.36 | 1.13 |
| 28 | (Z,Z,Z)-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid | 0.74 | 0.29 | – |
| 29 | (Z)-13-Docosenamide | 6.34 | – | 1.41 |
| Acids/% | 10.64 | 2.40 | 4.89 | |
| 30 | 15-Isobutyl-(13αH)-isocopalane | 1.46 | – | – |
| 31 | 8,14-Seco-3,19-epoxyandrostane-8,14-di-one, 17-acetoxy-3β-methoxy-4,4-dimethyl- | 0.39 | – | – |
| 32 | (3β,24Z)-Stigmasta-5,24(28)-dien-3-ol | – | – | – |
| 33 | (3β)-9,19-Cyclolanost-24-en-3-ol | 13.51 | 10.69 | – |
| Terpenes/% | 15.36 | 10.69 | 0 | |
| 34 | Docosanoic acid, methyl ester | – | 0.41 | – |
| 35 | (Z,Z,Z)-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester | – | – | – |
| 36 | Tetracosanoic acid, methyl ester | – | 3.81 | 1.72 |
| 37 | Hexacosanoic acid, methyl ester | – | 1.26 | 0.72 |
| 38 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 0.41 | – | 0.79 |
| 39 | Heptanoic acid, docosyl ester | – | – | – |
| 40 | (Z,Z)-9-Hexadecenoic acid, 9-octadecenyl ester | – | 0.24 | – |
| 41 | Oleic acid, 3-(octadecyloxy)propyl ester | – | – | – |
| 42 | Oleic acid, eicosyl ester | 0.37 | – | – |
| Lipids% | 0.78 | 5.72 | 3.23 | |
| 43 | 2,2-Methylenebis[6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methyl-phenol] | 1.42 | – | – |
| 44 | Vitamin E | 2.42 | 2.03 | 1.51 |
| Derivatives/% | 3.84 | 2.03 | 1.51 | |