Table 1
Descriptive statistics for primes and targets used in Experiment 1.
| 2nd constituent of compound word | 2nd constituent of compound nonword | target word | |
|---|---|---|---|
| word frequency | 196.82 | 137.13 | 145.69 |
| number of syllables | 1.10 | 1.06 | 1.10 |
| number of phonemes | 3.37 | 3.33 | 3.27 |
| number of letters | 4.27 | 4.25 | 4.13 |
| orthographic neighbourhood | 8.73 | 8.02 | 7.40 |
| phonological neighbourhood | 19.44 | 17.04 | 16.50 |
| 1st constituent of compound word | 1st constituent of compound nonword | target word | |
| word frequency | 139.19 | 118.95 | 172.31 |
| number of syllables | 1.10 | 1.04 | 1.08 |
| number of phonemes | 3.21 | 3.29 | 3.33 |
| number of letters | 4.12 | 4.12 | 4.21 |
| orthographic neighbourhood | 7.06 | 7.88 | 8.92 |
| phonological neighbourhood | 16.79 | 15.71 | 19.38 |
Table 2
Table 2 shows mean lexical decision times (ms) and error rates (%) for word targets in Experiment 1, averaged across participants. Standard errors are shown in parentheses.
| Condition | Reaction times | Error Rates | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| compound word | 544 (10) | 1.3 (0.5) | textbook-TEXT |
| compound-nonword | 558 (11) | 2.5 (0.8) | textpile-TEXT |
| non-compound nonword | 557 (11) | 2.5 (0.9) | textpime-TEXT |
| unrelated | 569 (10) | 2.7 (0.8) | jailbook-TEXT |
| compound word | 545 (10) | 1.5 (0.5) | textbook-BOOK |
| compound-nonword | 557 (12) | 1.2 (0.4) | pilebook-BOOK |
| non-compound nonword | 548 (9) | 3.1 (0.9) | pimebook-BOOK |
| unrelated | 569 (14) | 1.9 (0.5) | textjail-BOOK |
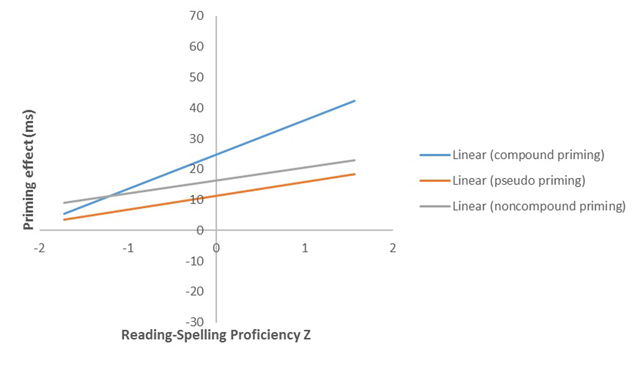
Figure 1
Priming effects for targets preceded by compound word, compound-nonword, and non-compound nonword primes (relative to the unrelated control condition), as a function of individual differences in reading and spelling proficiency. Positive proficiency scores represent individuals who are better readers than spellers. Negative proficiency scores represent individuals who are better spellers than readers.
Table 3
Table 3 shows mean lexical decision times (ms) and error rates (%) for word targets in Experiment 2, averaged across participants. Standard errors are shown in parentheses.
| Condition | Reaction times | Error Rates | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| edge-aligned | 552 (12) | 2.8 (0.9) | pimebook-BOOK |
| outer | 561 (11) | 6.8 (1.1) | bopimeok-BOOK |
| mid | 563 (12) | 5.2 (1.0) | pibookme-BOOK |
| unrelated | 564 (12) | 5.6 (0.9) | pimejail-BOOK |
