(1) Overview
Introduction
Wikipedia2 is one of the most frequently visited websites in the world and the most extensive online encyclopaedia. As of December 2024, it ranked among the top ten most popular websites globally, occupying 5th place according to Semrush3 and 7th place according to Similarweb.4 Internal statistics from the February 2025 report approximately 6,956,076 content pages and 48,729,378 registered users on the English version alone.5 Due to its decentralized organization and independently managed communities, Wikipedia has attracted significant attention in academic research [123], serving as a valuable resource for studies on knowledge representation and information dissemination.
Extensive research has leveraged Wikipedia for diverse applications, including training neural networks [456], extracting structured data [78], and conducting computational social science investigations. In this context, Wikipedia has been used for bias detection and large-scale analyses of biographies to explore cultural evolution [9101112]. Additionally, it plays a central role in Natural Language Processing (NLP) research, serving as a training corpus for models such as MAVEN, BERT, and Wikiformer [131415].
Beyond textual analysis, Wikipedia’s hyperlink structure has inspired numerous graph-based studies. Consonni et al. [16] released a multilingual link network dataset covering nine languages, with data snapshots spanning the years 2001 to 2018. Aspert et al. [17] developed a graph-structured dataset that integrates spatio-temporal data, although it is limited to the English edition. The YAGO project, including YAGO2 and YAGO3, introduced a knowledge base that enriches Wikipedia with disambiguation and temporal/spatial metadata, enhancing its semantic structure across multiple languages [181920]. Similarly, Wu et al. [21] proposed a framework for constructing knowledge graphs from online encyclopaedias using heuristic matching and semi-supervised learning.
In addition to the previous, Wikipedia has proven to be a valuable resource for research on semantic relatedness and knowledge representation. For instance, Yeh et al. [22] measured semantic similarity between concepts using Wikipedia’s content. More recently, Wang et al. [23] introduced WikiGraphs, a dataset that pairs graph structures with textual data to support tasks such as conditional text generation and representation learning. Similarly, Arroyo-Machado et al. [24] developed Wikinformetrics, a richly structured English Wikipedia dataset that links articles, categories, authors, external links, and references—providing a valuable foundation for informetric and bibliometric studies. Complementing this, Yang and Colavizza [25] investigated Wikipedia’s growing use of academic citations, a trend Lewowieski [26] explored across 309 language editions, revealing significant differences in citation behaviour across cultures.
Moreover, several studies have explicitly focused on the link network structure of Wikipedia. Works such as Jatowt et al. [11], Consonni et al. [16], and Gabella [27] emphasise the need to resolve redirects to their final target pages to ensure accurate network representations—an essential preprocessing step before any formal analysis.
In the field of historical and cultural network analysis, high-quality Wikipedia graph data has been used to uncover latent patterns and relationships. Studies by Schwartz [28] and Miccio et al. [2930] demonstrate the value of clean and structured Wikipedia datasets for exploring cultural narratives and historiographical trends. This body of work highlights the utility of Wikipedia as an open data source and the importance of robust, reproducible methods for extracting and refining its complex graph structure.
Despite the substantial work in this area, effectively utilising Wikipedia’s vast and dynamic content requires efficient extraction and processing tools. Several tools have been developed to address this challenge. “WikiExtractor” and “Cirrus Extractor” are Python-based tools designed to extract and clean plain text from Wikipedia XML dumps for applications in text analysis, graph construction, and machine learning [31].6 The “wiki-dump-parser,” implemented in Java, converts Wikipedia XML dumps into a structured JSON format, relying on “WikiExtractor” for text cleaning [32].7 Another alternative is “Pywikibot” [33], a Python library that interacts directly with Wikipedia’s MediaWiki API, enabling real-time data retrieval and redirect resolution but at the cost of significantly slower processing compared to raw dump extraction.
While existing tools and research have significantly advanced Wikipedia-based data extraction, they still exhibit critical gaps: some cannot parse data efficiently, others focus solely on a single language edition [1724] or rely heavily on external databases for multilingual integration [181920], and many are not user-friendly enough to accommodate researchers with varied technical expertise [3132]. WikiTextGraph addresses these shortcomings by providing a unified, scalable, and user-friendly solution that combines essential functionalities—parsing, text cleaning, graph extraction, redirect resolution, and broken link handling—into one coherent framework. This comprehensive approach enhances data quality for language modelling and refines graph-based analyses by eliminating distortions caused by unresolved redirects and non-content pages. Furthermore, WikiTextGraph is optimised for speed, memory efficiency, and multilingual processing, making it valuable for both high- and low-resource languages. For example, in about seven hours, it can complete extraction, cleaning, and graph construction for the English Wikipedia dump (January 2025). By consolidating these capabilities, WikiTextGraph streamlines workflows and offers a versatile, adaptable platform for large-scale Wikipedia research.
Following Wikipedia’s open-edit philosophy, WikiTextGraph is openly available, allowing researchers to contribute improvements or extend language support via pull requests. The tool is accessible on GitHub.8
Implementation And Architecture
WikiTextGraph is designed to efficiently process large-scale Wikipedia XML dumps, extract relevant textual content, and—if prompted—construct graph representations of Wikipedia’s internal link network. The software follows a modular architecture that enables scalability, efficient memory management, multilingual support and extensibility. This section outlines the general structure of the software’s workflow and its key components.
At a high level, the WikiTextGraph workflow consists of two main stages (see Figure 1):
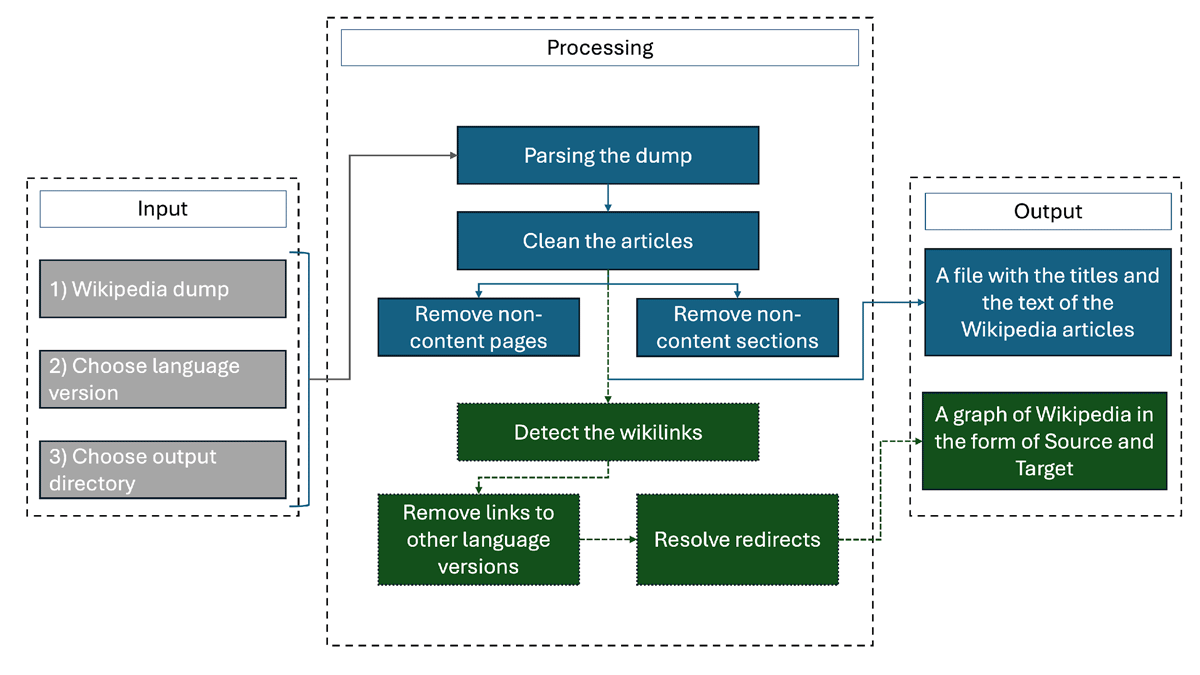
Figure 1
Workflow of how the software parses and, if prompted, generates the graph.
Parsing and Cleaning: Wikipedia XML dumps are incrementally processed to extract relevant textual content, while filtering out non-content pages and removing non-content sections, infoboxes, and other irrelevant elements.
Graph Construction (optional): The extracted links between Wikipedia articles are structured into a directed graph, ensuring data integrity through deduplication, broken link removal, and redirect resolution.
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Advanced users can configure the software through various parameters such as the Wikipedia dump file path, language code, and output directory:
python wikitextgraph.py --dump_filepath /path/to/dump.bz2 \
--language_code en \
--base_dir /output/directory \
--generate_graph
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
A GUI is also available to provide an interactive workflow for users unfamiliar with command-line operations, guiding them through selecting input files, language preferences, and whether to generate a graph (see Figure 2). After clicking the “Start Processing” button, the GUI closes to free up some memory. The GUI can be used again by running the program anew.
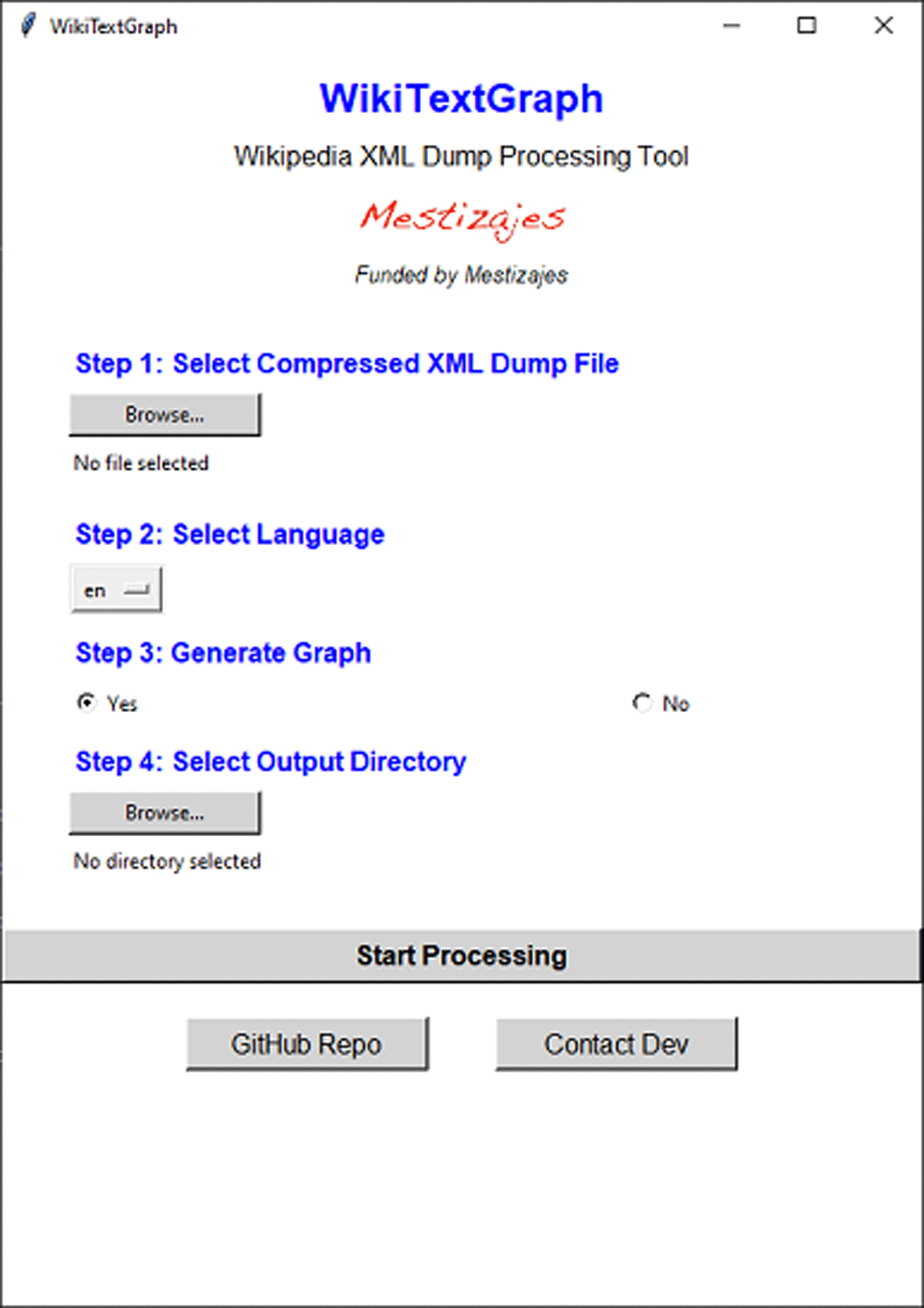
Figure 2
The Graphic User Interface (GUI) of the WikiTextGraph algorithm.
Installation and Execution
Clone the Repository
Install Dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run the Software
python wikitextgraph.py
Data Management and Processing
This section describes how each stage in WikiTextGraph’s pipeline is carried out, explaining the motivations for each filtering strategy and data-handling step. Figure 1 provides a visual overview of the process.
Input
WikiTextGraph requires the following inputs to execute its pipeline:
A compressed Wikipedia XML dump file (e.g., .bz2) corresponding to one of the supported language editions.9
A language code indicating which Wikipedia language version to process (e.g., en for English, es for Spanish, etc.).10
A valid path to the output directory where the cleaned text files and, optionally, the graph files will be stored.
Parsing and Filtering Wikipedia Articles
The parser_module parses the compressed Wikipedia XML dump in batches (by default, 10,000 articles per batch) using a SAX-based approach11 and systematically extracts the core content from each article while excluding non-informative pages (see Table 1) and sections (see Table 2). This step ensures that for each content page, only the textual content of each article is retained for subsequent analyses. After processing each batch, the system writes the cleaned content to disk immediately to reduce memory overhead.
Table 1
Pages the algorithm removes during the text cleaning phase for each language version supported by the algorithm.
| ENGLISH (en) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wiktionary: | Category: | Draft: | File: | List of |
| MediaWiki: | Module: | Template: | Wikipedia: | Index of |
| Help: | Portal: | Image: | (disambiguation) | |
| SPANISH (es) | ||||
| Wiktionary: | Categoría: | File: | Archivo: | Image: |
| MediaWiki: | Plantilla: | Wikipedia: | Anexo: | Módulo: |
| Portal: | Help: | Ayuda: | Wikiproyecto: | Usuario: |
| User: | (desambiguación) | |||
| GREEK (el) | ||||
| Wiktionary: | Κατηγορία: | Αρχɛίο: | File: | Image: |
| MediaWiki: | Module: | Πρότυπο: | Wikipedia: | Βικιπαίδɛια: |
| (αποσαφήνιση) | Portal: | Πύλη: | Βοήθɛια: | Topic: |
| Χρήστης: | User: | |||
| POLISH (pl) | ||||
| Wikipedia: | Pomoc: | Szablon: | MediaWiki: | Kategoria: |
| Wikiprojekt: | Portal: | Plik: | Moduł: | User: |
| Wątek: | Topic: | (ujednoznacznienie) | ||
| ITALIAN (it) | ||||
| Wikipedia: | Aiuto: | Template: | MediaWiki: | Categoria: |
| Progetto: | Portale: | File: | Modulo: | Topic: |
| (disambigua) | (disambiguazione) | |||
| DUTCH (nl) | ||||
| Wikipedia: | Help: | Sjabloon: | MediaWiki: | Categorie: |
| Portaal: | Bestand: | Module: | (disambiguatie:) | (disambiguation) |
| User: | ||||
| BASQUE (eu) | ||||
| Wikipedia: | Laguntza: | Txantilloi: | MediaWiki: | Kategoria: |
| Maila: | Atari: | Ataria: | Usuario: | Modulu: |
| Fitxategi: | Wikiproiektua: | Eranskina: | Txikipedia: | Zerrenda: |
| (argipena) | ||||
| HINDI (hi) | ||||
| विकिपीडिया: | साँचा: | श्रेणी: | मीडियाविकि: | सहायता: |
| रवेशद्वार: | चित्र: | विकिपरियोजना: | मॉड्यूल: | (बहुविकल्पी) |
| GERMAN (de) | ||||
| Wikipedia: | Hilfe: | Vorlage: | MediaWiki: | Kategorie: |
| Portal: | Benutzer: | Modul: | Datei: | Liste der |
| Liste des | Liste von | (begriffsklärung) | ||
| VIETNAMESE (vi) | ||||
| Wikipedia: | MediaWiki: | Trợ giúp: | Bản mẫu: | Tập tin: |
| Thể loại: | Sách: | Danh sách: | Cổng thông tin: | Mô đun: |
| (định hướng) | ||||
Table 2
Sections where extracting text stops. If one of these sections appears in the article, it indicates the stopping point for extracting content.
| ENGLISH (en) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also | Publications | References | Notes | |
| Footnotes | External links | Further Reading | Draft: | |
| SPANISH (es) | ||||
| Véase también | Referencias | Notas | Enlaces externos | |
| Bibliografía | Otra lectura | |||
| GREEK (el) | ||||
| Δɛίτɛ ɛπίσης | Παραπομπές | Σημɛιώσɛις | Εξωτɛρικοί σύνδɛσμοι | |
| Προτɛινόμɛνη βιβλιογραφία | Βιβλιογραφία | Περαιτέρω ανάγνωση | ||
| POLISH (pl) | ||||
| Zobacz też | Uwagi | Bibliografia | Przypisy | |
| Linki zewnętrzne | Literatura w języku polskim | |||
| ITALIAN (it) | ||||
| Note | Bibliografia | Altri progetti | Collegamenti esterni | |
| Riferimenti | Voci correlate | |||
| DUTCH (nl) | ||||
| Noten | Bibliografie | Appendix | Externe links | |
| Referenties | Bronnen | Zie ook | Overig | |
| Ander | Literatuur | Voetnoten | ||
| BASQUE (eu) | ||||
| Oharrak | Bibliografia | Ahultasunak | Kanpo estekak | |
| Erreferetziak | Ikus, gainera | |||
| HINDI (hi) | ||||
| िप्पणियांट | यह भी देखिए | संदर्भ सूची | बाहरी कड़ियाँ | |
| सन्दर्भ | इन्हें भी देखें | इसके अतिरिक्त पठन | ||
| GERMAN (de) | ||||
| Weblinks | Einzelnachweise | Einzelnachweise und Anmerkungen | Anmerkungen | |
| Literatur | Siehe auch | Fußnoten | Veröffentlichungen | |
| VIETNAMESE (vi) | ||||
| Xem thêm | Tham khảo | Liên kết ngoài | Tài liệu tham khảo | |
| Tài liệu | Ghi chú | Chú thích | Tài liệu khác | |
| Hình ảnh | Đọc thêm | |||
Removing Irrelevant Content
Pages for administrative or bibliographical purposes are identified through regular-expression checks (e.g., Draft:, Template:) and omitted from further processing (see Table 1). Configurable patterns in LANG_SETTINGS can be refined for additional languages or unique research needs.
Producing Cleaned and Structured Text
After filtering pages, WikiTextGraph applies cleaning routines to remove HTML comments, <ref> tags and extraneous wikitext templates that may exist inside an article. Sections such as References or External links are also discarded (see Table 2). The result is a structured, cleaned version of the main body for each article, ready for text-based analyses.
Building the Directed Graph
If a user requests graph construction (through the CLI or GUI), the graph module creates a Source-Target dataset for each internal link, producing a directed network suitable for graph-based research. Node names are saved in a numerical format (i.e., each node is assigned a unique numerical ID), allowing faster loading and processing of large graphs later.
Extracting Internal Links
Internal links are identified using a regular expression that captures various wiki markup patterns (e.g., sections, alternative text) while preserving only the main article link. The regular expression used is shown below:
r’\[\[‘
r’([^#|]+)’
r’(?:#([^|]]))?’
r’(?:\|([^]]*))?’
r’\]\]’
The following example (dummy text generated by ChatGPT) demonstrates how various patterns of wikilinks can appear in an article and what the regular expression is going to capture (text in bold):
Quantum dots are [[semiconductor]] nanocrystals that exhibit [[quantum confinement|unique optical properties]]. These structures can be used in various applications, including [[display technology#Quantum dots|advanced display technology]] and [[solar cells#Efficiency]] research. Unlike traditional materials, [[quantum dots#Excitonic behavior|their excitonic behavior]] allows for highly tunable optical properties. The development of [[nanotechnology]] has accelerated research in this field.
Ensuring Graph Quality
The algorithm begins by correcting malformed links through normalisation, for example, converting underscores to spaces (e.g., for instance, Murray_Bookchin will be converted to Murray Bookchin in order to match the actual Wikipedia page). Redirects are resolved by mapping them to their corresponding target, ensuring uniformity across page references in an article. To preserve the integrity of the dataset, links to other language editions are excluded, thereby limiting the network to a single language version (see Table 3). Additionally, self-loops and duplicate edges are removed to eliminate redundancy. Together, these validation steps produce a cleaner and more coherent graph that more accurately reflects meaningful inter-article connections. By filtering out structural noise introduced by non-existent connections and navigational features, such as redirects and interlanguage links, the resulting topology is better suited for downstream tasks, including community detection.
Table 3
Table with the keywords to detect redirects for each language version.
| ENGLISH (en) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #redirect | ||||
| SPANISH (es) | ||||
| #redirección | #redirect | |||
| GREEK (el) | ||||
| #ανακατɛύθυνση | #redirect | |||
| POLISH (pl) | ||||
| #patrz | #redirect | #przekieruj | #tam | |
| ITALIAN (it) | ||||
| #rinvia | #redirect | |||
| DUTCH (nl) | ||||
| #doorverwijzing | #redirect | |||
| BASQUE (eu) | ||||
| #birzuzendu | #redirect | |||
| HINDI (hi) | ||||
| #अनुप्रेषित | #पुनर्प्रेषित | #redirect | ||
| GERMAN (de) | ||||
| #weiterleitung | #redirect | |||
| VIETNAMESE (vi) | ||||
| #đổi | #redirect | |||
Parquet Format for Graph Data
The resulting source-target pairs are stored in parquet files in a numerical format, offering advantages in compression and read/write and space-storing efficiency. This columnar format permits partial column reading during queries or large-scale analyses, making it well-suited to network exploration tasks.
Compressed Redirect Mappings
WikiTextGraph stores redirect information in a compressed pickle file, mapping each redirect page to its canonical target in an inverse-dictionary format. This design minimises disk usage and lookup times, allowing researchers to analyse redirect patterns independently and enabling near-instant lookups during graph construction.
Final Output
The software produces two main directories:
output: Contains two columns, one for the article titles and the other for the cleaned text.
graph: Stores the constructed graph with nodes represented by numerical IDs for fast loading and analysis (two columns in the format of Source and Target). This directory includes a lookup table for redirects-to-target and an ID-to-article’s title mapping.
Quality control
Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of WikiTextGraph is very important, particularly in the absence of an official validation pipeline. We design and implement a comprehensive quality control framework consisting of multiple validation steps to achieve this. These checks assess the consistency of the extracted data at each stage of the extraction process across all supported language versions, ensuring alignment with the intended final output. The validation steps are as follows:
Language Evaluation: To assess the effectiveness of the algorithm in different language versions, we conduct an evaluation with native (L1) speakers. This step verifies the algorithm’s ability to accurately capture language-specific patterns and nuances.
Text Extraction and Filtering: We verify that predefined sections, such as references and external links, are correctly removed during the extraction process. Additionally, we ensure that non-content pages are effectively excluded from the dataset as defined by our filtering criteria. Our evaluation confirms that the algorithm performs as expected in both cases.
Edge Validity Check: We validate that all extracted edges correspond strictly to valid Wikipedia pages. This step eliminates invalid or extraneous links, including self-loops, broken links, and links pointing to specific sections within pages, thereby maintaining the structural integrity of the constructed graph.
Node Count Verification: To confirm completeness, we compare the number of nodes in the generated graphs with the official count of content pages reported by Wikipedia for each language version. While the observed node count is slightly lower than the reported numbers, this discrepancy is expected due to the deliberate removal of certain pages (see Table 4).
Graph Structural Analysis: To validate the network structure, we analyse the degree distributions of the constructed graphs. The results confirm that these distributions exhibit heavy-tailed, power-law-like behaviour, a characteristic feature of Wikipedia’s hyperlink network (see Figures 3, 4, and Table 4) [2734].
Redirects and Interlanguage Link Validation: We manually inspect randomly sampled entries during the graph construction phase to ensure correct link resolution. This evaluation confirms that all interlanguage links have been successfully removed and that all redirects are correctly replaced with their corresponding target pages.
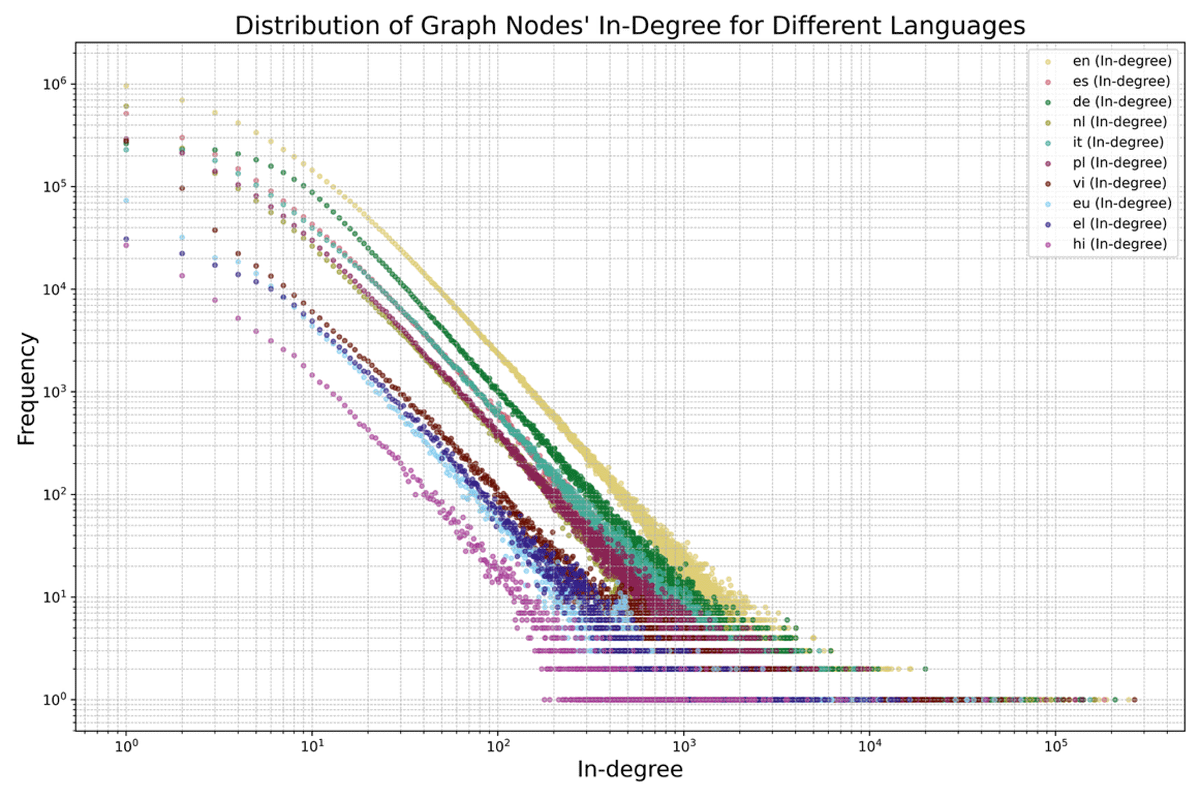
Figure 3
Log-log plot of the in-degree12 distribution for each language version. The x-axis represents the in-degree (i.e., the number of incoming links to a node), whereas the y-axis represents the frequency of nodes for each in-degree value. Each curve corresponds to a different language version, as indicated in the legend.
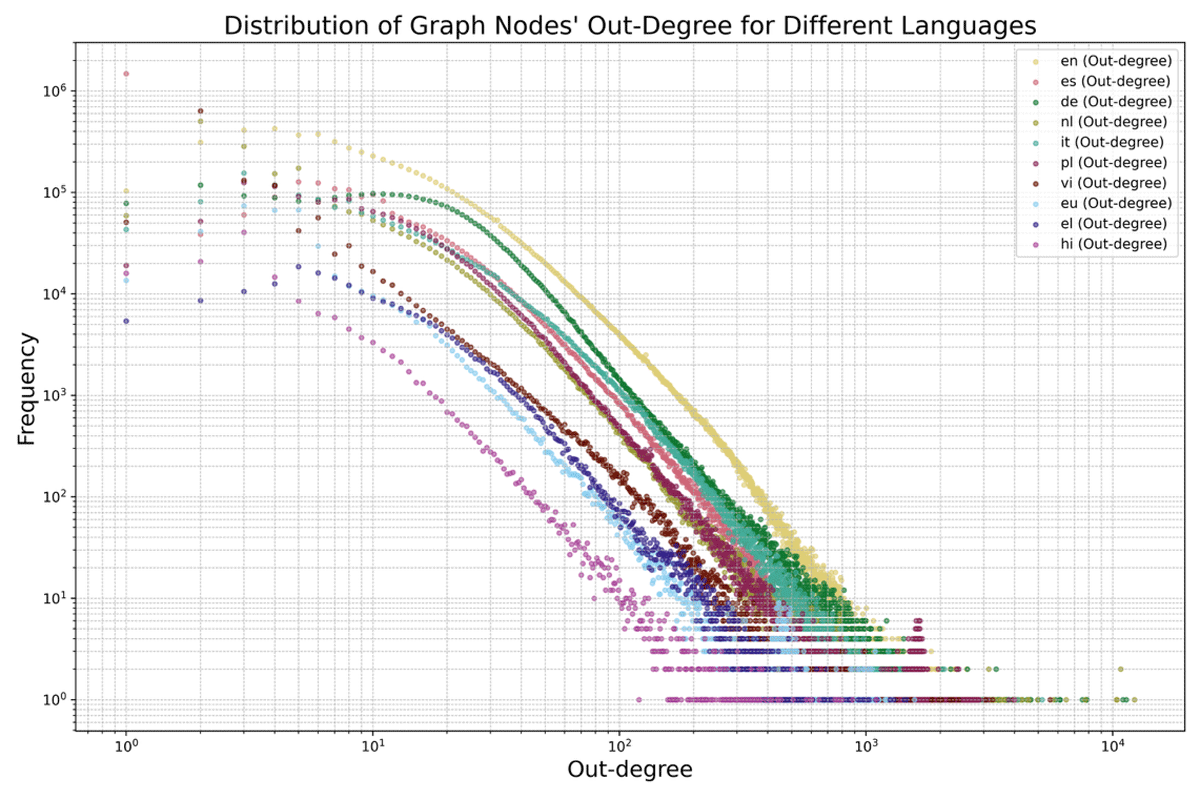
Figure 4
Log-log plot of the out-degree13 distribution for each language version. The x-axis represents the out-degree (i.e., the number of outgoing links from a node), whereas the y-axis represents the frequency of nodes for each out-degree. Each curve corresponds to a different language version, as indicated in the legend.
Table 4
Summary statistics of the Wikipedia language versions supported (at the time of writing) and processed by WikiTextGraph. Each row corresponds to a different language version, identified by its name and ISO 639 language code in parentheses. The columns report the following metrics calculated using the Python library NetworkX [35]. Order is the number of nodes (Wikipedia articles) in the directed network; Size is the number of edges (links between articles); Average In/Out degree is the average number of incoming and outgoing links per node; Max In/Out-degree is the highest number of incoming and outgoing links respectively; Density is the ratio of actual links to all possible links14; Date is the month and the year that corresponds to the version of the Wikipedia dump collected and processed.
| LANGUAGE | ORDER | SIZE | AVERAGE IN/OUT DEGREE | MAX IN-DEGREE | MAX OUT-DEGREE | DENSITY (×10–6) | DATE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English (en) | 6,736,622 | 159,598,688 | 23.6 | 247,992 | 4,615 | 4 | Jan. 2025 |
| German (de) | 3,001,074 | 77,213,282 | 25.7 | 209,493 | 11,359 | 9 | Nov. 2024 |
| Dutch (nl) | 2,169,658 | 27,487,945 | 12.6 | 163,525 | 12,263 | 6 | Nov. 2024 |
| Spanish (es) | 1,905,582 | 39,473,628 | 20.7 | 205,662 | 4,083 | 11 | Nov. 2024 |
| Italian (it) | 1,820,884 | 42,649,948 | 23.4 | 153,337 | 5,179 | 13 | Nov. 2024 |
| Polish (pl) | 1,620,570 | 30,140,616 | 18.5 | 138,619 | 3,800 | 11 | Nov. 2024 |
| Vietnamese (vi) | 1,284,928 | 8,977,353 | 6.9 | 266,137 | 5,576 | 5 | Jan. 2025 |
| Basque (eu) | 435, 429 | 4,436,022 | 10.1 | 65,339 | 1,573 | 23 | Dec. 2024 |
| Greek (el) | 237,016 | 4,319,401 | 18.2 | 16,314 | 1,464 | 77 | Nov. 2024 |
| Hindi (hi) | 152,990 | 1,097,849 | 7.1 | 42,123 | 3,993 | 47 | Nov. 2024 |
(2) Availability
Operating System
Linux (tested: Mint 21.3), macOS (tested: macOS 12 and newer), Windows (tested: Windows 10 and newer).
Programming Language
Python versions 3.9 and newer.
Additional System Requirements
The software was developed and primarily tested in the following environment:
Operating System: Linux Mint 21.3
Kernel: Version 5.15
Processor: Intel Core i7 (4 cores, 8 threads, 3.6 GHz)
Memory: Minimum 8 GB RAM
Disk: At least 15 GB of free storage
Swap15: Minimum 2 GB
Graphics: Integrated GPU (e.g., Intel HD Graphics 630)
The software is cross-platform and has been tested on macOS (Monterey and newer) and Windows 10. Disk usage depends on the specific Wikipedia edition processed. For reference, processing the English Wikipedia snapshot dated 2025-01-23 requires a minimum of 36 GB of free disk space.
Dependencies
click == 8.1.8
cloudpickle == 3.1.1
colorama == 0.4.6
contourpy == 1.0.1
cramjam == 2.9.1
dask == 2023.5.0
fastparquet == 2024.2.0
fonttools == 4.22.0
fsspec == 2025.2.0
importlib_metadata == 8.5.0
kiwisolver == 1.3.1
locket == 1.0.0
numpy == 1.24.4
packaging == 24.2
pandas == 2.0.3
partd == 1.4.1
Pillow == 10.3.0
pyarrow == 17.0.0
pyparsing == 3.1.2
PySide6 == 6.6.3.1
PySide6_Addons == 6.6.3.1
PySide6_Essentials == 6.6.3.1
python-dateutil == 2.9.0.post0
pytz == 2025.1
PyYAML == 6.0.2
regex == 2024.11.6
shiboken6 == 6.6.3.1
six == 1.16.0
toolz == 1.0.0
tqdm == 4.67.1
tzdata == 2025.1
wcwidth == 0.2.13
wikitextparser == 0.56.3
zipp == 3.20.2
tkinter == 8.5
Software Location
Code repository
Name: GitHub
Identifier: https://github.com/PaschalisAg/WikiTextGraph
Licence: Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004
Date published: 02/03/2025
Archive
Name: Zenodo
Identifier: https://zenodo.org/records/16260544
Publisher: Paschalis Agapitos
Version: v1.0.0
Licence: Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004
Date published: 21/07/2025
Language
English
(3) Reuse Potential
WikiTextGraph’s robust design and flexible functionality make it inherently reusable across a broad spectrum of research and application domains, including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Data Mining, Graph-based studies, and Computational or Digital Humanities. By parsing, filtering, and analysing structured Wikipedia text—and optionally generating a graph representation—it supports an array of data-centric tasks such as automated content extraction, entity recognition, and information retrieval.
In network science, WikiTextGraph helps construct and examine knowledge graphs and graph-based databases, revealing hidden relationships among entities and enabling advanced semantic search. Incorporating pandas, pyarrow, and the parquet format readily handles large-scale datasets, ensuring efficient big data analytics and providing a foundation for machine learning workflows. The graph-first paradigm further facilitates social network analysis, clarifying complex interconnections among concepts. Researchers in computational linguistics and multilingual text analysis also benefit from its modular design, which enables straightforward cross-lingual content processing and contributes to projects focused on low-resource languages.
Moreover, WikiTextGraph’s modular architecture underscores its adaptability. Language-specific filtering and parsing rules within the LANG_SETTINGS.yml file can be tailored for individual research agendas, allowing domain- or language-specific customization. Its code is cleanly split into distinct components—graph.py for graph structures, gui.py for the user interface, parser_module.py for parsing logic, and utils.py for support functions—making it more straightforward to either extend existing features or embed the software within other analytic pipelines. This clear structure promotes code reuse and effortless scalability, effectively lowering the barrier for researchers to integrate WikiTextGraph into their projects.
Finally, the software’s open availability and support ecosystem further amplify its reusability. Users can contribute bug reports or improvements through GitHub pull requests or issues, while direct assistance is accessible via the “Contact us” button in the GUI (refer to Figure 2). Through this collaborative environment, we want to ensure that WikiTextGraph remains a versatile and evolving tool for the research community.
Data Accessibility Statement
All code created and used in this research is available at: https://github.com/PaschalisAg/WikiTextGraph. It has been archived and is persistently available at: https://zenodo.org/records/16260544.
Notes
[9] A Wikipedia dump that contains all the articles for a given language version can be found at https://dumps.wikimedia.org/backup-index.html. Users should navigate to the section “Sql/XML dumps issues” to find entries corresponding to different language versions listed in the format {language_code}wiki: Dump complete. Selecting one of these entries leads to a list of downloadable files. The relevant file follows the naming convention {language_code}wiki-{yyyymmdd}-pages-articles-multistream.xml.bz2. This file serves as the input to the software and should be downloaded and saved locally on the user’s computer.
[11] SAX is an event-driven XML parsing method that allows efficient, memory-light processing of large files by reading them sequentially without loading the entire document into memory.
Ethics And Consent
The article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere gratitude to the native (L1) speakers who contributed their time and expertise in evaluating the results for each language version during the development of WikiTextGraph. Following the order in which the languages appear in the GUI, we would like to acknowledge the following individuals for their support formally:
For Spanish (es) and Basque (eu): Amaia Elizaran Mendarte and Ane Escobar Fernández
For Polish (pl): Adam Olejniczak and Zuzanna Lawera
For Italian (it): Valerio Di Lisio
For Hindi (hi): Anish Rao
For German (de): Balthasar Braunewell
For Vietnamese (vi): Phuong Thu Le
Their contributions were significant in ensuring the model’s quality and linguistic accuracy across multiple language settings.
Competing Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Author Contributions
Paschalis Agapitos software development, data analysis, conceptualisation, and writing, including original draft preparation, review, and editing.
Juan Luis Suárez contributed to writing through review and editing.
Gustavo Ariel Schwartz conceptualisation, data analysis, software review, writing (original draft, review, and editing), and secured funding for the project.
