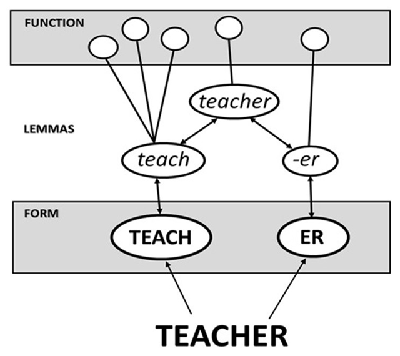
Figure 1
The obligatory morphological decomposition model illustrated with the derived word teacher being represented by a lemma that is activated via lemma units representing its component morphemes (adapted from Taft & Nguyen-Hoan, 2010).
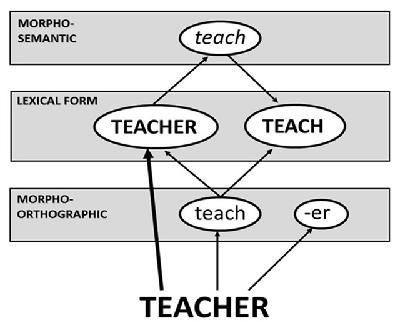
Figure 2
The dual-pathways model of Diependaele et al. (2013) where a whole-word lexical form for teacher is activated in parallel with morpho-orthographic decomposition. Post-lexical decomposition also occurs at the morpho-semantic level. The lexical level only represents existing words. Morpho-orthographic decomposition requires precise processing of letter position while whole-word access does not.
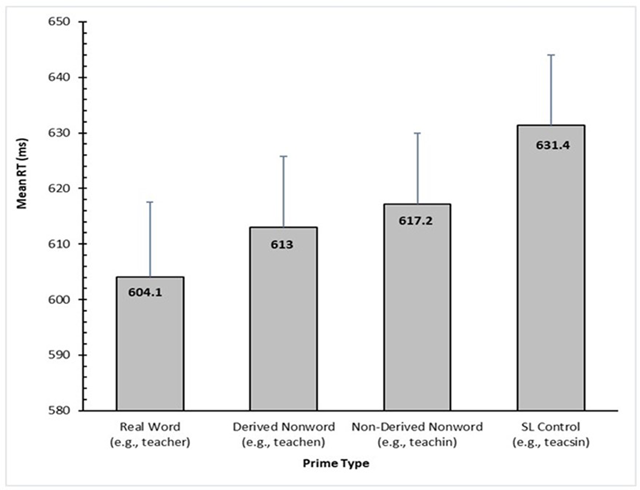
Figure 3
Adjusted condition means for RT (in ms) based on the final LME model for Experiment 1. Error bars represent standard error.
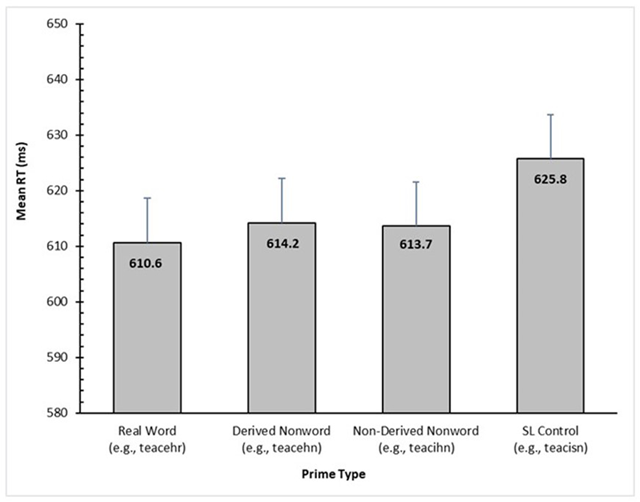
Figure 4
Adjusted condition means for RT (in ms) based on the final LME model for Experiment 2. Error bars represent standard error.
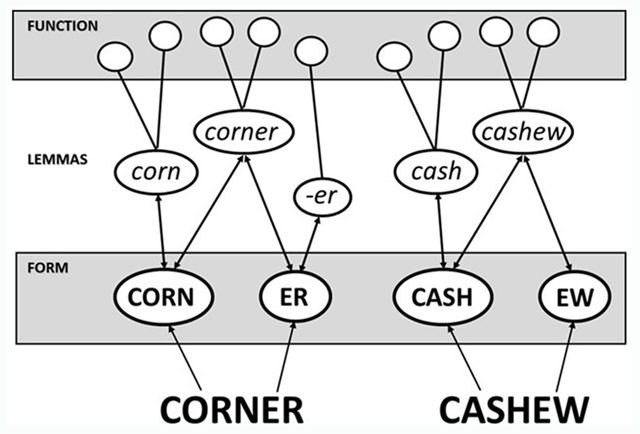
Figure 5
The way in which pseudo-derived words (e.g., corner) and non-derived words (e.g, cashew) might be represented within the lemma model proposed by Taft and Nguyen-Hoan (2010).
