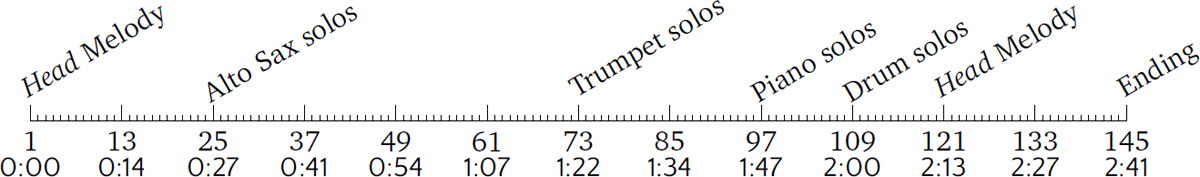
Figure 1
The parts of “Au Privave” by Charlie Parker. The upper scale measures the bars, lower scale the time (m:ss).
Table 1
The 14 components of creativity and assigned weights (as percentages) suiting the domain of musical improvisational creativity. This table is adopted from Jordanous (2012a, p.169).
| No. | Component | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Social Interaction and Communication | 14.9 |
| 2 | Domain Competence | 12.5 |
| 3 | Intention and Emotional Involvement | 13.9 |
| 4 | Active Involvement and Persistence | 7.8 |
| 5 | Variety, Divergence, and Experimentation | 7.1 |
| 6 | Dealing with Uncertainty | 6.4 |
| 7 | Originality | 5.8 |
| 8 | Spontaneity/Subconscious Processing | 5.4 |
| 9 | Independence and Freedom | 5.4 |
| 10 | Progression and Development | 5.4 |
| 11 | Thinking and Evaluation | 5.1 |
| 12 | Value | 5.1 |
| 13 | Generation of Results | 3.7 |
| 14 | General Intellect | 1.4 |
| 100.0 |
Table 2
p-values of all LMEMs. The components on the left are sorted by their importance for the domain of musical improvisation. The stars indicate the level of significance by Bonferroni-Holm adjusted p-values (p ≤ 0.05:*/p ≤ 0.01:**/p ≤ 0.001:***). Except System (column 2), none of the effect variables (columns 3–6) were significant at all.
| Component | System=ED | IR_first=yes | Instr.=P | Exper.=A | Exper.=E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Interaction and Communication | 0.0061 | * | 0.0481 | 0.8389 | 0.3929 | 0.1100 |
| Domain Competence | 0.1216 | 0.3794 | 0.4727 | 0.4705 | 0.4202 | |
| Intention and Emotional Involvement | 0.0004 | ** | 0.1788 | 0.7318 | 0.3087 | 0.4393 |
| Active Involvement and Persistence | 0.2246 | 0.8116 | 0.5858 | 0.4631 | 0.9929 | |
| Variety, Divergence, and Experimentation | <0.0001 | *** | 0.3618 | 0.9635 | 0.4432 | 0.5929 |
| Dealing with Uncertainty | 0.0122 | 0.2001 | 0.7533 | 0.3194 | 0.5945 | |
| Originality | 0.0002 | ** | 0.2930 | 0.9278 | 0.3603 | 0.8921 |
| Spontaneity and Subconscious Processing | 0.0006 | ** | 0.2208 | 0.3999 | 0.2875 | 0.6610 |
| Independence and Freedom | 0.0275 | 0.5705 | 0.9913 | 0.1467 | 0.7528 | |
| Progression and Development | 0.0018 | * | 0.5831 | 0.4789 | 0.5680 | 0.5717 |
| Thinking and Evaluation | 0.1313 | 0.4586 | 0.5767 | 0.5947 | 0.5151 | |
| Value | 0.2633 | 0.9229 | 0.9322 | 0.6092 | 0.2832 | |
| Generation of Results | 0.0005 | ** | 0.4434 | 0.5161 | 0.2760 | 0.5380 |
| General Intellect | 0.0119 | 0.6103 | 0.5818 | 0.2206 | 0.8446 | |
| Mean Rating | 0.0020 | * | 0.3172 | 0.7691 | 0.2920 | 0.5314 |
| Weighted Mean Rating | 0.0016 | * | 0.2387 | 0.8476 | 0.3075 | 0.4258 |
Table 3
Results of the ratings on both systems sorted by adjusted p-value.
| Component | β(System = ED) | p-value | adj. p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variety, Divergence, and Experimentation | 4.3000 | <0.0001 | 0.0005 |
| Originality | 4.1500 | 0.0002 | 0.0028 |
| Intention and Emotional Involvement | 2.8500 | 0.0004 | 0.0050 |
| Generation of Results | 3.4500 | 0.0005 | 0.0059 |
| Spontaneity and Subconscious Processing | 3.6000 | 0.0006 | 0.0068 |
| Progression and Development | 3.2000 | 0.0018 | 0.0183 |
| Social Interaction and Communication | 1.8000 | 0.0061 | 0.0485 |
| Dealing with Uncertainty | 1.7500 | 0.0122 | 0.0834 |
| General Intellect | 2.4500 | 0.0119 | 0.0834 |
| Independence and Freedom | 2.1000 | 0.0275 | 0.1373 |
| Domain Competence | 0.8500 | 0.1216 | 0.4864 |
| Active Involvement and Persistence | 0.6000 | 0.2246 | 0.4864 |
| Thinking and Evaluation | 1.3500 | 0.1313 | 0.4864 |
| Value | 1.0000 | 0.2633 | 0.4864 |
| Mean Rating | 2.3893 | 0.0020 | 0.0183 |
| Weighted Mean Rating | 1.5984 | 0.0016 | 0.0171 |
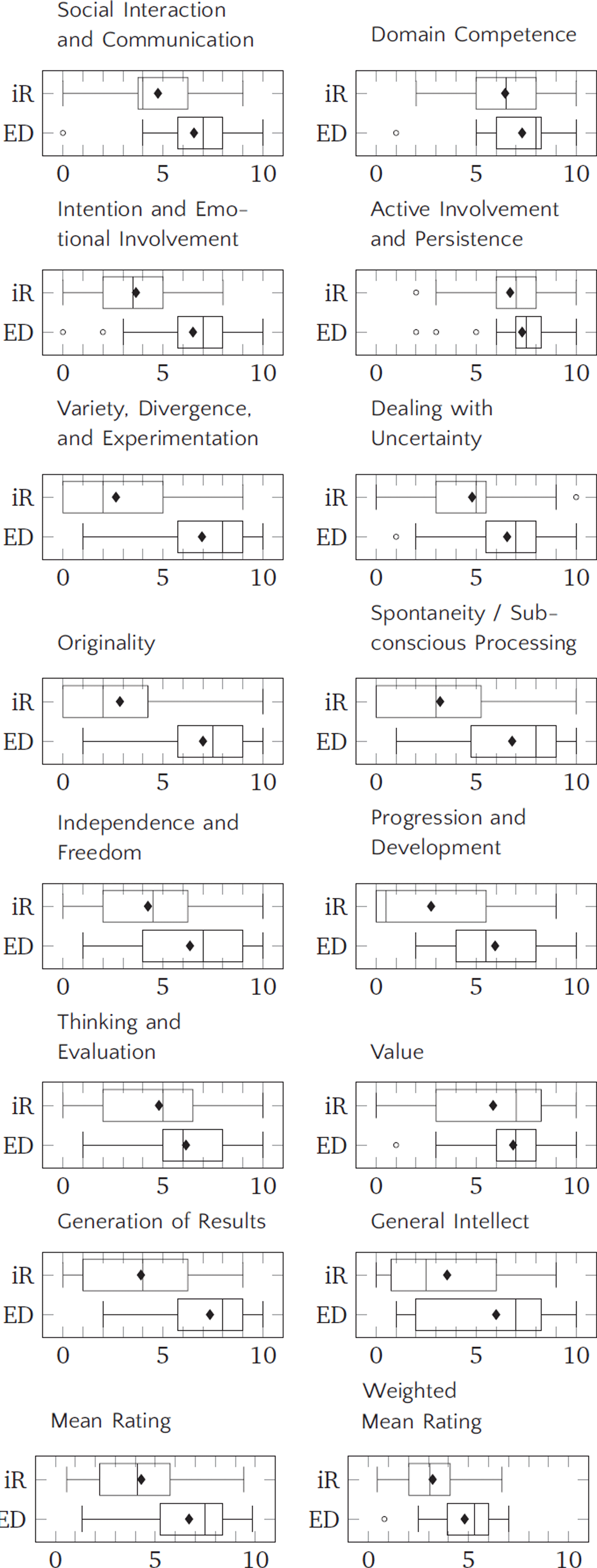
Figure 2
Boxplots for the ratings on each SPECS component for iReal (iR) and EAR Drummer (ED).
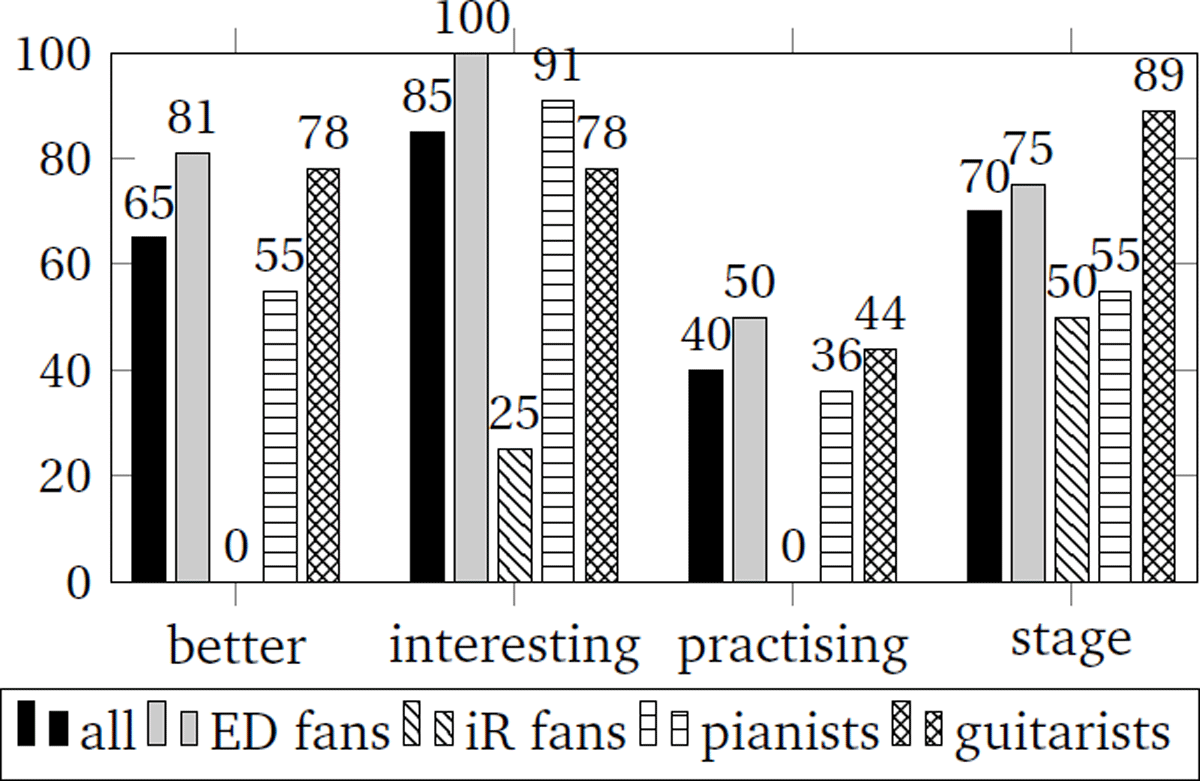
Figure 3
Statistics of the statements of preference. The bars show the percentage of user votes for EAR Drummer.
