Table 1
Short description of the files contained in the Moosh directory.
| File name | Calling Sequence | Description |
|---|---|---|
| structure.m | Describes the whole structure parameters including permittivity and permeability of every materials, how they are stacked and the thickness of every layer. | |
| Beam.m | Beam | Simulates the propagation of a gaussian beam in the structure and maps the resulting field. |
| Green.m | Green | Computes the electromagnetic wave emitted by a source located inside one of the layers. |
| coefficient.m | coefficient (theta,lambda) | Computes the reflection and transmission coefficient of the structure. |
| absorption.m | absorption (theta,lambda) | Computes the percentage of the incident energy that is absorbed inside each layer, along the with reflection and transmission coefficients when the structure is illuminated with a plane wave. |
| Angular.m | Angular | Angular uses absorption to compute the absorption in each layer, the reflection and transmission coefficients as a function of the incidence angle of light, for a plane wave. |
| Spectrum.m | Spectrum | Spectrum uses absorption to compute the absorption in each layer, the reflection and transmission coefficients as a function of the wavelength of light in vacuum, for a plane wave. |
| dispersion.m | dispersion (kx,lambda) | A function that vanishes whenever a guided mode of the structure has kx as a propagation constant for a given lambda. The dispersion relation can thus be written as dispersion(kx,lambda)=0 |
| descent.m | descent (z0,step,stop) | Steepest descent in the kx complex plane, starting at z0 with an initial step step and stopping when the absolute value returned by dispersion is smaller than stop. |
| Map.m | Map | This function maps the response of the dispersion function in the complex plan. This function allows visualizing the position of guided modes in the complex plane. |
| Guidedmodes.m | Guidedmodes | This function uses descent to found zeros of the dispersion function to find modes of the structure. |
| Profile.m | Profile(kx,lambda) | Computes the field profile of a guided mode characterized by its propagation constant kx (computed using descent). |
| extsqrt.m | extsqrt(z) | Square root with a different cut from what is used by default in computers – intented for external layers when searching for guided modes. |
| Photo.m | Photo | Computes the theoretical short-circuit current, shows the absorption spectrum. |
| cascade.m | cascade(S,T) | Cascades two scattering matrices into one single scattering matrix |
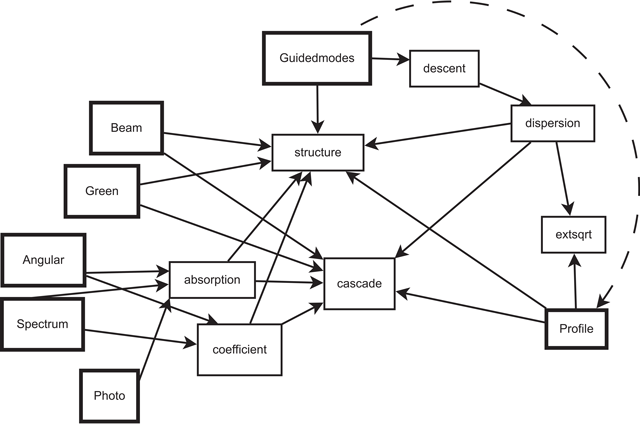
Figure 1
Diagram of Moosh indicating the main programs (bold border) and the functions that are called. Guidedmodes needs to be run before using Profile.
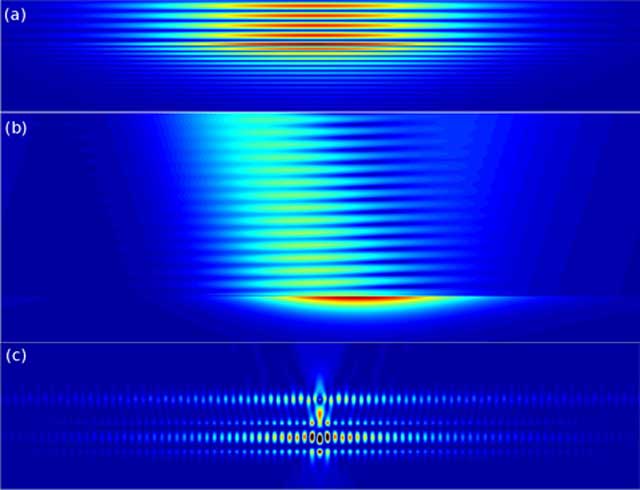
Figure 2
Output examples. (a) Reflection by a Bragg mirror, in which the light penetrates before being totally reflected (b) Excitation of a surface plasmon resonance (c) Excitation of a light wheel by a source placed in the dielectric waveguide.
