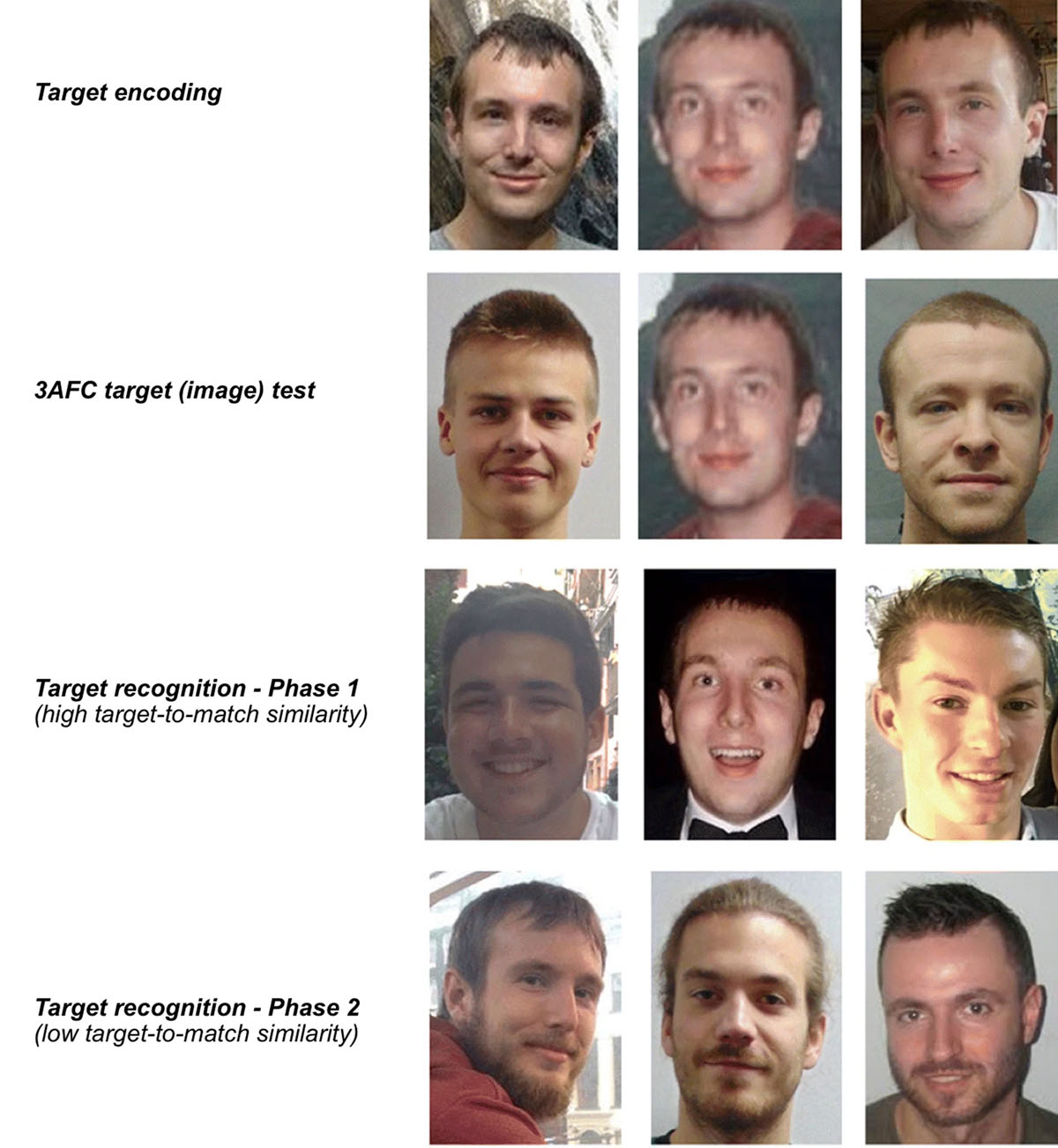

Figure 1
Examples of stimuli presented in the Model Matching Test across test phases. Images are reproduced from Bate et al. (2018) under a Creative Commons Licence (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Table 1
Demographic information of observers assigned to the three versions of the Models Memory Test (MMT). Groups were exposed to different combinations of Target Prevalence across Phases 1 and 2, which contained only target present trials (TP), or included target absent trials (TA) (as in Bate et al.’s (2018) original study). For all groups, Phase 1 and Phase 2 were characterized by high and low Target-to-Match Similarity, respectively, due to the degree of ambient changes among images across phases. Each group first completed the first, “easier”, followed by the second, “harder” phase (with lesser vs. greater ambient changes). For Group 1, Phase 1 had low Target Prevalence (TA/TP; i.e. target absent and target present trials) and Phase 2 had high Target Prevalence (TP; i.e. only target present trials). This pattern of Target Prevalance was reversed in Group 2, where Phase 1 had high (TP), followed by low Target Prevalance in Phase 2.
| CONTEXT (PHASE1–PHASE2) | CULTURAL EXPOSURE OF PARTICIPANTS ASSIGNED TO CONTEXTS N (MALE/FEMALE); AGE ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| WESTERN CAUCASIAN (WC) | SOUTH ASIAN (SA) | MIXED (SAWC) | |
| Group 1: Low-to-high Target Prevalence (TA/TP—TP) | 7 (3/4); 35 ± 6 | 7 (3/4); 45 ± 13 | 6 (4/2); 41 ± 11 |
| Group 2: High-to-low Target Prevalence (TP—TA/TP) | 7 (3/4); 40 ± 12 | 6 (3/3); 43 ± 14 | 6 (2/4); 34 ± 9 |
| Group 3: Low-to-low Target Prevalence* (TA/TP—TA/TP*) | 6 (4/2); 43 ± 18 | 7 (3/4); 39 ± 12 | 7 (5/2); 39 ± 11 |
[i] * NB: This is the original MMT reported by Bate et al. (2018). TA/TP: indicates that a phase contains both target absent (TA) and target present (TP) trials. TP: indicates that a phase contains only target present (TP) trials.
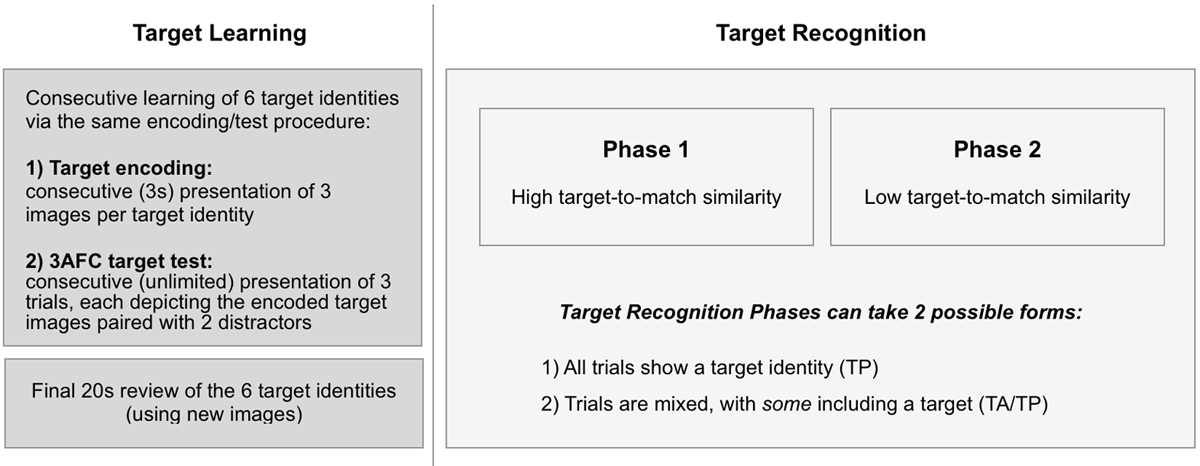
Figure 2
Experimental design. The experiment starts with Target Learning followed by Target Recognition. During Target Learning, observers sequentially encode three images of a given target identity, followed by a 3-alternative forced-choice (3AFC) target test of the encoded images. Target learning of all six target identities finishes with a final 20s review of target identities using novel images. Target Recognition comprises two phases, which differ in their Target-to-Match Similarity (Phase 1: high; Phase 2: low; see Methods). Target Recognition Phases can differ in terms of Target Prevalence, i.e., they can either contain only trials depicting targets (Target-Present; TP), or mixed trials (Target-Absent/Target-Present; TA/TP). Our three groups (see Table 1) were subjected to different experimental Contexts, which represent our possible combinations of Target Prevalence (TP; TA/TP), across Target Recognition Phases with fixed order of Target-to-Match Similarity (low, followed by high).
Table 2
Comparison of behavioral performance between the cohort reported for the original Models Memory Test (Bate et al., 2018) and our sample (Group 3).
| ORIGINAL MMT N = 40 (33Y) | GROUP 3 N = 20 (37Y) | DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MMT VERSIONS | EFFECT SIZE OF DIFFERENCE COHEN’S D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ACC ± SD | .54 ± .14 | .57 ± .16 | t(19) = 0.72, p = .4777 > .05 | .16 |
| Hit Rate ACC ± SD | .51 ± .20 | .53 ± .16 | t(19) = 0.62, p = .5422 > .05 | .14 |
| Correct Rejection Rate ACC ± SD | .57 ± .23 | .60 ± .21 | t(19) = 0.61, p = .5474 > .05 | .14 |
| d’ ± SD | .26 ± .84 | .38 ± .93 | t(19) = 0.58, p = .38 > .05 | .13 |

Figure 3
Multi-level models per factor independently of group. Numbers below each model name represent (in order) the Bayesian information criterion (BIC), the Bayes Factor (BF), and the BF’s logarithmic expression (Log10). Black font indicates models showing better evidence of explaining the variance among participants in comparison with the inferior level’s model. The highest model in black is gathered for further analyses.
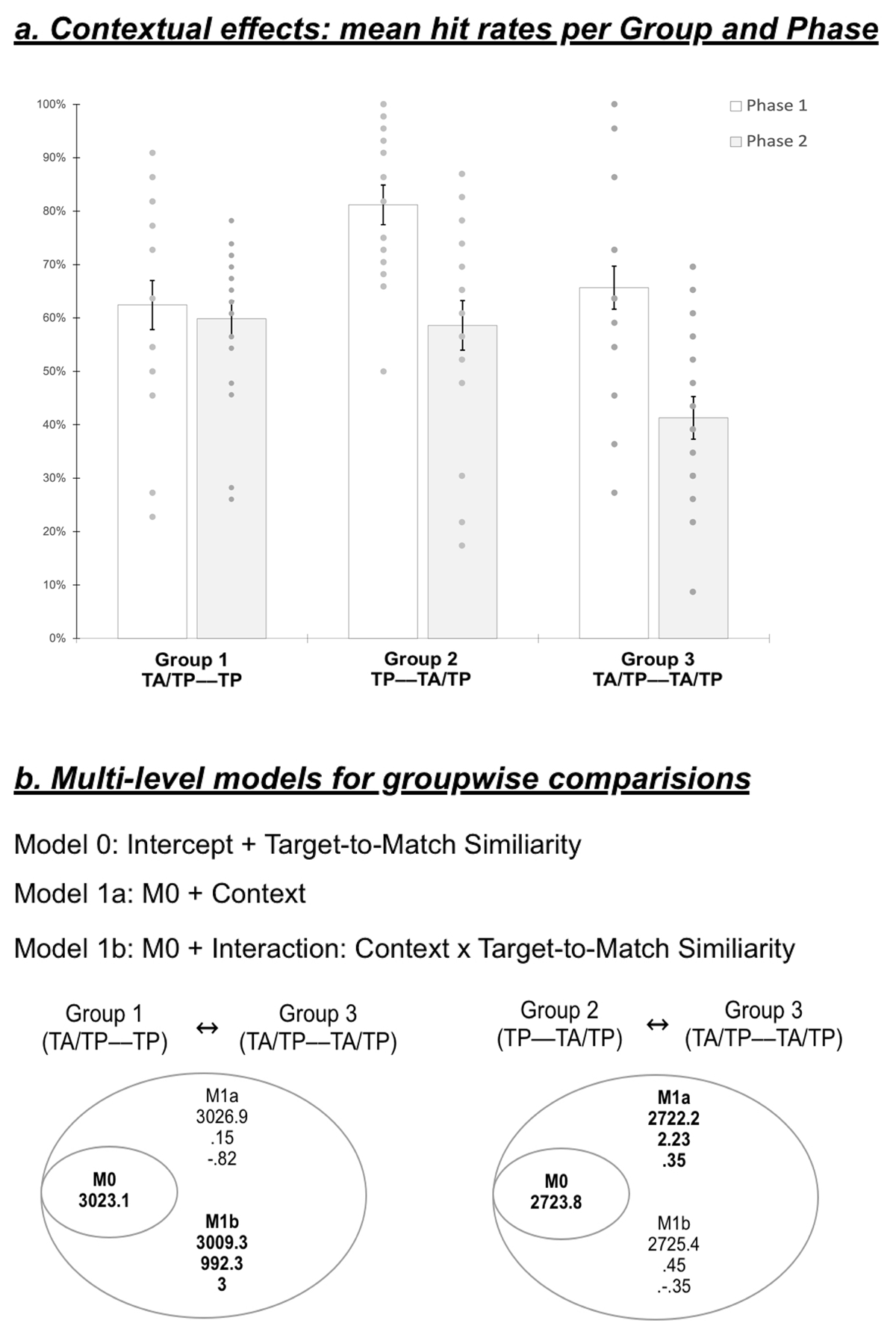
Figure 4
Groups’ performance and multi-level model results. a. Mean hit rates per group and Target Recognition Phase. Multi-level model results for b. Group 1 vs. Group 3, and c. Group 2 vs. Group 3. Numbers below each model name represent (in order) the Bayesian information criterion (BIC), the Bayes Factor (BF), and the BF’s logarithmic expression (Log10). Black font indicates models showing better evidence of explaining the variance among participants in comparison with the inferior level’s model. The highest model in black is gathered for further analyses.
